јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Hogben L. Ч Handbook of Linear Algebra
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Linear Algebraјвтор: Hogben L. јннотаци€: The Handbook of Linear Algebra provides comprehensive coverage of linear algebra concepts, applications, and computational software packages in an easy-to-use handbook format. The esteemed international contributors guide you from the very elementary aspects of the subject to the frontiers of current research. The book features an accessible layout of parts, chapters, and sections, with each section containing definition, fact, and example segments. The five main parts of the book encompass the fundamentals of linear algebra, combinatorial and numerical linear algebra, applications of linear algebra to various mathematical and nonmathematical disciplines, and software packages for linear algebra computations. Within each section, the facts (or theorems) are presented in a list format and include references for each fact to encourage further reading, while the examples illustrate both the definitions and the facts. Linearization often enables difficult problems to be estimated by more manageable linear ones, making the Handbook of Linear Algebra essential reading for professionals who deal with an assortment of mathematical problems.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2006 оличество страниц: 1400ƒобавлена в каталог: 30.06.2008ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Controlled-NOT gate, quantum computation 62Ч4 Controlled-NOT gate, universal quantum gates 62Ч8 Controller, LTI systems 57Ч13 Controlling random vectors 52Ч4 Convergence rates, CG 41Ч14 to 41Ч15 Convergence rates, GMRES 41Ч15 to 41Ч16 Convergence rates, MINRES 41Ч14 to 41Ч15 Convergence, implicitly restarted Arnoldi method 44Ч9 to 44Ч10 Convergence, nonnegative and stochastic matrices 9Ч2 Convergence, reducible matrices 9Ч8 9Ч11 Convergence, Toeplitz matrices 16Ч6 Convergent regular splitting 9Ч17 Convex hull 66Ч2 Convex linear combination 50Ч13 Convex polytopes 27Ч10 to 27Ч12 Convexity, affine spaces 65Ч2 Convexity, Euclidean point space 66Ч2 Convexity, fundamentals PЧ2 Convexity, phase 2 geometric interpretation 50Ч13 Convexity, vector norms 37Ч3 Convexity, vector seminorms 37Ч4 Convolution identities, discrete theory 58Ч10 Convolution identities, Fourier analysis 58Ч5 Convolution, Fourier analysis 58Ч3 Convolution, signal processing 64Ч2 Convolutional codes 61Ч11 to 61Ч13 Coordinate matrix 60Ч2 Coordinate vectors 60Ч2 Coordinates, change of basis 2Ч10 to 2Ч12 Coordinates, Euclidean point space 66Ч1 Coordinates, NMR protein structure determination 60Ч2 Coordinatization theorem 69Ч13 Copositive matrices 35Ч11 to 35Ч12 Coppersmith and Winograd studies 47Ч9 Coprime elements 23Ч2 Core 26Ч5 to 26Ч7 Corless, Robert M. 72Ч1 to 72Ч21 Corner minor 21Ч7 see Corrected seminormal equations 39Ч6 Correlation coefficient 52Ч3 Correlation matrix, positive definite matrices 8Ч6 Correlation matrix, random vectors 52Ч4 Correlation, random vectors 52Ч3 Correlations and variates 53Ч7 to 53Ч8 Cosine and sine 11Ч11 Cospectral graphs 28Ч5 costs, Mathematica