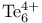јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. Ч Chemistry of the Elements
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Chemistry of the Elementsјвторы: Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. јннотаци€: When this innovative textbook first appeared in 1984 it rapidly became a great success throughout the world and has already been translated into several European and Asian languages. Now the authors have completely revised and updated the text, including more than 2000 new literature references to work published since the first edition. No page has been left unaltered but the novel features which proved so attractive have been retained. The book presents a balanced, coherent and comprehensive account of the chemistry of the elements for both undergraduate and postgraduate students. This crucial central area of chemistry is full of ingenious experiments, intriguing compounds and exciting new discoveries. The authors specifically avoid the term `inorganic chemistry' since this evokes an outmoded view of chemistry which is no longer appropriate in the final decade of the 20th century.
язык: –убрика: ’ими€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: second edition√од издани€: 1997 оличество страниц: 1340ƒобавлена в каталог: 18.02.2007ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Cadmium iodide structure type, relation to NiAs 556 680 680 Cadmium, abundance 1204 Cadmium, chalcogenides 1208 1210 Cadmium, coordination chemistry 1215Ч1217 Cadmium, discovery 1201 Cadmium, halides 1211Ч1212 Cadmium, organometallic compounds 1221 Cadmium, oxides 1211 1212 Cadmium, production and uses 1202Ч120 Cadmium, toxicity 1224 see Caesium, abundance 70 Caesium, compounds with oxygen 83Ч86 Caesium, discovery 69 Calamine (smithsonite) 1202 Calcite 109 Calcium see УAlkaline earth metalsФ УLimeФ etc. Calcium in biochemical processes 125 Calcium, carbide 297 298 320 Calcium, carbonate see УLimestoneФ Calcium, cyclopentadienyl 136 137 Calcium, history of 108 Calcium, organometallic compounds 136 137 Calcium, phosphates 524Ч526 Caliche (Chilean nitre) 796 Californium 1252 1262 see Calomel 1213 Capped octahedral complexes 916 Capped trigonal prismatic complex 916 Caprolactam, for nylonЧ6 422 Carat 272 1176 Carbaboranes see УCarboranesФ Carbene ligands 929 Carbides 297Ч301 Carbides, silicon (SiC) 334 Carbido complexes 927 1107Ч1108 Carbohydrates, photosyntheses of 125 Carbon dioxide 305 314 Carbon dioxide in photosynthesis 125 Carbon dioxide, aqueous solutions (acidity of) 309 310 Carbon dioxide, asaligand 312 313 Carbon dioxide, atmospheric 273Ч274 Carbon dioxide, coordination chemistry 312 Carbon dioxide, industrial importance 307 308 Carbon dioxide, insertion into M-C bonds 134 312 Carbon dioxide, physical properties 305 Carbon dioxide, production and uses of 311 Carbon dioxide, use in 310 Carbon monoxide 305Ч310 Carbon monoxide, as a ligand 926Ч929 Carbon monoxide, bonding in 926 927 Carbon monoxide, chemical reactions 306 308 Carbon monoxide, industrial importance 307 Carbon monoxide, physical properties 306 Carbon monoxide, poisoning effect of 306 1101 Carbon monoxide, preparation of pure 306 Carbon monoxide, similarity to 496 Carbon, abundance 270 Carbon, allotropes 274Ч278 see Carbon, atomic properties 276 372Ч372 Carbon, chalcogenides 314Ч319 Carbon, chemical properties 289 Carbon, coordination numbers 290. 