|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ito K. — Encyclopedic Dictionary of Mathematics |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Distribution(s) one-side stable for exponent 1/2 App. A Table
Distribution(s) operator-valued 150.D
Distribution(s) p-dimensional noncentral Wishart 374.C
Distribution(s) Pearson 397.D
Distribution(s) pluriharmonic 21.C
Distribution(s) Poisson 341.D 397.F App. Table
Distribution(s) polynomial App. A Table
Distribution(s) population 396.B 401.F
Distribution(s) positive 125.C
Distribution(s) posterior 401.B 403.G
Distribution(s) predictive 403.G
Distribution(s) prior 401.B 403.G
Distribution(s) probability 342.B App. Table
Distribution(s) probability, of a random variable 342.C
Distribution(s) purely discontinuous 341.D
Distribution(s) quasistable 341.G
Distribution(s) random 395.H 407.C
Distribution(s) random, in the wider sense 395.C 407.C
Distribution(s) random, with independent values it every point 407.C
Distribution(s) rapidly decreasing 125.O
Distribution(s) rectangular App. A Table
Distribution(s) sampling 374.A
Distribution(s) semistable 341.G
Distribution(s) simple, potential of 338.A
Distribution(s) simultaneous 342.C
Distribution(s) slowly increasing 125.N
Distribution(s) stable 341.G
Distribution(s) standard Gaussian 176.A
Distribution(s) standard normal 341.D
Distribution(s) strictly stationary random 395.H
Distribution(s) strongly stationary random 395.H
Distribution(s) substituted 125.Q
Distribution(s) t- 341.D 374.B App. Table
Distribution(s) tempered 125.N
Distribution(s) two-sided exponential App. A Table
Distribution(s) ultra-, of class 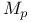 or or 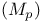 125.U 125.BB 125.U 125.BB
Distribution(s) uniform 341.D App. Table
Distribution(s) unit 341.D
Distribution(s) value 124.A
Distribution(s) waiting time 307.C
Distribution(s) weakly stationary random 395.C
Distribution(s) Wishart 374.C
Distribution(s) z- 341.D 374.B App. Table
Distribution(s), entropy of a 403.B
Distribution(s), exponential family of 396.G
Distribution-free (test) 371.A
Distribution-free method 371.A
Distributive algebra 231.A
Distributive lattice 243.E
Distributive law (in a lattice) 243.E
Distributive law (in a ring) 368.A
Distributive law (in algebra of sets) 381.B
Distributive law (on cardinal numbers) 49.C
Distributive law (on natural numbers) 294.B
Distributive law complete (in a lattice-ordered group) 243.G
Disturbance 128.C
Diurnal aberration 392
Div (divergence) 442.D
diverge 87.B 87.E 379.A
Diverge to  87.D 87.D
Divergence (of a differentiable vector field) 442.D
Divergence (of a vector field with respect to a Riemannian metric) 105.W
Divergence (of a vector field with respect to a volume element) 105.W
Divergence form 323.D
Divergence infrared 146.B
Divergence theorem 94.D
Divergence ultraviolet 146.B
Divergent (double series) 379.E
Divergent (infinite product) 379.G
Divergent (integral) 216.E
Divergent (sequence of real numbers) 87.B
Divergent (series) 379.A
Divergent properly 379.A
Divide (a bounded domain) 384.F
Divided difference 223.D
Dividing cycle (on an open Riemann surface) 367.I
Divisibility relation (in a ring) 67.H
Divisible (Abelian p-group) 2.D
Divisible (additive group) 2.E
Divisible (element of ring) 67.H 277.D
Divisible (fractional ideal) 14.E
Divisible (general Siegel domain) 384.F
Divisible (number) 297.A
Divisible A-module 277.D
Divisible subgroup (of a discrete Abelian group) 422.G
Division (of a pseudomanifold) 65.A
Division algebra 29.A
Division algorithm of natural numbers 297.A
Division algorithm of polynomials 337.C
Division algorithm Weierstrass type (for microdifferential operators) 274.E
Division ring 368.B
Division simplicial 65.A
Division theorem Spath type (for microdifferential operators) 274.E
Divisor 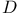 -linearly equivalent (on an algebraic curve) 9.F -linearly equivalent (on an algebraic curve) 9.F
Divisor (in a closed Riemann surface) 11.D
Divisor (in a complex manifold) 72.F
