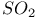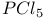|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Smith M.B., March J. — March's Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Substitution,  and branching effects 432 and branching effects 432
Substitution,  and electrophilic addition to alkenes 972 and electrophilic addition to alkenes 972
Substitution,  and enolate anion alkylations 550 and enolate anion alkylations 550
Substitution,  and epoxides 461 and epoxides 461
Substitution,  and Marcus theory 287 and Marcus theory 287
Substitution,  and mass spectrometry 392 and mass spectrometry 392
Substitution,  and organocuprate reactions 539—540 and organocuprate reactions 539—540
Substitution,  and stereochemistry 142 and stereochemistry 142
Substitution,  and the Finkelstein reaction 517 and the Finkelstein reaction 517
Substitution,  and the Hammond postulate 285 and the Hammond postulate 285
Substitution,  and the Menshutkin reaction 393 and the Menshutkin reaction 393
Substitution,  and the nucleophile 438—443 and the nucleophile 438—443
Substitution,  and Walden inversion 391 and Walden inversion 391
Substitution,  crossover experiments 393 crossover experiments 393
Substitution,  effect of effect of  - or - or  -substituents 436 -substituents 436
Substitution,  intermediate mechanism 401 intermediate mechanism 401
Substitution,  internal 406 internal 406
Substitution,  internal, epoxides from 478 internal, epoxides from 478
Substitution,  kinetics 390 kinetics 390
Substitution,  mechanism 390—393 mechanism 390—393
Substitution,  neighboring group mechanism 404 neighboring group mechanism 404
Substitution,  participation by dioxane solvent 402 participation by dioxane solvent 402
Substitution,  pseudo-first order kinetics 390 pseudo-first order kinetics 390
Substitution,  rate expression 390 rate expression 390
Substitution,  rate of reaction for alkyl substrates 432 rate of reaction for alkyl substrates 432
Substitution,  transition state 390 transition state 390
Substitution,  vs. vs. 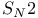 422 422
Substitution, 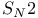 422—424 422—424
Substitution, 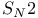 and and 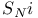 422 422
Substitution, 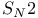 and conjugate addition to alkenes 980 and conjugate addition to alkenes 980
Substitution, 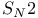 stereochemistry 422 stereochemistry 422
Substitution, 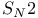 with cuprates 423 with cuprates 423
Substitution, 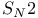 with cyclopropylmethyl halides 423 with cyclopropylmethyl halides 423
Substitution, 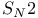 with organocuprates 540 with organocuprates 540
Substitution, 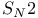 with vinyl epoxides and organocuprates 547 with vinyl epoxides and organocuprates 547
Substitution, 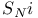 and formation of gem-dichlorides 1196 and formation of gem-dichlorides 1196
Substitution, 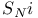 mechanism 420 mechanism 420
Substitution, 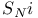 stereochemistry 420 stereochemistry 420
Substitution, 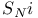 UIPAC nomenclature 420 UIPAC nomenclature 420
Substitution, 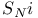 422—423 422—423
Substitution, 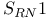 and vinylic halides 431 and vinylic halides 431
Substitution, electrophilic  -complexes 679 -complexes 679
Substitution, electrophilic  -substitution, mechanism 702 -substitution, mechanism 702
Substitution, electrophilic alternant hydrocarbons 690
Substitution, electrophilic and activation hardness 692
Substitution, electrophilic and double bond shifts 766
Substitution, electrophilic and hardness 692
Substitution, electrophilic and HSAB 692
Substitution, electrophilic and nitronium ion 680
Substitution, electrophilic and SET mechanism 694
Substitution, electrophilic and strain 690
