|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Smith M.B., March J. — March's Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Spiropentanes, from carbene additions 1086
Squalene 1019
Squalene 2,3-oxide 1019
Squaric acid and aromaticity 70
Squaric acid, 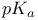 70 70
Stability criteria for, carbanions 229—232
Stability of arenium ions, table 679
Stability of carbanions, by S, Si and P 231
Stability of carbocations 219—225 1384
Stability of diazonium salts 816
Stability of radicals 241
Stability order for carbanions 228 229
Stability order for carbocations 219
Stability thermodynamic and double bond migration 773
Stabilization of Grignard reagents by ethers 235
Stabilomer 1396
Starands 107
Statistical effects and acid strength 345—346
Staudinger reaction 1555
Steady state approximation 292
Stephen reduction 1204
Stephens — Castro coupling 868
Stereochemistry 125—191
Stereochemistry and 1,2 shifts 1380
Stereochemistry and 1,2-alkyl shifts 1383
Stereochemistry and carbanions 233
Stereochemistry and ester hydrolysis 472
Stereochemistry and ion pairs 398—400
Stereochemistry and mechanism 290
Stereochemistry and nonclassical ions 409
Stereochemistry and ozonolysis 1524
Stereochemistry and the 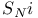 mechanism 420 mechanism 420
Stereochemistry in the Diels — Alder reaction 1064
Stereochemistry in [1,3]- and [l,5]-alkyl sigmatropic rearrangements 1441
Stereochemistry of  reactions 397 reactions 397
Stereochemistry of  reactions 142 reactions 142
Stereochemistry of  with Walden inversion 391 with Walden inversion 391
Stereochemistry of 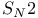 reactions 422 reactions 422
Stereochemistry of autoxidation of alkenes with singlet oxygen 922
Stereochemistry of carbene insertion with alkenes 1087
Stereochemistry of the SET mechanism and substitution 403
Stereoelectronic control and the tetrahedral mechanism 427
Stereoelectronic effects and radicals 903
Stereoelectronic effects and the tetrahedral mechanism 427
Stereogenic carbon, definition 128
Stereogenic centers 136
Stereogenic centers and Fischer projections 137
Stereogenic centers more than one 144—147
Stereoisomers also see “Diastereomers” “Enantiomers”
Stereoisomers and chirality 125—139
Stereoisomers and cis/trans isomers 157—160
Stereoisomers and E2 elimination 1301
Stereoisomers and enantiomer definition 125
Stereoisomers and substituted cyclohexanes 175
Stereoisomers diastereomers 144—147
Stereoisomers topological, catenanes 114
Stereoisomers torsional diastereomers 133
Stereoselective synthesis 147—150 166—167
Stereoselective, definition 166
Stereoselectivity and chiral auxiliaries 149
Stereoselectivity and Cram’s rule 147—148
Stereoselectivity and the Felkin — Ahn model 148
Stereoselectivity and the Wittig reaction 1235
Stereoselectivity in the aldol reaction 1221
Stereoselectivity Lindlar reduction of alkynes 1004
Stereoselectivity of epoxide hydrolysis and Co-salen catalysts 468
Stereoselectivity of hydride reduction of aldehydes and ketones 1198
Stereoselectivity of Michael additions 977
Stereoselectivity of radical addition to alkenes 978
Stereoselectivity of radical hydrogen abstraction 903
Stereospecific synthesis 166—167
Stereospecific, definition 166
Stereospecificity bromine addition to alkenes 973
Stereospecificity electrocyclic rearrangements 1427
Steric effects and acid strength 346
Steric effects and base strength 347
Steric effects and elimination reactions 1319
Steric effects and radicals 900
Steric effects and structure 365—368
Steric effects B strain 366
Steric effects hindrance see “Steric hindrance”
Steric effects I strain 366
Steric effects masochistic 1080
Steric effects quantitative treatment 374
Steric effects radical addition to alkenes 985
Steric hindrance and ester formation 485
Steric hindrance and ester hydrolysis 470
Steric hindrance and high pressure reactions 458
Steric hindrance and hydrogenation of alkynes 1005
Steric hindrance and nucleophilic addition 1174
Steric hindrance and nucleophilic strength 444
Steric hindrance definition 365
Steric inhibition, of resonance 699
Steric strain see “Strain”
Steroids,  nomenclature 146 nomenclature 146
Stevens rearrangement 878 1419—1421 1454
Stevens rearrangement and sulfur ylids 1420
Stevens rearrangement and the Sommelet — Hauser rearrangement 1420
Stevens rearrangement labeling 1419
Stieglitz rearrangement 1416
Stilbenes 288
Stilbenes photochemical isomerization 391—320
Stilbenes photocyclization 1436
Stille reaction 931—932
Stille reaction and cine substitution 932
Stobbe condensation 1224
Stork enamine reaction 787
Stork enamine reaction and Michael reactions 787
Stork enamine reaction enantioselectivity 788
Stork enamine reaction regioselectivity 787
Stork enamine reaction synthesis 555
Stork — Eschenmoser hypothesis 1019
Story synthesis 1355
Strain and  -bond rearrangements 1459 -bond rearrangements 1459
Strain and bent bonds 181
Strain and betweenanenes 186
Strain and bond length 184
Strain and Bredt’s rule 188
Strain and cleavage of non-enolizable ketones 814
Strain and conformational transmission 368
Strain and electrophilic aromatic substitution 690
Strain and geared molecules 189
Strain and heat of atomization 180
Strain and NMR 181
