јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Hogben L. Ч Handbook of Linear Algebra
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Handbook of Linear Algebraјвтор: Hogben L. јннотаци€: The Handbook of Linear Algebra provides comprehensive coverage of linear algebra concepts, applications, and computational software packages in an easy-to-use handbook format. The esteemed international contributors guide you from the very elementary aspects of the subject to the frontiers of current research. The book features an accessible layout of parts, chapters, and sections, with each section containing definition, fact, and example segments. The five main parts of the book encompass the fundamentals of linear algebra, combinatorial and numerical linear algebra, applications of linear algebra to various mathematical and nonmathematical disciplines, and software packages for linear algebra computations. Within each section, the facts (or theorems) are presented in a list format and include references for each fact to encourage further reading, while the examples illustrate both the definitions and the facts. Linearization often enables difficult problems to be estimated by more manageable linear ones, making the Handbook of Linear Algebra essential reading for professionals who deal with an assortment of mathematical problems.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2006 оличество страниц: 1400ƒобавлена в каталог: 30.06.2008ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Nondefective matrices 4Ч6 Nondegenerate properties, bilinear forms 12Ч2 Nondegenerate properties, sesquilinear forms 12Ч6 Nonderogatory matrices 4Ч6 Nondifferentiation 18Ч3 Nonempty sets, row and column indices 1Ч4 Nonhomogenous products 9Ч22 Nonlinear preservers 22Ч7 to 22Ч8 Nonnegative IEPs (NIEPs), fundamentals 20Ч5 Nonnegative IEPs (NIEPs), merging results 20Ч8 Nonnegative IEPs (NIEPs), nonzero spectra 20Ч7 to 20Ч8 Nonnegative IEPs (NIEPs), spectra 20Ч6 to 20Ч7 Nonnegative IEPs (NIEPs), sufficient conditions 20Ч8 to 20Ч10 Nonnegatives, constraints 50Ч3 Nonnegatives, factorization 9Ч22 Nonnegatives, fundamentals 9Ч1 Nonnegatives, integer rank 30Ч8 Nonnegatives, matrices, fundamentals 9Ч1 to 9Ч2 Nonnegatives, matrices, inequalities 17Ч11 Nonnegatives, matrices, inverse eigenvalue problem 9Ч22 Nonnegatives, matrices, irreducible matrices 9Ч2 to 9Ч7 Nonnegatives, matrices, max algebra 9Ч23 Nonnegatives, matrices, nonhomogenous products 9Ч22 Nonnegatives, matrices, nonnegative factorization 9Ч22 Nonnegatives, matrices, P-, 35Ч17 to 35Ч18 Nonnegatives, matrices, permanents 31Ч7 Nonnegatives, matrices, Perron Ч Frobenius theorem 26Ч2 Nonnegatives, matrices, product form 9Ч23 Nonnegatives, matrices, reducible matrices 9Ч7 to 9Ч15 Nonnegatives, matrices, scaling 9Ч20 to 9Ч23 Nonnegatives, matrices, sets 9Ч23 Nonnegatives, matrix factorization 63Ч5 to 63Ч8 Nonnegatives, sign pattern matrices 33Ч12 Nonnegatives, stable matrices 9Ч17 Nonnegatives, vectors 26Ч2 Nonnormality constant 44Ч10 Nonprimary matrix function 11Ч2 Nonrandom matrices 52Ч3 Nonrandom vectors 52Ч3 Nonregular matrices 32Ч7 to 32Ч9 Nonscalar multiplications, approximation algorithms 47Ч6 Nonscalar multiplications, fast algorithms 47Ч2 Nonseparability 35Ч2 Nonsingular properties, distribution 53Ч8 Nonsingular properties, fundamentals 2Ч9 to 2Ч10 Nonsingular properties, isomorphism 3Ч7 to 3Ч8 Nonsingular properties, matrices 1Ч12 Nonsingular properties, multivariate normal distribution 53Ч3 Nonsquare case 32Ч2 to 32Ч12 Nonsymmetric eigenproblems 