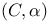 -summation 379.M -summation 379.M
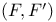 -free (compact oriented G-manifold) 431.G -free (compact oriented G-manifold) 431.G
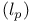 or or 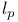 (a sequence space) 168.B (a sequence space) 168.B
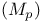 , ultradistribution of class 125.U , ultradistribution of class 125.U
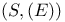 -valued random variable 342.C -valued random variable 342.C
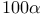 %-point 396.C %-point 396.C
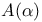 -stability 303.G -stability 303.G
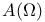 (the totality of functions bounded and continuous on the closure of (the totality of functions bounded and continuous on the closure of  and holomorphic in and holomorphic in  ) 168.B ) 168.B
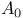 -stability 303.G -stability 303.G
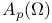 (the totality of functions f that are holomorphic in (the totality of functions f that are holomorphic in  and that satisfy and that satisfy 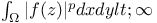 ) 168.B ) 168.B
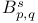 (Besov spaces) 168.B (Besov spaces) 168.B
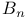 set 22.D set 22.D
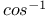 131.E 131.E
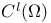 (the totality of l times continuously differentiable functions in (the totality of l times continuously differentiable functions in  ) 168.B ) 168.B
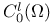 (the totality of functions in (the totality of functions in 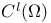 whose supports are compact subsets of whose supports are compact subsets of  ) 168.B ) 168.B
 - - -stable 126.H -stable 126.H
 -conjugacy, -conjugacy,  -conjugate 126.B -conjugate 126.B
 -equivalence, -equivalence,  -equivalent 126.B -equivalent 126.B
 -flow 126.B -flow 126.B
 -foliation 154.G -foliation 154.G
 -function in a -function in a 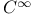 -manifold 105.G -manifold 105.G
 -manifold 105.D -manifold 105.D
 -manifold compact 105.D -manifold compact 105.D
 -manifold paracompact 105.D -manifold paracompact 105.D
 -manifold with boundary 105.E -manifold with boundary 105.E
 -manifold without boundary 105.E -manifold without boundary 105.E
 -mapping 105.J -mapping 105.J
 -norm 126.H -norm 126.H
 -structurally stable 126.H -structurally stable 126.H
 -structure 108.D -structure 108.D
 -structure on a topological manifold 114.B -structure on a topological manifold 114.B
 -structure subordinate to (for a -structure subordinate to (for a 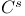 -structure) 108.D -structure) 108.D
 -triangulation 114.C -triangulation 114.C
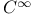 topology, weak 401.C topology, weak 401.C
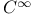 -function (of many variables) 58.B -function (of many variables) 58.B
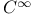 -function germ of (at the origin) 58.C -function germ of (at the origin) 58.C
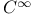 -function preparation theorem for 58.C -function preparation theorem for 58.C
 -function rapidly decreasing 168.B -function rapidly decreasing 168.B
 -function slowly increasing 125.O -function slowly increasing 125.O
 -functions and quasi-analytic functions 58 -functions and quasi-analytic functions 58
 -homomorphism (between Lie groups) 249.N -homomorphism (between Lie groups) 249.N
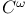 -isomorphism (between Lie groups) 249.N -isomorphism (between Lie groups) 249.N
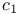 -bundle 237.F -bundle 237.F
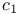 -mapping 237.G -mapping 237.G
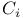 -field 118.F -field 118.F
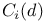 -field 118.F -field 118.F
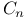 set 22.D set 22.D
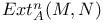 200.G 200.G
 200.K 200.K
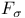 set 270.C set 270.C
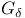 -set 270.C -set 270.C
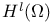 (Sobolev spaces) 168.B (Sobolev spaces) 168.B
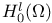 (Sobolev spaces) 168.B (Sobolev spaces) 168.B
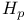 (Hardy spaces) 168.B (Hardy spaces) 168.B
 297.G 297.G
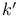 -space 425.CC -space 425.CC
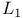 -algebra (of a locally compact Hausdorff group) 36.L -algebra (of a locally compact Hausdorff group) 36.L
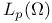 (the space of measurable functions f(x) on (the space of measurable functions f(x) on  such that such that 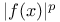 , , 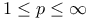 , is integrable) 168.B , is integrable) 168.B
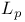 -space, abstract 310.G -space, abstract 310.G
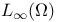 168.B 168.B
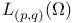 (the Lorentz spaces) 168.B (the Lorentz spaces) 168.B
