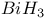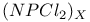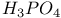јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. Ч Chemistry of the Elements
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Chemistry of the Elementsјвторы: Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. јннотаци€: When this innovative textbook first appeared in 1984 it rapidly became a great success throughout the world and has already been translated into several European and Asian languages. Now the authors have completely revised and updated the text, including more than 2000 new literature references to work published since the first edition. No page has been left unaltered but the novel features which proved so attractive have been retained. The book presents a balanced, coherent and comprehensive account of the chemistry of the elements for both undergraduate and postgraduate students. This crucial central area of chemistry is full of ingenious experiments, intriguing compounds and exciting new discoveries. The authors specifically avoid the term `inorganic chemistry' since this evokes an outmoded view of chemistry which is no longer appropriate in the final decade of the 20th century.
язык: –убрика: ’ими€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: second edition√од издани€: 1997 оличество страниц: 1340ƒобавлена в каталог: 18.02.2007ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Nonaqueous solvent systems, 561 655 Nonaqueous solvent systems, 664 700 759 Nonaqueous solvent systems, HCl 819 Nonaqueous solvent systems, HF 570 816Ч819 Nonaqueous solvent systems, ICl 827 Nonaqueous solvent systems, superacids 570 Nonstoichiometry in chalcogenides 765 766 Nonstoichiometry in oxides 642Ч644 Nonstoichiometry in sulfides 679 Nuclear fission 1256 Nuclear fission, products 1257 1260 Nuclear fission, spontaneous 1253 1262 Nuclear fuels 1257Ч1262 Nuclear fuels, breeding 1259 Nuclear fuels, enrichment 1259 Nuclear fuels, reprocessing 1097 1260Ч1262 Nuclear reactions in stars 7Ч13 Nuclear reactors 1256Ч1260 Nuclear reactors, different types 1258 Nuclear reactors, natural 1257 Nuclear structure of atoms 22 Nuclear waste, storage 1257 1261 Nucleic acid and H bonding 60 62 Nucleic acid, double helix structure of 474 Nucleogenesis 2ff Nylon-6 and -66 422 Obsidian 342 Octahedral complexes 914Ч916 922Ч923 Octahedral complexes of octahedral 996 Octahedral complexes of octahedral 1089 Octahedral complexes of tetrahedral complexes of 1158 Octahedral complexes, distortions in 915Ч916 (see also УJahn Ч Teller effectФ) Oddo's rule 3 Oklo phenomenon 1257 Oligomerization of acetylene 1172 Olivine 109 347 One-dimensional conductors 1156 1165 Onyx 342 Opal 342 Open-hearth process 1072 Optical activity 919 1125 Optical isomers 915 919 1125 Optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) 1125 Optically active metal cluster compound 667 Orbital contribution to magnetic moment of high-spin complexes of 1132 Orbital degeneracy 1244 Orbital quantum number, l 26 Orford process 1146 Organometallic compounds 924Ч943 Organometallic compounds, classification 924Ч925 Organometallic compounds, definition 924 Organometallic compounds, dihapto ligands 930Ч933 Organometallic compounds, heptahapto ligands 941 Organometallic compounds, hexahapto ligands 940Ч941 Organometallic compounds, monohapto ligands 925Ч930 Organometallic compounds, octahapto ligands 941Ч943 Organometallic compounds, pentahapto ligands 937Ч940 Organometallic compounds, tetrahapto ligands 935Ч937 Organometallic compounds, trihapto ligands 933Ч935 Orpiment see УArsenic sulfide Orthonitrate ion, 472 Orthoperiodic acid see УPeriodic acidsФ Orthophosphates 523Ч526 Orthophosphates, 526 Orthophosphates, uses of 524Ч525 Orthophosphoric acid see УPhosphoric acidФ Osmates 1082 Osmiamates 1085 Osmium, abundance 1071 Osmium, anomalous atomic weight of in Re ores 19 Osmium, atomic and physical properties 1074Ч1075 Osmium, carbidocarbonyls 1107Ч1108 Osmium, carbonyl halides 1108 Osmium, carbonyl hydrides and carbonylate anions 1105Ч1108 Osmium, carbonyls 928 929 1104Ч1105 Osmium, chalcogenides 1081 Osmium, complexes with 702 Osmium, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1091Ч1098 