75Ч17 to 75Ч20 Nonsymmetric eigenvalue problems 75Ч11 to 75Ч13 Nonsymmetric Lanczos process, Arnoldi process 49Ч10 Nonsymmetric Lanczos process, large-scale matrixcomputations 49Ч8 to 49Ч10 Nonsymmetric Lanczos process, linear dynamical systems 49Ч15 Nonsymmetric problems, ARPACK 76Ч8 Nonzero spectra 20Ч7 to 20Ч8 norm command, Matlab software 71Ч17 Norm estimation 18Ч9 to 18Ч10 Norm, Maple software 72Ч3 72Ч5 Norm, Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч26 73Ч27 Norm, Mathematica software, matrix algebra 73Ч10 73Ч11 Norm, Mathematica software, vectors 73Ч3 73Ч5 Normal equations, least squares problems 5Ч14 Normal equations, linear statistical models 52Ч8 Normal vector, Euclidean point space 66Ч2 Normal, Mathematica software 73Ч6 73Ч8 Normalization 23Ч5 Normalized properties, floating point numbers 37Ч11 Normalized properties, immanant 31Ч13 Normalized properties, matrices 25Ч6 Normalized properties, scaling nonnegative matrices 9Ч20 Norms, matrices 37Ч4 to 37Ч6 Not invertible 1Ч12 see Notation index NЧ1 to NЧ9 Notebooks, Mathematica software 73Ч1 Nth-derived algebra 70Ч3 null command, Matlab software 71Ч8 71Ч17 Null graphs 28Ч2 Null recurrent state 54Ч7 to 54Ч9 Null spaces, dimension theorem 2Ч6 to 2Ч9 Null spaces, kernel and range 3Ч5 Null spaces, linear independence, span, and bases 2Ч6 Null spaces, matrix range 2Ч6 to 2Ч9 Null spaces, rank 2Ч6 to 2Ч9 Nullity, linear independence, span, and bases 2Ч6 Nullity, matrix equalities and inequalities 14Ч12 to 14Ч15 NullSpace, Maple software, matrix factoring 72Ч9 NullSpace, Maple software, modular arithmetic 72Ч14 to 72Ч15 NullSpace, Mathematica software, fundamentals 73Ч27 NullSpace, Mathematica software, matrix algebra 73Ч10 73Ч12 Nullspaces 39Ч4 Numerical linear algebra, Maple software 72Ч13 to 72Ч15 Numerical linear algebra, support routines 77Ч1 Numerical methods, affine parameterized IEPs 20Ч11 to 20Ч12 Numerical methods, fast matrix multiplication 47Ч1 to 47Ч10 Numerical methods, high relative accuracy computation 46Ч1 to 46Ч16 Numerical methods, implicitly restarted Arnoldi method 44Ч1 to 44Ч12 Numerical methods, iterative solution methods 41Ч1 to 41Ч17 Numerical methods, large-scale matrixcomputations 49Ч1 to 49Ч15 Numerical methods, linear systems, direct solutions 38Ч1 to 38Ч17 Numerical methods, linear systems, efficiency 37Ч1 to 37Ч21 Numerical methods, linear systems, error analysis 37Ч1 to 37Ч21 Numerical methods, linear systems, factorizations 38Ч1 to 38Ч17 Numerical methods, linear systems, least squares solutions 39Ч1 to 39Ч12 Numerical methods, linear systems, matrix norms 37Ч1 to 37Ч21 Numerical methods, linear systems, sparse matrix methods 40Ч1 to 40Ч18 Numerical methods, linear systems, stability 37Ч1 to 37Ч21 Numerical methods, linear systems, vector norms 37Ч1 to 37Ч21 Numerical methods, Markov chains 54Ч12 to 54Ч14 Numerical methods, singular value decomposition 45Ч1 to 45Ч12 Numerical methods, stability and instability 37Ч18 to 37Ч21 Numerical methods, structured matrix computations 48Ч1 to 48Ч9 Numerical methods, symmetric matrix techniques 42Ч1 to 42Ч22 Numerical methods, unsymmetric matrix techniques 43Ч1 to 43Ч11 Numerical orthogonality 46Ч2 Numerical radius 18Ч1 Numerical range, boundary points 18Ч3 to 18Ч4 Numerical range, dilations 18Ч9 to 18Ч10 Numerical range, examples 18Ч1 to 18Ч3 Numerical range, fundamentals 18Ч1 Numerical range, location 18Ч4 to 18Ч6 Numerical range, matrix mappings 18Ч11 Numerical range, matrix products 18Ч8 to 18Ч9 Numerical range, norm estimation 18Ч9 to 18Ч10 