software 73Ч24 Coupling time 25Ч9 Courant Ч Fischer inequalities 14Ч4 Courant Ч Fischer theorem, eigenvalues 14Ч4 Courant Ч Fischer theorem, Hermitian matrices 8Ч3 Covariance matrix, positive definite matrices 8Ч9 Covariance matrix, random vectors 52Ч3 Covariance, random vectors 52Ч3 Cover, combinatorial matrix theory 27Ч2 CramerТs Rule 4Ч3 37Ч17 Craven and Csordas studies 21Ч11 to 21Ч12 Critical digraphs 25Ч6 25Ч7 see Critical vertices 25Ч6 Cross correlation 64Ч4 Cross, Mathematica software 73Ч3 73Ч5 Cross-covariance matrix 52Ч4 Cross-positives 26Ч13 CrossProduct, Maple software 72Ч3 CRS (compressed row storage) scheme 40Ч4 Csordas, Craven and, studies 21Ч11 to 21Ч12 Cubics, Mathematica software 73Ч14 73Ч15 Cui, Feng 60Ч13 Cumulative distribution function 52Ч2 Cut lattice 30Ч2 Cut space 30Ч2 Cut vertices 36Ч3 Cuthill Ч McKee algorithm 40Ч16 Cycle conditions 35Ч9 Cycle of length 28Ч1 28Ч2 Cycle products, digraphs 29Ч4 to 29Ч6 Cycle-clique 35Ч14 Cycles of length 33Ч2 Cycles, digraphs 29Ч2 Cycles, Jacobi method 42Ч18 Cycles, matrices 48Ч2 Cycles, pattern 33Ч9 Cycles, simplex method 50Ч12 Cycles, time 25Ч8 Cyclic code 61Ч6 Cyclic normal form, digraphs 29Ч9 to 29Ч11 Cyclic normal form, imprimitive matrices 29Ч10 Cyclic simplexes 66Ч12 Cyclically real ray pattern 33Ч14 Cyclicity theorem 25Ч8 Cyclicity, matrix power asymptotics 25Ч8 D-optimal matrices, balanced matrices 32Ч12 D-optimal matrices, fundamentals 32Ч1 D-optimal matrices, nonregular matrices 32Ч7 to 32Ч9 D-optimal matrices, nonsquare case 32Ч2 to 32Ч12 D-optimal matrices, regular matrices 32Ч5 to 32Ч7 D-optimal matrices, square case 32Ч2 to 32Ч4 D-stability 19Ч5 to 19Ч7 Damped least squares 39Ч9 to 39Ч10 Dangling node 63Ч11 Daniel studies 44Ч4 Data Encryption Standard (DES) cryptographysystem 62Ч17 Data fitting 39Ч3 to 39Ч4 Data matrix 53Ч2 to 53Ч3 Data perturbations 38Ч2 Datta, Biswa Nath 37Ч1 to 37Ч21 DavidsonТs method 43Ч10 Day, Jane 1Ч1 to 1Ч15 DCT see ЂDiscrete Fourier transform (DFT)ї de Oliveria studies 20Ч3 De RijkТs row-cyclic pivoting 46Ч4 DeAlba, Luz M. 4Ч1 to 4Ч11 Decoder 61Ч2 Decoding 61Ч2 Decomposable tensors 13Ч3 Decomposition, direct solution of linear systems 38Ч7 to 38Ч15 Decomposition, high relative accuracy 46Ч7 to 46Ч10 Decomposition, least squares solutions 39Ч11 to 39Ч12 Decomposition, Mathematica software 73Ч18 to 73Ч19 Decomposition, matrix group 67Ч1 Decomposition, Morse, dynamical systems 56Ч7 to 56Ч9 Decomposition, rank revealing decomposition 39Ч11 to 39Ч12 Decomposition, semisimple and simple algebras 70Ч4 Decomposition, singular values 17Ч15 Decomposition, symmetric and Grassmann tensors 13Ч13 Decomposition, symmetric factorizations 38Ч15 Decomposition, tensors, multilinear algebra 13Ч7 Deconvolution, Fourier analysis 58Ч8 Deconvolution, functional and discrete theories 58Ч16 Decoupling Principle 59Ч1 59Ч2 Deeper properties 21Ч9 to 21Ч12 Defective matrices 4Ч6 Definite matrices see ЂPositive definite matrices (PSD)ї Definite pencils 15Ч10 Deflation 42Ч2 Degenerate characteristics, sesquilinear forms 12Ч6 Degenerate characteristics, simplex method 50Ч12 Degree, certain integral domains 23Ч2 Degree, characters 68Ч5 Degree, control