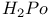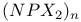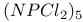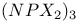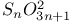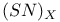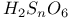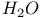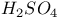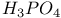јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. Ч Chemistry of the Elements
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Chemistry of the Elementsјвторы: Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. јннотаци€: When this innovative textbook first appeared in 1984 it rapidly became a great success throughout the world and has already been translated into several European and Asian languages. Now the authors have completely revised and updated the text, including more than 2000 new literature references to work published since the first edition. No page has been left unaltered but the novel features which proved so attractive have been retained. The book presents a balanced, coherent and comprehensive account of the chemistry of the elements for both undergraduate and postgraduate students. This crucial central area of chemistry is full of ingenious experiments, intriguing compounds and exciting new discoveries. The authors specifically avoid the term `inorganic chemistry' since this evokes an outmoded view of chemistry which is no longer appropriate in the final decade of the 20th century.
язык: –убрика: ’ими€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: second edition√од издани€: 1997 оличество страниц: 1340ƒобавлена в каталог: 18.02.2007ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Phosphoric triamide 532 Phosphorus acid, 512 514 Phosphorus oxoacids 510Ч531 (see also УPhosphoric acidФ УPhosphatesФ) Phosphorus oxoacids, lower oxoacids 516Ч517 Phosphorus oxoacids, nomenclature 511Ч512 517 Phosphorus oxoacids, standard reduction potentials 513 Phosphorus oxoacids, structural principles 510Ч512 517 Phosphorus oxoacids, volt-equivalent diagram 513 Phosphorus pentahalides 495 498Ч501 Phosphorus pentahalides, ammonolysis of 535 Phosphorus pentahalides, fluxionality of 498 Phosphorus pentahalides, industrial production of 500 Phosphorus pentahalides, ionic and covalent forms 498Ч501 537 Phosphorus pentahalides, mixed pentahalides 499 Phosphorus pentahalides, organo derivatives 499Ч501 Phosphorus pentahalides, reactions of 535 Phosphorus pentahalides, structural isomerism 499 500 Phosphorus tribromide 496 497 500 Phosphorus trichloride, chemical reactions 497 Phosphorus trichloride, hydrolysis to phosphates 514 Phosphorus trichloride, industrial production 496 Phosphorus trichloride, organophosphorus derivatives 496 497 514 Phosphorus trifluoride 495 496 Phosphorus trifluoride as a poison 1101 Phosphorus trifluoride, similarity to CO as ligand 496 Phosphorus triiodide 495 497 Phosphorus, abundance and distribution 475 Phosphorus, allotropes 473 474 479Ч483 Phosphorus, alloys 492 Phosphorus, atomic propertie 482Ч483 Phosphorus, black allotropes 481Ч483 551 Phosphorus, bond energies 483 Phosphorus, catenation 473 483 485 Phosphorus, chemical reactivity 483 578 Phosphorus, cluster anions 491 588 Phosphorus, coordination geometries 483 Phosphorus, disproportionation in aqueous solutions 511Ч513 Phosphorus, encapsulated 554 Phosphorus, fertilizers 474 477Ч479 520 604 Phosphorus, halides 495 Phosphorus, history 473 474 Phosphorus, Hittorf's violet allotrope 481 Phosphorus, hydrides 492Ч495 (see also УPhosphineФ) Phosphorus, mixed halides 495 Phosphorus, multiple bond formation 473 Phosphorus, organic compounds 542Ч546 Phosphorus, oxides 503Ч506 (see also УPhosphorus trioxideФ УPhosphorus Phosphorus, oxohalides 501 502 Phosphorus, oxosulfides 507 Phosphorus, pentaphenyl 545 Phosphorus, peroxide, 506 Phosphorus, production and uses 479 480 520 525 Phosphorus, pseudohalides 495 501 Phosphorus, radioactive 482 Phosphorus, red, amorphous 481 482 483 Phosphorus, stereochemistry 485Ч486 Phosphorus, sulfides 506Ч509 Phosphorus, sulfides, industrial uses of 509 Phosphorus, sulfides, organic derivatives 509 Phosphorus, sulfides, physical properties 507 Phosphorus, sulfides, stoichiometry 506 Phosphorus, sulfides, structures 507 Phosphorus, sulfides, synthesis 506 508 Phosphorus, thiohalides 498 501Ч503 508 Phosphorus, triangulo- 587 588 Phosphorus, white, 480Ч481 483 551 Phosphorus, ylides 545 Phosphoryl, halides, 502 