јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Hogben L. Ч Handbook of Linear Algebra
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Linear Algebraјвтор: Hogben L. јннотаци€: The Handbook of Linear Algebra provides comprehensive coverage of linear algebra concepts, applications, and computational software packages in an easy-to-use handbook format. The esteemed international contributors guide you from the very elementary aspects of the subject to the frontiers of current research. The book features an accessible layout of parts, chapters, and sections, with each section containing definition, fact, and example segments. The five main parts of the book encompass the fundamentals of linear algebra, combinatorial and numerical linear algebra, applications of linear algebra to various mathematical and nonmathematical disciplines, and software packages for linear algebra computations. Within each section, the facts (or theorems) are presented in a list format and include references for each fact to encourage further reading, while the examples illustrate both the definitions and the facts. Linearization often enables difficult problems to be estimated by more manageable linear ones, making the Handbook of Linear Algebra essential reading for professionals who deal with an assortment of mathematical problems.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2006 оличество страниц: 1400ƒобавлена в каталог: 30.06.2008ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
31Ч8 35Ч12 to 35Ч13 (MRRR) multiple relatively robust representations 42Ч15 to 42Ч17 1hs, Mathematica software 73Ч20 Abelian, Lie algebras 70Ч2 Abs, Mathematica software 73Ч26 Absolute bound 28Ч11 Absolute errors, conditioning and condition numbers 37Ч7 Absolute errors, floating point numbers 37Ч13 37Ч16 Absolute irreducibility 67Ч1 Absolute matrix norms 37Ч4 Absolute values 17Ч1 Absolute vector norm 37Ч2 Absolute, simple graphs 36Ч9 to 36Ч10 Absorbing, irreducible classes 54Ч5 Absorbing, vector norms 37Ч3 Absorbing, vector seminorms 37Ч4 Access equivalence irreducible classes 54Ч5 Access equivalence, irreducible matrices 29Ч6 29Ч7 Access equivalence, max-plus eigenproblem 25Ч6 Access equivalence, nonnegative and stochastic matrices 9Ч2 Action, group representations 68Ч2 Active branch, algebraic connectivity 36Ч5 Active constraints 51Ч1 Acyclic matrices multiplicative D-stability 19Ч6 Acyclic matrices rank revealing decompositions 46Ч9 Ad-nilpotency 70Ч4 Ad-semisimple linear transformation 70Ч4 Adaptive filtering, signal processing 64Ч12 to 64Ч13 Addition 1Ч1 1Ч3 Additive coset 2Ч5 Additive D-stability 19Ч7 to 19Ч8 Additive identity axiom 1Ч1 Additive IEPs (AIEPs) 20Ч10 Additive inverse axiom 1Ч1 Additive preservers 22Ч7 to 22Ч8 Adjacency convex set points 50Ч13 Adjacency digraphs 29Ч3 to 29Ч4 Adjacency graphs 28Ч5 to 28Ч7 Adjacency Hermitian matrices 8Ч2 Adjacency linear preservers 22Ч7 Adjacency vertices 28Ч2 Adjoint linear transformation 51Ч3 Adjoint map, Lie algebras 70Ч2 Adjoints of linear operators, inner product spaces 5Ч5 to 5Ч6 Adjoints of linear operators, semidefinite programming 51Ч3 Adjoints, inner product spaces 13Ч22 Adjugates, determinants 4Ч3 Adjusting random vectors 52Ч4 Admissibility, control theory 57Ч2 Admittance matrix 28Ч7 Advanced linear algebra, bilinear forms 12Ч1 to 12Ч9 Advanced linear algebra, cone invariant departure, matrices 26Ч1 to 26Ч14 Advanced linear algebra, equalities, matrices 14Ч1 to 14Ч17 Advanced linear algebra, functions of matrices 11Ч1 to 11Ч12 Advanced linear algebra, inequalities, matrices 14Ч1 to 14Ч17 Advanced linear algebra, inertia, matrices 19Ч1 to 19Ч10 Advanced linear algebra, integral