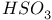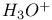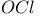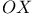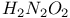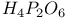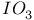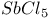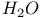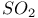јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. Ч Chemistry of the Elements
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Chemistry of the Elementsјвторы: Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. јннотаци€: When this innovative textbook first appeared in 1984 it rapidly became a great success throughout the world and has already been translated into several European and Asian languages. Now the authors have completely revised and updated the text, including more than 2000 new literature references to work published since the first edition. No page has been left unaltered but the novel features which proved so attractive have been retained. The book presents a balanced, coherent and comprehensive account of the chemistry of the elements for both undergraduate and postgraduate students. This crucial central area of chemistry is full of ingenious experiments, intriguing compounds and exciting new discoveries. The authors specifically avoid the term `inorganic chemistry' since this evokes an outmoded view of chemistry which is no longer appropriate in the final decade of the 20th century.
язык: –убрика: ’ими€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: second edition√од издани€: 1997 оличество страниц: 1340ƒобавлена в каталог: 18.02.2007ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Hafnium see also УGroup 4 elementsФ Hafnium, abundance 955 Hafnium, alkyls and aryls 973 Hafnium, carbonyls 973 Hafnium, complexes, +3 oxidation state 969 Hafnium, complexes, +4 oxidation state 967Ч969 Hafnium, complexes, lower oxidation states 971 Hafnium, compounds with oxoanions 966 967 Hafnium, cyclopentadienyls 973Ч975 Hafnium, dioxide 962 Hafnium, discovery 954 Hafnium, halides 964Ч966 Hafnium, neutron absorber 965 1258 Hafnium, organometallic compounds 973Ч975 Hafnium, production and uses 956 Hafnium, sulfides 962 Hahnium see УDubniumФ Halates, 862Ч866 Halates, 885 Halates, 855 Halic acids, 862Ч863 Halides 819Ч824 Halides, astatide 886 Halides, intercalation into graphite 294 295 Halides, synthesis of 819Ч823 Halides, trends in properties 823 Halites, 859Ч862 Hall effect 258 549 552 1017 Halogen cations, 842Ч844 (see also УPolyhalonium cationsФ) Halogen(I) fluorosulfates, 883Ч885 Halogen(I) nitrates, XONO 883 884 Halogen(I) perchlorates, 883 884 Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At) 784Ч887 (see also УInterhalogen compoundsФ) Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), abundance and distribution 795 796 Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), atomic and physical properties 800Ч804 Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), charge-transfer complexes 806Ч809 Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), history (time charts) 790 791 Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), origin of name 789 790 Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), production and uses 796 800 Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), reactivity towards graphite 296 Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), stereochemistry 806 Halous acids, HOXO 859 861 Hammett acidity function 51 52 Hapticity, classification of organometallic compounds 925 Hapticity, distinction from connectivity 925 928 Hassium 1281 1283 Hausmannite 1041 1049 Heat of vaporization, influence of H bonding 54 Heavy water 39 Helium see also УNoble gasesФ Helium, abundance in universe 3 Helium, atomic and physical properties 891 890 Helium, discovery 888 Helium, production and uses 889 890 Helium, thermonuclear reactions in stars 10 Hemimorphite 348 Hertzsprung Ч Russell diagrams 6 Heteropoly blues 1015 Heteropolymolybdates 1013 1015 Heteropolytungstates 1013 1015 Hexamethylphosphoramide 532 Hexathionates, 717 718 851 High temperature superconductivity 945 1183 1232 High-alumina cement 251 High-spin complexes 923 Hittorf's allotrope of phosphorus 482 Holmium 1229 (see also УLanthanide elementsФ) Hume Ч Rothery rules 1178 Hydrargillite 243 245 Hydrazido complexes with metals 430 (see also УDinitrogen as a ligandФ) Hydrazine 408 422 427Ч431 Hydrazine, acid-base properties 428 