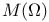 (the set of all essentially bounded measurable functions on (the set of all essentially bounded measurable functions on  ) 168.B ) 168.B
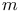 matrix 269.A matrix 269.A
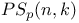 (projective symplectic group over K) 60.L (projective symplectic group over K) 60.L
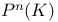 (projective space) 343.H (projective space) 343.H
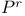 -figure 343.B -figure 343.B
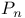 set 22.D set 22.D
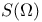 (totality of measurable functions on (totality of measurable functions on  that take finite value almost everywhere) 168.B that take finite value almost everywhere) 168.B
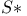 -number 430.C -number 430.C
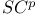 -manifold 178.G -manifold 178.G
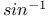 131.E 131.E
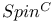 bundle 237.F bundle 237.F
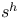 -factorial experiment 102.H -factorial experiment 102.H
 131.E 131.E
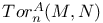 200.D 200.D
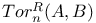 200.K 200.K
 -statistic Hotelling’s 280.B -statistic Hotelling’s 280.B
 -statistic noncentral Hotelling 374.C -statistic noncentral Hotelling 374.C
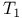 -uniform space 436.C -uniform space 436.C
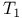 -uniformity 436.C -uniformity 436.C
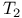 -topological group 423.B -topological group 423.B
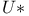 -number 430.C -number 430.C
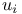 -scale 19.D -scale 19.D
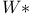 -algebra 308.C -algebra 308.C
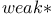 Dirichlet algebra 164.G Dirichlet algebra 164.G
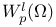 (Sobolev space) 168.B (Sobolev space) 168.B
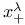 (distribution) 125.EE (distribution) 125.EE
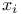 -axis (of a Euclidean space) 140 -axis (of a Euclidean space) 140
 -capacity 169.C -capacity 169.C
 -excessive function 261.D -excessive function 261.D
 -limit point 126.D -limit point 126.D
 -limit set (of an orbit) 126.D -limit set (of an orbit) 126.D
 -perfect, -perfect,  -perfectness 186.J -perfectness 186.J
 -point (of a meromorphic function) 272.B -point (of a meromorphic function) 272.B
 -pseudo-orbit 126.J -pseudo-orbit 126.J
 -quartile 396.C -quartile 396.C
 -string 248.L -string 248.L
 -trimmed mean 371.H -trimmed mean 371.H
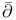 -cohomology groups 72.D -cohomology groups 72.D
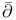 -complex 72.D -complex 72.D
 see beta see beta
 -KMS state 402.G -KMS state 402.G
 -shadowed 126.J -shadowed 126.J
 -traced 126.J -traced 126.J
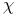 -equivalent (closed on G-manifolds) 431.F -equivalent (closed on G-manifolds) 431.F
 see Delta see Delta
 -measure 270.D -measure 270.D
 -refinement (of a covering) 425.R -refinement (of a covering) 425.R
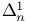 -set 22.D -set 22.D
 see gamma see gamma
 -equivalent (points) 122.A -equivalent (points) 122.A
 -extension 14.L -extension 14.L
 -matrices, Dirac 415.G -matrices, Dirac 415.G
 -perfect 186.J -perfect 186.J
 -perfectness 186.J -perfectness 186.J
 -point of the kth order (of a holomorphic function) 198.C -point of the kth order (of a holomorphic function) 198.C
 -structure 90.D 105.Y -structure 90.D 105.Y
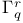 -structure 154.E -structure 154.E
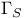 -foliation 154.H -foliation 154.H
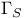 -structure 154.H -structure 154.H
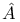 -characteristic class (of a real oriented vector bundle) 237.F -characteristic class (of a real oriented vector bundle) 237.F
 -recursiveness 356.G -recursiveness 356.G
 -function 32.C -function 32.C
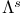 (Lipschitz spaces) 168.B (Lipschitz spaces) 168.B
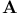 -number 430.C -number 430.C
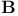 -complete (locally convex space) 424.X -complete (locally convex space) 424.X
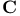 (complex numbers) 74.A 294.A (complex numbers) 74.A 294.A
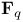 (finite field with q elements) 450.Q (finite field with q elements) 450.Q
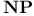 71.E 71.E
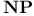 co- 71.E co- 71.E
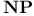 -complete 71.E -complete 71.E
 -completeness 71.E -completeness 71.E
 -hard 71.E -hard 71.E
 -space 71.E -space 71.E
 -time 71.E -time 71.E
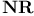 (neighborhood retract) 202.D (neighborhood retract) 202.D
 (natural numbers) 294.A 249.B (natural numbers) 294.A 249.B
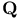 (rational numbers) 294.A 294.D (rational numbers) 294.A 294.D
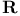 (real numbers) 294.A 355.A (real numbers) 294.A 355.A
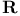 -action (continuous) 126.B -action (continuous) 126.B