domains, matrices over 23Ч1 to 23Ч10 Advanced linear algebra, inverse eigenvalue problems 20Ч1 to 20Ч12 Advanced linear algebra, linear preserver problems 22Ч1 to 22Ч8 Advanced linear algebra, matrix equalities and inequalities 14Ч1 to 14Ч17 Advanced linear algebra, matrix perturbation theory 15Ч1 to 15Ч16 Advanced linear algebra, matrix stability and inertia 19Ч1 to 19Ч10 Advanced linear algebra, max-plus algebra 25Ч1 to 25Ч14 Advanced linear algebra, multilinear algebra 13Ч1 to 13Ч26 Advanced linear algebra, numerical range 18Ч1 to 18Ч11 Advanced linear algebra, perturbation theory, matrices 15Ч1 to 15Ч16 Advanced linear algebra, pseudospectra 16Ч1 to 16Ч15 Advanced linear algebra, quadratic forms 12Ч1 to 12Ч9 Advanced linear algebra, sesquilinear forms 12Ч1 to 12Ч9 Advanced linear algebra, similarity of matrix families 23Ч1 to 23Ч10 Advanced linear algebra, singular values and singular value inequalities 17Ч1 to 17Ч15 Advanced linear algebra, stability, matrices 19Ч1 to 19Ч10 Advanced linear algebra, total negativity, matrices 21Ч1 to 21Ч12 Advanced linear algebra, total positivity, matrices 21Ч1 to 21Ч12 Affine algebraic variety 24Ч8 Affine function 50Ч1 Affine parameterized IEPs (PIEPs) 20Ч10 to 20Ч12 Affine subspace determination 65Ч2 Affine-independence 65Ч2 AIEPs (additive IEPs) 20Ч10 Aissen studies 21Ч12 Aitken estimator 52Ч8 Akian, Marianne 25Ч1 to 25Ч14 Akivis algebra 69Ч16 to 69Ч17 Albert algebra 69Ч4 69Ч14 Alexandroff inequality 25Ч10 AlexandrovТs inequality 31Ч2 Algebra PЧ1 Algebra applications see also ЂNonassociative algebraї Algebra applications, group representations 68Ч1 to 68Ч11 Algebra applications, Lie algebras 70Ч1 to 70Ч10 Algebra applications, matrix groups 67Ч1 to 67Ч7 Algebra applications, nonassociative algebra 69Ч1 to 69Ч25 Algebraic aspects, least squares solutions 39Ч4 to 39Ч5 Algebraic connectivity, absolute, simple graphs 36Ч9 to 36Ч10 Algebraic connectivity, Fiedler vectors 36Ч7 to 36Ч9 Algebraic connectivity, generalized Laplacian 36Ч10 to 36Ч11 Algebraic connectivity, matrix representations 28Ч7 Algebraic connectivity, multiplicity 36Ч10 to 36Ч11 Algebraic connectivity, simple graphs 36Ч1 to 36Ч4 36Ч9 Algebraic connectivity, trees 36Ч4 to 36Ч6 Algebraic connectivity, weighted graphs 36Ч7 to 36Ч9 Algebraic eigenvalues 25Ч9 see Algebraic function, matrix similarities 24Ч1 Algebraic geometric Goppa (AG) code 61Ч10 Algebraic multigrid, preconditioners 41Ч11 Algebraic multiplicity 4Ч6 Algebraic Riccati equation (ARE) 57Ч10 57Ч12 Algorithms see specific algorithm Algorithms, Arbitrary Precision Approximating (APA) 47Ч6 Algorithms, Arnoldi 41Ч7 Algorithms, BiCGSTAB 41Ч8 Algorithms, biconjugate gradient (BCG/BiCG) 41Ч7 49Ч13 Algorithms, bilinear noncommutative 47Ч2 Algorithms, bit flipping algorithm 61Ч11 Algorithms, Conjugate Gradient (CG) 41Ч4 41Ч6 Algorithms, conjugate gradient squared (CGS) 41Ч8 Algorithms, Denardo 25Ч8 Algorithms, error analysis 37Ч16 to 37Ч17 Algorithms, ESPRIT 64Ч17 Algorithms, EuclidТs 23Ч2 Algorithms, fast matrix multiplication 47Ч2 to 47Ч7 Algorithms, Full Orthogonalization Method (FOM) 41Ч7 Algorithms, Generalized Minimal Residual (GMRES) 41Ч7 49Ч13 Algorithms, Lanczos algorithm 41Ч4 to 41Ч5 Algorithms, least squares solutions 39Ч6 to 39Ч7 Algorithms, left-preconditioned BiCGSTAB algorithm 41Ч12 Algorithms, Levinson-Durbin algorithm 64Ч8 Algorithms, Minimal Residual (MINRES) 41Ч4 41Ч6 Algorithms, MUSIC 64Ч17 Algorithms, non-Hermitian Lanczos algorithm 41Ч7 Algorithms, noncommutative 47Ч2 Algorithms, policy iteration 25Ч7 Algorithms, power algorithm 25Ч7 Algorithms, preconditioned conjugate gradient (PCG) 41Ч13 Algorithms, quasi-minimal residual (QMR) 41Ч8 49Ч13 Algorithms, restarted GMRES algorithm 41Ч7 Algorithms, singular value decomposition 45Ч4 to 45Ч12 Algorithms, transpose-free quasi-minimal residual (TFQMR) 49Ч14 Algorithms, two-sided Lanczos algorithm 41Ч7 All-ones matrix 52Ч4 Allowing characteristics, random vectors 52Ч4 Allowing characteristics, sign-pattern matrices 33Ч9 to 33Ч11 Alphabet, coding theory 61Ч1 Alt multiplication 13Ч17 to 13Ч19 Alternate path, single arc 35Ч14 Alternating bilinear forms 12Ч5 to 12Ч6 Alternative algebras 69Ч2 69Ч10 Alternative bimodule 69Ч10 Alternator 13Ч12 AMG code 41Ч12 Analysis applications, control theory 57Ч1 to 57Ч17 Analysis applications, differential equations 55Ч1 to 55Ч16 Analysis applications, dynamical systems 56Ч1 to 56Ч21 Analysis applications, Fourier analysis 58Ч1 to 58Ч20 Analysis applications, LTI systems 57Ч7 to 57Ч10 Analysis applications, stability 55Ч1 to 55Ч16 Analytical similarity 24Ч1 Analyzing fill 40Ч10 to 40Ч13 Angles, inner product spaces 5Ч1 Annihilator 3Ч8 to 3Ч9 Anti-identity matrices 48Ч2 Anticommutative algebra 69Ч2 Anticommutativity 70Ч2 Anticommutator 69Ч3 Antisymmetric maps 13Ч10 to 13Ч12 Antisymmetry 12Ч5 Aperiodicity, characterizing 9Ч3 Aperiodicity, irreducible classes 54Ч5 Aperiodicity, irreducible matrices 9Ч3 Aperiodicity, reducible matrices 9Ч7 Append, Mathematica software, linear systems 73Ч23 Append, Mathematica software, matrices manipulation 73Ч13 Append, Mathematica software, vectors 73Ч3 AppendColumns, Mathematica software 73Ч13 Appending, vertices 36Ч3 AppendRows, Mathematica software 73Ч13 Applications, algebra, group representations 68Ч1 to 68Ч11 Applications, algebra, Lie algebras 70Ч1 to 70Ч10 Applications, algebra, matrix groups 67Ч1 to 67Ч7 Applications, algebra, nonassociative algebra 69Ч1 to 69Ч25 Applications, analysis, control theory 57Ч1 to 57Ч17 Applications, analysis, differential equations 55Ч1 to 55Ч16 Applications, analysis, dynamical systems 56Ч1 to 56Ч21 Applications, analysis, Fourier analysis 58Ч1 to 58Ч20 Applications, analysis, stability 55Ч1 to 55Ч16 Applications, biological sciences 60Ч1 to 60Ч13 Applications, computer science, coding theory 61Ч1 to 61Ч13 Applications, computer science, information retrieval 63Ч1 to 63Ч14 Applications, computer science, quantum computation 62Ч1 to 62Ч19 Applications, computer science, signal processing 64Ч1 to 64Ч18 Applications, computer science, Web searches 63Ч1 to 63Ч14 Applications, fast matrix multiplication 47Ч9 to 47Ч10 Applications, geometry, Euclidean geometry 66Ч1 to 66Ч15 Applications, geometry, geometry 65Ч1 to 65Ч9 Applications, optimization, linear programming 50Ч1 to 50Ч24 Applications, optimization, semidefinite programming 51Ч1 to 51Ч11 Applications, physical sciences 59Ч1 to 59Ч11 Applications, probability and statistics, linear statistical models 52Ч1 to 52Ч15 Applications, probability and statistics, Markov chains 54Ч1 to 54Ч14 Applications, probability and statistics, multivariate statistical analysis 53Ч1 to 53Ч14 Applications, probability and statistics, random vectors 52Ч1 to 52Ч15 Applications, semidefinite programming 51Ч9 to 51Ч11 Apply, Mathematica software 73Ч3 73Ч5 73Ч27 Approximate Jordan form, Maple software 72Ч15 Approximate prescribed-line-sum scalings 9Ч21 to 9Ч22 Approximation, fast matrix multiplication 47Ч6 to 47Ч7 Approximation, linear programming 50Ч20 to 50Ч23 Approximation, orthogonal projection 5Ч7 ArbitraryPrecision Approximating (APA) algorithms 47Ч6 ArcSin, Mathematica software 73Ч26 ARE see ЂAlgebraic Riccati equation (ARE)ї Arithmetic Euclidean vector space 66Ч1 Arm, stars 34Ч10 Arnold Hypothesis, Strong 28Ч9 28Ч10 Arnoldi algorithm 41Ч7 41Ч8 