јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Hogben L. Ч Handbook of Linear Algebra
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Linear Algebraјвтор: Hogben L. јннотаци€: The Handbook of Linear Algebra provides comprehensive coverage of linear algebra concepts, applications, and computational software packages in an easy-to-use handbook format. The esteemed international contributors guide you from the very elementary aspects of the subject to the frontiers of current research. The book features an accessible layout of parts, chapters, and sections, with each section containing definition, fact, and example segments. The five main parts of the book encompass the fundamentals of linear algebra, combinatorial and numerical linear algebra, applications of linear algebra to various mathematical and nonmathematical disciplines, and software packages for linear algebra computations. Within each section, the facts (or theorems) are presented in a list format and include references for each fact to encourage further reading, while the examples illustrate both the definitions and the facts. Linearization often enables difficult problems to be estimated by more manageable linear ones, making the Handbook of Linear Algebra essential reading for professionals who deal with an assortment of mathematical problems.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2006 оличество страниц: 1400ƒобавлена в каталог: 30.06.2008ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Linear algebra, isomorphism 3Ч7 to 3Ч8 Linear algebra, kernel 3Ч5 to 3Ч6 Linear algebra, least-squares problems 5Ч14 to 5Ч16 Linear algebra, linear functionals 3Ч8 to 3Ч9 Linear algebra, linear independence 2Ч1 to 2Ч3 Linear algebra, linear transformations 3Ч1 to 3Ч9 Linear algebra, LU factorization 1Ч13 to 1Ч15 Linear algebra, Maple software 72Ч12 to 72Ч13 Linear algebra, matrices 1Ч3 to 1Ч6 1Ч11 2Ч6 3Ч3 Linear algebra, nilpotence 2Ч12 Linear algebra, nonsingularity characterizations 2Ч9 to 2Ч10 3Ч7 Linear algebra, null space 2Ч6 to 2Ч9 Linear algebra, orthogonal projection 5Ч6 to 5Ч8 Linear algebra, orthogonality 5Ч3 to 5Ч10 Linear algebra, projections 3Ч6 to 3Ч7 Linear algebra, pseudo-inverse 5Ч12 to 5Ч14 Linear algebra, QR factorization 5Ч8 to 5Ч10 Linear algebra, range 3Ч5 to 3Ч6 Linear algebra, rank 2Ч6 to 2Ч9 Linear algebra, similarity 3Ч4 Linear algebra, singular value decomposition 5Ч10 to 5Ч12 Linear algebra, span 2Ч1 to 2Ч3 Linear algebra, systems of linear equations 1Ч9 to 1Ч11 Linear algebra, transformations, linear 3Ч1 to 3Ч9 Linear algebra, vectors 1Ч1 to 1Ч3 2Ч3 3Ч2 Linear block codes 61Ч3 to 61Ч4 Linear characters 68Ч5 Linear code classes 61Ч6 to 61Ч11 Linear combination, Euclidean point space 66Ч2 Linear combination, span and linear independence 2Ч1 Linear constraints 50Ч1 Linear dependence 2Ч1 66Ч2 Linear differential equation of order 55Ч1 Linear differential equations, differential equations 55Ч1 to 55Ч5 Linear differential equations, dynamical systems 56Ч2 to 56Ч4 Linear differential equations, numerical methods 54Ч12 Linear differential-algebraic equations 55Ч7 to 55Ч10 55Ч14 Linear dynamical systems 49Ч14 to 49Ч15 56Ч5 see ЂLinear Linear equality-constrained least squares problems 