Hydrazine, as a bridging ligand 431 Hydrazine, hydrate 429 430 Hydrazine, industrial production 429 Hydrazine, methyl derivatives as fuels 429 Hydrazine, molecular structure and conformation 427 428 Hydrazine, oxidation of 434 Hydrazine, preparation 427 Hydrazine, properties of 427 Hydrazine, reaction with nitrous acid 432 Hydrazine, reducing properties 430 Hydrazine, uses 429 Hydrazine, water treatment using 429 Hydrides, binary 64Ч67 Hydrides, binary and periodic table 65 Hydrides, binary of boron see УBoranesФ Hydrides, binary of sulfur see УSulfanesФ Hydrides, binary, acid strength of 48 Hydrides, binary, bonding in 64 Hydrides, binary, classificatidn of 64 Hydrides, binary, complex 67 Hydrides, binary, covalent 64 67 Hydrides, binary, interstitial 67 Hydrides, binary, ionic 64 65 Hydrides, binary, nonstoichiometric 66 67 Hydroboration see УDiboraneФ Hydrochloric acid, HCl(aq) 790 792 809 812 Hydrochloric acid, HCl(aq), azeotrope 815 Hydrofluoric acid, HF(aq) 790 Hydrofluoric acid, HF(aq), acid strength of 814 Hydrofluoric acid, HF(aq), azeotrope 815 Hydrofluoric acid, HF(aq), preparation of fluorides using 820Ч821 Hydroformylation of alkenes 309 1135 1140 Hydrogen see also УDihydrogenФ Hydrogen as the essential element in acids 32 Hydrogen azide, 432 433 Hydrogen bond 33 52Ч64 Hydrogen bond and ferroelectricity 57 Hydrogen bond and proton nmr 56 Hydrogen bond and vibrational spectroscopy 56 Hydrogen bond in ammonia 423 Hydrogen bond in aquo complexes 625 Hydrogen bond in DNA 61 62 Hydrogen bond in HF 812 813 Hydrogen bond in proteins and nucleic acids 61 62 Hydrogen bond in water 623 Hydrogen bond, bond lengths (table) 60 Hydrogen bond, comparison with BHB bonds 64 Hydrogen bond, influence on properties 53 Hydrogen bond, influence on structure 59 Hydrogen bond, strength of X-ray and neutron diffraction 56 Hydrogen bond, theory of 63 Hydrogen bromide, HBr, azeotrope 815 Hydrogen bromide, HBr, hydrates 815 Hydrogen bromide, HBr, physical properties 813 Hydrogen bromide, HBr, production and uses 811 812 Hydrogen chloride, HCl see also УHydrochloric acidФ Hydrogen chloride, HCl, hydrates 813 814 Hydrogen chloride, HCl, nonaqueous solvent properties 813 Hydrogen chloride, HCl, physical properties 813 Hydrogen chloride, HCl, production and uses 811Ч812 Hydrogen dinitrate ion, 468 Hydrogen fluoride, HF 809Ч810 (see also УHydrofluoric acidФ) Hydrogen fluoride, HF, H bonding in 52Ч53 812 Hydrogen fluoride, HF, hydrates 814 Hydrogen fluoride, HF, nonaqueous solvent properties 816Ч818 Hydrogen fluoride, HF, physical properties 812 813 Hydrogen fluoride, HF, preparation of fluorides using 820 Hydrogen fluoride, HF, production and uses 809Ч811 Hydrogen fluoride, HF, skin burns, treatment of 810 Hydrogen halides, HX 809Ч819 Hydrogen halides, HX, chemical reactivity 813Ч816 Hydrogen halides, HX, nonaqueous solvent properties 816Ч819 Hydrogen halides, HX, physical properties 812 813 Hydrogen halides, HX, preparation and uses 809Ч812 Hydrogen iodide, HI, azeotrope 815 Hydrogen iodide, HI, hydrates 815 Hydrogen iodide, HI, physical properties 812 Hydrogen iodide, HI, production and uses 811 812 Hydrogen peroxide 633 Hydrogen peroxide, acid-base properties 636Ч638 Hydrogen peroxide, chemical properties 634 638 Hydrogen peroxide, physical properties 633 634 635 Hydrogen peroxide, preparation 633 Hydrogen peroxide, production statistics 634 Hydrogen peroxide, redox properties 634Ч637 Hydrogen peroxide, structure 635 Hydrogen peroxide, uses of 633Ч634 Hydrogen sulfate ion, 705 706 711Ч713 Hydrogen sulfide, see also УSulfanesФ УWackenroder's Hydrogen sulfide, 665 673 Hydrogen sulfide, 682 Hydrogen sulfide, 682 767 Hydrogen sulfide, 646Ч648 651 771 Hydrogen sulfide, 682 767 Hydrogen sulfide, 682 Hydrogen sulfide, 683 Hydrogen sulfite ion, 705 719 Hydrogen, abundance (terrestrial) 32 Hydrogen, abundance in universe 2 Hydrogen, atomic properties 34 Hydrogen, chemical properties 43 Hydrogen, cyanide, H bonding in 55 Hydrogen, history of 32 33 Hydrogen, industrial production 38 Hydrogen, ionized forms of 36 Hydrogen, isotopes of 34 (see also УDeuteriumФ УTritiumФ) Hydrogen, ortho- and para- 32 35 Hydrogen, physical properties of 34 Hydrogen, portable generator for 39 Hydrogen, preparation 38 Hydrogen, stereochemistry of 44 Hydrogen, thermonuclear reactions in stars 9 Hydrogen, variable atomic weight of 17 Hydrogen-ion concentration see УpH scaleФ Hydrometalation 926 Hydronitrous acid see УNitroxylic acidФ Hydroperoxides 636 Hydroxonium ion, 628Ч631 814 815 Hydroxyl