Osmium, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1088Ч1089 Osmium, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1086Ч1088 Osmium, complexes, +5 oxidation state 1086 Osmium, complexes, +6 oxidation state 1085Ч1086 Osmium, complexes, +7 oxidation state 1085 Osmium, complexes, +8 oxidation state 1085 Osmium, coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1078 Osmium, cyclooctatetraene complex 943 Osmium, discovery 1070 Osmium, halides and oxohalides 1082Ч1083 Osmium, organometallic compounds 1104Ч1112 Osmium, oxidation states 1077 1079 Osmium, oxides 1079 1081 Osmium, oxoanions 1082 Osmium, production and uses 1072Ч1074 Osmium, reactivity of element 1075 Osmium, relationship with other transition elements 1075Ч1079 Osmium, standard reduction potentials 1077 Osmocene 937 1111 Osmyl complexes 1085 1086 Outer-sphere reactions 1124 Oxidation state, periodic trends in 27Ч28 Oxidation state, variability of 27 905 Oxides 640Ч644 Oxides, acid-base properties 628 640 641 Oxides, classification 640Ч642 Oxides, nonstoichiometry in 642Ч644 Oxides, structure types 641 753 OXO process (hydroformylation) 309 1135 1140 Oxonium ion 48 Oxovanadium (vanadyl) ion 982 995 Oxygen see also УDioxygenФ УOzoneФ Oxygen carriers see also УDioxygenФ Oxygen carriers, complexes of cobalt 1132 Oxygen carriers, haemocyanin 1199 Oxygen carriers, haemoglobin and synthetic models 1098Ч1101 Oxygen carriers, Vaska's compound 615 617 1136 1137 Oxygen, abundance 600 602 Oxygen, allotropes 607 Oxygen, atomic 611 612 Oxygen, atomic properties 604 605 Oxygen, chemical properties 612Ч615 Oxygen, coordination geometries 613Ч615 Oxygen, crown ether compounds 95Ч97 124 601 Oxygen, difluoride 638 Oxygen, fluoride 638Ч640 Oxygen, history 600 601 604 Oxygen, industrial production 604 Oxygen, industrial uses 604 Oxygen, isotopes, separation of 604 Oxygen, liquefaction 601 604 Oxygen, liquid 601 603Ч604 606 Oxygen, occurrence in atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere 600 602 605 Oxygen, origin of blue colour in liquid 607 Oxygen, origin of, in atmosphere 602 Oxygen, oxidation states 613 Oxygen, physical properties 605 Oxygen, preparation 603 604 Oxygen, radioactive isotopes 605 Oxygen, reduction potential, pH dependence 628Ч629 Oxygen, roasting of metal sulfides 676Ч678 Oxygen, standard reduction potentials 628 629 737 Oxyhyponitrous acid see alsoУHyponitric acidФ Ozone, see also УChlorofluorocarbonsФ Ozone, 607 608 Ozone, 609Ч611 848 849 Ozone, 607 Ozone, 608 848 Ozone, 608 Ozone, 607 608 708 Ozone, 607 608 Ozone, 609 611 Ozonide ion, 610 Ozonides (organic) 610 611 Ozonolysis 610 611 849 P-N compounds 531Ч 542 p-process in stars 13 p-type semiconductors see УSemiconductorФ УTransistorФ Palladium, 953 1172 Palladium, absorption of hydrogen 1150 1151 Palladium, abundance 1145 Palladium, alkene and alkyne complexes 1170Ч1172 Palladium, alkyls and aryls 1167 1168 Palladium, atomic and physical properties 1148Ч1149 Palladium, carbonyl chloride 1168 Palladium, chalcogenides 1152 Palladium, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1156Ч1166 Palladium, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1154 1156 Palladium, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1154 Palladium, complexes, zero oxidation state 1166Ч1167 Palladium, coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1150 Palladium, discovery 1144 Palladium, halides 1152Ч1154 Palladium, organometallic compounds 1167Ч1172 Palladium, oxidation states 1150 Palladium, oxides 1151 1152 Palladium, production and uses 1146 1147 Palladium, reactivity of element 1149 Paraperiodic acid see УPeriodic acidsФ Parathion 509 Patronite 977 Pauli exclusion principle 22 P Pearlite 1075 Pentaborane, 154 159 163 Pentaborane, 171 172 Pentaborane, 171 Pentaborane, 171Ч173 Pentaborane, 165 Pentaborane, 170 Pentaborane, 171 Pentagonal bipyramidal complexes 916 Pentathionates, 717 718 851 Pentlandite 1145 Perbromates, 871Ч872 Perbromates, 789 871 Perbromates, 871 Perbromates, 854 855 872 Perbromates, 871 Perbromic acid, 871 Perbromyl fluoride, 881 Perchlorates, 865Ч871 Perchlorates, 791 868Ч871 Perchlorates, 868Ч871 Perchlorates, 791 868Ч871 1020 Perchlorates, 791 868Ч871 