Strain and p and s character 181
Strain and substitution 432—433
Strain and twisted molecules 19
Strain angle, cyclobutane 182
Strain angle, cyclopropane 181
Strain B 366
Strain back 366
Strain conformations and reactivity 366
Strain eclipsing and reactivity 366
Strain energy 180
Strain energy calculation 180
Strain energy cyclotetradecane 214
Strain energy, cycloalkanes 185—186
Strain for ring categories 1851 366
Strain in fused ring benzene derivatives 45
Strain in organic molecules 180—191
Strain large-angle 184
Strain Pitzer 184
Strain polycyclic small-ring systems 182—183
Strain ring and ester hydrolysis 473
Strain ring and leaving groups 446
Strain ring size and reactivity 366
Strain rings other than 3 or 4 184—186
Strain small rings 180—184
Strain small-angle 180
Strain steric 180
| Strain transannular 184
Strain twisted amides 185
Strain unavoidable crowding 189
Strained molecules, by the Wurtz reaction 536
Strecker synthesis 1240
Strength, of nucleophiles 439
Structure and acid-base strength 342—349
Structure and field effects 363
Structure and reactivity 368—375
Structure and steric effects 365—368
Structure and the Hammett equation 368
Structure of enolate anions 236—237
Structure of organolithium reagents 236
Structure resonance effect 363
Structures, Lewis 12
Strychnine, and resolution 151
Substituent effects  -substitution 435 -substitution 435
Substituent effects  -substitution 436 -substitution 436
Substituent effects  -unsaturation 434 -unsaturation 434
Substituent effects and aryl radicals 904
Substituent effects and electrophilic aromatic substitution 683—684 691
Substituent effects elimination reactions 1319
Substituent effects hybridization 433
Substituent effects in alkene metathesis 1457
Substituent effects in the Claisen rearrangement 1451
Substituent effects in the Diels — Alder reaction 1067
Substituent effects inductive effects 436
Substituent effects on  reactions 433—435 reactions 433—435
Substituent effects on  reactions 436 reactions 436
Substituent effects rate and the Diels — Alder reaction 1065
Substitution  676 676
Substitution  and electrophilic aromatic substitution 681 and electrophilic aromatic substitution 681
Substitution  and aromatic compounds 853 and aromatic compounds 853
Substitution 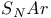 850—853 850—853
Substitution 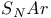 , activating groups 858 , activating groups 858
Substitution 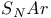 , and Meisenheimer salts 851 , and Meisenheimer salts 851
Substitution 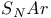 , and the Hammett relationship 859 , and the Hammett relationship 859
Substitution 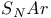 , base catalysis 852 , base catalysis 852
Substitution 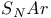 , dimer mechanism 852 , dimer mechanism 852
Substitution 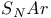 , isolation of intermediates 851 , isolation of intermediates 851
Substitution 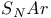 , isotope effects 852 , isotope effects 852
Substitution 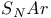 , leaving group effects 860 , leaving group effects 860
Substitution 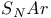 , partitioning effect 852 , partitioning effect 852
Substitution 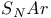 , substrate effects 857 , substrate effects 857
Substitution 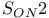 862 862
Substitution 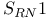 855—856 855—856
Substitution  and radicals 856 and radicals 856
Substitution  and ultrasound 856 and ultrasound 856
Substitution and anchimeric assistance 404
Substitution and neighboring group mechanism 404—407
Substitution at ally lie carbon 421—424
Substitution benzyne 854
Substitution bimolecular see “ ” ”
Substitution cine and the benzyne mechanism 854
Substitution cine and the Stille reaction 932
Substitution electrophilic, mechanism 275
Substitution free radical, mechanism of 896
Substitution Grignard reagents and aryl oxazolines 868
Substitution mixed  - - 400—402 400—402
Substitution nucleophilic bimolecular see “Substitution
Substitution nucleophilic internal see “Substitution
Substitution nucleophilic unimolecular see “Substitution
Substitution nucleophilic, effect of nucleophile 861
Substitution nucleophilic, intramolecular 879
Substitution nucleophilic, leaving group effects 860
Substitution nucleophilic, other mechanisms 857
Substitution nucleophilic, substrate effects 857
Substitution radical 897—899
Substitution radical and ipso substitution 905
Substitution radical, mechanism of 898
Substitution reactions and alkyne carbon 433
Substitution reactions and bromonium ions 405
Substitution reactions and chain reactions 403
Substitution reactions and entropy of activation 404
Substitution reactions and isotope effects 299
Substitution reactions and neighboring group participation 407—420
Substitution reactions and radicals 402—404
Substitution reactions and SET mechanism 433
Substitution reactions at vinyl carbon 433
Substitution reactions B strain 432—433
Substitution reactions branching effects 431
Substitution reactions competition with elimination 1320
Substitution reactions IUPAC rules 382—383
Substitution reactions reactivity 431—462
