|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Smith M.B., March J. — March's Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Mechanisms and bromomum ions 971
Mechanisms and catalysis 289
Mechanisms and electrofuge 385
Mechanisms and emission spectroscopy 321
Mechanisms and equilibrium 293
Mechanisms and first order reaction 291
Mechanisms and formation of thioethers 496
Mechanisms and half-life 294—295
Mechanisms and heterolytic bond cleavage 274
Mechanisms and homolytic bond cleavage 275
Mechanisms and isotopic effects 297—300
Mechanisms and isotopic labeling 289—290
Mechanisms and kinetics 290—296
Mechanisms and leaving group 275
Mechanisms and Marcus theory 286—287
Mechanisms and microscopic reversibility 285—286
Mechanisms and molecularlity 291
Mechanisms and nucleofuge 275 385
Mechanisms and phenonium ions 411 413
Mechanisms and primary isotope effects 298
Mechanisms and product determination 287
Mechanisms and rate constants 291
Mechanisms and rate determining step 291—292
Mechanisms and rate law 290
Mechanisms and second order reaction 291
Mechanisms and secondary isotope effects 298
Mechanisms and solvent isotope effects 299
Mechanisms and steady state approximation 292
Mechanisms and stereochemistry 290
Mechanisms and symproportionation 1017
Mechanisms and the Hammond postulate 285
Mechanisms and third order reactions 291
Mechanisms anhydride hydrolysis 469
Mechanisms arenium ion mechanism 675—680
Mechanisms arenium ion, mercuration of aryl compounds 793
Mechanisms aromatic compound cleavage 731
Mechanisms aromatic compounds and acyl peroxides 932
Mechanisms aromatic formylation 715
Mechanisms aromatic radical substitution 898
Mechanisms aromatic sulfonation 702
Mechanisms aryl halides with alkoxides 862
Mechanisms arylation of aryl diazonium salts 929
Mechanisms azides with active methylene compounds 781
Mechanisms Baeyer — Villager rearrangement 1418
Mechanisms Bamberger rearrangement 879
Mechanisms Bamford — Stevens reaction 1335
Mechanisms Barton reaction 1463
Mechanisms Beckmann rearrangement 1416
Mechanisms benzidine rearrangement 1455—1456
Mechanisms benzoin condensation 1243
Mechanisms benzyne, and aromatic substitution 854
Mechanisms bimolecular 759—763
Mechanisms bimolecular,  390 390
Mechanisms biradical, for Diels — Alder reactions 1067
Mechanisms Birch reduction of aromatic compounds 1010
Mechanisms bisdecarboxylation of dicarboxylic acids 1530
Mechanisms borane and hydroperoxide anion 797
Mechanisms borane reaction with halo carbonyls 560
Mechanisms boranes, elimination with alkenes 1339
Mechanisms Bucherer reaction 865
Mechanisms Cannizzaro reaction 1565
Mechanisms carbamate hydrolysis 474
Mechanisms carbanion, elimination 1308—1312
Mechanisms carbene disproportionation 790
Mechanisms carbene insertion 789 1086 1087
Mechanisms carbocations and hydrocarbons 786
Mechanisms Chapman rearrangement 1464
Mechanisms Claisen condensation 570
Mechanisms Claisen reaction 1224
Mechanisms Claisen rearrangement 1449—1450
Mechanisms concentration of reactants 293—294
Mechanisms conducted tour mechanism 766
Mechanisms conducted tour, and double bond migration 771
Mechanisms conversion of isocyanates to carbodiimides 1246
Mechanisms Cope elimination 1333
Mechanisms Cope rearrangement 1446—1447
Mechanisms coupling of boranes 939
Mechanisms Criegee, for ozonolysis 1523—1525
Mechanisms Curtius rearrangement 1412
Mechanisms cyanoborohydride reduction of tosylhydrazones 1548
Mechanisms cyclic, and addition to alkenes 979
Mechanisms cyclic, and the Prins reaction 1242
Mechanisms cyclobutane cycloreversion 1081
Mechanisms Dakin reaction 1528
Mechanisms decarbonylation of aldehydes 945