Divisor (in an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor (in an algebraic variety) 16.M
Divisor (of a fractional ideal) 14.E
Divisor (of a number) 297.A
Divisor (of an algebraic function field of dimension 1) 9.D
Divisor (of an algebraic number field) 14.F
Divisor (of an element of a ring) 67.H
Divisor ample 16.N
Divisor branch (in a covering) 9.I
Divisor canonical (of a Jacobian variety) 9.E
Divisor canonical (of a Riemann surface) 11.D
Divisor canonical (of an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor canonical (of an algebraic variety) 16.O
Divisor Cartier 16.M
Divisor class (on a Riemann surface) 11.D
Divisor class canonical 11.D
Divisor class differential 11.D
Divisor class group (of a Riemann surface) 11.D
Divisor common (of elements of a ring) 67.H
Divisor complex line bundle determined by 72.F
Divisor differential (of an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor effective (on a variety) 16.M
Divisor effective (on an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor elementary (of a matrix) 269.E
Divisor embedded prime (of an ideal) 67.F
Divisor finite prime 439.H
Divisor function 295.C
Divisor function generalized 295.C
Divisor greatest common 297.A
Divisor greatest common (of an element of a ring) 67.H
Divisor group (of a compact complex manifold) 72.F
Divisor imaginary infinite prime 439.H
Divisor infinite prime 439.H
Divisor integral (of an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor integral (of an algebraic number field) 14.F
Divisor integral (on a Riemann surface) 11.D
Divisor isolated prime (of an ideal) 67.F
Divisor k-rational (on an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor linearly equivalent (of a complex manifold) 72.F
Divisor maximal prime (of an ideal) 67.F
Divisor minimal prime (of an ideal) 67.F
Divisor nondegenerate 16.N
Divisor nondegenerate (on an Abelian variety) 3.D
Divisor numerically connected 232.D
Divisor of a differential form (on an algebraic variety) 16.O
Divisor of a function (on an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor of a function (on an algebraic variety) 16.M
Divisor pole (of a function on an algebraic variety) 16.M
Divisor positive (of an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor positive (on a Riemann surface) 11.D
Divisor prime (of an algebraic function field of dimension 1) 9.D
Divisor prime (of an algebraic number field or an algebraic function field of one variable) 439.H
Divisor prime (of an ideal) 67.F
Divisor prime (on a Riemann surface) 11.D
| Divisor prime rational, over a field (on an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor principal (on a Riemann surface) 11.D
Divisor principal (on an algebraic curve) 9.C
Divisor problem, Dirichlet 242.A
Divisor real infinite prime 439.H
Divisor real prime 439.H
Divisor sheaf of ideals of (of a complex manifold) 72.F
Divisor special 9.C
Divisor very ample 16.N
Divisor zero (of a function on an algebraic variety) 16.M
Divisor zero (of a ring) 368.B
Divisor zero, with respect to M/P 284.A
Divisor, complete linear system defined by 16.N
Dixmier theorem, Rellich — 351.C
Dixmier, Jacques(1924-) 18.I 36.r 68.I 308.F 308.r 351.C 437.r
Dixon — Ferrar formula App. A Table
Dixon, A.C.(1865-1936) App.A Table
DK method 301.F
DKA method 301.F
DLR equation 402.G
Dmitriev, N.A. 44.r
DN App. A Table
do Carmo, Manfrcdo Perdigao 111.r 275.A 275.B 365.G 365.r
Dobrushin, Roland L’vovich(1929-) 250.r 340.B 340.r 402.G 407.B
dodecahedron 357.B
Doerge, Karl(1898-1975) 337.F
Doetsch three-line theorem 43.E
Doetsch, Gustav(1892-1977) 43.E 208.r 240.r 379.M
Doi, Koji(1934-) 450.L
Doig, Alison G. 215.D
Dolansky, Ladislav NTR
Dolbeault cohomology group 72.D
Dolbeault complex 72.D
Dolbeault lemma 72.D
Dolbeault theorem 72.D
Dolbeault, Pierre(1924-) 72.D
Dolbeault—Lemoine, Simone 365.E
Dold, Albrecht E.(1928) 70.F 70.r 201.r
Dolgachev, Igor V. App.A Table
Dollard, John Day(1937-) 375.B
Domain kernel (of a sequence of domains) 333.C
Domain(s) (in a topological space) 79.A
Domain(s) (of a correspondence) 358.B
Domain(s) (of a mapping) 37.C 381.C
Domain(s) (of a variable) 165.C
Domain(s) angular 333.A
