јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Hogben L. Ч Handbook of Linear Algebra
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Linear Algebraјвтор: Hogben L. јннотаци€: The Handbook of Linear Algebra provides comprehensive coverage of linear algebra concepts, applications, and computational software packages in an easy-to-use handbook format. The esteemed international contributors guide you from the very elementary aspects of the subject to the frontiers of current research. The book features an accessible layout of parts, chapters, and sections, with each section containing definition, fact, and example segments. The five main parts of the book encompass the fundamentals of linear algebra, combinatorial and numerical linear algebra, applications of linear algebra to various mathematical and nonmathematical disciplines, and software packages for linear algebra computations. Within each section, the facts (or theorems) are presented in a list format and include references for each fact to encourage further reading, while the examples illustrate both the definitions and the facts. Linearization often enables difficult problems to be estimated by more manageable linear ones, making the Handbook of Linear Algebra essential reading for professionals who deal with an assortment of mathematical problems.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2006 оличество страниц: 1400ƒобавлена в каталог: 30.06.2008ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Distance, coding theory 61Ч2 Distance, Euclidean point space 66Ч2 Distance, Euclidean spaces 65Ч4 Distance, graphs 28Ч1 Distance, inner product spaces 5Ч1 Distance, NMR protein structure determination 60Ч2 Distance, numerical range 18Ч1 Distance-regular graph 28Ч11 Distinguished eigenvalues, cone invariant departure, matrices 26Ч3 to 26Ч5 Distinguished eigenvalues, nonnegative and stochastic matrices 9Ч2 Distinguished face 26Ч5 Distributivity 69Ч1 Distributivity axiom 1Ч1 Divide and Conquer Bidiagonal singular value decomposition 45Ч10 Divide and conquer method 42Ч12 to 42Ч14 Division algebra 69Ч2 69Ч4 Division property 6Ч11 DLAR2V LAPACK subroutine 42Ч9 DLARGV LAPACK subroutine 42Ч9 DLARTV LAPACK subroutine 42Ч9 Document vector 63Ч1 Documents, retrieved 63Ч2 Domain decomposition methods 41Ч12 Domain, linear transformations 3Ч1 Dominant eigenvalue 42Ч2 Dong, Qunfeng 60Ч13 Dongarra, Jack 74Ч1 to 74Ч7 75Ч1 77Ч1 DORGTR LAPACK subroutine 42Ч8 Dot product, Bernstein Ч Vazirani problem 62Ч11 Dot product, floating point numbers 37Ч14 Dot product, inner product spaces 5Ч2 Dot, Mathematica software, matrices 73Ч8 Dot, Mathematica software, vectors 73Ч4 DotProduct, Maple software 72Ч3 Double directed tree 29Ч2 Double echelon form 21Ч2 Double generalized stars 34Ч11 to 34Ч14 Double path, generalized stars 34Ч11 DOUBLE PRECISION 37Ч13 double stars 34Ч11 Doubly nonnegative matrices 35Ч10 to 35Ч11 Doubly stochastic matrices, combinatorial matrix theory 27Ч10 to 27Ч12 Doubly stochastic matrices, fundamentals 9Ч15 Doubly stochastic matrices, permanents 31Ч3 to 31Ч4 Downdating 39Ч8 to 39Ч9 Downer branch 34Ч2 Downer vertex 34Ч2 Drazin inverse 55Ч7 Drmac, Zlatko 46Ч1 to 46Ч16 Drop, Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч27 Drop, Mathematica software, matrices manipulation 73Ч13 Drop, Mathematica software, vectors 73Ч3 Drop-off condition 21Ч12 DROT BLAS routine 42Ч9 DSBTRD LAPACK subroutine 42Ч9 DSDRV ARPACK routine 42Ч21 DSTEBZ LAPACK subroutine 42Ч15 DSTEDC LAPACK subroutine 42Ч14 DSTEGR LAPACK subroutine 42Ч17 DSTEIN LAPACK subroutine 42Ч15 DSTU (diagonally scaled totally unimodular) matrices, rank revealing decomposition 46Ч8 DSTU (diagonally scaled totally unimodular) matrices, rank revealing decompositions 46Ч9 DSYEV LAPACK subroutine 42Ч11 DSYTRD LAPACK subroutine 42Ч8 Dual linear program 25Ч5 Duality theorem 51Ч7 Duality, code 61Ч3 Duality, cones 8Ч11 26Ч2 Duality, control theory 57Ч2 Duality, inner product spaces 13Ч23 Duality, linear functionals and annihilator 3Ч8 Duality, linear