јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Hogben L. Ч Handbook of Linear Algebra
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Linear Algebraјвтор: Hogben L. јннотаци€: The Handbook of Linear Algebra provides comprehensive coverage of linear algebra concepts, applications, and computational software packages in an easy-to-use handbook format. The esteemed international contributors guide you from the very elementary aspects of the subject to the frontiers of current research. The book features an accessible layout of parts, chapters, and sections, with each section containing definition, fact, and example segments. The five main parts of the book encompass the fundamentals of linear algebra, combinatorial and numerical linear algebra, applications of linear algebra to various mathematical and nonmathematical disciplines, and software packages for linear algebra computations. Within each section, the facts (or theorems) are presented in a list format and include references for each fact to encourage further reading, while the examples illustrate both the definitions and the facts. Linearization often enables difficult problems to be estimated by more manageable linear ones, making the Handbook of Linear Algebra essential reading for professionals who deal with an assortment of mathematical problems.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2006 оличество страниц: 1400ƒобавлена в каталог: 30.06.2008ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Partitioned matrices, random vectors 52Ч3 Partitioned matrices, Schur complements 10Ч6 to 10Ч8 Partitioned matrices, submatrices 10Ч1 to 10Ч3 Partitioned matrices, submatrices and block matrices 10Ч1 Partly decomposable 27Ч3 Pascal matrices, factorizations 21Ч6 Pascal matrices, totally positive and negative matrices 21Ч4 Passage class 54Ч5 Path cover number 34Ч4 Path of length 28Ч1 28Ч2 Path, digraphs 29Ч2 Path, modeling and analyzing fill 40Ч10 Path, sign-pattern matrices 33Ч2 Path-connection PЧ5 Pattern block triangular form 35Ч2 Patterns 27Ч1 see Payoff matrix 50Ч18 Peak characteristics 26Ч9 peaks function, Matlab software 71Ч17 PEIEPs (prescribed entries inverse eigenvalue problems) 20Ч1 to 20Ч3 PEIPs see ЂAffine parameterized IEPs (PIEPs)ї Pencils, matrix, generalized eigenvalue problem 43Ч2 Pencils, matrix, linear differential-algebraic equations 55Ч7 Pencils, matrix, matrices over integral domains 23Ч9 to 23Ч10 Pendant path 34Ч2 Penrose conditions 5Ч12 Perfect code 61Ч2 Perfect elimination ordering, bipartite graphs 30Ч4 Perfect elimination ordering, reordering effect 40Ч14 Perfect matching 30Ч2 Perfectly well determined, high relative accuracy 46Ч8 Period, complex sign and ray patterns 33Ч14 Period, Fourier analysis 58Ч2 Period, imprimitive matrices 29Ч10 Period, irreducible matrices 9Ч3 Period, linear dynamical systems 56Ч5 Period, reducible matrices 9Ч7 Period, SimonТs problem 62Ч13 Periodic characteristics, Fourier analysis 58Ч2 Periodic characteristics, irreducible classes 54Ч5 Periodic characteristics, linear dynamical systems 56Ч5 Periodic linear differential equations 56Ч12 to 56Ч14 Peripheral eigenvalues 26Ч6 Peripheral spectrum, cone invariant departure, matrices 26Ч5 to 26Ч7 Peripheral spectrum, Perron Ч Schaefer condition 26Ч6 perm, Mathematica software 73Ч19 permanent, Mathematica software 73Ч12 Permanental dominance conjecture 31Ч13 Permanents, 31Ч8 Permanents, binary matrices 