Phosphoryl, pseudohalides 501 Photographic image intensification with 662 Photographic process 790 1185Ч1187 Photosynthesis see also УChlorophyllsФ Photosynthesis as origin of atmospheric 602 Photosynthesis, 601 602 Photosynthesis, manganese in 1061 Photosynthesis, NADP in 125 Photosystem II 1056 1061 Phyllo-silicates 347 349Ч354 Physical properties, periodic trends in 23 Piezoelectricity 58 345 Pig-iron 1072 Pitchblende 1250 1255 Plagioclase see УFeldsparsФ Plaster of Paris 122 Platinum metals, definition 1070 Platinum, 926 Platinum, 934 1172 Platinum, abundance 1145 Platinum, alkene and alkyne complexes 1170Ч1172 Platinum, alkyls and aryls 1167Ч1168 Platinum, anti-tumour compounds 1163 Platinum, atomic and physical properties 1148Ч1149 Platinum, black 1148 Platinum, blues 1165 Platinum, carbonylate anions 1169 Platinum, catalytic uses 466 467 1145 Platinum, chalcogenides 1152 Platinum, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1156Ч1166 Platinum, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1155Ч1156 Platinum, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1154Ч1155 Platinum, complexes, +6 and +5 oxidation states 1154 Platinum, complexes, with 702 Platinum, complexes, with S 666 Platinum, complexes, zero oxidation state 1166Ч1167 Platinum, coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1150 Platinum, halides 1152Ч1154 Platinum, optical resolution of 670 Platinum, organometallic compounds 931 932 1167Ч1172 Platinum, oxidation states 1150 Platinum, oxides 1151 1152 Platinum, production and uses 1146 1147 Platinum, reactivity of element 1149 Platinum, sulfide, structure 679 Plutonium see also УActinide elementsФ Plutonium economy 1259 Plutonium, bis(cyclooctatetraene) 942 Plutonium, critical mass 1261 Plutonium, discovery 1252 Plutonium, extraction from irradiated nuclear fuel 1260 1261 Plutonium, natural abundance 1253 Plutonium, redox behaviour 1265Ч1267 Plutonium, self-heating 1264 Plutonium, УbreedingФ 1259 Point groups 1290Ч1292 Pollution, atmospheric by 646 698Ч699 710 УWaterФ) Polonium, abundance 747 Polonium, allotropy 751 Polonium, atomic and physical properties 753 754 890 Polonium, chemical reactivity 754Ч759 Polonium, coordination geometries 756 Polonium, dioxide 780 Polonium, discovery 747 Polonium, halides 767 768 769 770 Polonium, hydride, 766 767 Polonium, hydroxide 781 Polonium, nitrate 786 Polonium, oxides 779Ч780 Polonium, polonides 765 766 Polonium, production and uses 750 Polonium, radioactivity 748 750 Polonium, redox properties 755 Polonium, selenate 786 Polonium, sulfate 786 Polonium, toxicity 757Ч759 Polyethene (polythene) 261 262 972 Polyhalide anions 827 829Ч831 834Ч839 Polyhalide anions, bonding 838 839 Polyhalide anions, containing astatine 887 Polyhalide anions, structural data 836Ч839 Polyhalonium cations 827 829Ч831 833Ч835 Polyhalonium cations, stoichiometries 839 Polyhalonium cations, structures 840 Polyiodides 806 835Ч839 Polymetaphosphoric acid 512 Polypeptide chains 61 62 Polyphosphates, factors affecting rate of degradation 523 (see also УChain polyphosphatesФ УCyclo-polyphosphatesФ) Polyphosphazenes 536 Polyphosphazenes, analogy with silicones 536 Polyphosphazenes, applications 542Ч543 Polyphosphazenes, basicities 540 Polyphosphazenes, bonding in 537Ч540 Polyphosphazenes, hydrolysis 541 Polyphosphazenes, melting points of 538 Polyphosphazenes, pentameric 538 Polyphosphazenes, preparation 536 537 Polyphosphazenes, reactions 540Ч542 Polyphosphazenes, structure 536Ч538 Polyphosphazenes, tetrameric 537 538 Polyphosphazenes, trimeric 537 Polyphosphoric acid 511 Polyphosphoric acid, catalyst for petrochemical processes 52 Polysulfanes see УSulfanesФ Polysulfates, 712 Polysulfides of chlorine see УSulfur chloridesФ Polysulfides of hydrogen see УSulfanesФ Polysulfides, use in Na/S batteries 678 Polythiazyl see Polythionates, 705 714 716Ч718 Polythionates, 717 782 Polythionic acids, 705 716 Polyurethane 305 422 Polywater 632 633 Porphin 126 Porphyrin complexes of Mg see УChlorophyllsФ Portland cement see also УHigh-alumina cementФ Portland cement, constitution of 252 Portland cement, manufacture of 252 Potassium see also УAlkali metalsФ Potassium chlorate, thermal decomposition to give 603 Potassium compounds as fertilizers 73 Potassium compounds, production and uses of 73 74 Potassium permanganate, thermal decomposition to give 603 Potassium, abundance 69 Potassium, compounds with oxygen 84Ч85 Potassium, discovery 68 Potassium, graphite intercalates 293Ч295 Potassium, nitrate, thermolysis