Mechanisms decarboxylation of aryl carboxylic acids 733
Mechanisms decarboxylation of carboxylate ions 733
Mechanisms decarboxylation of glycidic acids 809
Mechanisms decarboxylation of keto acids 810
Mechanisms definition 274
Mechanisms dehydration of oxime tosylates 1349
Mechanisms detection of intermediates 288—289
Mechanisms determination of 287—300
Mechanisms di- - methane rearrangements 1461 - methane rearrangements 1461
Mechanisms diazo transfer with active methylene compounds 781
Mechanisms diazoalkanes and alcohols 479
Mechanisms diazomethane homologation of aldehydes and ketones 1407
Mechanisms diazotization of aromatic amines 817
Mechanisms dichromate oxidation of aldehydes 918
Mechanisms Dieckmann condensation 570
Mechanisms Diels — Alder reactions 1066—1067
Mechanisms dihydroxylation of alkenes with 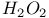 1049 1049
Mechanisms diimide reduction of alkenes 1007
Mechanisms diion, and ketene-imine cycloaddition 1250
Mechanisms diion, for [2+2]-cycloadditions 1080
Mechanisms dimer mechanism and 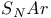 852 852
Mechanisms diradical, and carbene insertion to alkenes 1087
Mechanisms diradical, and Cope rearrangement 1447
Mechanisms diradical, and cyclobutane cycloreversion 1081
Mechanisms diradical, for [2+2]-cycloadditions 1080
Mechanisms DMSO oxidation of alkyl halides 1536
Mechanisms E1 1306—1308
Mechanisms E1cB 1308—1312
Mechanisms E2 1300—1306
Mechanisms E2C 1313
Mechanisms Eglinton reaction 928
Mechanisms electrocyclic rearrangements 1427
Mechanisms electrophilic 274
Mechanisms electrophilic addition to alkenes 970—975
Mechanisms electrophilic addition to cyclopropanes 989
Mechanisms elimination 276
Mechanisms elimination of alkyl halides 1337
Mechanisms elimination of epoxides with 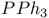 1341 1341
Mechanisms elimination-addition, at vinyl carbon 430
Mechanisms ene reaction 1022
Mechanisms enol ester hydrolysis 474
Mechanisms enolate anion alkylations 550
Mechanisms ester formation 485
Mechanisms ester formation with DCC 485
Mechanisms ester hydrolysis 470—473
Mechanisms Etard reaction 1534
Mechanisms Favorskii rearrangement 1403
Mechanisms Fischer indole synthesis 1453
Mechanisms flash photolysis 321
Mechanisms fragmentation of alkene alcohols 1351
Mechanisms free radical 275
Mechanisms free radical substitution 896
Mechanisms Friedel — Crafts acylation 714
Mechanisms Friedel — Crafts alkylation 710—711
Mechanisms Fries rearrangement 727
Mechanisms gem-dichloride formation from aldehydes or ketones 1196
Mechanisms Glaser reaction 928
Mechanisms Gomberg — Bachmann pinacol synthesis 1560
Mechanisms Grignard reaction with aldehydes and ketones 1208
Mechanisms haloform reaction 813
Mechanisms halogenation of enolate anions 776
Mechanisms halogenation of ketones and aldehydes 776
Mechanisms halogenation of organometallic compounds 799
Mechanisms Heck reaction 931
Mechanisms heterogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes 1005
| Mechanisms Hofmann elimination 1332
Mechanisms Hofmann rearrangement 1411
Mechanisms Hofmann — Loffler reaction 1462
Mechanisms homogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes 1006
Mechanisms Hunsdiecker reaction 943
Mechanisms hydrate formation 1176
Mechanisms hydration of alkenes 993
Mechanisms hydrolysis of  -lactones 473 -lactones 473
Mechanisms hydrolysis of  -lactones 473 -lactones 473
Mechanisms hydrolysis of C=N compounds 1177
Mechanisms hydrolysis of enamines 1178
Mechanisms interfacial, phase transfer catalysis 455
Mechanisms ion pairs and [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement 1454
Mechanisms ion-pair and substitution 400