Perchlorates, 865 867 Perchlorates, 854 855 Perchlorates, 868 Perchloric acid, 865Ч868 Perchloric acid, 867 868 Perchloric acid, 867 Perchloric acid, 865 866 Perchloric acid, 865 866 Perchloric acid, 868 Perchloryl fluoride, 876 879 880 Perhalates, 854 855 865Ч875 Perhalic acids, 865Ч875 Periodates 872Ч875 Periodates, reaction schemes 874 Periodates, redox systematics 854 855 Periodates, structural relations 873 Periodates, synthesis 872 873 Periodates, transition metal complexes 875 Periodic acids 872Ч875 Periodic acids, acid-base systematics 874 Periodic acids, nomenclature 872 Periodic acids, preparation 873 Periodic acids, redox systematics 854 855 Periodic acids, structural relations 873 Periodic reactions, Belousov Ч Zhabotinskii reactions 865 865 Periodic reactions, Bray's reaction 865 Periodic table and atomic structure 20Ч23 Periodic table and predictions of new elements 29Ч31 Periodic table, history of 20 21 Permanganates 1050 1051 Perosmate 1082 1085 Perovskite structure 963 Perovskite structure in ternary sulfides 681 Peroxo anions 638 Peroxo complexes of 616 Peroxo compounds, fluorinated 639 640 Peroxochromium complexes 637 1024 Peroxodiphosphoric acid, 512 Peroxodisulfates, 713 Peroxodisulfuric acid, 713 Peroxomonophosphoric acid, 512 Peroxomonosulfuric acid, 705 712 Peroxonitric acid, 458 Peroxonitrous acid, HOONO 459 Peroxoselenous acid 783 Peroxotellurates 783 Perrhenates 1050 Perruthenates 1082 Pertechnetate ion 1050 Perxenates, 901 pH scale 32 49 Phase rule 676 Phase-transfer catalysis 97 Phenacite 347 Phlogiston theory 30 600 601 793 Phlogopite see УMicasФ Phosgene 305 Phospha-alkenes 545 Phospha-alkynes 545 Phosphate cycles in nature 475Ч479 Phosphate rock, occurrence and reserves 476 Phosphate rock, phosphorus production from 480 520 525 Phosphate rock, statistics of uses 525 Phosphates see УChain phosphatesФ УCyclophosphatesФ УOrthophosphatesФ УSuperphosphatesФ УTripolyphosphatesФ Phosphatic fertilizers 474 477Ч479 520 524Ч526 Phosphazenes 534Ч536 Phosphides 489Ч492 Phosphine, 492 493 Phosphine, 557 Phosphine, 493 Phosphine, 493Ч495 Phosphine, 492 493 Phosphine, 492 Phosphine, 494 Phosphinic acid see УHypophosphorous acidФ Phosphinoboranes 211 Phosphites 513 514 Phosphonic acid see УPhosphorous acidФ Phosphonitrilic chloride 408 (see also УPolyphosphazenesФ) Phosphoramidic acid 532 Phosphorescence of arsenic 550 Phosphorescence of phosphorus 474 485 Phosphoric acid, 516 517 518Ч522 Phosphoric acid, 518 Phosphoric acid, 518Ч521 Phosphoric acid, 520 Phosphoric acid, 521Ч522 Phosphoric acid, 520 Phosphoric acid, 522 Phosphoric acid, 518 598 Phosphoric acid, 518 Phosphoric acid, 518 Phosphoric acid, 518 Phosphoric acid, 519 521 Phosphoric acid, 518 Phosphoric acid, 521 522 Phosphoric acid, 520 521
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



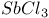
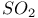
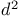 ions
ions 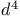 ions
ions 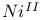
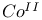
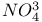
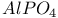 , structural analogy with
, structural analogy with 
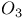
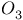
 -allylic complexes
-allylic complexes 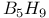
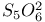 , preparation and structure
, preparation and structure 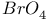


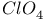
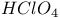
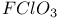
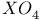
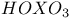
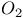
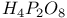
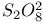
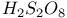
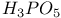

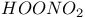
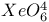
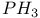 , chemical reactions
, chemical reactions 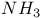 ,
, 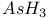 ,
, 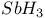 ,
,