Numerical range, properties 18Ч1 to 18Ч3 Numerical range, radius 18Ч6 to 18Ч8 Numerical range, special boundary points 18Ч3 to 18Ч4 Numerical range, spectrum 18Ч3 to 18Ч4 Numerical range, unitary similarity 7Ч2 Numerical rank 39Ч11 Numerical stability and instability, error analysis 37Ч18 to 37Ч21 Numerical stability and instability, StrassenТs algorithm 47Ч4 Numerically orthogonal matrices 46Ч2 numnull command, Matlab software 71Ч13 O and o PЧ5 Objective function 50Ч1 Oblique Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, eigenvalue Oblique Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, computations 49Ч12 Oblique Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, large-scale matrix computations 49Ч2 Observability Hessenberg form 57Ч9 Observability Kalman decomposition 57Ч7 Observability matrix 57Ч7 Observableness, control theory 57Ч2 Observer equation 57Ч2 Octonions, generalized 69Ч4 Odd cycle 33Ч2 Oettli Ч Prager theorem 38Ч3 Off-diagonal entry 1Ч4 Off-norm, Jacobi method 42Ч17 One(1)-chordal graphs 35Ч2 One(1)-norm 37Ч2 One-bit quantum gate 62Ч2 One-dimensional harmonic oscillator 59Ч8 One-sided Jacobi SVD algorithm, high relative accuracy 46Ч2 to 46Ч5 One-sided Jacobi SVD algorithm, positive definite matrices 46Ч11 One-sided Jacobi SVD algorithm, preconditioned Jacobi SVD algorithm 46Ч6 One-sided Jacobi SVD algorithm, singular value decomposition 45Ч5 One-sided Jacobi SVD algorithm, symmetric indefinite matrices 46Ч15 One-to-one, kernel and range 3Ч5 Onto, kernel and range 3Ч5 Open halfspaces 66Ч2 Open sector 33Ч14 Operations and functions, Maple software 72Ч3 72Ч5 Operator norms, matrix norms 37Ч4 Operator norms, unitary similarity 7Ч2 Optimal control problem 57Ч14 Optimal estimation problem 57Ч12 Optimal Krylov space methods 41Ч4 to 41Ч11 Optimal pivoting strategy 42Ч17 Optimal solution 50Ч1 Optimal value 50Ч1 Optimality conditions 51Ч5 to 51Ч7 Optimality theorem 51Ч6 Optimization, linear programming 50Ч1 50Ч1 Optimization, matrix games 50Ч18 Optimization, semidefinite programming 51Ч1 to 51Ч11 Optimization, standard row tableaux 50Ч8 Orbit, linear dynamical systems 56Ч5 Orbit, simultaneous similarity 24Ч8 Order predictable signals 64Ч7 Order sequence 58Ч8 Order, control theory 57Ч2 Order, graphs 28Ч1 Order, reducible matrices 26Ч9 Ordinary least squares estimator 52Ч8 Ordinary least squares solution 52Ч8 Orientation 13Ч24 to 13Ч26 Orientation preservation 56Ч5 Oriented incidence matrix 28Ч7 orth command, Matlab software 71Ч17 Orthogonal Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, Arnoldi process 49Ч10 Orthogonal Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, large-scale matrix computations 49Ч2 Orthogonal Petrov Ч Galerkin projection, symmetric Lanczos process 49Ч7 Orthogonal properties, classical groups 67Ч5 Orthogonal properties, complement 5Ч3 Orthogonal properties, congruence 25Ч10 Orthogonal properties, Euclidean point space 66Ч2 Orthogonal properties, Euclidean spaces 65Ч4 Orthogonal properties, fundamentals 5Ч3 to 5Ч5 Orthogonal properties, general properties 69Ч5 Orthogonal properties, least squares solutions 39Ч5 to 39Ч6 Orthogonal properties, linear inequalities and projections 25Ч10 Orthogonal properties, projection 5Ч6 to 5Ч8 Orthogonal properties, rank revealing decomposition 39Ч11 Orthogonal properties, sign-pattern matrices 33Ч16 to 33Ч17 Orthogonal properties, symmetric bilinear forms 12Ч3 Orthogonal properties, symmetric indefinite matrices 46Ч14 Orthogonal properties, symmetric matrix eigenvalue techniques 42Ч2 Orthogonal