Mechanisms ion-pair and the Sommelet — Hauser rearrangement 878
Mechanisms ketene-imine cycloaddition 1250
Mechanisms keto-enol tautomerism, catalyzed 774
Mechanisms ketones and diazonium salts 780
Mechanisms Kolbe reaction 942
Mechanisms lead tetraacetate oxidation of alcohols 919
Mechanisms Lossen rearrangement 1413
Mechanisms Mannich reaction 1190
Mechanisms Meerwein arylation 930
Mechanisms metal hydride addition-elimination 772
Mechanisms mixed  400—402 400—402
Mechanisms Neber rearrangement 1410
Mechanisms Nef reaction 1178
Mechanisms neighboring-group 404—407
Mechanisms nonsynchronous, and [3+2]-cycloadditions 1061
Mechanisms nucleophilic 275
Mechanisms nucleophilic addition to alkenes 975—976
Mechanisms nucleophilic rearrangements 1378—1388
Mechanisms organocuprate conjugate addition 1030
Mechanisms organolithium reagents and alkyl halides 807
Mechanisms organolithiums with aldehydes or ketones 1209
Mechanisms oxidation of alkyl side chains on aromatic rings 1528
Mechanisms oxidation of aromatic amides with Caro’s acid 1539
Mechanisms oxidation of aromatic diols 1518
Mechanisms oxidation of hydroquinones 1511
Mechanisms oxidation of selenoxides to selenones 1542
Mechanisms oxidation with Fenton’s reagent 917
Mechanisms oxidation-reduction 277
Mechanisms oxidation-reduction, addition-elimination 1509
Mechanisms oxidation-reduction, and direct electron transfer 1508
Mechanisms oxidation-reduction, and ester intermediates 1508
Mechanisms oxidation-reduction, displacement 1509
Mechanisms oxidation-reduction, hydride transfer 1508
Mechanisms oxidation-reduction, hydrogen atom transfer 1508
Mechanisms oxidative cleavage of alkenes 1526
Mechanisms oxidative cleavage of diols with lead tetraacetate 1520—1521
Mechanisms oxidative decarboxylation of carboxylic acids 1529
Mechanisms ozonolysis of alkenes 1523—1525
Mechanisms Passerini reaction 1252
Mechanisms pericyclic 275 1427
Mechanisms pericyclic and the Prins reaction 1242
Mechanisms permanganate oxidation of aldehydes 918
Mechanisms peroxide coupling of thiols to disulfides 1544
Mechanisms peroxide oxidation of tertiary amines 1541
Mechanisms photochemical dimerization of ketones 1560
Mechanisms photochemical Wolff rearrangement 1406
Mechanisms photochemical [2+2]-cycloadditions 1082
Mechanisms photolysis of 2,5-cyclohexadienones 1461
Mechanisms photolysis of pyrazoles 1353
Mechanisms pinacol rearrangement 1397
Mechanisms Prevost reaction 1050
Mechanisms Prins reaction 1241
Mechanisms pseudo first order 293
Mechanisms Pummerer rearrangement 1566
Mechanisms pyrolytic eliminations 1322—1326
Mechanisms quasi-Favorskii rearrangement 1405
Mechanisms radical addition of aldehydes to alkenes 1034
Mechanisms radical addition to alkenes 977
Mechanisms radical allylic bromination 912
Mechanisms radical halogenation of hydrocarbons 909
Mechanisms radical ring enlargement 1400
Mechanisms radical, addition of HBr to alkenes 992
Mechanisms radical, and oxidative decarboxylation 1529
Mechanisms radical, and reduction of nitro compounds 531
Mechanisms radical, and the Gif systems 1533
Mechanisms radical, and the Hofmann — Loeffler reaction 1462
Mechanisms radical, in autoxidation of aromatic diols 1518
Mechanisms radical, Stevens rearrangement 1420
Mechanisms Ramberg — Backlund reaction 1342
Mechanisms reaction of alkenes and peroxyacids 1052
Mechanisms reaction of alkenes with hypohalous acids 1044
Mechanisms reaction of alkenes, CO, and water 1036
Mechanisms reaction of carboxylate salts with BrCN 1247
Mechanisms reaction of diazomethane with aldehydes or ketones 1248
Mechanisms reaction of Grignard reagents with nitriles 1217
Mechanisms reaction of isonitriles and water 1251
