|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Fuhrhop J., Penzlin G. — Organic Synthesis: Concepts, Methods, Starting materials |

Îáñóäèòå êíèãó íà
Íàøëè îïå÷àòêó?
Âûäåëèòå åå ìûøêîé è íàæìèòå Ctrl+Enter
|
Íàçâàíèå: Organic Synthesis: Concepts, Methods, Starting materials
Àâòîðû: Fuhrhop J., Penzlin G.
ßçûê: 
Ðóáðèêà: Õèìèÿ/
Ñòàòóñ ïðåäìåòíîãî óêàçàòåëÿ: Ãîòîâ óêàçàòåëü ñ íîìåðàìè ñòðàíèö
ed2k:
Èçäàíèå: second edition, rewise and enlarged
Ãîä èçäàíèÿ: 1994
Êîëè÷åñòâî ñòðàíèö: 432
Äîáàâëåíà â êàòàëîã: 29.10.2005
Îïåðàöèè: Ïîëîæèòü íà ïîëêó |
Ñêîïèðîâàòü ññûëêó äëÿ ôîðóìà | Ñêîïèðîâàòü ID
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
Reductive cleavage see “Hydrogenolysis” “Ring
Reductive cleavage of alcohols 97 113—114 202—203 277
Reductive cleavage of haloalkanes see “Reduction”
Reductive cleavage of ketone derivs. 109 114—115 155—156
Reductive cleavage of nitriles (decyanation) 280
Reductive cleavage of peroxides 276—277
Reductive cleavage of protecting groups 156—159 162—165 167
Reductive cleavage of steroids with 10-alkyl 287—288
Reductive cleavage of sulfonamides 247
Reductive cleavage of sulfones 70
Reductive cleavage of thioethers 26 39 76 82 98 109 110—111 113—114 156 273
Reductive cleavage of tosylhydrazones 109 141—142
Reductive coupling of alkenes via boranes 37
Reductive coupling of alkynes via boranes 37—38
Reductive coupling of allylic halides via Ni complexes 42
Reductive coupling of allylic halides via thioethers 39
Reductive coupling of carbonyl compounds with arylic esters, 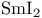 69 69
Reductive coupling of carbonyl compounds, acyloin coupling 53—54
Reductive coupling of carbonyl compounds, Barton olefination 35
Reductive coupling of carbonyl compounds, McMurry olefination 41
Reductive coupling of carbonyl compounds, pinacol coupling 53
Reductive coupling of haloalkanes 36
Reductive coupling of nitroarenes 305
Reductive deoxysulfonatibn 34
Reductive desulfurization see “Sulfones” “Thiiranes” “Thioethers”
Reductive ring opening see “Ring opening”
Reetz reagent ( 5:1) 21 5:1) 21
Reformatsky reaction of  -bromo carboxylic esters 44—45 301 -bromo carboxylic esters 44—45 301
Reformatsky reaction of allylic bromides 44—45
Regioselectivity of aldol type reactions 55—58 93 318
Regioselectivity of alkylations of  -allylpalladium complexes 27 -allylpalladium complexes 27
Regioselectivity of alkylations of 1,3-dioxo dianions 9—10 24 204 326
Regioselectivity of alkylations of enamines 13—14 25—26
Regioselectivity of alkylations of oxiranes 21 44 64
Regioselectivity of alkylations,  or or 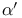 of of 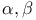 -unsatd. ketones 25 -unsatd. ketones 25
Regioselectivity of alkylations,  of of 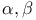 -unsatd. ketones 20—21 -unsatd. ketones 20—21
Regioselectivity of amination of  -allylpalladium 164 -allylpalladium 164
Regioselectivity of Baeyer — Villiger oxidation 136—137
Regioselectivity of cyclopropanations 75—76
Regioselectivity of enolization of 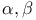 -unsaturated ketones 25 58 -unsaturated ketones 25 58
Regioselectivity of enolization of ketones 11—13 57—58
Regioselectivity of halohydrinations 77 160 275—276 286 287
Regioselectivity of halolactonization 275 319—320 335—336
Regioselectivity of heterocycle syntheses 149—153 291—298 307—309
Regioselectivity of hydration of alkynes with Hg(2+) 52 57
Regioselectivity of hydroborations 37—38 47—48 89—90 107—108 130—131 319—320
Regioselectivity of hydrozirconations 132
Regioselectivity of Michael type additions 71—74 318
Regioselectivity of ox. cleavage of arenes and dienes 87—88
Regioselectivity of oxidation of alkenes 118—119 285—286
Regioselectivity of oxidation of allylic CH 119—121
