јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Hogben L. Ч Handbook of Linear Algebra
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Linear Algebraјвтор: Hogben L. јннотаци€: The Handbook of Linear Algebra provides comprehensive coverage of linear algebra concepts, applications, and computational software packages in an easy-to-use handbook format. The esteemed international contributors guide you from the very elementary aspects of the subject to the frontiers of current research. The book features an accessible layout of parts, chapters, and sections, with each section containing definition, fact, and example segments. The five main parts of the book encompass the fundamentals of linear algebra, combinatorial and numerical linear algebra, applications of linear algebra to various mathematical and nonmathematical disciplines, and software packages for linear algebra computations. Within each section, the facts (or theorems) are presented in a list format and include references for each fact to encourage further reading, while the examples illustrate both the definitions and the facts. Linearization often enables difficult problems to be estimated by more manageable linear ones, making the Handbook of Linear Algebra essential reading for professionals who deal with an assortment of mathematical problems.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2006 оличество страниц: 1400ƒобавлена в каталог: 30.06.2008ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Chordal symmetric Hamiltonian, minimally 35Ч15 Chromatic index 27Ч10 Chromatic number 28Ч9 Chu, Ka Lok 53Ч14 circul function, Matlab software 71Ч6 Circulant matrices, Maple software 72Ч18 Circulant matrices, nonnegative inverse eigenvalue problems 20Ч5 Circulant matrices, structured matrices 48Ч2 Circumcenter 66Ч8 Circumscribed hypersphere 66Ч8 Class functions, orthogonality relations 68Ч6 Classical Gram-Schmidt (CGS) scheme 44Ч3 to 44Ч4 Classical groups 67Ч5 to 67Ч7 Classical Turing machine 62Ч2 Classification Theorem 24Ч9 24Ч11 Classification, states 54Ч7 to 54Ч9 Classifications I and II 24Ч7 to 24Ч11 Clifford algebra 69Ч13 CliffordТs theorem, characters 68Ч9 CliffordТs theorem, matrix groups 67Ч2 Cline, Alan Kaylor 45Ч1 to 45Ч12 Clique number 28Ч9 Clique, graph parameters 28Ч9 Clique, graphs 35Ч2 Close cones 8Ч10 Closed ball of radius 61Ч2 Closed halfspace 66Ч2 Closed subset 50Ч13 Closed under matrix direct sums 35Ч2 Closed under permutation similarity 35Ч2 Closed under taking principal submatrices 35Ч2 Closed walk 54Ч5 Closed-loop ODE 57Ч2 Closed-loop system 57Ч13 Closure under addition 1Ч2 Closure under scalar multiplication 1Ч2 Co-cover 27Ч2 Co-index 9Ч7 Cockades 30Ч4 Cocktail party graph 28Ч4 Coclique 28Ч9 Codewords 61Ч1 Codimension 66Ч2 Coding theory, convolutional codes 61Ч11 to 61Ч13 Coding theory, distance bounds 61Ч5 to 61Ч6 Coding theory, fundamentals 61Ч1 to 61Ч2 Coding theory, linear block codes 61Ч3 to 61Ч4 Coding theory, linear code classes 61Ч6 to 61Ч11 Coding theory, main linear coding problem 61Ч5 to 61Ч6 Codomain 3Ч1 Coefficient matrices, Bezout domains 23Ч9 Coefficient matrices, linear differential equations 55Ч1 Coefficients, determination 52Ч8 Coefficients, multiple determination 52Ч8 Coefficients, systems of linear equations 1Ч9 Cofactors, determinants 4Ч1 Cogame utility, ATLAST 71Ч20 71Ч22 Colin de Verdiere parameter 28Ч9 28Ч10 Collatz-Wielandt sets, cone invariant departure, matrices 26Ч3 to 26Ч5 Collatz-Wielandt sets, irreducible matrices 9Ч5 Collineation, projective spaces 65Ч7 Colonius, Fritz 56Ч1 to 56Ч21 Color class 28Ч9 ColorFunction, Mathematica software 73Ч27 colormap command, Matlab software 71Ч15 colspace command, Matlab software 71Ч17 Column-stochastic matrices 9Ч15 