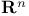 -valued random variable 342.C -valued random variable 342.C
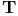 -number (transcendental number) 430.C -number (transcendental number) 430.C
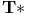 -number (transcendental number) 430.C -number (transcendental number) 430.C
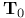 -space 425.Q -space 425.Q
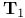 -space 425.Q -space 425.Q
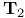 -space 425.Q -space 425.Q
 -space 425.Q -space 425.Q
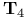 -space 425.Q -space 425.Q
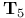 -space 425.Q -space 425.Q
 -space 425.Q -space 425.Q
|  (integers) 294.A 294.C (integers) 294.A 294.C
 -action (continuous) 126.B -action (continuous) 126.B
 -action of class -action of class  126.B 126.B
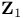 -extension 14.L -extension 14.L
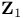 -extension basic 14.L -extension basic 14.L
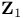 -extension cyclotomic 14.L -extension cyclotomic 14.L
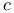 (a sequence space) 168.B (a sequence space) 168.B
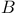 -measurable function 270.J -measurable function 270.J
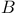 -measurable set 270.C -measurable set 270.C
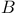 -regular measure 270.F -regular measure 270.F
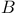 -summable series 379.O -summable series 379.O
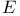 -function 46.C -function 46.C
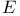 -space 193.N -space 193.N
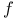 -metric 136.F -metric 136.F
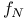 -metric 136.F -metric 136.F
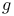 -lattice (of a separable algebra) 27.A -lattice (of a separable algebra) 27.A
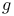 -lattice integral 27.A -lattice integral 27.A
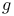 -lattice normal 27.A -lattice normal 27.A
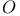 -differential (on an algebraic curve) 9.F -differential (on an algebraic curve) 9.F
 -genus (of an algebraic curve) 9.F -genus (of an algebraic curve) 9.F
 -ideal integrated two-sided 27.A -ideal integrated two-sided 27.A
 -ideal two-sided 27.A -ideal two-sided 27.A
 -linearly equivalent divisors (on an algebraic curve) 9.F -linearly equivalent divisors (on an algebraic curve) 9.F
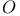 -specialty index (of a divisor of an algebraic curve) 9.F -specialty index (of a divisor of an algebraic curve) 9.F
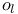 -ideal, left 27.A -ideal, left 27.A
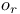 -ideal, right 27.A -ideal, right 27.A
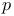 -adic exponential valuation 439.F -adic exponential valuation 439.F
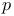 -adic extension (of the field of quotients of a Dedekind domain) 439.F -adic extension (of the field of quotients of a Dedekind domain) 439.F
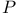 -function, Weierstrass 134.F App. Table -function, Weierstrass 134.F App. Table
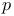 -index (of a central simple algebra over a finite algebraic number field) 29.G -index (of a central simple algebra over a finite algebraic number field) 29.G
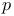 -invariant (of a central simple algebra over a finite algebraic number field) 29.G -invariant (of a central simple algebra over a finite algebraic number field) 29.G
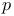 -primary ideal 67.F -primary ideal 67.F
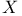 -minimal function 367.E -minimal function 367.E
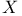 -valued holomorphic 251.G -valued holomorphic 251.G
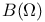 ( (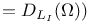 168.B 168.B
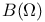 (the space of hyperfunctions) 125.V (the space of hyperfunctions) 125.V
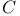 -group 52.M -group 52.M
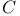 -theory, Serre 202.N -theory, Serre 202.N
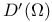 125.B 125.B
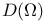 125.B 168.B 125.B 168.B
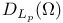 (the totality of functions (the totality of functions 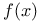 in in 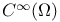 such that for all such that for all  , , 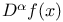 belongs to belongs to 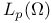 with respect to Lebesgue measure) 168.B with respect to Lebesgue measure) 168.B
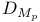 , , 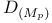 168.B 168.B
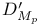 , , 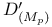 125.U 125.U
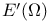 125.I 125.I
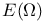 ( = ( = 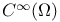 ) 125.I 168.B ) 125.I 168.B
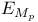 , , 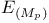 168.B 168.B
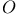 -module 383.I -module 383.I