programming 50Ч13 to 50Ч17 Duality, optimality conditions 51Ч6 Duality, projective spaces 65Ч7 Duality, rectangular matrix multiplication 47Ч5 Duality, semidefinite programming 51Ч5 to 51Ч7 Duality, vector norms 37Ч2 Dulmage Ч Mendelsohn Decomposition theorem 27Ч4 Dynamic compensator 57Ч13 Dynamic programming 25Ч3 Dynamical systems, chain recurrence 56Ч7 to 56Ч9 Dynamical systems, eigenvalues and eigenvectors 4Ч11 Dynamical systems, flag manifolds 56Ч9 to 56Ч11 Dynamical systems, Floquet theory 56Ч12 to 56Ч14 Dynamical systems, fundamentals 56Ч1 to 56Ч2 Dynamical systems, Grassmannians 56Ч9 to 56Ч11 Dynamical systems, linear differential equations 56Ч2 to 56Ч4 Dynamical systems, linear dynamical systems 56Ч5 to 56Ч7 Dynamical systems, linear skew product flows 56Ч11 to 56Ч12 Dynamical systems, linearization 56Ч19 to 56Ч21 Dynamical systems, Morse decompositions 56Ч7 to 56Ч9 Dynamical systems, periodic linear differential equations 56Ч12 to 56Ч14 Dynamical systems, random linear dynamical systems 56Ч14 to 56Ч16 Dynamical systems, robust linear systems 56Ч16 to 56Ч19 Eckart Ч Young low rank approximation theorem 5Ч11 ED (Euclidean domain) 23Ч2 ED-RCF (elementarydivisors rational canonical form) matrix 6Ч8 to 6Ч9 EDD (elementary divisor domain) 23Ч2 Edge cut 36Ч3 Edges, digraphs 29Ч1 Edges, Euclidean simplexes 66Ч7 Edges, graphs 28Ч1 28Ч4 Effects of reordering 40Ч14 to 40Ч18 Efficacy, methods comparison 42Ч21 Efficiency, error analysis 37Ч16 to 37Ч17 egn, Mathematica software 73Ч21 egns, Mathematica software 73Ч20 eig command, Matlab software, eigenvalues 15Ч5 eig command, Matlab software, fundamentals 71Ч9 71Ч17 71Ч18 eig command, Matlab software, implicitly restarted Arnoldi method 44Ч1 eig command, Matlab software, Lanczos methods 42Ч21 EigenConditionNumbers, Maple software 72Ч15 Eigenpairs, eigenvalue problems 15Ч10 Eigenpairs, matrix perturbation theory 15Ч1 Eigenproblems, max-plus algebra 25Ч6 to 25Ч8 Eigenproblems, nonsymmetric, LAPACK subroutine package 75Ч17 to 75Ч20 Eigensharp characteristic 30Ч8 Eigenspaces, eigenvalues and eigenvectors 4Ч6 Eigenspaces, max-plus eigenproblem 25Ч6 Eigenspaces, nonnegative and stochastic matrices 9Ч2 Eigensystem, Mathematica software 73Ч14 73Ч15 73Ч16 Eigentriplets, eigenvalue problems 15Ч9 to 15Ч10 Eigentriplets, matrix perturbation theory 15Ч1 Eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) 42Ч2 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, adjacency matrix 28Ч5 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, canonical forms 6Ч2 to 6Ч3 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, cone invariant departure, matrices 26Ч3 to 26Ч5 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, fundamentals 4Ч6 to 4Ч11 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, generalized eigenvalue problem 43Ч1 to 43Ч3 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, graphs 28Ч5 to 28Ч7 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, Hermitian matrices 17Ч13 to 17Ч14 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, inequalities 17Ч9 to 17Ч10 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, LAPACK subroutine package 75Ч9 to 75Ч11 75Ч11 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, large-scale matrix computations 49Ч12 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, Maple software 72Ч11 to 72Ч12 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, Mathematica software 73Ч14 to 73Ч16 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, Matlab software 71Ч9 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, matrix equalities and inequalities 14Ч1 to 14Ч5 14Ч8 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, multiplicity lists 34Ч7 to 34Ч8 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, numerical stability and instability 37Ч20 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, pseudoeigenvalues and pseudo-eigenvectors 16Ч1 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, reducible matrices 9Ч8 to 9Ч9 9Ч11 