Columns, equivalence 23Ч5 Columns, feasibility 50Ч14 Columns, indices 23Ч9 Columns, linear independence, span, and bases 2Ч6 Columns, matrices 1Ч3 Columns, pivoting 46Ч5 Columns, rank 25Ч13 Columns, sign solvability 33Ч5 Columns, signing, balanced 33Ч5 Columns, sum vector 27Ч7 Columns, vectors 1Ч3 Combinatorial matrix theory, algebraic connectivity 36Ч1 to 36Ч11 Combinatorial matrix theory, bipartite graphs and matrices 30Ч1 to 30Ч10 Combinatorial matrix theory, classes of (0, 1)-matrices 27Ч7 to 27Ч10 Combinatorial matrix theory, completion problems 35Ч1 to 35Ч20 Combinatorial matrix theory, convex polytopes 27Ч10 to 27Ч12 Combinatorial matrix theory, D-optimal matrices 32Ч1 to 32Ч12 Combinatorial matrix theory, digraphs 29Ч1 to 29Ч13 Combinatorial matrix theory, doubly stochastic matrices 27Ч10 to 27Ч12 Combinatorial matrix theory, fundamentals 27Ч1 to 27Ч12 Combinatorial matrix theory, graphs 28Ч1 to 28Ч12 Combinatorial matrix theory, monotone class 27Ч7 to 27Ч8 Combinatorial matrix theory, multiplicity lists 33Ч1 to 33Ч17 Combinatorial matrix theory, permanents 31Ч1 to 31Ч13 Combinatorial matrix theory, sign-pattern matrices 33Ч1 to 33Ч17 Combinatorial matrix theory, square matrices 27Ч3 to 27Ч6 Combinatorial matrix theory, strong combinatorial invariants 27Ч3 to 27Ч5 Combinatorial matrix theory, structure and invariants 27Ч1 to 27Ч3 Combinatorial matrix theory, tournament matrices 27Ч8 to 27Ч10 Combinatorial matrix theory, weak combinatorial invariants 27Ч5 to 27Ч6 Combinatorial orthogonality 33Ч16 Combinatorial problems 47Ч10 Combinatorial symmetric partial matrix 35Ч2 Combinatorial symmetric sign pattern matrices 33Ч9 Communication, irreducible classes 54Ч5 Communication, irreducible matrices 29Ч6 Communication, nonnegative and stochastic matrices 9Ч2 Commutative algebras 69Ч2 Commutative ring, certain integral domains 23Ч1 Commutative ring, permanents 31Ч1 Commutativity and Jordan identity 69Ч12 Commutativty axiom 1Ч1 Commutators, nonassociative algebra 69Ч2 Commutators, SchrodingerТs equation 59Ч7 Commute, matrices 1Ч4 Commute, vector spaces 3Ч2 Companion matrices, eigenvalues and eigenvectors 4Ч6 Companion matrices, rational canonical forms 6Ч8 CompanionMatrix, Maple software 72Ч17 Comparison matrices 19Ч9 Compatibility 33Ч2 Complement, binary matrices 31Ч5 Complement, fundamentals PЧ1 Complement, graphs 28Ч2 Complementary parameters 64Ч8 Complementary projections 3Ч6 Complementary slackness, duality 50Ч14 Complementary slackness, duality and optimality conditions 51Ч6 Complementary slackness, max-plus eigenproblem 25Ч7 Complete bipartite graphs 28Ч2 30Ч1 see Complete flag 56Ч9 Complete graphs 28Ч2 see Complete min-plus semiring 25Ч1 Complete orthogonal decomposition 39Ч11 Complete orthogonal set 5Ч3 Complete pivoting 38Ч10 see Complete reducibility, matrix group 67Ч1 Complete reducibility, modules 70Ч7 Complete reducibility, square matrices, weak combinatorial invariants 27Ч5 Completed max-plus semiring 25Ч1 Completely positive matrices, completion problems 35Ч10 to 35Ч11 Completely positive matrices, nonnegative factorization 9Ч22 Completion problems, matrices, completely positive matrices 35Ч10 to 35Ч11 Completion problems, matrices, copositive matrices 35Ч11 to 35Ч12 Completion problems, matrices, doubly nonnegative matrices 35Ч10 to 35Ч11 Completion problems, matrices, entry sign symmetric P-, 35Ч19 to 35Ч20 Completion problems, matrices, entry weakly sign symmetric P-, 35Ч19 to 35Ч20 Completion problems, matrices, Euclidean distance matrices 35Ч9 to 35Ч10 Completion problems, matrices, fundamentals 35Ч1 to 35Ч8 Completion problems, matrices, inverse M-matrices 35Ч14 to 35Ч15 Completion problems, matrices, M- and 35Ч12 to 35Ч13 Completion problems, matrices, nonnegative