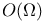 (space of holomorphic functions in (space of holomorphic functions in  ) 168.B ) 168.B
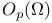 168.B 168.B
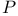 -acyclic 200.Q -acyclic 200.Q
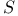 (the totality of rapidly decreasing (the totality of rapidly decreasing 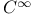 -functions) 168.B -functions) 168.B
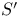 (the totality of tempered distributions) 125.N (the totality of tempered distributions) 125.N
 -absolutely continuous (additive set function) 380.C -absolutely continuous (additive set function) 380.C
 -completion 270.D -completion 270.D
 -conformal function 352.B -conformal function 352.B
 -constant stratum 418.E -constant stratum 418.E
 -integrable 221. B -integrable 221. B
 -measurable 270.D -measurable 270.D
 -null set 370.D -null set 370.D
 -operator, bounded 356.B -operator, bounded 356.B
 -singular (additive set function) 380.C -singular (additive set function) 380.C
 -conjugate 126.H -conjugate 126.H
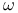 -connected space 79.C -connected space 79.C
 -connected space, locally 79.C -connected space, locally 79.C
 -consistent (system) 156.E -consistent (system) 156.E
 -equivalent 126.H -equivalent 126.H
 -explosion 126.J -explosion 126.J
 -group 190.E -group 190.E
 -homomorphism (between -homomorphism (between  -groups) 190.E -groups) 190.E
 -isomorphism (between -isomorphism (between  -groups) 190.E -groups) 190.E
 -limit point 126.D -limit point 126.D
 -limit set 126.D -limit set 126.D
 -modules, duality theorem for 422.L -modules, duality theorem for 422.L
 -stability theorem 126.J -stability theorem 126.J
 -stable, -stable,  - 126.H - 126.H
 -subgroup (of an -subgroup (of an  -group) 190.E -group) 190.E
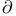 -functor 200.I -functor 200.I
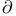 -functor universal 200.I -functor universal 200.I
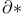 -functor 200.I -functor 200.I
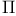 theorem 116 theorem 116
 topology 424.R topology 424.R
 -group 151.F -group 151.F
 -length (of a group) 151.F -length (of a group) 151.F
 -manifold 114.I -manifold 114.I
 -series(of a group) 151.F -series(of a group) 151.F
 -solvable group 151.F -solvable group 151.F
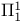 set 22.A set 22.A
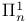 set 22.D set 22.D
 -set 308.I -set 308.I
 -additive measure 270.D -additive measure 270.D
 -additivity 270.D -additivity 270.D
 -algebra 270.B -algebra 270.B
 -algebra optional 407.B -algebra optional 407.B
 -algebra predictable 407.B -algebra predictable 407.B
 -algebra tail 342.G -algebra tail 342.G
 -algebra topological 270.C -algebra topological 270.C
 -algebra well-measurable 407.B -algebra well-measurable 407.B
 -compact space 425.V -compact space 425.V
 -complete (vector lattice) 310.C -complete (vector lattice) 310.C
 -complete lattice 243.D -complete lattice 243.D
 -complete lattice conditionally 243.D -complete lattice conditionally 243.D
 -discrete (covering of a set) 425.R -discrete (covering of a set) 425.R
 -field Bayer sufficient 396.J -field Bayer sufficient 396.J
 -field boundedly complete 396.E -field boundedly complete 396.E
 -field complete 396.E -field complete 396.E
 -field D-sufficient 396.J -field D-sufficient 396.J
 -field decision theoretically sufficient 396.J -field decision theoretically sufficient 396.J
 -field minimal sufficient 396.F -field minimal sufficient 396.F
 -field pairwise sufficient 396.F -field pairwise sufficient 396.F
 -field test sufficient 396.J -field test sufficient 396.J
 -finite (measure space) 270.D -finite (measure space) 270.D
 -function, of Weierstrass 134.F App. Table -function, of Weierstrass 134.F App. Table
 -locally finite covering (of a set) 425.R -locally finite covering (of a set) 425.R
 -process (of a complex manifold) 72.H -process (of a complex manifold) 72.H
 -space 425.Y -space 425.Y
 -subfield necessary 396.E -subfield necessary 396.E
 -subfield sufficient 396.E -subfield sufficient 396.E
 -weak topology 308.B -weak topology 308.B
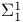 set 22.A set 22.A
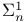 set 22.D set 22.D
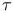 -function 150.D -function 150.D
 (topology) 424.R (topology) 424.R
 , Eddington’s App. A Table , Eddington’s App. A Table
 -covering 273.B -covering 273.B
 -entropy 213.E -entropy 213.E
 -expansion 111.C -expansion 111.C
 -factor 450.N -factor 450.N
 -flat 178.D -flat 178.D
 -Hermitian form 60.O -Hermitian form 60.O
 -independent partitions 136.E -independent partitions 136.E
 -induction, axiom of 33 -induction, axiom of 33
 -neighborhood (of a point) 273.C -neighborhood (of a point) 273.C
 -number 312.C -number 312.C
 -operator, Hilbert 411.J -operator, Hilbert 411.J
 -quantifier, Hilbert 41J J -quantifier, Hilbert 41J J
 -sphere (of a point) 273.C -sphere (of a point) 273.C
 -symbol, Hilbert 411.J -symbol, Hilbert 411.J
 -tensor product 424.R -tensor product 424.R
 -theorem (in predicate logic) 411J -theorem (in predicate logic) 411J
 -trace form 60.O -trace form 60.O
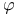 -subsequence 354.E -subsequence 354.E