291 292 Carbon, cycle (global) 273 Carbon, disulfide 313Ч318 653 Carbon, halides 301 304 Carbon, history of 268Ч270 Carbon, hond lengths (interatomic distances) 290 292 Carbon, hydrides of 301 Carbon, interatomic distances in compounds 290Ч292 Carbon, occurrence and distribution 270Ч274 Carbon, oxides 305 see УCarbon Carbon, radioactive 276 Carbon, suboxides 305 Carbon, УmonofluorideФ 289 Carbonates, terrestrial distribution 274 273 Carbonic acid 310 Carbonic anhydrase 1225 Carbonyl fluoride, reaction with OF2 640 Carbonyl halides see УCarhon oxohalidesФ Carbonyls see УCarbon monoxide as a ligandФ see Carboplatin 1165 Carborundum see УSilicon carhideФ Carbosilanes 362 Carbyne ligands 928Ч930 Carhoranes 161 181 Carhoranes, bonding 181 Carhoranes, chemical reactions 186 189 Carhoranes, isomerization 185Ч187 Carhoranes, preparation 181Ч185 Carhoranes, structures 181 185 Carhoxypeptidase A 1224 Carnotite 977 Caro's acid see УPeroxomonosulfuric acidФ Cassiterite see УTin dioxideФ Cast-iron 1071 Castner Ч Kellner process (chlor-alkali) 790 1203 Catalysis see УCatalystsФ Catalysis, 317 Catalysis, 317 Catalysis, 284 Catalysis, 35 Catalysis, 603 Catalysis, 725 Catalysis, ammonia(1)/metal solutions, effects of impurities 78 Catalysis, ammonia, oxidation to NO, 423 465 466 Catalysis, C-H bonds, homogeneous catalytic activity of 494 Catalysis, C-N-o cycle in stars 9 Catalysis, carhonylation of $\mathrm{B_{12}H_{12}^{2-}} 180 Catalysis, chlorination of organic compounds hy CuCl 798 Catalysis, chlorination of organic compounds hy CuCl, 694 Catalysis, chlorination of organic compounds hy CuCl, 689 Catalysis, chlorination of organic compounds hy CuCl, SiC to 811 Catalysis, claus process for recovery of S from 651 699 Catalysis, CO, organic reactions of 309 Catalysis, conjuncto boranes, preparation of 162 Catalysis, contact process for 646 700 708 981 Catalysis, Fischer-Tropsch process 309 1106 Catalysis, fluorination of ammonia by Cu 439 Catalysis, fluorination of ammonia by Cu 685 Catalysis, fluorination of ammonia by Cu 640 Catalysis, fluorination of ammonia by Cu graphite by acid 289 Catalysis, graphite 278 Catalysis, HCN, production of 321 Catalysis, hydrazine, decomposition by heavy metals 428 Catalysis, hydrodesulfurization (HDS) by Mo compounds 1005 Catalysis, hydroformylation of alkenes 309 593 1135 1140 Catalysis, hydrogen ation by metal hydrides 47 Catalysis, hydrogen peroxide, decomposition of 635 Catalysis, hydrogen peroxide, production of 634 Catalysis, hydrogenation of alkenes 1134Ч1135 Catalysis, hydrogenation of alkenes, NO by Pt/charcoal 431 Catalysis, hydrogenation of alkenes, unsaturated organic compounds 38 43 1146 Catalysis, hypohalous acids, decomposition of 858 Catalysis, hyponitrous acid (HONNOH), base decomposition of 460 Catalysis, nitramide ( 459 Catalysis, organotin compounds, synthesis of 399 Catalysis, oxidation of 687 Catalysis, oxidation of 700 708 Catalysis, phase transfer catalysis by Br-containing, compounds 794 Catalysis, phase transfer catalysis by Br-containing, cryptands 97 Catalysis, propene, dimerization by $\mathrm{AlPr_3^n} 260 Catalysis, Reppe synthesis by 309 1167 1172 Catalysis, silanes, formation by Cu 338 363 Catalysis, silanes, formation by Cu, hydrolysis by base 339 Catalysis, silanes, formation by Cusilicone polymers, cross linking of 365 Catalysis, steam-hydrocarbon reforming process 39 421 Catalysis, synthesis (Haher-Bosch) 43 421Ч422 Catalysis, Wacker process by 1172 Catalysis, water-gas shift reaction 38Ч39 311 421 1106 Catalysis, УclockФ reactions, autocatalysis 864 Catalysts see УCatalysisФ Catalysts, 199 200 686 Catalysts, 317 