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, SchrodingerТs equation 59Ч7 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, sign-pattern matrices 33Ч9 to 33Ч11 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, singular values and singular value inequalities 17Ч13 to 17Ч14 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, sparse eigenvalue solvers, software 77Ч2 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, spectrum and boundary points 18Ч3 Eigenvalues, high relative accuracy, accurate SVD 46Ч2 to 46Ч5 46Ч7 Eigenvalues, high relative accuracy, fundamentals 46Ч1 to 46Ч2 Eigenvalues, high relative accuracy, one-sided Jacobi SVD algorithm 46Ч2 to 46Ч5 Eigenvalues, high relative accuracy, positive definite matrices 46Ч10 to 46Ч14 Eigenvalues, high relative accuracy, preconditioned Jacobi SVD algorithm 46Ч5 to 46Ч7 Eigenvalues, high relative accuracy, rank revealing decomposition 46Ч7 to 46Ч10 Eigenvalues, high relative accuracy, structured matrices 46Ч7 to 46Ч10 Eigenvalues, high relative accuracy, symmetric indefinite matrices 46Ч14 to 46Ч16 Eigenvalues, Maple 72Ч11 72Ч12 72Ч14 Eigenvalues, Maple software 72Ч15 Eigenvalues, Mathematica software, eigenvalues 73Ч14 73Ч15 Eigenvalues, Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч27 Eigenvalues, Mathematica software, singular values 73Ч17 Eigenvalues, numerical methods, high relative accuracy computation 46Ч1 to 46Ч16 Eigenvalues, numerical methods, implicitly restarted Arnoldi method 44Ч1 to 44Ч12 Eigenvalues, numerical methods, iterative solution methods 41Ч1 to 41Ч17 Eigenvalues, numerical methods, singular value decomposition 45Ч1 to 45Ч12 Eigenvalues, numerical methods, symmetric matrix techniques 42Ч1 to 42Ч22 Eigenvalues, numerical methods, unsymmetric matrix techniques 43Ч1 to 43Ч11 Eigenvalues, problems, generalized 15Ч9 to 15Ч11 Eigenvalues, problems, perturbation theory 15Ч1 to 15Ч6 15Ч9 Eigenvalues, problems, relative perturbation theory 15Ч13 to 15Ч15 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, bisection method 42Ч14 to 42Ч15 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, comparison ofmethods 42Ч21 to 42Ч22 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, divide and conquer method 42Ч12 to 42Ч14 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, fundamentals 42Ч1 to 42Ч2 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, implicitly shifted QR method 42Ч9 to 42Ч11 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, inverse iteration 42Ч14 to 42Ч15 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, Jacobi method 42Ч17 to 42Ч19 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, Lanczos method 42Ч19 to 42Ч21 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, method comparison 42Ч21 to 42Ч22 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, methods 42Ч2 to 42Ч5 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, multiple relatively robust representations 42Ч15 to 42Ч17 Eigenvalues, symmetric matrix techniques, tridiagonalization 42Ч5 to 42Ч9 Eigenvalues, unsymmetric matrix techniques, dense matrix techniques 43Ч3 to 43Ч9 Eigenvalues, unsymmetric matrix techniques, fundamentals 43Ч1 Eigenvalues, unsymmetric matrix techniques, generalized eigenvalue problem 43Ч1 to 43Ч3 Eigenvalues, unsymmetric matrix techniques, sparse matrix techniques 43Ч9 to 43Ч11 Eigenvectors, Maple software 72Ч11 Eigenvectors, Mathematica software 73Ч14 EIGS subroutine package 76Ч9 to 76Ч10 eigshow command, Matlab software 71Ч9 eigtool, Matlab software 16Ч12 71Ч20 Eijkhout, Victor 74Ч1 to 74Ч7 77Ч1 Electron density distribution function 60Ч7 Electrostatics 59Ч11 Element of volume 13Ч25 Element, Mathematica software 73Ч24 Elementary analytic results 26Ч12 to 26Ч13 Elementary bidiagonal matrices 21Ч5 Elementary column operations 6Ч11 Elementary divisors 6Ч8 to 6Ч11 Elementary divisors rational canonical form (ED-RCF) matrix 6Ч8 to 6Ч9 Elementary matrices 1Ч12 Elementary row operations, Gaussian and Gauss-Jordan elimination 1Ч7 Elementary row operations, matrix equivalence 23Ч5 