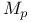 , ultradistribution of class 125.U , ultradistribution of class 125.U
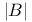 -summable series 379.0 -summable series 379.0
(B,N)-pair 151.J
(DF)-space 424.P
(F)-space 424.I
(H, p)-summable 379.M
(LF)-space 424.W
(M)-space (= Montel space) 424.O
(n + 2)-hyperspherical coordinates 79.A 90.B
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



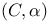 -summation
-summation 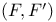 -free (compact oriented G-manifold)
-free (compact oriented G-manifold) 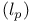 or
or 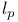 (a sequence space)
(a sequence space) 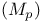 , ultradistribution of class
, ultradistribution of class 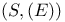 -valued random variable
-valued random variable 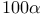 %-point
%-point 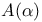 -stability
-stability 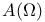 (the totality of functions bounded and continuous on the closure of
(the totality of functions bounded and continuous on the closure of  and holomorphic in
and holomorphic in 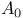 -stability
-stability 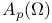 (the totality of functions f that are holomorphic in
(the totality of functions f that are holomorphic in 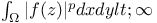 )
) 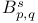 (Besov spaces)
(Besov spaces) 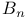 set
set 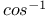
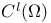 (the totality of l times continuously differentiable functions in
(the totality of l times continuously differentiable functions in 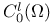 (the totality of functions in
(the totality of functions in  -
-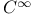 -manifold
-manifold 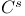 -structure)
-structure) 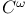 -homomorphism (between Lie groups)
-homomorphism (between Lie groups) 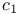 -bundle
-bundle 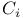 -field
-field 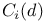 -field
-field 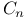 set
set 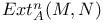

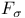 set
set 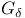 -set
-set 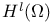 (Sobolev spaces)
(Sobolev spaces) 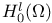 (Sobolev spaces)
(Sobolev spaces) 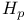 (Hardy spaces)
(Hardy spaces) 
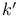 -space
-space 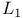 -algebra (of a locally compact Hausdorff group)
-algebra (of a locally compact Hausdorff group) 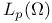 (the space of measurable functions f(x) on
(the space of measurable functions f(x) on 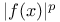 ,
, 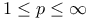 , is integrable)
, is integrable) 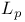 -space, abstract
-space, abstract 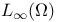
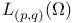 (the Lorentz spaces)
(the Lorentz spaces) 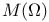 (the set of all essentially bounded measurable functions on
(the set of all essentially bounded measurable functions on 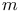 matrix
matrix 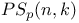 (projective symplectic group over K)
(projective symplectic group over K) 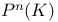 (projective space)
(projective space) 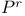 -figure
-figure 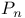 set
set 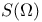 (totality of measurable functions on
(totality of measurable functions on 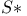 -number
-number 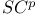 -manifold
-manifold 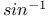
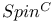 bundle
bundle 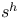 -factorial experiment
-factorial experiment 
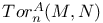
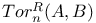
 -statistic Hotelling’s
-statistic Hotelling’s 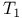 -uniform space
-uniform space 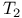 -topological group
-topological group 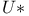 -number
-number 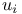 -scale
-scale 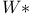 -algebra
-algebra 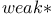 Dirichlet algebra
Dirichlet algebra 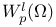 (Sobolev space)
(Sobolev space) 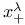 (distribution)
(distribution) 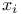 -axis (of a Euclidean space)
-axis (of a Euclidean space)  -capacity
-capacity 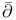 -cohomology groups
-cohomology groups 
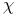 -equivalent (closed on G-manifolds)
-equivalent (closed on G-manifolds) 
 -measure