508 800 Catalysts, 1018 Catalysts, 458 Catalysts, 504 Catalysts, 304 Catalysts, 708 981 Catalysts, alumina (activated) 243 245 Catalysts, carbon (activated) 274 305 321 694 Catalysts, carbonyl complexes of metals 309 593 1106 1135 1142 Catalysts, crown ethers in synthesis of organoantimony compounds 596 Catalysts, dithiolato complexes in polymerizations and oxidations 674 Catalysts, Friedel Crafts 171 176 186 199 235Ч236 338 385 Catalysts, HBr 812 Catalysts, HCl in hydrolysis of glucose 812 Catalysts, heteropolymetallates in petrochemical industry 1014 Catalysts, HF 200 810 Catalysts, Ir 321 1115 Catalysts, lanthanide oxides 1232 Catalysts, metalloenzymes in biological systems 1138 Catalysts, NEt3 in malathion production 509 Catalysts, Ni, Pd, Pt 43 321 421 431 603 634 646 810 1148 Catalysts, NO complexes in homogeneous catalysis 450 452 Catalysts, nonstoichiomeiric oxides in heterogeneous catalysis 644 Catalysts, organotin compounds for polyurethanes 400 Catalysts, Pi/Re for lead-free petroleum products 1043 Catalysts, polymerization catalysts 105 200 229 Catalysts, polyphosphoric acid in petrochemical processes 520 Catalysts, Rh 321 1115 Catalysts, tin oxide systems 385 Catalysts, Vaska's compound 615 1135Ч1136 Catalysts, Wilkinson's catalyst 43 1134Ч1135 Catalysts, zeolites 309 359 Catalysts, Zielgter Ч Natta catalysts 260 261 972 Catalysts, Уmagic acidФ in organic catalytic processes 570 Catena- 660 662 Catena- 656 659 Catena- 660 Catenation in Group 14 elements 374 402 Caustic soda see УSodium hydroxideФ Cellophane 317 Cement 251 252 Cementite 1075 Cerium 1229 see Cerium, +4 oxidation state 1236 1239 1244 Cerium, diiodide 1240 Cerium, production 1230 Chabazite see УZeolitesФ Chain polyphosphates 526Ч529 see УSodium УGraham's УKurrol's УMaddrell's Chain polyphosphates, diphosphates 526 Chain polyphosphates, tripolyphosphates 528 528 Chain reactions, nuclear 1256 1261 Chalcocite (copper glance) 1174 Chalcogens, group trends 754Ч759 see Se Te –o Chalcophile elements 646. 648 Chalcopyrite (copper pyrite) 649 1174 1365 Chaoite 275 276 Chelate effect 910Ч911 Chelation 906 910 Chemical periodicity 20 Chemical properties of the elements, periodic trends in 23 Chemical shear structures 644 see Mo W Re etc. Chemiluminebcence of phosphorus 483 Chernobyl, nuclear reactor disaster 146 Chevrel phases 1018 1031 Chile saltpetre 407 see Chlorates, 862Ч865 Chlorates, 1001 1002 Chloric acid, 863 Chlorides, synthesis of 821 822 see Chlorin 126 Chlorine see УHalogensФ Chlorine, abundance and distribution 795 Chlorine, atomic and physical properties 800Ч804 Chlorine, cations 842 843 Chlorine, dioxide, cё2 844 845 846Ч848 Chlorine, history 790Ч793 Chlorine, hleaching power 790 793 Chlorine, hydrate 790 Chlorine, monofluorides 824Ч827 832 Chlorine, oxide fluorides 875Ч880 Chlorine, oxides 844Ч850 Chlorine, oxoacids and oxoacid salts 853 Chlorine, oxoacids and oxoacid salts, nomenclature 853 Chlorine, oxoacids and oxoacid salts, redox properties 853Ч855 see УHypochlorous УHypochloritesФ УChlorous etc. Chlorine, penrafluoride 832Ч834 Chlorine, production and uses 797Ч798 Chlorine, radioactive isotopes 801 802 Chlorine, reactivity 805 Chlorine, standard reduction potentials 850 Chlorine, stereochemistry 806 Chlorine, toxicity 793 Chlorine, trifluoride 827Ч830 852 Chlorine, volt equivalent diagram 855 Chlorite 355 357 413 Chlorites, 854 855 859Ч862 1002 1007Ч1009 Chlorofluorocarbons 608 793 848 Chlorophylls 109 125Ч127 Chloroplatinic acid 1154 Chlorosulfanes see УSulfur chloridesФ Chlorous acid, 854. 