Substitution, electrophilic and the Baker — Nathan order 685
Substitution, electrophilic and the Hammett equation 692
Substitution, electrophilic and the Hammond postulate 681
Substitution, electrophilic and the ortho/para ratio 685
Substitution, electrophilic arenium ion mechanism 675—680
Substitution, electrophilic arenium ions 676
Substitution, electrophilic arenium ions, isolation of 678
Substitution, electrophilic aromatic, activating groups 681—684
Substitution, electrophilic benzenonium ions 678
Substitution, electrophilic bromination, reagents for 705
Substitution, electrophilic chlorination 679
Substitution, electrophilic deactivating groups 681—684
Substitution, electrophilic deuteration, reagents for 696
Substitution, electrophilic deuterium exchange 695
Substitution, electrophilic electrophiles 692
Substitution, electrophilic encounter complexes 680
Substitution, electrophilic encounter-complex 694
Substitution, electrophilic estimating isomer distribution 691
Substitution, electrophilic field effects 681
Substitution, electrophilic fluorination, reagents for 707
Substitution, electrophilic Friedel — Crafts see “Friedel — Crafts”
Substitution, electrophilic Friedel — Crafts acylation 712—714
Substitution, electrophilic Friedel — Crafts alkylation 707—711
Substitution, electrophilic fused ring aromatics 689—690
Substitution, electrophilic halogenation, reagents for 705—706
Substitution, electrophilic heterocycles 688
Substitution, electrophilic hydrogen exchange 696
Substitution, electrophilic iodination, reagents for 706
Substitution, electrophilic ipso attack 686
Substitution, electrophilic ipso attack, migration 687
Substitution, electrophilic ipso position 686
Substitution, electrophilic isotope effects 676
Substitution, electrophilic leaving group effects 695
Substitution, electrophilic meta- 681
Substitution, electrophilic migration 687
Substitution, electrophilic Mills — Nixon effect 690
Substitution, electrophilic monosubstituted benzenes 681—687
Substitution, electrophilic multiple substituents 687
Substitution, electrophilic nitration 679
Substitution, electrophilic nitration, reagents for 697
Substitution, electrophilic nitronium ion 697
Substitution, electrophilic on zeolites 705
Substitution, electrophilic ortho effect 688
Substitution, electrophilic ortho- 681
Substitution, electrophilic other ring systems 688—690
Substitution, electrophilic para- 681
Substitution, electrophilic partial rate factor 685 690
Substitution, electrophilic partition factor 677
Substitution, electrophilic partitioning effect 677
Substitution, electrophilic pentamethylbenzenonium ion 678
Substitution, electrophilic polycyclic aromatics 688—690
Substitution, electrophilic predicting product distributions 691
Substitution, electrophilic rate determining step 694
Substitution, electrophilic rate of reaction 688 690
Substitution, electrophilic regioselectiviry 681—687
Substitution, electrophilic relative rates of substitution 694
Substitution, electrophilic resonance effects 681
Substitution, electrophilic resonance interaction 682
Substitution, electrophilic steric inhibition of resonance 699
Substitution, electrophilic substituent effects 683—684 691
Substitution, electrophilic substrate reactivity 690
Substitution, electrophilic sulfonation, and 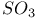 702 702
Substitution, electrophilic sulfonation, and sulfone side products 702
Substitution, electrophilic sulfonation, mechanism 702
Substitution, electrophilic the  mechanism 681 mechanism 681
Substitution, electrophilic the Hammett — Brown relationship 693
Substitution, electrophilic the Herz reaction 704
Substitution, electrophilic the selectivity relationship 692
Substitution, electrophilic tritiation, reagents for 696
Substitution, electrophilic tritium exchange 696
Substitution, electrophilic Vilsmeier reaction 715
Substitution, electrophilic Wheland intermediates 676
Substitution, electrophilic with iodine 706
Substitution, electrophilic with nitrites 705
Substitution, electrophilic, aromatic also see “Friedel — Crafts acylation” —
Substitution, nucleophilic ambident substrates 461