Regioselectivity of oxidation of dienes 82 123—124 126—129 156—157
Regioselectivity of oxidation,  of ketones 121—122 of ketones 121—122
Regioselectivity of protection of functional groups 154—167
Regioselectivity of reduction of 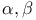 -unsaturated carbonyl compounds, C=C reduction 73 103—104 322—323 -unsaturated carbonyl compounds, C=C reduction 73 103—104 322—323
Regioselectivity of reduction of 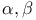 -unsaturated carbonyl compounds, C=O reduction 105—107 265 273 -unsaturated carbonyl compounds, C=O reduction 105—107 265 273
Regioselectivity of reduction of diynes 100—101
Regioselectivity of reduction of tosylhydrazones 141—142
Regioselectivity of ring expansion of ketones with 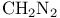 83 83
Regioselectivity of [2+2]cycloadditions 78 276 297—298
Regioselectivity of [2+4]cycloadditions 85—86
Remote oxidation 116 118 285—286
Resin, anion exchange see “Hunig base polymeric”
Resin, cation-exchange see “Sulfonic acids”
Resolution of racemats see “Optical resolution”
Resorcinols see “1
Restriction endonucleases 243
retention see “Racemization prevention
Retention of cis/trans- or -R/S-con figuration, organyl coupling of boranes 37—38
Retention of cis/trans- or -R/S-con figuration, organyl coupling of cuprates 20
Retention of cis/trans- or -R/S-con figuration, ox. cleavage of triorganylboranes 130—131
Retention of cis/trans-configuration, alkylation of vinylic halides 20
Retention of cis/trans-configuration, amination of allyl acetates via allyl-Pd 164
Retention of cis/trans-configuration, Baeyer — Villiger oxidations 136—137
Retention of cis/trans-configuration, fragmentations 89—90
Retention of cis/trans-configuration, hydrolysis of triorganylboranes 37—38
Retention of cis/trans-configuration, [1+2]cycloadditions 75
Retention of cis/trans-configuration, [2+4]cycloadditions 85—86 280—281 297
Retention of R/S-configuration,  -alkylation of N,O-protected proline 299 -alkylation of N,O-protected proline 299
Retention of R/S-configuration, 1-alkylation of carboxylic acid derivs. 46
Retention of R/S-configuration, alkylation of allyl acetates via  -allyl-Pd 27 -allyl-Pd 27
Retention of R/S-configuration, diazotization of ec-amino acids 202—203
Retention of R/S-configuration, displacement of OH. 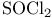 , ,  288—289 288—289
Retention of R/S-configuration, glycosylation, 2-O-acyl neighboring group participation 270—271
Retention of R/S-configuration, oxidation of benzylic CH 120
Retinal  -carotene from 41 -carotene from 41
Retinol (vitamin A), acetate, synthesis 31
Retro-aldol type cleavage see “Decarboxylations”
Retro-aldol type cleavage of 1,3-dioxo compounds 81 88 207
Retro-aldol type cleavage of 17-(methoxyoxoacetyl) chlorin 259
Retro-aldol type cleavage of pyrroles in Knorr’s synthesis 150—151
Retro-aldol type transform 194
Retro-Diels — Alder type cleavage, 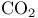 elimination by 80 92 331 elimination by 80 92 331
Retro-Diels — Alder type cleavage, 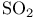 elimination by 80 153 elimination by 80 153
Retro-Diels — Alder type cleavage, CO elimination by 337
Retro-Diels — Alder type transform 194 210 212
retro-Synthesis see “Retro-synthetic analysis”
Retro-synthetic analysis 171 193—213
Retro-synthetic analysis, commercial starting materials 171—192
Retro-synthetic analysis, enantioselective 200—204
Retro-synthetic analysis, exercises 213—214
Retro-synthetic analysis, symbols and terminology 193—196
Reverse transcriptase 242
Rhodium(1+) complexes, [2+2]cycIoreversion of cyclobutanes 332
Rhodium(1+), chiral “binap” complexes, asymmetric hydrogenation with 102—103
Rhodium(1+), tris(triphenylphosphine)-, hydroboration catalyst 131