31Ч5 to 31Ч7 Permanents, determinant connections 31Ч12 to 31Ч13 Permanents, doubly stochastic matrices 31Ч3 to 31Ч4 Permanents, evaluation 31Ч11 to 31Ч12 Permanents, fundamentals 31Ч1 to 31Ч3 Permanents, matrices over 31Ч8 to 31Ч9 Permanents, max-plus algebra 25Ч9 to 25Ч10 Permanents, nonnegative matrices 31Ч7 Permanents, rook polynomials 31Ч10 to 31Ч11 Permanents, subpermanents 31Ч9 to 31Ч10 permMatr, Mathematica software 73Ч19 Permutation invariants, absolute norm 17Ч5 Permutation invariants, vector norms 37Ч2 Permutation matrix, fundamentals 1Ч6 Permutation matrix, Gauss elimination 38Ч7 Permutation matrix, matrices 1Ч4 Permutation matrix, systems oflinear equations 1Ч13 Permutations, eigenvalue problems 15Ч2 Permutations, equivalence 31Ч1 Permutations, fundamentals PЧ5 Permutations, pattern 33Ч2 Permutations, representation 68Ч3 Permutations, restricted positions 31Ч6 Permutations, similarity 27Ч5 33Ч2 Perpendicular bisectors 65Ч4 Perpendicular hyperplanes 66Ч2 Perron branch 36Ч5 Perron component 36Ч10 Perron spaces, Collatz Ч Wielandt sets 26Ч4 Perron spaces, K-reducible matrices 26Ч10 Perron value, convergence properties 9Ч9 to 9Ч10 Perron value, irreducible matrices 9Ч4 to 9Ч5 Perron value, nonnegative and stochastic matrices 9Ч2 Perron value, nonzero spectra 20Ч7 Perron value, reducible matrices 9Ч8 to 9Ч10 Perron Ч Frobenius theorem, cone invariant Perron Ч Frobenius theorem, departure, matrices 26Ч1 to 26Ч3 Perron Ч Frobenius theorem, elementary analytic results 26Ч12 Perron Ч Frobenius theorem, irreducible matrices 9Ч4 29Ч6 Perron Ч Frobenius-type results 9Ч10 Perron Ч Schaefer condition 26Ч5 to 26Ч7 PerronТs theorem 9Ч3 Persistently exciting of order 64Ч12 Personalization vector 63Ч11 Pertinent pages, Web search 63Ч9 Perturbation theory, matrices, eigenvalue problems 15Ч1 to 15Ч6 15Ч9 15Ч13 Perturbation theory, matrices, polar decomposition 15Ч7 to 15Ч9 Perturbation theory, matrices, relative distances 15Ч13 to 15Ч16 Perturbation theory, matrices, singular value problems 15Ч6 to 15Ч7 15Ч12 15Ч15 Perturbations 38Ч2 to 38Ч5 Perturbed linear system 38Ч2 Petersen graphs, adjacency matrices 28Ч7 Petersen graphs, embedding 28Ч5 Petersen graphs, graph parameters 28Ч10 Petersen graphs, Laplacian 28Ч9 Petersen graphs, nonsquare case 32Ч11 Petrie matrix 30Ч4 30Ч5 30Ч7 Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, Arnoldi process 49Ч10 Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, eigenvalue computations 49Ч12 Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, Krylov subspaces 49Ч5 Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, large-scale matrixcomputations 49Ч2 Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, symmetric Lanczos process 49Ч7 Pfaffian properties 12Ч5 Phase 2 geometric interpretation 50Ч13 Phillips regularization 39Ч9 Physical sciences applications 59Ч1 to 59Ч11 Pi function, Mathematica software 73Ч26 pi function, Matlab software 71Ч4 Pi theorem 47Ч8 47Ч9 PickТs inequalities 14Ч2 PID (principal ideal domain) 23Ч2 Pierce decomposition 69Ч13 PillaiТs trace statistic 53Ч13 Pinching, inequalities 17Ч7 PisarenkoТs method 64Ч14 Pivot column 1Ч7 Pivot row 1Ч7 Pivot step 50Ч10 Pivoted QR factorization 39Ч11 Pivoting, elements, Jacobi method 42Ч17 Pivoting, elimination 1Ч7 38Ч7 Pivoting, Gauss Ч Jordan elimination 1Ч7 Pivoting, Jacobi method 42Ч17 42Ч18 Pivoting, linear programming 50Ч10 to 50Ч11 Pivoting, LU decomposition 38Ч10 