theory 57Ч2 Degree, convolutional codes 61Ч11 Degree, frequency-domain analysis 57Ч6 Degree, general properties 69Ч5 Degree, graphs 28Ч2 Degree, group representations 68Ч1 Degree, matrix group 67Ч1 Degree, matrix representations 68Ч3 Degree, max-plus permanent 25Ч9 Deletion, edges and vertices 28Ч4 DelsarteТs Linear Programming Bound 28Ч12 Delta function 58Ч2 demand, Mathematica software 73Ч24 Demmel Ч Kahan singular value decomposition 45Ч7 to 45Ч8 Demmel, James 75Ч1 to 75Ч23 Denardo algorithm 25Ч8 Denman Ч Beavers iteration 11Ч11 Dense matrices, fundamentals 43Ч1 Dense matrices, large-scale matrix computations 49Ч2 Dense matrices, software 77Ч2 Dense matrices, techniques 43Ч3 to 43Ч9 Depth, Jordan canonical form 6Ч3 Derangements 31Ч6 Derivation, Lie algebras 70Ч1 Derived algebra 70Ч3 Derogatory matrices 4Ч6 DES (Data Encryption Standard) cryptography system 62Ч17 DesarguesТ theorem 65Ч8 65Ч9 Design matrices, D-optimal matrices 32Ч1 Design matrices, linear statistical models 52Ч8 Design, square case 32Ч2 det command, Matlab software 71Ч17 det function, Matlab software 71Ч3 Det, Mathematica software 73Ч10 73Ч11 Detection, control theory 57Ч2 Determinant, Maple software 72Ч5 Determinantal region 33Ч14 Determinantal relations 14Ч10 to 14Ч12 Determinants, advanced results 4Ч3 to 4Ч6 Determinants, connections 31Ч12 to 31Ч13 Determinants, fast matrix multiplication 47Ч10 Determinants, fundamentals 4Ч1 to 4Ч3 Determinants, invariants 23Ч5 Deterministic Markov decision process 25Ч3 Deterministic spectral estimation 64Ч14 Deutsch-Jozsa problem 62Ч9 to 62Ч11 DeutschТs problem 62Ч8 to 62Ч9 DeveloperТHessenbergDecompositionТ, Mathematica software 73Ч27 DGEMM BLAS subroutine package 42Ч21 DGKS mechanism 44Ч4 Dhillon, Inderjit S. 45Ч1 to 45Ч12 diag, Mathematica software 73Ч16 Diagonal entry 1Ч4 23Ч5 Diagonal matrices 1Ч4 Diagonal pattern 33Ч2 Diagonal product 27Ч10 Diagonal stability 19Ч9 Diagonalization, eigenvalue problems 15Ч10 Diagonalization, eigenvalues and eigenvectors 4Ч6 4Ч7 Diagonally dominant matrices 9Ч17 Diagonally scaled representation 46Ч10 Diagonally scaled totally unimodular (DSTU) 46Ч8 46Ч9 DiagonalMatrix, Mathematica software, eigenvalues 73Ч15 73Ч16 DiagonalMatrix, Mathematica software, matrices 73Ч6 73Ч8 Diagonals, square matrices 27Ч3 Diameter, eigenvalues 34Ч7 Diao, Zijian 62Ч1 to 62Ч19 Dias da Silva, Jose A. 13Ч1 to 13Ч26 Differentiable functions 56Ч5 Differential equations, constant coefficients 55Ч1 to 55Ч5 Differential equations, eigenvalues and eigenvectors 4Ч10 to 4Ч11 Differential equations, linear different equations 55Ч1 to 55Ч5 Differential equations, linear differential-algebraic equations 55Ч7 to 55Ч10 55Ч14 Differential equations, linear ordinary differential equations 55Ч5 to 55Ч6 55Ч10 Differential equations, linearization 56Ч19 Differential equations, stability 55Ч10 to 55Ч16 Differential quotient-difference (dqds) step 45Ч8 to 45Ч9 Differential-algebraic equations 55Ч1 Differential-algebraic equations of order 55Ч2 Digits, Maple software 72Ч14 Digraphs, adjacency matrix 29Ч3 to 29Ч4 Digraphs, cycle products 29Ч4 to 29Ч6 Digraphs, cyclic normal form 29Ч9 to 29Ч11 Digraphs, directed