P-, 35Ч17 to 35Ч18 Completion problems, matrices, P-, 35Ч15 to 35Ч17 Completion problems, matrices, positive definite matrices 35Ч8 to 35Ч9 Completion problems, matrices, positive P-matrices 35Ч17 to 35Ч18 Completion problems, matrices, positive semidefinite matrices 35Ч8 to 35Ч9 Completion problems, matrices, strictly copositive matrices 35Ч11 to 35Ч12 Completion property 35Ч2 Complex conjugate 68Ч5 Complex elements, Maple software 72Ч7 Complex numbers, fundamentals PЧ1 to PЧ2 Complex numbers, nonassociative algebra 69Ч4 Complex polynomial 19Ч3 Complex sign patterns 33Ч14 to 33Ч15 Complexity, convolutional codes 61Ч12 Component backward stable 38Ч6 Component-wise perturbation theory 39Ч7 Component-wise relative backward errors, linear system 38Ч2 Component-wise relative distance 46Ч10 Composite cycle 33Ч2 Composition algebras 69Ч8 to 69Ч10 Composition, symmetric and Grassmann tensors 13Ч13 Compound matrix 4Ч3 Compressed column storage (CCS) scheme 40Ч3 Compressed row storage (CRS) scheme 40Ч4 Computational linear algebra, fast matrix multiplication 47Ч1 to 47Ч10 Computational linear algebra, large-scale matrix computations 49Ч1 to 49Ч15 Computational linear algebra, structured matrix computations 48Ч1 to 48Ч9 Computational methods 69Ч20 to 69Ч25 Computational modes 76Ч8 to 76Ч9 Computational software, freeware 77Ч1 to 77Ч3 Computational software, Maple 72Ч1 to 72Ч21 Computational software, Mathematica 73Ч1 to 73Ч27 Computational software, Matlab 71Ч1 to 71Ч22 Computational software, subroutine packages, ARPACK 76Ч1 to 76Ч10 Computational software, subroutine packages, BLAS 74Ч1 to 74Ч7 Computational software, subroutine packages, EIGS 76Ч1 to 76Ч10 Computational software, subroutine packages, LAPACK 75Ч1 to 75Ч23 Computations, large-scale matrices, Arnoldi process 49Ч10 to 49Ч11 Computations, large-scale matrices, dimension reduction 49Ч14 to 49Ч15 Computations, large-scale matrices, eigenvalue computations 49Ч12 Computations, large-scale matrices, fundamentals 49Ч1 to 49Ч2 Computations, large-scale matrices, Krylov subspaces 49Ч5 to 49Ч6 Computations, large-scale matrices, linear dynamical systems 49Ч14 to 49Ч15 Computations, large-scale matrices, linear systems, equations 49Ч12 to 49Ч14 Computations, large-scale matrices, nonsymmetric Lanczos process 49Ч8 to 49Ч10 Computations, large-scale matrices, sparse matrix factorizations 49Ч2 to 49Ч5 Computations, large-scale matrices, symmetric Lanczos process 49Ч6 to 49Ч7 Computations, pseudospectra 16Ч11 to 16Ч12 Computations, singular value decomposition 45Ч1 to 45Ч12 Computations, structured matrices, direct Toeplitz solvers 48Ч4 to 48Ч5 Computations, structured matrices, fundamentals 48Ч1 to 48Ч4 Computations, structured matrices, iterative Toeplitz solvers 48Ч5 Computations, structured matrices, linear systems 48Ч5 to 48Ч8 Computations, structured matrices, total least squares problems 48Ч8 to 48Ч9 Computer science applications, coding theory 61Ч1 to 61Ч13 Computer science applications, information retrieval 63Ч1 to 63Ч14 Computer science applications, quantum computation 62Ч1 to 62Ч19 Computer science applications, signal processing 64Ч1 to 64Ч18 Computer science applications, Web searches 63Ч1 to 63Ч14 Concentration, metabolites 60Ч10 Conceptual PageRank 63Ч11 see cond, Mathematica software 73Ч18 Condensation digraph 29Ч7 Condensation method 4Ч4 Condition numbers, linear system perturbations 38Ч2 Condition numbers, polar decomposition 15Ч8 Condition numbers, sensitivity 39Ч7 Conditioning of eigenvalues, Maple software 72Ч15 Conditioning, condition numbers 37Ч7 to 37Ч9 Conditioning, linear systems 37Ч9 to 37Ч11 ConditionNumber, Maple software 72Ч9 Conductance 28Ч9 Conductivity 66Ч13 Cone invariant departure, matrices, Collatz-Wielandt