855 859 861 Chromate alum 1028 Chromateion 1009 1024 1193 Chrome ochre 1003 Chromic acid 1007 Chromite 1003 Chromium, abundance 1003 Chromium, bis(cyclopentadienyl) 939. 1038 Chromium, borazine complex 210 Chromium, carbonyls 928Ч929 1037 Chromium, carbyne complexes 929 Chromium, chalcogenides 680 1017 1018 Chromium, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1031Ч1035 Chromium, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1027Ч1031 Chromium, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1025Ч1027 Chromium, complexes, +5 oxidation state 1024Ч1025 Chromium, complexes, +6 oxidation state 1023Ч1024 Chromium, complexes, with S 666 Chromium, compounds with quadruple metal-metal bonds 1032Ч1034 Chromium, cyclooctatetraene complex 943 Chromium, cyclopentadienyls 939 1037 Chromium, dibenzene УsandwichФ compound 940 1039 Chromium, discovery 1002 Chromium, dithiolene complex redox series 675 Chromium, halides and oxohalides 1019Ч1023 Chromium, hexacarhonyl 928. 1037 Chromium, importance of 914 1027 Chromium, organometallic compounds 371 373Ч375 1207Ч1210 Chromium, oxides 1007Ч1009 Chromium, peroxo complexes 636. 637 Chromium, polynuclear complexes in dyeing and tanning 1030 Chromium, production and uses 1003 Chromium, sulfides, nonstoic biometry in 679 see Chromium, УpolyphenylФ compounds 940 Chromocene 1038 Chrysotile 351 352 357 Cinnabar (vermillion}, HgS 649 1202 1210 Circular dichroism (CD) 1125 Cisplalin 1164 Class-a and class-b metal ions 909 see Clathrate compounds 893 1161 Claus process (S from 651 652 699 Claus process (S from 356 Clock reaction (H. Landolt) 864 Cluster and cage structure 918 see Cluster compounds of germanium, tin and lead 383 392 396 455Ч458 Cluster compounds of indium 256Ч257 Cluster compounds, 161 761 Cluster compounds, boranes incorporating P, As or Sh 212
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



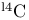 syntheses
syntheses 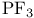 as a ligand
as a ligand 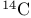
 , chlorination by
, chlorination by  and by
and by 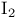
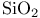 or
or 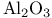
 , hydroxylation by base
, hydroxylation by base 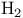 , ortho-para conversion by paramagnetic species
, ortho-para conversion by paramagnetic species 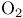 , preparation from
, preparation from 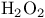
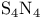 , depolymenzation to
, depolymenzation to  by
by 
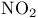
 to
to  by c or
by c or 
 to
to  hy
hy 
 by
by 
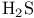

 by CsF
by CsF 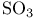 by AgF
by AgF 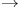 diamond transition by molten metals
diamond transition by molten metals 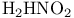 ), base decomposition of
), base decomposition of 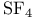 by
by 
 complexes
complexes 
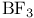
 in hydrogenations
in hydrogenations 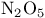 in decomposition of ozone
in decomposition of ozone  as an o atom transfer catalyst
as an o atom transfer catalyst  in fluorinations
in fluorinations 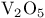
 diradical
diradical 
 point
point 


 ,
, 


 in early coordination chemistry
in early coordination chemistry