Substitution reactions substrate 431—438
Substitution reactions with aryl substrates 433
Substitution vicarious nucleophilic substitution of H 872
Substitution,  763—767 763—767
Substitution,  and carbanions 764 and carbanions 764
Substitution,  and electrofuges 769 and electrofuges 769
Substitution,  and ion pairs 768 and ion pairs 768
Substitution,  and racemization 763—764 and racemization 763—764
Substitution,  and solvent effects 764 and solvent effects 764
Substitution,  and tautomerization 763 and tautomerization 763
Substitution,  and the leaving group 764 and the leaving group 764
Substitution,  conducted tour mechanism 766 conducted tour mechanism 766
Substitution,  effect of leaving groups 768 effect of leaving groups 768
Substitution,  effect of substrates 768 effect of substrates 768
Substitution,  isoinversion 765 isoinversion 765
Substitution,  isoracemization 765 isoracemization 765
Substitution,  isotopic exchange 765 isotopic exchange 765
Substitution,  solvent effects 769 solvent effects 769
Substitution, 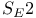 759—763 759—763
Substitution, 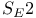 absolute configuration 761 absolute configuration 761
Substitution, 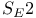 and bridgehead carbons 761 and bridgehead carbons 761
Substitution, 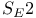 and EDA complexes 763 and EDA complexes 763
Substitution, 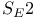 760 767 760 767
Substitution, 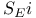 759—763 759—763
Substitution, 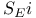 salt effects 763 salt effects 763
Substitution, 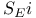 solvent effects 763 solvent effects 763
Substitution,  767 767
Substitution,  and adamantyl compounds 433 and adamantyl compounds 433
Substitution,  and ambident nucleophiles 460 and ambident nucleophiles 460
Substitution,  and bicyclic systems 397 and bicyclic systems 397
Substitution,  and branching effects 432 and branching effects 432
Substitution,  and bridgehead carbons 764 and bridgehead carbons 764
Substitution,  and carbocation stability 395 and carbocation stability 395
Substitution,  and Markovnikov’s rule 984 and Markovnikov’s rule 984
Substitution,  and reactions of alcohols with and reactions of alcohols with 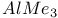 544 544
Substitution,  and rearrangements 1381 and rearrangements 1381
Substitution,  and the Hammett relationship 436 and the Hammett relationship 436
Substitution,  and the Hammond postulate 432 and the Hammond postulate 432
Substitution,  and trifluoroacetic acid as a solvent 451 and trifluoroacetic acid as a solvent 451
Substitution,  at vinylic carbon 430 at vinylic carbon 430
Substitution,  common ion effect 395 common ion effect 395
Substitution,  cubyl cation and ab initio calculations 397 cubyl cation and ab initio calculations 397
Substitution,  effect of effect of  -substitution 436 -substitution 436
Substitution,  effect on rate of effect on rate of  -unsaturation 434 -unsaturation 434
Substitution,  effects of effects of  -substitution 435 -substitution 435
Substitution,  influence of inductive effects 436 influence of inductive effects 436
Substitution,  ion pairing 397—400 ion pairing 397—400
Substitution,  IUPAC mechanistic description 394 IUPAC mechanistic description 394
Substitution,  kinetic studies 396 kinetic studies 396
Substitution,  limiting 394 limiting 394
Substitution,  mass law effect 395 mass law effect 395
Substitution,  mechanism 393—400 mechanism 393—400
Substitution,  planar intermediates 396 planar intermediates 396
Substitution,  rate law 394 rate law 394
Substitution,  reaction rates of alkyl tosylates 434 reaction rates of alkyl tosylates 434
Substitution,  salt effect 395 salt effect 395
Substitution,  solvation 394 solvation 394
Substitution,  solvolysis rates for alkyl halides 432 solvolysis rates for alkyl halides 432
Substitution,  stereochemistry 397 stereochemistry 397
Substitution, 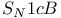 448 448
Substitution, 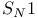 423 423
Substitution,  ab initio studies 393 ab initio studies 393
Substitution,  anchimeric assistance 404 anchimeric assistance 404
Substitution,  and and 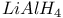 reduction of epoxides 529 reduction of epoxides 529
Substitution,  and ambident nucleophiles 460 and ambident nucleophiles 460
Substitution,  and backside attack 390 and backside attack 390
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 mechanism
mechanism  reactions
reactions  reactions
reactions 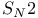 reactions
reactions  nomenclature
nomenclature  -bond rearrangements
-bond rearrangements  -substitution
-substitution  -substitution
-substitution 
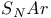
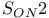
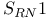
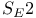
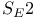
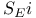

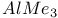
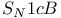
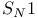
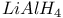 reduction of epoxides
reduction of epoxides