Ribonucleic acid see “RNA”
Ring cleavage, electrocyclic (cycloreversion), [1+1+2]-, double CO elimination 78 339
Ring cleavage, electrocyclic (cycloreversion), [1+4]-, 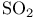 elimination 80 153 elimination 80 153
Ring cleavage, electrocyclic (cycloreversion), [1+4]-, CO elimination 337
Ring cleavage, electrocyclic (cycloreversion), [2+2+2]-, diademane opening 333
Ring cleavage, electrocyclic (cycloreversion), [2+2]-, benzene elimination 331 332—333
Ring cleavage, electrocyclic (cycloreversion), [2+2]-, prismane opening 330—331
Ring cleavage, electrocyclic (cycloreversion), [2+2]-, rhodium(1+)-catalysed 332
Ring cleavage, electrocyclic (cycloreversion), [2+2]-, thermal 79—80
Ring cleavage, electrocyclic (cycloreversion), [2+4]-, 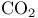 elimination 80 92 331 elimination 80 92 331
Ring closure see “Cyclization”
Ring contraction by extrusion of carbon dioxide 80
Ring contraction by extrusion of carbon monoxide 330
Ring contraction by extrusion of molecular nitrogen 35 331 334
Ring contraction by extrusion of sulfur 38—39 338
Ring contraction by extrusion of sulfur dioxide 80
Ring contraction by Favorskii rearrangement 78 84 211
Ring contraction by oxn. of cycloalkenes with Tl(3+) 129—130
Ring contraction by pinacol rearrangement 32
Ring contraction by Wolff rearr. of  -diazo ketones 337 -diazo ketones 337
Ring contraction via ox. cleavage of cyclic ketones 82
Ring contraction via ox. cleavage of cycloalkenes 81—82
Ring expansion, 1,4-benzodiazepinedruns 307
Ring expansion, cationic, of 1,2-diols 32
Ring expansion, cationic, of cyclopropanes 76—78 79 83
Ring expansion, cationic, of ketones with 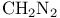 83 83
Ring expansion, cationic, of penams to cephams 314 315
Ring expansion, electrocyclic, by 1,2-cyclohexadiene opening 332—334
Ring expansion, electrocyclic, by cyclobutene opening 53—54
Ring expansion, electrocyclic, of cyclopropanemethanimines 298—299
Ring expansion, electrocyclic, of vinylcyclopropanes 77 83
Ring expansion, fragmentation of fused ring systems 89—90
Ring expansion, ozonolysis and re-cyclization 91—92 280
Ring expansion, reduction of cyclopropanes 76
Ring expansion, transamidation (”zip” reaction) 249—250
Ring opening, base-catalysed, of 4-tosyl-2-oxazolines 49
Ring opening, base-catalysed, of cyclopropanols (”homoenolates”) 77
Ring opening, electrocyclic, of 1,3-cyclohexadienes 289 332 334
Ring opening, electrocyclic, of cyclobutenes 53—54 330—331
Ring opening, fragmentative 89—90 141—142
Ring opening, Lewis acid catalysed, of cyclopropanone ketals 14—15 70
Ring opening, nucleophilic, of 1,2-dione mono(dithioketals) 79
Ring opening, nucleophilic, of cyclopropanes 14—15 69—70 76—77 83—84 276
Ring opening, nucleophilic, of oxiranes see “Oxiranes”
| Ring opening, oxidative, of 1,2-arenediol derivs. 87—88
Ring opening, oxidative, of cyclic ketones 79 82 136—137
Ring opening, oxidative, of cyclic thioethers 314—315
Ring opening, oxidative, of cycloalkenes 81—82 87—88 259 280
Ring opening, oxidative, of tert-cycloalkanols 136
Ring opening, reductive, of cyclopropanes 76 105
Ring opening, reductive, of oxiranes 98 114 274—275 319—320
Ring opening, retro-aldol type 88
Ring sizes, favored see “Cyclizations”
Robinson anellation 71—73 93
Robinson anellation of enamines 298
Robinson anellation with  -amines activated enones 73 -amines activated enones 73
Rolitetracyciine 318
Rose Bengal, xanthene dye, photosensitizer 277
Ruthenium(2+), chiral “binap” complexes, asym. hydrogenation with 102—103 325—326
Ruthenium(8+) oxide, oxidation with, of alcohols to ketones (catalytic) 267
Ruthenium(8+) oxide, oxidation with, of alkynes to 1,2-diones (catalytic) 117 132
Ruthenium(8+) oxide, oxidation with, of ethers to esters 118 134—135