Elementary row operations, Smith normal form 6Ч11 Elementary symmetric function PЧ2 to PЧ3 Elementarydivisor domain (EDD) 23Ч2 Eliminate, Mathematica software 73Ч20 73Ч23 Elimination graph 40Ч11 Elimination ordering 40Ч14 Elimination sequence 40Ч14 ELMAT directory, Matlab software 71Ч5 Elsner theorem 15Ч2 Embedding graphs 28Ч3 Embree, Mark 16Ч1 to 16Ч15 Empty graphs 28Ч2 Empty matrix 68Ч3 Encoder, coding theory 61Ч1 Encoder, linear block codes 61Ч3 Encoding 61Ч2 Endpoint 28Ч1 Energy norm 37Ч2 Entry weakly sign symmetric P-, 35Ч19 to 35Ч20 Entry, matrices 1Ч3 Entrysign symmetric P-, 35Ч19 to 35Ч20 Envelope method 40Ч16 Envelope, reordering effect 40Ч14 Epsilon-pseudospectrum, square matrix 71Ч20 eqns, Mathematica software 73Ч20 Equal matrices 1Ч3 Equalities and inequalities, matrices, determinantal relations 14Ч10 to 14Ч12 Equalities and inequalities, matrices, eigenvalues 14Ч1 to 14Ч5 14Ч8 Equalities and inequalities, matrices, inversions 14Ч15 to 14Ч17 Equalities and inequalities, matrices, nullity 14Ч12 to 14Ч15 Equalities and inequalities, matrices, rank 14Ч12 to 14Ч15 Equalities and inequalities, matrices, singular values 14Ч8 to 14Ч10 Equalities and inequalities, matrices, spectrum localization 14Ч5 to 14Ч8 Equality-constrained least squares problems 75Ч6 to 75Ч7 Equation solving, Maple software 72Ч9 to 72Ч11 Equations of motion 59Ч3 Equicorrelation matrix and structure 52Ч9 Equilibrium, linear dynamical systems 56Ч5 Equilibrium, matrix games 50Ч18 Equivalence class modulo 25Ч10 Equivalence relation PЧ3 Equivalence, bilinear forms 12Ч2 Equivalence, group representations 68Ч1 Equivalence, Hermitian forms 12Ч8 Equivalence, linear block codes 61Ч3 Equivalence, linear dynamical systems 56Ч5 Equivalence, linear independence, span, and bases 2Ч7 Equivalence, matrix equivalence 23Ч5 Equivalence, matrix representations 68Ч3 Equivalence, scaling nonnegative matrices 9Ч20 Equivalence, sesquilinear forms 12Ч6 Equivalence, systems oflinear equations 1Ч9 Equivalence, trees 34Ч8 Equivalence, vector norms 37Ч3 Ergodic class matrices 9Ч15 Ergodic flow 56Ч14 Ergodicity coefficient, bounds 9Ч5 Ergodicity coefficient, irreducible matrices 9Ч5 Ergodicity coefficient, nonnegative and stochastic matrices 9Ч2 Ergodicity coefficient, reducible matrices 9Ч10 to 9Ч11 Error analysis, algorithms 37Ч16 to 37Ч17 Error analysis, conditioning and condition numbers 37Ч7 to 37Ч9 Error analysis, efficiency 37Ч16 to 37Ч17 Error analysis, floating point numbers 37Ч11 to 37Ч16 Error analysis, fundamentals 37Ч1 to 37Ч2 Error analysis, linear systems conditioning 37Ч9 to 37Ч11 Error analysis, matrix norms 37Ч4 to 37Ч6 Error analysis, numerical stability and instability 37Ч18 to 37Ч21 Error analysis, vector norms 37Ч2 to 37Ч3 Error analysis, vector seminorms 37Ч3 to 37Ч4 Errors, estimation 41Ч16 to 41Ч17 Errors, Krylov subspaces and preconditioners 41Ч2 Errors, linear prediction 64Ч7 Errors, LTI systems 57Ч14 Errors, protection, coding theory 61Ч1 Errors, vectors 61Ч2 ESPRIT algorithm 64Ч17 Estimated principal components 53Ч5 Estimation error 57Ч14 Estimation of state 57Ч11 to 57Ч13 Estimation, correlations and variates 53Ч7 to 53Ч8 Estimation, least squares 53Ч11 to 53Ч12 Euclidean algorithm 6Ч11 Euclidean distance matrices 35Ч9 to 35Ч10 Euclidean Distance Matrix 51Ч9 Euclidean distance, Euclidean point space 66Ч2 Euclidean distance, metric multidimensional scaling 53Ч14 Euclidean domain (ED), certain integral domains 23Ч2 Euclidean domain (ED), matrix equivalence 23Ч6 Euclidean domain (ED), matrix similarity 24Ч2 Euclidean geometry, fundamentals 66Ч1 Euclidean geometry, Gram matrices 66Ч5 to 66Ч7 Euclidean geometry, point spaces 66Ч1 to 66Ч5 Euclidean geometry, resistive electrical networks 66Ч13 to 66Ч15 Euclidean geometry, simplexes 66Ч7 to 66Ч13 Euclidean norm, matrix norms 37Ч4 Euclidean norm, one-sided Jacobi SVD algorithm 46Ч4
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



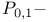 and
and 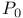 -matrices
-matrices