Mechanisms reaction of nitroso compounds and hydroxylamines 819
Mechanisms reaction of organometallics and alkenes 792
Mechanisms reaction with boranes with CO 1422
Mechanisms rearrangement 276
Mechanisms rearrangement of aldehydes and ketones 1401
Mechanisms rearrangement of N-nitro amines 727
Mechanisms reduction of acyl halides 532
Mechanisms reduction of aldehydes or ketones with Na/EtOH 1199
Mechanisms reduction of aromatic nitro compound 1553
Mechanisms Sandmeyer reaction 936
Mechanisms Schiemann reaction 875
Mechanisms Schmidt reaction 1414
Mechanisms semi-benzilic mechanism 1405
Mechanisms, IUPAC  763 763
Mechanisms, IUPAC 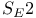 760 760
Mechanisms, IUPAC 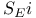 760 760
Mechanisms, IUPAC 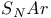 851 851
Mechanisms, IUPAC 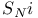 420 420
Mechanisms, IUPAC 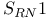 855 855
Mechanisms, IUPAC allylic rearrangement 421
Mechanisms, IUPAC and ester hydrolysis 471—472
Mechanisms, IUPAC arenium ion 675
Mechanisms, IUPAC E1 1307
Mechanisms, IUPAC E2 1300
Mechanisms, IUPAC electrophilic addition to alkenes 970
Mechanisms, IUPAC leaving groups 445
Mechanisms, IUPAC nomenclature, and ester formation 485
Mechanisms, IUPAC nucleophilic addition to alkenes 975
Mechanisms, IUPAC pyrolytic eliminations 1323
Mechanisms, IUPAC radical substitution 897
Mechanisms, IUPAC rules 384
Mechanisms, IUPAC tetrahedral mechanism 424
Mechanisms, SET 402—404
Mechanisms, SET  393—400 420 393—400 420
Mechanisms, SET  , and aromatic compounds 853 , and aromatic compounds 853
Mechanisms, SET  , hydrolysis of acetals 466 , hydrolysis of acetals 466
Mechanisms, SET  , ion pairing 397—400 , ion pairing 397—400
Mechanisms, SET  390—393 390—393
Mechanisms, SET  , and stereochemistry 142 , and stereochemistry 142
Mechanisms, SET 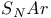 850—853 857 850—853 857
Mechanisms, SET 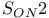 , and formation of aryl ethers 862 , and formation of aryl ethers 862
Mechanisms, SET 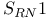 855—856 855—856
Mechanisms, SET and coupling of organometallics with RX 537
Mechanisms, SET and electrophilic aromatic substitution 694
Mechanisms, SET and enolate anion alkylations 550—551
Mechanisms, SET and enolate anions with aryl halides 870
Mechanisms, SET and formation of Grignard reagents 806
Mechanisms, SET and sulfur nucleophiles 495
Mechanisms, SET and the Williamson reaction 478
Mechanisms, SET Shapiro reaction 1334
Mechanisms, SET Simmons-Smith reaction 1088
Mechanisms, SET Sommelet — Hauser rearrangement 878
Mechanisms, SET Stevens rearrangement 1419—1420
Mechanisms, SET substitution 275
Mechanisms, SET sulfite reduction of diazonium salts 1556
Mechanisms, SET sulfonyloxaziridine oxidation of ketones 916
Mechanisms, SET sulfur ylids with aldehydes or ketones 1247
Mechanisms, SET tetrahedral 424—428 (also see “Tetrahedral mechanism”)
Mechanisms, SET tetrahedral, and nucleophilic addition to carbonyls 1173
Mechanisms, SET transannular rearrangement 1388
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте




 - methane rearrangements
- methane rearrangements 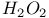
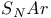
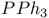
 -lactones
-lactones  -lactones
-lactones 

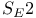
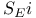
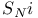
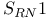

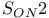 , and formation of aryl ethers
, and formation of aryl ethers