of 468 469 541 Potassium, orthonitrate 474 Potassium, phosphates 524 Potassium, polysulfides 681 682 Potassium, polythionates, preparation and structure 717 Potassium, production of metal 73 74 Potassium, silyl 339 340 Potassium, terrestrial distribution of 70 Powder metallurgy 1005 1144 Praseodymium 1229 (see also УLanthanide elementsФ) Praseodymium, +4 oxidation state 1237 1239 1244 Praseodymium, diiodide 1441 Praseodymium-oxygen system, ordered defects and nonstoichiometry in 643Ч644 Principal quantum number n 22 Promethium 1228 (see also УLanthanide elementsФ) Protactinium see also УActinide elementsФ Protactinium, abundance 1253 Protactinium, bis(cyclooctatetraene) 942 Protactinium, discovery 1250 Protactinium, redox behaviour 1265Ч1267 Proton, hydration of 951 952 ionized and Proton-switch conduction in 623 Proton-switch conduction in 843 Proton-switch conduction in 518 Protoporphyrin IX (PIX) 1099 Prout's hypothesis 888 Prussian blue 1094 Pseudohalogen concept 319 324 PTFE see УTeflonФ Purex process 1261 Purple of Cassium 1177 PVC plastics, organotin stabilizers for 409 Pyrite structure 555 557 680 Pyrochlore 977 Pyrophosphoric acid see УDiphosphoric acidФ Pyrophosphoryl halides 502 503 506 Pyrophyllite 352Ч355 413 Pyrrhotite 649 Quadruple metal-metal bonds 1031Ч1035 Quantum numbers 22 Quartz 342Ч344 Quartz, enantiomorphism 342 Quartz, uses 346 Quaternary arsonium compounds 594 Quaternary bismuth cations, 599 Quaternary phosphonium cations 485 495 498Ч501 545 546 r-process in stars 12 Racah parameter see УInterelectronic repulsion parameterФ Radial functions 1285Ч1287 Radioactive decay series 1254 Radioactive elements, discovery 21 Radioactive elements, varying atomic weights of 18 Radiocarbon dating 277 Radium, history of 108 (see also УAlkaline earth elementsФ) Radius ratio rules 80 Radon see also УNoble gasesФ Radon, atomic and physical properties 890 891 Radon, difluoride 903 Radon, discovery 889 Radon, fluoro complexes 903 Rare earths see УLanthanide elementsФ Raschig synthesis of hydrazine 427 428 Rayon 317 422 653 Realgar see УArsenic sulfideФ У Red cake 977 Red lead, 385 388 Reduction potentials see УStandard reduction potentialsФ Reinecke's salt 1028 Relativistic effects 599 1180 Reppe synthesis 309 1167 1172 Rhenates 1051 Rhenium, abundance 1041 Rhenium, alkyls 1062 1068Ч1069 Rhenium, carbidocarbonyls 1065Ч1066 Rhenium, carbonyls 928 1062Ч1064 Rhenium, chalcogenides 1049 Rhenium, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1058 Rhenium, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1057Ч1058 Rhenium, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1056 Rhenium, complexes, +5 oxidation state 1055 Rhenium, complexes, +6 oxidation state 1055 Rhenium, complexes, +7 oxidation state 1054 Rhenium, complexes, lower oxidation states 1061 Rhenium, compounds with metal-metal multiple bonds 1057 1058 1230 Rhenium, cyclopentadienyls 1067Ч1068 Rhenium, discovery 1040 Rhenium, halides and oxohalides 1051Ч1054 Rhenium, nine-coordinate hydrido complex 1046 1054 Rhenium, organometallic compounds 1062Ч1068 Rhenium, oxides 1045Ч1049 Rhenium, production and uses 1041 Rhenium, trioxide 1047 Rhenium, trioxide, structure of 1047 Rhodium, abundance 1113 Rhodium, atomic and physical properties 1114Ч1115 Rhodium, carbidocarbonyls 1141Ч1142 Rhodium, carbonyls 928 1140Ч1143 Rhodium, complexes, +1 oxidation state 1133Ч1136 Rhodium, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1129 Rhodium, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1122Ч1129 Rhodium, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1121 Rhodium, complexes, lower oxidation states 1137 Rhodium, complexes, with 702 Rhodium, coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1117
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 with liquid
with liquid 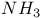
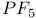
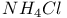 -diphosphazenes
-diphosphazenes 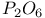
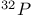
 -
-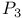 species
species  -
-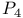

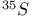
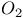
 tracer experiments
tracer experiments  -elimination in alkyls and aryls
-elimination in alkyls and aryls  -allylic complexes
-allylic complexes 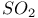
![$[Pt(S_{5})_{3}]^{2Ч}$](/math_tex/48cd636c1815857065e059a3adb801db82.gif)