Pivoting, positions 1Ч7 Pivoting, preconditioned Jacobi SVD algorithm 46Ч5 Pivoting, reordering effect 40Ч18 Planar graphs 28Ч4 PlanckТs constant 59Ч6 Plane, affine spaces 65Ч2 planerot function, Matlab software 42Ч9 PLDU factorization 1Ч14 to 1Ч15 plot command, Matlab software 71Ч14 Plotkin bound 61Ч5 PLU factorization 1Ч13 Plus algebra 69Ч3 Plus, Mathematica software 73Ч27 PO (potentially orthogonality) 33Ч16 Poincare Ч Bendixson theorem 56Ч8 Poincare Ч Birkhoff Ч Witt theorem, Lie algebras 70Ч3 Poincare Ч Birkhoff Ч Witt theorem, Malcev algebras 69Ч17 Poincare Ч Birkhoff Ч Witt theorem, nonassociative algebra 69Ч3 Point spaces 66Ч1 to 66Ч5 Point-wise bounded 37Ч3 Point-wise similarity 24Ч1 Pointed cones 8Ч10 Points, affine spaces 65Ч2 Points, Euclidean point space 66Ч1 Points, projective spaces 65Ч6 PoissonТs equation, discrete theory 58Ч12 PoissonТs equation, GreenТs functions 59Ч11 Polar cones 51Ч3 Polar decomposition, perturbation theory 15Ч7 to 15Ч9 Polar decomposition, singular values 17Ч1 Polar form, positive definite matrices 8Ч7 Polar form, singular values 17Ч1 PolarDecomposition, Mathematica software 73Ч19 Polarization formula 12Ч8 Polarization identity 5Ч3 13Ч11 Policy iteration algorithm 25Ч7 Polya matrix 21Ч11 Polyhedral cones 26Ч4 Polynomials, adjacency matrix 28Ч5 Polynomials, certain integral domains 23Ч1 Polynomials, eigenvalues and eigenvectors 4Ч6 4Ч8 Polynomials, interpolation 11Ч2 Polynomials, linear code classes 61Ч7 Polynomials, numerical hull 41Ч16 Polynomials, restarting 44Ч5 to 44Ч6 Polynomials, span and linear independence 2Ч2 Polynomials, stability 19Ч3 Polynomials, vector spaces 1Ч3 Polynomials, zeros 37Ч8 PolynomialTools, Maple software 72Ч20 72Ч21 Population 52Ч2 Population canonical correlations and variates 53Ч7 Population principal component 53Ч5 Positionally symmetric partial matrix 35Ч2 Positive definite Jacobi EVD 46Ч11 Positive definite matrices (PSD) see ЂCompletely positive matricesї Positive definite matrices (PSD), completion problems 35Ч8 to 35Ч9 Positive definite matrices (PSD), fundamentals 8Ч6 to 8Ч12 Positive definite matrices (PSD), high relative accuracy 46Ч10 to 46Ч14 Positive definite matrices (PSD), inner product spaces 5Ч2 Positive definite matrices (PSD), symmetric factorizations 38Ч15 Positive definite properties, Hermitian forms 12Ч8 Positive definite properties, matrix norms 37Ч4 Positive definite properties, symmetric bilinear forms 12Ч3 Positive definite properties, vector norms 37Ч2 Positive definite properties, vector seminorms 37Ч3 Positive properties see ЂNonnegativesї Positive properties, eigenvectors 9Ч11 Positive properties, Fiedler vectors 36Ч7 Positive properties, generalized eigenvectors 9Ч11 Positive properties, half-life 13Ч24 Positive properties, matrix mapping 18Ч11 Positive properties, orientation 13Ч24 Positive properties, P-matrices 35Ч17 to 35Ч18 Positive properties, Perron Ч Frobenius theorem 26Ч2 Positive properties, recurrent state 54Ч7 to 54Ч9 Positive properties, root, semisimple and simple algebras 70Ч4 Positive properties, stability 19Ч3 26Ч13 Positive properties, stable matrices 9Ч17 Positive properties, vector seminorms 37Ч3 Positive semidefinite properties, completion problems 35Ч8 to 35Ч9 Positive semidefinite properties, Hermitian forms 12Ч8 Positive semidefinite properties, matrix completion problems 35Ч8 Positive semidefinite properties, positive definite matrices 8Ч6 Positive