Substitution, nucleophilic and ambident nucleophiles 458—461
Substitution, nucleophilic and aprotic solvents 441
Substitution, nucleophilic and bridgehead atoms 437
Substitution, nucleophilic and cryptands 443
Substitution, nucleophilic and high pressure 457
Substitution, nucleophilic and I strain 437
Substitution, nucleophilic and ionic strength of the medium 451
Substitution, nucleophilic and microwave irradiation 457
Substitution, nucleophilic and phase transfer catalysis 454—456
Substitution, nucleophilic and reaction medium 450—454
Substitution, nucleophilic and solvent mixtures 452
Substitution, nucleophilic and solvent polarity 450
Substitution, nucleophilic and steric hindrance of nucleophiles 444
Substitution, nucleophilic and the Baker — Nathan order 437
Substitution, nucleophilic and the common-ion effect 451
Substitution, nucleophilic and the salt effect 451
Substitution, nucleophilic and the Swain — Scott equation 444
Substitution, nucleophilic and ultrasound 456—458
Substitution, nucleophilic at vinylic carbon 428—431
Substitution, nucleophilic basicity and leaving group ability 445
Substitution, nucleophilic cyclic substrates 437
Substitution, nucleophilic effect of bridgeheads 437
Substitution, nucleophilic effect of deuterium 438
| Substitution, nucleophilic influence of the nucleophile 438—445
Substitution, nucleophilic leaving group effects 445—449
Substitution, nucleophilic leaving groups 434
Substitution, nucleophilic leaving groups, order of leaving 449
Substitution, nucleophilic mechanism 275 424—428
Substitution, nucleophilic nucleophilic strength 439
Substitution, nucleophilic nucleophilicity 444
Substitution, nucleophilic order of nucleophilic strength 443
Substitution, nucleophilic product spread 421
Substitution, nucleophilic reaction rate and anion size 451
Substitution, nucleophilic solvation rule 450
Substitution, nucleophilic solvent effects and nucleophilic strength 443
Substitution, nucleophilic substrate reactivity 439
Substitution, nucleophilic synthetic reactions 440—441
Substitution, nucleophilic tetrahedral mechanism and synthetic reactions 442
Substitution, nucleophilic the alpha effect 445
Substitution, nucleophilic types of transition states 450
Substitution, nucleophilic vicarious 872
Substitution, nucleophilic with ally lie rearrangement 421—424
Substitution, radical ally lie chlorination 914
Substitution, radical allylic brommation 911—913
Substitution, radical and iodine 908
Substitution, radical and racemization 897
Substitution, radical IUPAC nomenclature 897
Substitution, radical mechanism 275
Substitution, radical neighboring group effects 899
Substitution, radical on side chains of aromatic rings 902
Substitution, radical transition state 897
Substitution, radical with alkanes, rate of abstraction 901
Substitution, radical with hydrocarbons, reagents for 908
Substitution, reaction type 275—276
Substitution, SET mechanism 402—404
Substitution, vinyl 428—431
Substitution, vinyl element effect 429
Substitution, vinyl elimination-addition 430
Substitution-elimination of benzylic halides 1543
Substrate effects branching 431
Substrate effects on substitution 431—438
Substrate factor in the Swain — Scott equation 444
Substrates ambident 461
Substrates and mechanism 274
Substrates effect on  reactions 768 reactions 768
Substrates reactivity toward nucleophilic substitution 439
Succinimidyl radical 913
Sugars see “Carbohydrates”
Sugars and ring-chain tautomerism 77
Sulfates from 1,2-diols 462
Sulfates ring opening 462
Sulfenamiides, reaction with alkenes 1058
Sulfene, and elimination of sulfonyl halides 1338
Sulfenyl chloride, aryl, reaction with aromatic compounds 704
Sulfenylation of amides 783
Sulfenylation of esters 783
Sulfenylation of ketones 783
Sulfides see “Thioethers”
Sulfides, epi, reaction with acyl halides 521
Sulfinates, alkyl, as side products 498
Sulfinic acid salts, reaction with alkyl halides 498
Sulfinic acids from sulfonyl chloride 577
Sulfinic acids reaction with ethers 494
Sulfite, sodium reduction of diazonium salts 1556
Sulfolene and Diels — Alder reactions 1066