75Ч6 to 75Ч7 Linear equations, cone invariant departure, matrices 26Ч11 to 26Ч12 Linear equations, matrices over integral domains 23Ч8 to 23Ч9 Linear equations, systems of linear equations 1Ч9 Linear form, linear functionals and annihilator 3Ч8 Linear form, linear programming 50Ч1 Linear functionals, annihilator 3Ч8 to 3Ч9 Linear hull 66Ч2 Linear independence and rank, Euclidean point space 66Ч2 Linear independence and rank, max-plus algebra 25Ч12 to 25Ч14 Linear independence and rank, span 2Ч1 to 2Ч3 Linear inequalities and projections 25Ч10 to 25Ч12 Linear least squares problems 75Ч4 to 75Ч6 Linear maps 3Ч1 13Ч8 see Linear matrix groups 67Ч3 to 67Ч5 Linear matrix similarities 24Ч1 Linear model problem 75Ч8 to 75Ч9 Linear operators, linear transformations 3Ч1 Linear operators, nonassociative algebra 69Ч3 Linear ordinary differential equations, fundamentals 55Ч5 to 55Ч6 Linear ordinary differential equations, stability 55Ч10 to 55Ч14 Linear output feedback 57Ч7 Linear prediction 64Ч7 to 64Ч9 Linear preserver problems, additive preservers 22Ч7 to 22Ч8 Linear preserver problems, fundamentals 22Ч1 to 22Ч2 Linear preserver problems, multiplicative preservers 22Ч7 to 22Ч8 Linear preserver problems, nonlinear preservers 22Ч7 to 22Ч8 Linear preserver problems, problems 22Ч4 to 22Ч7 Linear preserver problems, standard forms 22Ч2 to 22Ч4 Linear programming, canonical forms 50Ч7 to 50Ч8 Linear programming, duality 50Ч13 to 50Ч17 Linear programming, formulation 50Ч3 to 50Ч7 Linear programming, fundamentals 50Ч1 to 50Ч2 Linear programming, geometric interpretation, phase 2 50Ч13 Linear programming, interior point methods 50Ч23 to 50Ч24 Linear programming, linear approximation 50Ч20 to 50Ч23 Linear programming, Mathematica software 73Ч23 to 73Ч24 Linear programming, matrix games 50Ч18 to 50Ч20 Linear programming, parametric programming 50Ч17 to 50Ч18 Linear programming, phase 2 geometric interpretation 50Ч13 Linear programming, pivoting 50Ч10 to 50Ч11 Linear programming, sensitivity analysis 50Ч17 to 50Ч18 Linear programming, simplex method 50Ч11 to 50Ч13 Linear programming, standard forms 50Ч7 to 50Ч8 Linear programming, standard row tableaux 50Ч8 to 50Ч10 Linear programs 50Ч2 Linear representation 68Ч1 Linear semidefinite programming 51Ч3 Linear skew product flows 56Ч11 to 56Ч12 Linear state feedback 57Ч7 Linear statistical models, fundamentals 52Ч8 to 52Ч15 Linear statistical models, random vectors 52Ч1 to 52Ч8 Linear subspaces 66Ч2 Linear system perturbations 38Ч2 to 38Ч5 Linear systems ofequations, LAPACK subroutine package 75Ч2 to 75Ч4 Linear systems ofequations, large-scale matrix computations 49Ч12 to 49Ч15 Linear systems, conditioning, error analysis 37Ч9 to 37Ч11 Linear systems, direct solution, fundamentals 38Ч1 Linear systems, direct solution, Gauss elimination 38Ч7 to 38Ч12 Linear systems, direct solution, LU decomposition 38Ч7 to 38Ч12 Linear systems, direct solution, orthogonalization 38Ч13 to 38Ч15 Linear systems, direct solution, perturbations 38Ч2 to 38Ч5 Linear systems, direct solution, QR decomposition 38Ч13 to 38Ч15 Linear systems, direct solution, symmetric factorizations 38Ч15 to 38Ч17 Linear systems, direct solution, triangular linear systems 38Ч5 to 38Ч7 Linear systems, dynamical 