Ruthenium, dihydrotetrakis(triphenylphosphine)-, double bond shift in alkenes 270
S1 Nuclease 242
Sakurai reaction, Michael type allylation 90
Samarium(2+) iodide (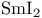 ), deoxygenation of distannoxanes 135 ), deoxygenation of distannoxanes 135
Samarium(2+) iodide (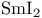 ), deoxygenation of N-, P-, and S-oxides 115 ), deoxygenation of N-, P-, and S-oxides 115
Samarium(2+) iodide (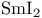 ), red. coupling of aldehydes or ketones with acrylic esters 69 ), red. coupling of aldehydes or ketones with acrylic esters 69
SAMP = (S)-2-(methoxymethyl)-1-pyrrolidinamine 26
Sand-sodium base see “Sodium-sand base”
Schering process 118—119
Schiff bases see “Imines”
sec. Amines, N-halo-, Stieglitz rearr. 77—78
sec. Amines, synthesis by hydrolysis of tert. carboxamides 301
sec. Amines, synthesis by reduction of sec. carboxamides 98 111—112 247
sec. Amines, synthesis by reduction of W-alkylimines 302
sec. Amines, synthesis by reductive detosylation 247
Seebach-Frater alkylation 27
Selenium(4+) oxide (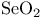 ), dehydrogenation with 122 138 139 ), dehydrogenation with 122 138 139
Selenium(4+) oxide (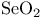 ), oxidation with, of allylic CH 116 119—120 ), oxidation with, of allylic CH 116 119—120
Selenium(4+) oxide (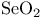 ), oxidation with, of allylic CH, ), oxidation with, of allylic CH,  of carbonyl compounds 116 122 137 of carbonyl compounds 116 122 137
Selenium(4+) oxide (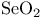 ), reagent with ), reagent with 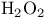 (selenous peracid), Baeyer — Villiger oxidation with 136—137 (selenous peracid), Baeyer — Villiger oxidation with 136—137
Selenium, phenyl-, bromide = benzeneselenenyl bromide, dehydrogenation with 138 139
Self-replication mechanisms in synthetic molecular complexes 347—348
Semibullvalene = 2a,2b,4a,4b-tetrahydrocyclopropa[cd]pentalene 331—332
Separation of enantiomers see “Optical resolution”
SFS (sodium formaldehyde-sulfoxylate) see “Methanesulfinic acid hydroxy-”
Sharpless epoxidation 124—127 265 321—325
Sheehan’s oxazolone protecting group 161 164
Silanamine, 1,1,1-trimethyi-N-(trimethylsiiyl)- (hexa-Si-methyldisilazane,  , HMDS), catalyst for , HMDS), catalyst for  -elimination of sulfoxides 315 -elimination of sulfoxides 315
Silanamine, 1,1,1-trimethyi-N-(trimethylsiiyl)- (hexa-Si-methyldisilazane,  , HMDS), sodium salt (HmdsNa), deprotonation with, of alkyiphosphonium salts 31 , HMDS), sodium salt (HmdsNa), deprotonation with, of alkyiphosphonium salts 31
Silanamine, 1,1,1-trimethyi-N-(trimethylsiiyl)- (hexa-Si-methyldisilazane,  , HMDS), sodium salt (HmdsNa), deprotonation with, of carbonyl compounds 10 44 , HMDS), sodium salt (HmdsNa), deprotonation with, of carbonyl compounds 10 44
Silane, (chloromethyl)trimethyl-, metalation of 6—7
Silane, (chloromethyl)trimethyl-, Peterson olefination with 33
Silane, (chloromethyl)trimethyl-, pr. 187
Silane, chiorotrimethyl- ( ), pr. 187 ), pr. 187
Silane, chiorotrimethyl- ( ), protection with see “Protection” ), protection with see “Protection”
Silane, ethenyltriphenyl-, carbanion addn. to 34
Silane, iodotrimethyl-, O-fert-butyl deblocking 283
Silane, trimethyl(2-propenyl)-, allyl 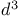 -synthon 90 -synthon 90
Silane, [(1-ethoxycyclopropyl)oxy]trimethyl-, 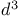 -synthon 15 70 -synthon 15 70
Silane, [(1-ethoxycyclopropyl)oxy]trimethyl-, synthesis steps 75
Silanes see “Protection”
Silanes, ( -oxoalkyl)-, desilylation with bases 73 -oxoalkyl)-, desilylation with bases 73
Silanes, (1-alkenyl)-, carbanion addn. to 6—7 34