Sulfolene thermolysis of 1066
Sulfonamides acyl, reduction of 1550
Sulfonamides and protection of amines 577
Sulfonamides from acyl sulfonamides 1687
Sulfonamides from alkenes 1687
Sulfonamides from alkyl halides 514
Sulfonamides from amines 1687
Sulfonamides from ammonia 1687
Sulfonamides from aryl nitro compounds 1687
Sulfonamides from boranes 1687
Sulfonamides from halo sulfonamides 1687
Sulfonamides from sulfonamides 1687
Sulfonamides from sulfonyl azides 1555 1687
Sulfonamides from sulfonyl chlorides 576
Sulfonamides from sulfonyl halides 1687
Sulfonamides hydrolysis 576
Sulfonamides reaction with alcohols 576
Sulfonate esters see “Esters sulfonate”
Sulfonation of aromatic rings 702
Sulfonation of naphthalene 682
Sulfones allyl vinyl and thio-Claisen rearrangement 1452
Sulfones anions, reaction with alkyl halides 555
Sulfones aryl, and the Smiles rearrangement 879
Sulfones aryl, reaction with hydroxide 879
Sulfones as side products or aromatic sulfonation 702
Sulfones bonding 45
Sulfones by Michael addition 1687
Sulfones by the Knoevenagel condensation 1687
Sulfones conjugated, reaction with organocuprates 1028
Sulfones conjugated, reduction with aluminum amalgam 1206
Sulfones coupling with organolithium reagents 544
Sulfones cyclic, extrusion of 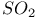 1354—1355 1354—1355
Sulfones cyclic, pyrolysis 1354—1355
Sulfones diaryl from aromatic compounds 704
Sulfones elimination with base 1336
Sulfones from aldehydes 1687
Sulfones from alkenes 1687
Sulfones from alkyl halides 498 499 1687
Sulfones from aromatic compounds 1687
Sulfones from aryl halides 1687
Sulfones from aryl nitro compounds 1687
Sulfones from esters 1687
Sulfones from halo sulfones 1687
Sulfones from ketones 1687
Sulfones from organometallic compounds 1687
Sulfones from sulfinate ions 1687
Sulfones from sulfinates 1687
Sulfones from sulfones 1687
Sulfones from sulfonic acid derivatives 1687
Sulfones from sulfonyl chlorides 577—578
Sulfones from sulfonyl halides 1687
Sulfones from sulfoxides 1541 1687
Sulfones from thioethers 1687
Sulfones fromboranes 1687
Sulfones halogenation of 778
Sulfones phenyl vinyl, in the Diels — Alder reaction 1062
Sulfones reaction with NBS or NCS 778
Sulfones reaction with RLi and Pd, for elimination 1336
Sulfones, halo and the Ramberg — Backlund reaction 1341
Sulfones, halo elimination with base 1341
Sulfones, halo from alkenes 1045
Sulfones, halo from sulfonyl halides 1045
Sulfonic acid esters, hydrolysis 465
Sulfonic acids and sulfonyl chlorides 575
Sulfonic acids aryl, by the Jacobsen reaction 734
Sulfonic acids aryl, from aromatic compounds 702 734
Sulfonic acids aryl, heating with sulfuric acid 734—735
Sulfonic acids aryl, reaction with hydroxide 862
Sulfonic acids by the Jacobsen rearrangement 1687
Sulfonic acids from aromatic compounds 1687
Sulfonic acids from aryl halides 1688
Sulfonic acids from disulfides 1540
Sulfonic acids from sulfonamides 576
Sulfonic acids from sulfonate esters 575
Sulfonic acids from sulfonation with rearrangement 1687
Sulfonic acids from sulfones 1540
Sulfonic acids from sulfonic acid derivatives 1687
Sulfonic acids from sulfonic anhydrides 575
Sulfonic acids from sulfoxides 1540
Sulfonic acids from sulfur compounds 1688
Sulfonic acids fromthiols 1540 1688
Sulfonic acids reaction with 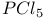 577 577
Sulfonic acids reaction with orthoformates 576
Sulfonic acids reaction with thionyl chloride 577
Sulfonic acids salts, reaction with thionyl chloride 944
Sulfonic anhydrides, hydrolysis of 575
Sulfonium compounds, elimination reactions 1336
Sulfonium salts from alkyl halides 497
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 and branching effects
and branching effects  - or
- or  -substituents
-substituents 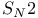
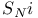
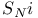
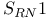 and vinylic halides
and vinylic halides  -complexes
-complexes  -substitution, mechanism
-substitution, mechanism 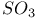
 mechanism
mechanism