Arnoldi decomposition 16Ч11 Arnoldi factorization, implicitly restarted Arnoldi method 44Ч2 to 44Ч4 Arnoldi factorization, pseudospectra 16Ч3 Arnoldi matrices 49Ч11 Arnoldi method see ЂImplicitly restarted Arnoldi method (IRAM)ї Arnoldi method, eigenvalue computations 49Ч12 Arnoldi method, implicit restarting 44Ч6 Arnoldi method, large-scale matrix computations 49Ч10 to 49Ч11 Arnoldi method, sparse matrices 43Ч9 43Ч11 Arnoldi vectors, Arnoldi factorization 44Ч3 Arnoldi vectors, Arnoldi process 49Ч11 ARPACK subroutine package, computational modes 76Ч8 to 76Ч9 ARPACK subroutine package, directory structure and contents 76Ч3 ARPACK subroutine package, fundamentals 76Ч1 to 76Ч2 76Ч4 ARPACK subroutine package, Lanczos methods 42Ч21 ARPACK subroutine package, MatlabТs EIGS 76Ч9 to 76Ч10 ARPACK subroutine package, naming conventions 76Ч3 to 76Ч4 ARPACK subroutine package, precisions 76Ч3 to 76Ч4 ARPACK subroutine package, pseudospectra computation 16Ч12 ARPACK subroutine package, reverse communication 76Ч2 ARPACK subroutine package, setup of problem 76Ч5 to 76Ч7 ARPACK subroutine package, sparse matrices 43Ч9 ARPACK subroutine package, types 76Ч3 to 76Ч4 ARPACK subroutine package, use 76Ч7 to 76Ч8 Array arithmetic, Maple software 72Ч8 Array, Maple software 72Ч1 72Ч2 Array, Mathematica software, matrices 73Ч6 Array, Mathematica software, vectors 73Ч3 73Ч4 ArrayPlot, Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч27 ArrayPlot, Mathematica software, matrices 73Ч7 73Ч9 ArrayRules, Mathematica software 73Ч6 Arrays, Fourier analysis 58Ч2 Arrays, manifold 64Ч16 Arrays, Maple software 72Ч8 to 72Ч9 Arrays, response vector 64Ч16 Arrays, response vector, Maple software 72Ч8 72Ч9 Arrival estimation direction 64Ч15 to 64Ч18 Arrow, Mathematica software 73Ч5 ArtinТs theorem 69Ч3 69Ч11 AspectRatio, Mathematica software 73Ч27 Assignment polytope 27Ч10 Associated divisor 61Ч10 Associated linear programming 50Ч14 Associated maps 13Ч19 to 13Ч20 Association schemes, graphs 28Ч11 to 28Ч12 Associations, generalized stars 34Ч11 Associative algebra 69Ч2 Associative center 69Ч5 Associative enveloping algebra 69Ч13 Associative nucleus 69Ч5 Associativity axiom 1Ч1 1Ч2 Associator ideal 69Ч5 Associator, nonassociative algebra 69Ч2 Asymmetric digraphs 35Ч2 see Asymptotic spectrum 47Ч8 Asymptotic stability, control theory 57Ч2 Asymptotic stability, linear differential-algebraic equations 55Ч14 Asymptotic stability, linear ordinary differential equations 55Ч10 Asymptotic stability, LTI systems 57Ч7 Asymptotics, matrix powers 25Ч8 to 25Ч9 ATLAST M-file collection 71Ч20 Attractor-repeller decompositions 56Ч7 Augmented matrices, Bezout domains 23Ч9 Augmented matrices, systems of linear equations 1Ч9 1Ч11 Augmented systems, least squares solution 39Ч4 Autocorrelation matrix 64Ч5 Autocorrelation sequence 64Ч4 Automatic, Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч27 Automatic, Mathematica software, singular values 73Ч17 Automorphism, Lie algebras 70Ч1 Automorphism, ring, linear preservers 22Ч7 Autonomy, control theory 57Ч2 Backward errors, analysis 37Ч20 Backward errors, numerical stability and instability 37Ч18 37Ч20 Backward errors, one-sided Jacobi SVD algorithm 46Ч2 Backward stability, numerical stability and instability 37Ч18 Backward stability, numerical stability and instability, one-sided Jacobi SVD algorithm 46Ч2 BackwardsSubstitute, Maple software 72Ч9 Bad columns 50Ч8 Bad rows 50Ч8 Badly-conditioned data 37Ч7 Bai, Zhaojun 75Ч1 to 75Ч23 Bailey, D. 47Ч5
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



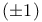 -matrices
-matrices 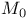 -matrices
-matrices