Silanes, (2-aIkenyl)-, ailyl 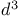 -synthons 90 -synthons 90
Silanes, aryl-, acidolysis 80 281
Silanes, aryl-, oxidative cleavage with 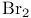 80 80
Silanes, tetraorganyl-, a-carbanions 6—7 33—34
Silanethiol, (1,1-dimethyiethyl)dimethyl-, Li salt, conversion of haloalkanes to thiols 169
Silicon compounds, pr. 187
Silver(1+) carbonate,  133 133
Silver(1+) nitrate ( ), deprotection of 1-silyl-1-alkynes 155 ), deprotection of 1-silyl-1-alkynes 155
Silver(1+) nitrate ( ), oxidative organyl coupling at ), oxidative organyl coupling at 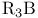 37 37
Silver(1+) oxide ( ), oxidative organyl coupling at ), oxidative organyl coupling at  for O-benzylation 157 158 for O-benzylation 157 158
Silver(1+) oxide ( ), oxidative organyl coupling at ), oxidative organyl coupling at  for oxidative coupling of enol silyl ethers 65 for oxidative coupling of enol silyl ethers 65
Silver(1+) silicate on aluminum oxide, reagent for inversion-glycosylation 271
Silver(1+) with 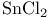 , , 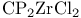 or or  270 270
Silver(1+), oxn. of alkenes,  127—128 127—128
Silver(1+), rearr. of 1-(chloroamino) alcohols 77—78
Silver(1+), rearr. of strained oligocycles 79—80 332—333
Silver(1+), transesterification of thioesters 146
Silvet(2+), oxide, oxn.  134 134
Silyl ethers see “Protection”
Simmons-Smith reaction 74—75 83
Sirenin, 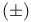 - = - =  -7-(5-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-pentenyl)-7-methylbicyclo[4.1.0]hept-2-ene-3-methanol, synth. step 20 -7-(5-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-pentenyl)-7-methylbicyclo[4.1.0]hept-2-ene-3-methanol, synth. step 20
Site-specific DNA cleavage 243 343—344
Site-specific DNA mutations 245—246 341—343
Snoutene = 2,2a,2b,3,5a,5b-hexahydro-1,2,3-metheno-1H-cycloprop[cd]indene 333
Soccerene = fullerene 357
Sodium amalgam, reductive desulfurization of sulfones 70
Sodium amalgam, reductive elimination of  -acyloxy sulfones 34 -acyloxy sulfones 34
Sodium borohydride see “Borate(1-) tetrahydro-”
Sodium, acyloin coupling with 53—54
Sodium, haloalkane (Wurts) couphng with 36
Sodium, reduction with see “Birch reduction”
Sodium, reductive cleavage of benzyl ethers 157—159
Sodium, reductive cleavage of “Ox”-protected amines 164
Sodium-complex or organic salts see corresponding acid or anion
Sodium-naphthalene reagent, reductive deblocking with 220
Sodium-sand base, non-nucleophilic base 58—59
Solid-phase synthesis of macrocyclic peptides 241
Solid-phase synthesis of oligonucleotides 221—224 341—343
Solid-phase synthesis of oligopeptides 232—237
Soret UV/VIS absorption band of porphyrins, shifts due to aggregation 348 349
Spiroanellation of  -methylene groups of carboxylic acid derivs. 23—24 298 300 -methylene groups of carboxylic acid derivs. 23—24 298 300
Spiroanellation of  -methylene groups of ketones 27 74 -methylene groups of ketones 27 74
Spiroanellation of ketones with Trost’s reagent 79 335—336
Spiroanellation, Diels — Alder type 86
Spiroanellation, intramol. alkene coupling in Fe complexes 44
Squalene, 18,19-glycol 2,3-oxide, acid-catalysed cyclisation of 91
Squalene, biological role 90 279 302
Squalene, pr. 186
Squaric acid 78
Squaric acid dichloride 339
Stannane, tributyl-, reduction of haloalkanes 97 114—115 275 319—320
Stannane, triphenyl-, red. desulfurization of thioethers 110—111
Stannanes, (1-alkenyl)-, synth. from alkynes 321
Stannanes, (1-alkenyl)-, transmetalation with MeLi 322—323
Stannanes, (2-alkenyl)-, 1-allylation of aldehydes 66—67 325—326
Stannanes, (2-alkenyl)-, allylation of bromoboranes 68—69
Stannanes, Stille coupling with 42 295
Stannoxanes, deoxygenation 115
Starburst dendrimers 354—355