sets 26Ч3 to 26Ч5 Cone invariant departure, matrices, core 26Ч5 to 26Ч7 Cone invariant departure, matrices, distinguished eigenvalues 26Ч3 to 26Ч5 Cone invariant departure, matrices, elementary analytic results 26Ч12 to 26Ч13 Cone invariant departure, matrices, fundamentals 26Ч1 Cone invariant departure, matrices, K-reducible matrices 26Ч8 to 26Ч10 Cone invariant departure, matrices, linear equations over cones 26Ч11 to 26Ч12 Cone invariant departure, matrices, peripheral spectrum 26Ч5 to 26Ч7 Cone invariant departure, matrices, Perron-Frobenius theorem 26Ч1 to 26Ч3 Cone invariant departure, matrices, Perron-Schaefer condition 26Ч5 to 26Ч7 Cone invariant departure, matrices, spectral theory 26Ч8 to 26Ч10 Cone invariant departure, matrices, splitting theorems 26Ч13 to 26Ч14 Cone invariant departure, matrices, stability 26Ч13 to 26Ч14 Cones, Perron-Frobenius theorem 26Ч1 to 26Ч3 Cones, positive definite matrices 8Ч10 Cones, programming 51Ч2 Cones, reducible matrices 26Ч8 Conformal and conformable partitions 10Ч1 Conformal partitions 10Ч1 Congruence, bilinear forms 12Ч2 Congruence, Hermitian and positive definite matrices 8Ч5 to 8Ч6 Congruence, Hermitian forms 12Ч8 Congruence, linear inequalities and projections 25Ч10 Congruence, sesquilinear forms 12Ч6 Conjugacy 56Ч5 Conjugate character 68Ч9 Conjugate Gradient (CG) algorithm, convergence rates 41Ч14 to 41Ч15 Conjugate Gradient (CG) algorithm, Krylov space methods 41Ч4 41Ч6 Conjugate Gradient Squared (CGS) algorithm 41Ч8 Conjugate partition PЧ2 Conjugates, linear dynamical systems 56Ч5 ConjugateTranspose, Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч27 ConjugateTranspose, Mathematica software, matrix algebra 73Ч9 73Ч11 ConjugateTranspose, Mathematica software, singular values 73Ч17 73Ч18 Connected properties and components, digraphs 29Ч2 Connected properties and components, graphs 28Ч1 28Ч2 Consecutive ones property 30Ч4 Consistency, least squares solution 39Ч1 Consistency, linear differential equations 55Ч2 Consistency, linear statistical models 52Ч8 Consistency, matrix norms 37Ч4 Consistency, systems of linear equations 1Ч9 Consistent sign pattern matrices 33Ч9 Constant Boolean function, Deutsch-Jozsa problem 62Ч9 Constant Boolean function, DeutschТs problem 62Ч8 Constant coefficients, differential equations 55Ч1 to 55Ч5 Constant coefficients, linear differential equations 55Ч1 Constant term 1Ч9 Constant vector 1Ч9 Constituents, characters 68Ч5 ConstrainedMax, Mathematica software 73Ч27 ConstrainedMin, Mathematica software 73Ч27 Constraint length 61Ч12 Constraint qualification, semidefinite programming 51Ч7 Constraint qualification, strong duality 51Ч7 Contact matrix 60Ч9 Containment gap 44Ч9 Content index, Web search 63Ч9 Continuation character backslash, Maple software 72Ч2 Continuous dynamical systems 56Ч5 Continuous invariants 24Ч11 Continuous real-valued functions 2Ч2 contour command, Matlab software 71Ч15 Contour integration 11Ч10 Contraction matrices 18Ч9 Contractions, graphs 28Ч4 Contragredient 68Ч3 Control design, LTI systems 57Ч13 to 57Ч17 Control system 57Ч2 Control theory, analysis, LTI systems 57Ч7 to 57Ч10 Control theory, control design, LTI systems 57Ч13 to 57Ч17 Control theory, frequency-domain analysis 57Ч5 to 57Ч6 Control theory, fundamentals 57Ч1 to 57Ч5 Control theory, LTI systems 57Ч7 to 57Ч10 57Ч13 Control theory, matrix equations 57Ч10 to 57Ч11 Control theory, state estimation 57Ч11 to 57Ч13 Control vector 57Ч2 Controllability Hessenberg form 57Ч9 Controllability matrix 57Ч7
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



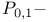 and
and 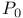 -matrices
-matrices 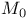 -matrices
-matrices