49Ч14 to 49Ч15 Linear systems, equations 49Ч12 to 49Ч15 Linear systems, fundamentals 1Ч9 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, CG convergence Linear systems, iterative solution methods, rates 41Ч14 to 41Ч15 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, convergence rates 41Ч14 to 41Ч16 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, error estimation 41Ч16 to 41Ч17 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, finite precision arithmetic 41Ч16 to 41Ч17 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, fundamentals 41Ч1 to 41Ч2 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, GMRES convergence rates 41Ч15 to 41Ч16 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, Hermitian problems 41Ч4 to 41Ч7 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, inexact preconditioners 41Ч16 to 41Ч17 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, Krylov subspaces 41Ч2 to 41Ч4 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, MINRES convergence rates 41Ч14 to 41Ч15 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, non-Hermitian problems 41Ч7 to 41Ч11 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, non-optimal Krylov space methods 41Ч7 to 41Ч11 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, optimal Krylov space methods 41Ч4 to 41Ч11 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, preconditioned algorithms 41Ч12 to 41Ч14 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, preconditioners 41Ч2 to 41Ч4 41Ч11 Linear systems, iterative solution methods, stopping criteria 41Ч16 to 41Ч17 Linear systems, large-scale matrix computations 49Ч12 to 49Ч15 Linear systems, least squares solutions, algebraic aspects 39Ч4 to 39Ч5 Linear systems, least squares solutions, algorithms 39Ч6 to 39Ч7 Linear systems, least squares solutions, damped least squares 39Ч9 to 39Ч10 Linear systems, least squares solutions, data fitting 39Ч3 to 39Ч4 Linear systems, least squares solutions, downdating 39Ч8 to 39Ч9 Linear systems, least squares solutions, fundamentals 39Ч1 to 39Ч3 Linear systems, least squares solutions, geometric aspects 39Ч4 to 39Ч5 Linear systems, least squares solutions, orthogonal factorizations 39Ч5 to 39Ч6 Linear systems, least squares solutions, QR factorization 39Ч8 to 39Ч9 Linear systems, least squares solutions, rank revealing decompositions 39Ч11 to 39Ч12 Linear systems, least squares solutions, sensitivity 39Ч7 to 39Ч8 Linear systems, least squares solutions, updating 39Ч8 to 39Ч9 Linear systems, Mathematica software 73Ч20 to 73Ч23 Linear systems, Matlab software 71Ч7 to 71Ч9 Linear systems, structured matrices computations 48Ч5 to 48Ч8 Linear time-invariant (LTI) systems, analysis 57Ч7 to 57Ч10 Linear time-invariant (LTI) systems, control theory 57Ч2 Linear time-invariant (LTI) systems, signal processing 64Ч1 Linear transformations, Euclidean spaces 65Ч4 Linear transformations, linear algebra 3Ч1 to 3Ч9 Linear unbiased estimator 52Ч9 Linear zero function 52Ч9 Linear-quadratic Gaussian (LQG) problem 57Ч14 Linear-quadratic regulator (LQR) problem 57Ч14 LinearAlgebra package, Maple 72Ч1 72Ч2 LinearAlgebra[Modular], Maple software 72Ч12 to 72Ч13 LinearAlgebraТCholeskyТ, Mathematica software 73Ч27 