ion, hydration of 630 632 Hydroxylamine 422 431Ч432 Hydroxylamine, configurational isomers 432 432 Hydroxylamine, hydroxylamides of sulfuric acid 744Ч746 Hydroxylamine, preparation 495 431 432 Hydroxylamine, properties 495 431 432 Hypersensitive bands in spectra of lanthanides 1244 Hypobromous acid, HOBr 853 855 857 858 HypochJorous acid, HOCl 853Ч859 HypochJorous acid, HOCl, preparation 857 HypochJorous acid, HOCl, reactions 858Ч859 HypochJorous acid, HOCl, uses 860 Hypochlorite, 854 855 857Ч859 Hypochlorite, 859 Hypofluorites (covalent) 639 688 Hypofluorous acid, HOF 638 639 Hypofluorous acid, HOF, preparation 791 853 856 Hypohalates, 853Ч859 Hypohalous acids, HOX 853Ч859 Hypoiodous acid, HOI 853Ч859 Hyponitric acid, 530 459 Hyponitrites 459Ч461 Hyponitrous acid, 459Ч459 Hypophosphites 513 516 Hypophosphoric acid (diphosphoric(IV) acid), 512 515Ч516 Hypophosphoric acid (diphosphoric(IV) acid), 515 Hypophosphorous acid, 512 513 Icosagens 227 Icosahedron, symmetry elements of 141 Ilmenite 955 960 963 Inclusion compounds 985 (see also УClathrate compoundsФ) Indium see also УGroup 13 elementsФ Indium, abundance 218 Indium, chalcogenides 252Ч254 Indium, discovery 216 Indium, IIIЧV compounds 255Ч258 Indium, lower halides 240 Indium, organometallic compounds 262 Indium, oxide 247 Indium, production and uses 219 Indium, trihalides 237 238 Industrial chemicals, production statistics 407 Industrial Revolution 1070 1072 Inert-pair effect 27 Inert-pair effect in Al, Ga, In, Tl 226 Inert-pair effect in Ge, Sn, Pb 374 Inert-pair effect in P, As, Sb, Bi 553 566 568 Inner-sphere reactions 1124 Ino-silicates 347 349Ч351 Interelectronic repulsion parameter for hexaquochromium(III) 1029 Interelectronic repulsion parameter for hexaquovanadium(III) 996 Interelectronic repulsion parameter for high-spin complexes of cobalt(II) 1132 Interelectronic repulsion parameter for high-spin complexes of cobalt(III) 1127 Interhalogen compounds 824Ч828 (see also УPojyhalide anionsФ УPolyhalonium Interhalogen compounds, diatomic, XY 824Ч828 833 Interhalogen compounds, first preparation 790 791 Interhalogen compounds, hexa-atomic, 832Ч835 Interhalogen compounds, octa-atomic, 832Ч835 Interhalogen compounds, tetra-atomic, 828Ч831 833 Invar 1146 Iodates, 862 863 Iodates, 866 Iodates, 854Ч856 Iodides, synthesis of 822 Iodine trichloride, complex and 568 Iodine, abundance and distribution 795 (see also УHalogensФ) Iodine, atomic and physical properties 800Ч804 Iodine, cations 842Ч844 Iodine, charge-transfer complexes 806Ч809 Iodine, colour of solutions 806Ч809 Iodine, crystal structure 803 Iodine, goitre treatment 790 794 Iodine, heptafluoride 832Ч835 Iodine, history 790 791 793 Iodine, Karl Fischer reagent for 627 Iodine, monohalides 824Ч828 833 Iodine, oxide fluorides 881Ч883 Iodine, oxides 851Ч853 Iodine, oxoacids and oxoacid salts 853 (see also УIodic acidФ УIodatesФ УPeriodic УPeriodatesФ) Iodine, oxoacids and oxoacid salts, nomenclature 853 Iodine, oxoacids and oxoacid salts, redox properties 854Ч856 Iodine, pentafluoride 832Ч834 Iodine, production and uses 799 800 Iodine, radioactive isotopes 801 802 Iodine, reactivity 805 Iodine, standard reduction potentials 854 Iodine, stereochemistry 806 Iodine, trichloride 828Ч829 831 833 Iodine, trifluoride 828 830 831 833 Iodine, volt equivalent diagram 855 Iodine, УpentoxideФ, 851Ч853 Iodyl fluorosulfate, 882 Ionic radii 80 81 Ionic radii, table of 1295 Ionic-bond model 79Ч81 963 Ionic-bond model, deviations from 81 Ionization energy, periodicity of 24 Iridium, abundance 1113 Iridium, atomic and physical properties 1115Ч1116 Iridium, carbonyls 928 1140Ч1143 Iridium, complexes, +1 oxidation state 1133Ч1137 Iridium, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1129Ч1130 Iridium, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1121 1127 1129 Iridium, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1121Ч1122 Iridium, complexes, +5 oxidation state 1121 Iridium, complexes, lower oxidation states 1137 Iridium, complexes, with 702 Iridium, coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1117 Iridium, cyclopentadienyls 1143 Iridium, discovery 1113
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте







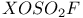

 , preparation and structure
, preparation and structure 
![$[H(NO_{3})_{2}]^{Ч}$](/math_tex/e218c62dffd859da220b74efbb22c0fc82.gif)
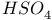
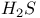
![$[SH_{3}]^{+}$](/math_tex/c0944a6846eec533322dbb7d203cc2ce82.gif)