Stereoelectronic control see “Electrocyclic reactions”
Stereoelectronic control,  -lactam stability 311—315 -lactam stability 311—315
Stereoelectronic control, fragmentation reactions 89—90
Stereoelectronic control, nucleophilic cyclizations 315—316
Stereoelectronic control, ox. cleavage of cyclic thioethers 314—315
Stereoelectronic control, prevention of  -eHmination 265 -eHmination 265
Stereoelectronic control, prevention of enolate formation 277
Stereoelectronic control, prevention of racemization 231 299
Stereoelectronic control, reduction of 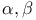 -unsatd. ketones 103—104 -unsatd. ketones 103—104
Stereoselective retro-synthetic analysis 200—204 206 209—211
Stereoselective retro-synthetic analysis, chiral synthons = “chirons” 202—203 211 272—273
Stereoselectivity see “Asymmetric induction” “Axial/equatorial-Selectivity” “cis/trans-Selectivity” “Enantio-Selectivity” “endo/exo-Selectivity” “erythro/threo-Selectivity” “Inversion” “Retention”
Stereoselectivity, definition (e.e.) 107 footnote
Steric hindrance, overcoming of, in acylations 145
Steric hindrance, overcoming of, in aldol type reactions 55—56
Steric hindrance, overcoming of, in corrin synthesis 261—262
Steric hindrance, overcoming of, in Diels — Alder cyclizations 86
Steric hindrance, overcoming of, in Michael type additions 90
Steric hindrance, overcoming of, in olefinations, Barton olefination 34—35
Steric hindrance, overcoming of, in olefinations, McMurry olefination 41
Steric hindrance, overcoming of, in olefinations, Peterson olefination 33
Steric hindrance, overcoming of, in syntheses of  -hydrdoxy ketones 52 -hydrdoxy ketones 52
Steric strain due to bridges (Bredt’s rule), effect on enolization 276 277 296 299
Steric strain due to bridges (Bredt’s rule), effect on p-lactam stability 311—315
Steric strain due to crowding, release of, in chlorophyll synthesis 258—259
Steric strain due to crowding, release of, in dodecahedrane synthesis 336—337
Steric strain due to crowding, release of, in meta-cyclophane rearrangement 38 338
Steric strain due to crowding, release of, in prismane synthesis 330
Steric strain due to crowding, release of, in tetrahedrane synthesis 330
Steric strain due to small angles, release of 79—80 330—333 337 3-membered” “Carbocycles 4-membered”)
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



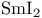
 5:1)
5:1)  -bromo carboxylic esters
-bromo carboxylic esters  -allylpalladium complexes
-allylpalladium complexes 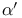 of
of 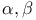 -unsatd. ketones
-unsatd. ketones  of
of 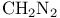
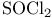 ,
, 
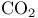 elimination by
elimination by 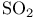 elimination by
elimination by 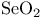 ), dehydrogenation with
), dehydrogenation with  (selenous peracid), Baeyer — Villiger oxidation with
(selenous peracid), Baeyer — Villiger oxidation with  , HMDS), catalyst for
, HMDS), catalyst for  ), pr.
), pr. 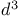 -synthon
-synthon 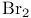

 ), deprotection of 1-silyl-1-alkynes
), deprotection of 1-silyl-1-alkynes 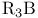
 ), oxidative organyl coupling at
), oxidative organyl coupling at  for O-benzylation
for O-benzylation 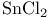 ,
, 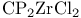 or
or 


 - =
- =  -7-(5-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-pentenyl)-7-methylbicyclo[4.1.0]hept-2-ene-3-methanol, synth. step
-7-(5-hydroxy-4-methyl-3-pentenyl)-7-methylbicyclo[4.1.0]hept-2-ene-3-methanol, synth. step