LinearAlgebraТMatrixManipulationТ package, Mathematica software 73Ч2 LinearAlgebraТMatrixManipulationТ, Mathematica software, decomposition 73Ч19 LinearAlgebraТMatrixManipulationТ, Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч26 LinearAlgebraТMatrixManipulationТ, Mathematica software, linear systems 73Ч22 LinearAlgebraТOrthogonalizationТ package, Mathematica software 73Ч4 73Ч5 LinearAlgebraТTridiagonalТ, Mathematica software 73Ч20 LinearEquationsToMatrices, Mathematica 73Ч20 73Ч22 Linearization, alternative algebras 69Ч11 Linearization, dynamical systems 56Ч19 to 56Ч21 Linearization, Jordan algebras 69Ч12 LinearProgramming, Mathematica software 73Ч24 LinearSolve, Maple software 72Ч9 LinearSolve, Mathematica software, decomposition 73Ч19 LinearSolve, Mathematica software, linear systems 73Ч20 73Ч21 73Ч22 Lines, affine spaces 65Ч2 Lines, Euclidean point space 66Ч2 Lines, matrices 27Ч2 Lines, projective spaces 65Ч6 lines, segments 50Ч13 65Ч2 Linklesly embedded graphs 28Ч4 ListDensityPlot, Mathematica software 73Ч27 Local invariant polynomials 23Ч9 Local Perron Ч Schaefer conditions 26Ч6 Local similarity 22Ч7 24Ч1 Local spectral radius 26Ч2 Local stable/unstable manifold 56Ч19 Location, numerical range 18Ч4 to 18Ч6 Loewner ordering 8Ч10 Loewner partial ordering 52Ч4 Loewy, Raphael 12Ч1 to 12Ч9 Log, Mathematica software 73Ч26 Log-barrier problem 51Ч8 Logarithms 11Ч6 Logical operators, Matlab software 71Ч12 Look-ahead strategies 40Ч17 41Ч10 Loop digraphs 29Ч2 Loop graphs 28Ч1 Lorentz cone 51Ч2 Lovasz parameter 28Ч10 Low density parity check (LDPC) codes 61Ч11 Lower bounds 47Ч8 Lower Collatz Ч Wielandt numbers 26Ч4 Lower Hessenberg matrices 10Ч4 Lower shift matrices 48Ч1 Lower triangular linear matrix 38Ч5 Lower triangular matrices 1Ч4 10Ч4 LowerDiagonalMatrix, Mathematica software 73Ч6 Lowering operator 59Ч8 59Ч9 Lowner partial ordering 52Ч4 LQG (linear-quadratic Gaussian) problem 57Ч14 LQR (linear-quadratic regulator) problem 57Ч14 LSI see ЂLatent semantic indexing (LSI)ї LTI (linear time-invariant) systems, analysis 57Ч7 to 57Ч10 LTI (linear time-invariant) systems, control theory 57Ч2 57Ч7 LTI (linear time-invariant) systems, signal processing 64Ч1 LU decomposition, direct solution of linear systems 38Ч7 to 38Ч12 LU decomposition, incomplete LU decomposition 41Ч11 LU factorizations, Gaussian Eliminations 1Ч13 to 1Ч15 LU factorizations, sparse matrix factorizations 49Ч3 LUBackSubstitute, Mathematica software 73Ч19 LUBackSubstitution, Mathematica software 73Ч20 73Ч22 LUDecomposition, Maple software 72Ч9 72Ч10 LUDecomposition, Mathematica software, decomposition 73Ч18 73Ч19 LUDecomposition, Mathematica software, linear systems 73Ч20 73Ч22 Luenberger observer 57Ч11 57Ч12 57Ч13 LUMatrices, Mathematica software 73Ч19 Lyapunov equation, differential equations 55Ч11 Lyapunov equation, differential-algebraic equations 55Ч15 to 55Ч16 Lyapunov equation, matrix equations 57Ч10 Lyapunov equation, semidefinite programming 51Ч9 Lyapunov exponents, Floquet theory 56Ч13 Lyapunov exponents, linear differential equations 56Ч2 Lyapunov exponents, linear skew product flows 56Ч11 Lyapunov exponents, linearization 56Ч21 Lyapunov exponents, random linear dynamical systems 56Ч15 56Ч16 Lyapunov