-measure 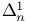 -set
-set 
 -equivalent (points)
-equivalent (points) 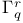 -structure
-structure 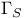 -foliation
-foliation 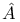 -characteristic class (of a real oriented vector bundle)
-characteristic class (of a real oriented vector bundle)  -recursiveness
-recursiveness  -function
-function 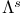 (Lipschitz spaces)
(Lipschitz spaces) 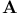 -number
-number 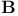 -complete (locally convex space)
-complete (locally convex space) 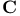 (complex numbers)
(complex numbers) 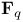 (finite field with q elements)
(finite field with q elements) 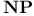
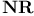 (neighborhood retract)
(neighborhood retract)  (natural numbers)
(natural numbers) 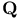 (rational numbers)
(rational numbers) 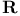 (real numbers)
(real numbers) 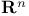 -valued random variable
-valued random variable 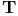 -number (transcendental number)
-number (transcendental number) 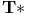 -number (transcendental number)
-number (transcendental number) 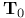 -space
-space 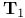 -space
-space 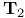 -space
-space  -space
-space 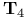 -space
-space 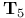 -space
-space 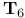 -space
-space 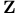 (integers)
(integers) 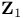 -extension
-extension 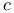 (a sequence space)
(a sequence space) 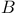 -measurable function
-measurable function 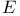 -function
-function 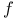 -metric
-metric 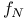 -metric
-metric 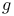 -lattice (of a separable algebra)
-lattice (of a separable algebra) 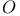 -differential (on an algebraic curve)
-differential (on an algebraic curve) 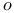 -ideal integrated two-sided
-ideal integrated two-sided 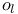 -ideal, left
-ideal, left 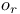 -ideal, right
-ideal, right 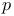 -adic exponential valuation
-adic exponential valuation 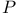 -function, Weierstrass
-function, Weierstrass 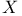 -minimal function
-minimal function 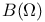 (
(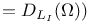
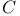 -group
-group 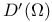
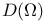
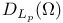 (the totality of functions
(the totality of functions 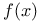 in
in 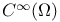 such that for all
such that for all 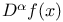 belongs to
belongs to 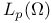 with respect to Lebesgue measure)
with respect to Lebesgue measure) 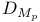 ,
, 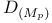
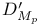 ,
, 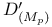
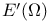
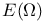 ( =
( = 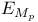 ,
, 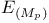
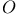 -module
-module 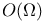 (space of holomorphic functions in
(space of holomorphic functions in 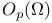
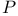 -acyclic
-acyclic 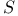 (the totality of rapidly decreasing
(the totality of rapidly decreasing 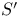 (the totality of tempered distributions)
(the totality of tempered distributions)  -absolutely continuous (additive set function)
-absolutely continuous (additive set function) 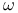 -connected space
-connected space 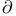 -functor
-functor 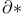 -functor
-functor  theorem
theorem  topology
topology 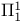 set
set 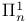 set
set  -set
-set  -additive measure
-additive measure 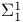 set
set 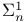 set
set 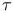 -function
-function  (topology)
(topology) 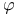 -subsequence
-subsequence 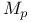 , ultradistribution of class
, ultradistribution of class 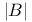 -summable series
-summable series