graphs 29Ч3 to 29Ч4 Digraphs, fundamentals 29Ч1 to 29Ч3 Digraphs, irreducible matrices 29Ч6 to 29Ч8 Digraphs, irreducible, imprimitive matrices 29Ч9 to 29Ч11 Digraphs, matrices 29Ч3 to 29Ч4 Digraphs, matrix completion problems 35Ч2 Digraphs, max-plus algebra 25Ч2 Digraphs, minimal connection 29Ч12 to 29Ч13 Digraphs, modeling and analyzing fill 40Ч11 Digraphs, nearly reducible matrices 29Ч12 to 29Ч13 Digraphs, nonnegative and stochastic matrices 9Ч2 Digraphs, P-, 35Ч15 to 35Ч16 Digraphs, primitive digraphs and matrices 29Ч8 to 29Ч9 Digraphs, sign-pattern matrices 33Ч2 Digraphs, strongly connected digraphs 29Ч6 to 29Ч8 Digraphs, walk products 29Ч4 to 29Ч5 Dihedral interior angle 66Ч7 Dilations, numerical range 18Ч9 to 18Ч10 Dimension reduction 49Ч14 to 49Ч15 Dimension theorem, kernel 3Ч5 Dimension theorem, matrix range 2Ч6 to 2Ч9 Dimension theorem, null space 2Ч6 to 2Ч9 Dimension theorem, range 3Ч5 Dimension theorem, rank 2Ч6 to 2Ч9 Dimension, doubly stochastic matrices 27Ч10 Dimension, Euclidean point space 66Ч2 Dimension, Euclidean simplexes 66Ч7 Dimension, grading 70Ч9 Dimension, nonassociative algebra 69Ч1 Dimension, simultaneous similarity 24Ч8 Dimension, vector space 2Ч3 Dimensional projective spaces and subspaces 65Ч6 Dimensions, Mathematica software 73Ч6 73Ч7 73Ч27 DiracТs bra-ket notation 62Ч2 Direct isometry 65Ч5 see Direct solution, linear systems, fundamentals 38Ч1 Direct solution, linear systems, Gauss elimination 38Ч7 to 38Ч12 Direct solution, linear systems, LU decomposition 38Ч7 to 38Ч12 Direct solution, linear systems, orthogonalization 38Ч13 to 38Ч15 Direct solution, linear systems, perturbations 38Ч2 to 38Ч5 Direct solution, linear systems, QR decomposition 38Ч13 to 38Ч15 Direct solution, linear systems, symmetric factorizations 38Ч15 to 38Ч17 Direct solution, linear systems, triangular linear systems 38Ч5 to 38Ч7 Direct sum, block diagonal and triangular matrices 10Ч4 Direct sum, decompositions 2Ч4 to 2Ч6 Direct sum, direct sum decompositions 2Ч5 Direct sum, group representations 68Ч3 Direct sum, nonassociative algebra 69Ч3 Direct sum, semisimple and simple algebras 70Ч3 Direct Toeplitz solvers 48Ч4 to 48Ч5 Directed arcs, digraphs 29Ч1 Directed bigraphs 30Ч4 Directed digraphs 29Ч1 Directed edges 29Ч1 Directed graphs 29Ч3 to 29Ч4 Directed multigraph 29Ч2 Direction space, affine spaces 65Ч2 Direction, arrival estimation 64Ч15 to 64Ч18 Directory structure and contents 76Ч3 Dirichlet conditions 59Ч10 Discrete approximation 58Ч13 Discrete event systems 25Ч3 to 25Ч4 Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) 58Ч9 Discrete invariants 24Ч11 Discrete stochastic process 54Ч1 Discrete theory 58Ч2 to 58Ч17 Discrete time Fourier transform 64Ч2 Discrete variables 52Ч2 Discrete Wiener filtering problem 64Ч10 Discriminant coordinates 53Ч6 Disjoint matrix multiplication 47Ч8 dispersion 21Ч7 Dispersion matrix 52Ч3 Dissection strategy 40Ч16 Dissimilarity 53Ч13 Dissimilarity matrix 53Ч14 Distance bounds 61Ч5 to 61Ч6 Distance matrix 60Ч2
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



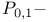 and
and 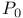 -matrices
-matrices