properties, diagonal stability 19Ч9 to 19Ч10 Lyapunov properties, scaling factor 19Ч9 Lyapunov properties, spectrum 56Ч16 56Ч17 Lyapunov properties, stability 55Ч10 55Ч14 Lyapunov spaces, Grassmannian and flag manifolds 56Ч10 56Ч11 Lyapunov spaces, linear differential equations 56Ч2 Lyapunov spaces, random linear dynamical systems 56Ч15 Lyapunov Stability Criterion 19Ч4 M- and 35Ч12 to 35Ч13 M-files, Matlab software 71Ч11 71Ч20 M-matrices, fundamentals 9Ч17 to 9Ч20 M-matrices, matrix completion problems 35Ч12 to 35Ч13 M-matrices, stability 19Ч4 M-norm 37Ч2 Machado, Armando 13Ч1 to 13Ч26 Machine epsilon 37Ч12 MackeyТs Subgroup theorem 68Ч9 Main angles, adjacency matrix 28Ч5 Main Coding Theory Problem 61Ч5 Main diagonal, matrices 1Ч4 Main Linear Coding Problem 61Ч5 to 61Ч6 61Ч12 Majorization PЧ4 Malcev algebras 69Ч2 69Ч3 69Ч16 Malcev module 69Ч16 Malcev theorem 67Ч2 Manipulation of matrices 73Ч13 to 73Ч14 Mantissa 37Ч11 Map, Mathematica software, decomposition 73Ч19 Map, Mathematica software, eigenvalues 73Ч16 Map, Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч26 Map, Mathematica software, matrices 73Ч7 Map, Mathematica software, matrix algebra 73Ч10 Map, Mathematica software, singular values 73Ч17 Maple software, arrays 72Ч8 to 72Ч9 Maple software, canonical forms 72Ч15 to 72Ч16 Maple software, eigenvalues and eigenvectors 72Ч11 to 72Ч12 Maple software, equation solving 72Ч9 to 72Ч11 Maple software, functions of matrices 72Ч19 to 72Ч20 Maple software, fundamentals 72Ч1 to 72Ч2 Maple software, linear algebra 72Ч12 to 72Ч13 Maple software, matrices 72Ч4 to 72Ч7 Maple software, matrix factoring 72Ч9 to 72Ч11 Maple software, modular arithmetic 72Ч12 to 72Ч13 Maple software, numerical linear algebra 72Ч13 to 72Ч15 Maple software, stability of matrices 72Ч20 to 72Ч21 Maple software, structured matrices 72Ч16 to 72Ч18 Maple software, vectors 72Ч2 to 72Ч4 Mapping theorems 16Ч2 MapThread, Mathematica software 73Ч13 Markov chains, censoring 54Ч11 Markov chains, doubly stochastic matrices 27Ч10 Markov chains, eigenvalues and eigenvectors 4Ч10 Markov chains, finite 54Ч9 to 54Ч11 Markov chains, fundamentals 54Ч1 to 54Ч5 Markov chains, irreducible classes 54Ч5 to 54Ч7 Markov chains, numerical methods 54Ч12 to 54Ч14 Markov chains, Perron Ч Schaefer condition 26Ч7 Markov chains, states classification 54Ч7 to 54Ч9 Markov decision process, deterministic 25Ч3 Markowitz cost 40Ч17 Markowitz scheme 40Ч18 MaschkeТs theorem, group representations 68Ч2 MaschkeТs theorem, matrix groups 67Ч2 MaschkeТs theorem, matrix representations 68Ч4 Matching, bipartite graphs 30Ч2 Mathematica software, appendix 73Ч25 to 73Ч27 Mathematica software, decompositions 73Ч18 to 73Ч19 Mathematica software, eigenvalues 73Ч14 to 73Ч16 Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч1 to 73Ч2 73Ч25 Mathematica software, linear programming 73Ч23 to 73Ч24 Mathematica software, linear systems 73Ч20 to 73Ч23 Mathematica software, manipulation of matrices 73Ч13 to 73Ч14 Mathematica software, matrices 73Ч5 to 73Ч9 Mathematica software, matrix algebra 73Ч9 to 73Ч12 Mathematica software, singular values 73Ч16 to 73Ч18
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



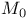 -matrices
-matrices