semidefinite properties, semidefinite programming 51Ч3 Positive semidefinite properties, symmetric bilinear forms 12Ч3 Positive/null recurrent state 54Ч7 to 54Ч9 Potent square sign or ray patterns 33Ч14 Potential energy, Lagrangian mechanics 59Ч5 Potential energy, oscillation modes 59Ч2 Potential energy, protein motion modes 60Ч9 Potential matrix 54Ч7 to 54Ч9 Potential stability 33Ч7 Potentially orthogonality (PO) 33Ч16 Potentials, duality 50Ч17 Powell-ReidТs complete pivoting 46Ч5 46Ч7 Power associative algebras, general properties 69Ч5 Power associative algebras, nonassociative algebra 69Ч14 to 69Ч16 Power, algorithm 25Ч7 Power, convergence properties 9Ч4 9Ч9 Power, irreducible matrices 9Ч4 Power, matrices 1Ч12 Power, method 42Ч2 Power, mth, matrices 1Ч12 Power, reducible matrices 9Ч9 Power, sign-pattern matrices 33Ч15 to 33Ч16 Power, symmetric and Grassmann tensors 13Ч12 Power, tensor products 13Ч3 Precision, Mathematica software 73Ч17 Precisions, ARPACK subroutine package 76Ч3 to 76Ч4 Precisions, floating point numbers 37Ч12 Precisions, vector space method 63Ч2 Preconditioned conjugate gradient (PCG) algorithm 41Ч13 Preconditioned Jacobi SVD algorithm 46Ч5 to 46Ч7 Preconditioners, iterative solution methods, algorithms 41Ч12 to 41Ч14 Preconditioners, iterative solution methods, fundamentals 41Ч11 to 41Ч12 Preconditioners, iterative solution methods, Krylov subspaces 41Ч2 to 41Ч4 Preconditioning, algorithms 41Ч12 to 41Ч14 Preconditioning, coefficient matrix 49Ч4 Preconditioning, iteration matrices 41Ч3 Preconditioning, Jacobi SVD algorithm 46Ч5 to 46Ч7 Preconditioning, Krylov subspaces and preconditioners 41Ч3 Preconditioning, sparse matrix factorizations 49Ч4 Predicable random signals 64Ч7 Prediction error 64Ч7 Prediction error filter 64Ч7 prefixes 74Ч2 Prepend, Mathematica software, matrices manipulation 73Ч13 Prepend, Mathematica software, vectors 73Ч3 Prescribed entries inverse eigenvalue problems (PEIEPs) 20Ч1 to 20Ч3 Prescribed-line-sum scalings 9Ч21 Preservation see ЂLinear preserver problemsї Preservation, bilinear forms 12Ч2 Preservation, linear dynamical systems 56Ч5 Preservation, Lyapunov diagonal stability 19Ч9 Preservation, multiplicative D-stability 19Ч5 Preservation, sesquilinear forms 12Ч6 Primal-dual interior point algorithm 51Ч8 to 51Ч9 Primary decomposition 6Ч9 Primary Decomposition Theorem, eigenvectors 6Ч2 Primary Decomposition Theorem, rational canonical form 6Ч10 Primary factors 6Ч9 Primary matrix function 11Ч2 Prime elements 23Ч2 Primitive Bose Ч Chadhuri Ч Hocquenghem (BCH) code 61Ч8 Primitive properties, certain integral domains 23Ч2 Primitive properties, digraphs and matrices 29Ч8 to 29Ч9 Primitive properties, elements 69Ч18 Primitive properties, gates 62Ч7 Principal angles 17Ч14 17Ч15 Principal Axes Theorem 7Ч5 to 7Ч6 Principal character 68Ч5 Principal component 26Ч12 Principal component analysis 53Ч5 to 53Ч6 Principal eigenprojection 26Ч12 Principal ideal domain (PID) 23Ч2 Principal ideals 23Ч2 Principal logarithm 11Ч6 Principal minors, determinants 4Ч3 Principal minors, stability 19Ч3 Principal parts 24Ч1 Principal square root 11Ч5 Principal submatrix, fundamentals 1Ч6 Principal submatrix, matrices 1Ч4 Principal submatrix, reducible matrices 9Ч7 Principal submatrix, submatrices and block matrices 10Ч1 Principal vectors 17Ч14
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



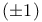 -matrices
-matrices