Domain(s) annular 333.A
Domain(s) Cartan pseudoconvex 21.I
Domain(s) circular 333.A
Domain(s) closed plane 333.A
Domain(s) complete Reinhardt 21.B
Domain(s) convergence (of a power series) 21.B
Domain(s) Courant — Cheng, theorem 391.H
Domain(s) d-pseudoconvex 21.G
Domain(s) Dirichlet 120.A
Domain(s) divisible bounded 284.F
Domain(s) effective 88.D
Domain(s) fundamental 234.C
Domain(s) generated Siegel 384.F
Domain(s) holomorphically complete 21.F
Domain(s) holomorphically convex 21.H
Domain(s) homogeneous bounded 384.A 412.F
Domain(s) individual 411.H
Domain(s) integral 368.B
Domain(s) irreducible symmetric bounded 412.F
Domain(s) Jordan 333.A
Domain(s) Levi pseudoconvex 21.I
Domain(s) locally Cartan pseudoconvex 21.I
Domain(s) locally Levi pseudoconvex 21.I
Domain(s) nodal 391.H
Domain(s) Noetherian 284.A
Domain(s) Noetherian integral 284.A
Domain(s) object 411.G
Domain(s) of a local homomorphism 423.O
Domain(s) of attraction 374.G
Domain(s) of class 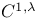 323.F 323.F
Domain(s) of dependence 325.B
Domain(s) of holomorphy 21.F
Domain(s) of influence 325.B
Domain(s) of integration 216.F
Domain(s) of operator 409.A
Domain(s) operator (of a group) 190.E
Domain(s) plane 333
Domain(s) principal ideal 67.K
Domain(s) pseudoconvex 21.G
Domain(s) Reinhardt 21.B
Domain(s) Siegel 384.A
Domain(s) Siegel, generalized 384.F
Domain(s) Siegel, irreducible 384.E
Domain(s) Siegel, of the first kind 384.A
Domain(s) Siegel, of the second kind 384.A
Domain(s) Siegel, of the third kind 384.A
Domain(s) slit 333.A
Domain(s) strongly pseudoconvex 21.G
Domain(s) sweepable bounded 284.F
Domain(s) symmetric bounded 412.F
Domain(s) unique factorization 40.H
Domain(s) universal 16. A
Domain(s) Weil 21.G
Domain(s) with regular boundary (in a 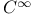 -manifold) 105.U -manifold) 105.U
Domain(s) with smooth boundary (in a 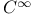 -manifold) 105.U -manifold) 105.U
Domain(s), Brouwer theorem on the invariance of 117.D
Domain(s), spectrum of 391.A
Domb, Cyril 361.r 402.r
Dominant (of a sequence of functions) 435.A
Dominant integral form (on a Cartan subalgebra) 248.W
Dominate (an imputation of a game) 173.D
Dominated (by a family of topological spaces) 425.M
Dominated (statistical structures) 396.F
Dominated ergodic theorem 136.B
Dominated weakly (statistical structure) 396.F
Dominating set 186.I
Domination principle 338.L
Domination principle inverse 338.L
Domination, number of 186.I
Donaldson, Simon K. 114.K 114.r
Donford — Schwartz integral, Bartle — 443.G
Dongarra, Jack J.(1950-) 298.r
Donin, Iosif Failovich(1945-) 72.G
Donnelly, Harold Gerard(1951-) 391.N
Donoghue, William F., Jr. 212
Donsker invariance principle 250.E
Donsker, Monroe David(1924-) 250.E 340.r
Doob — Meyer decomposition theorem 262.D
Doob, Joseph Leo(1910—) 5.r 45.r 62.E 86.E 115.r 136.B 162 193.T 207.C 250.r 260.J 261.A 261.F 261.r 262.A 262.B 262.D 341.r 342.r 395.r 406.A 407.A 407.r
Doolittle method 302.B
Doolittle, M.H. 302.B
Doplichcr, Sergio(1940-) 150.E
Dorfmeister, Josef F.(1946-) 384.r
Dorn, William Schroeder(1928-) 349.r
Dornhoff, Larry 362.r
Dotted indices 258.B
Dotted spinor of rank k 258.B
Douady space 23.G
Douady, Adrien(1935-) 23.G 72.G
Double chain complex 200.E
Double complex 200.H
Double coset (of two subgroups of a group) 190.C
Double distribution, potential of 338.A
Double exponential formula 299.B
Double integral 216.F
Double integral theorem, Fourier 160.B
Double layer, potential of 338.A
Double mathematical induction 294.I)
Double negation, discharge of 411.I
Double point, rational 418.C
Double ratio 343.E
Double sampling inspection 404.C
Double sequence 379.E
Double series 379.E
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



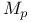 or
or 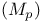

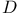 -linearly equivalent (on an algebraic curve)
-linearly equivalent (on an algebraic curve) 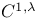
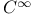 -manifold)
-manifold)