properties, unitary similarity 7Ч1 Orthogonality relations 68Ч6 to 68Ч8 Orthogonalization 38Ч13 to 38Ч15 Oscillation modes 59Ч2 to 59Ч5 Oscillatory matrices 21Ч2 Oseledets theorem 56Ч14 to 56Ч15 Ostrowski theorem, eigenvalue problems 15Ч13 Ostrowski theorem, spectrum localization 14Ч6 to 14Ч7 Outer normal, Euclidean simplexes 66Ч7 Outer, Mathematica software 73Ч2 73Ч3 73Ч4 Outerplanar graphs 28Ч4 OuterProductMatrix, Maple software 72Ч3 Outlets 66Ч13 Output Feedback 57Ч7 57Ч13 Output space 57Ч2 Output vector 57Ч2 Output, algorithms and efficiency 37Ч16 Output, LTI systems 57Ч14 Ovals of Cassini 14Ч6 to 14Ч7 Overall constraint length 61Ч12 Overflow, floating point numbers 37Ч12 P-, 35Ч15 to 35Ч17 P-, 19Ч3 p-Lie algebra 70Ч2 p-Norm 37Ч2 Packed format 74Ч2 Pade approximate 11Ч10 to 11Ч11 11Ч12 Pade iterations 11Ч12 Pade models, dimension reduction 49Ч14 Pade models, linear dynamical systems 49Ч15 PadRight, Mathematica software 73Ч13 Page repository 63Ч9 Page, Larry 54Ч4 63Ч9 63Ч10 PageRank, fundamentals 63Ч10 PageRank, information retrieval 63Ч10 to 63Ч14 PageRank, Markov chains 54Ч4 to 54Ч5 PageRank, vector 63Ч11 PageRank, Web search 63Ч9 Pairwise orthogonality 7Ч5 Paley Ч Wiener theorem 64Ч3 to 64Ч4 Pan, V. 47Ч7 PappusТ theorem 65Ч8 65Ч9 Parabolic subgroup 67Ч4 Parabolic subgroup, BN structure 67Ч5 Parallel hyperplanes 66Ч2 Parallel vector subspace 65Ч2 Parallelepiped, Gram matrices 66Ч5 Parallelogram law, inner product spaces 5Ч3 Parallelogram, Gram matrices 66Ч5 Parameters, graphs 28Ч9 to 28Ч11 Parametric programming 50Ч17 to 50Ч18 Parametrization ofcorrelation matrices 8Ч8 Parity check, matrix 61Ч3 Parity check, polynomial 61Ч7 Parlett and Reinsch studies 43Ч3 ParlettТs recurrence 11Ч10 11Ч11 ParsevalТs Inequality 5Ч4 Parter vertices 34Ч2 to 34Ч4 Parter Ч Wiener theorem, given multiplicities 34Ч9 Parter Ч Wiener theorem, multiplicities and Parter vertices 34Ч2 Parter Ч Wiener vertex 34Ч2 Partial 35Ч12 to 35Ч13 Partial completely positive matrices 35Ч10 Partial copositive matrices 35Ч11 Partial correlarandom vectors 52Ч4 Partial correlation coefficient, linear prediction 64Ч8 Partial correlation matrix 52Ч4 Partial covariance matrix 52Ч4 Partial differential equations 58Ч7 Partial doubly nonnegative matrices 35Ч10 Partial entry sign symmetric P-, 35Ч19 to 35Ч20 Partial entry weakly sign symmetric P-, 35Ч19 to 35Ч20 Partial Euclidean distance matrices 35Ч10 Partial inverse M-matrices 35Ч14 Partial M-matrices 35Ч12 to 35Ч13 Partial matrices 35Ч2 Partial matrix multiplication 47Ч8 Partial nonnegative P-, 35Ч17 to 35Ч18 Partial order, checkerboard 21Ч9 Partial P-, 35Ч15 Partial pivoting 40Ч18 see Partial positive definite matrices 35Ч8 Partial positive P-matrices 35Ч17 Partial positive semidefinite matrices 35Ч8 Partial Schur decomposition 44Ч6 44Ч8 Partial semidefinite ordering, positive definite matrices 8Ч10 Partial semidefinite ordering, random vectors 52Ч4 Partial strictly copositive matrices 35Ч11 Partition, Mathematica software 73Ч14 Partitioned matrices, block diagonal matrices 10Ч4 to 10Ч6 Partitioned matrices, block matrices 10Ч1 to 10Ч3 Partitioned matrices, block triangular matrices 10Ч4 to 10Ч6 Partitioned matrices, Kronecker products 10Ч8 to 10Ч9
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



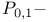 and
and 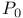 -matrices, completion problems
-matrices, completion problems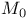 -matrices
-matrices 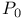 -matrices
-matrices