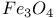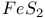јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. Ч Chemistry of the Elements
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Chemistry of the Elementsјвторы: Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. јннотаци€: When this innovative textbook first appeared in 1984 it rapidly became a great success throughout the world and has already been translated into several European and Asian languages. Now the authors have completely revised and updated the text, including more than 2000 new literature references to work published since the first edition. No page has been left unaltered but the novel features which proved so attractive have been retained. The book presents a balanced, coherent and comprehensive account of the chemistry of the elements for both undergraduate and postgraduate students. This crucial central area of chemistry is full of ingenious experiments, intriguing compounds and exciting new discoveries. The authors specifically avoid the term `inorganic chemistry' since this evokes an outmoded view of chemistry which is no longer appropriate in the final decade of the 20th century.
язык: –убрика: ’ими€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: second edition√од издани€: 1997 оличество страниц: 1340ƒобавлена в каталог: 18.02.2007ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Iridium, halides 1119Ч1121 Iridium, organometallic compounds 1139Ч1143 Iridium, oxidation states 1117 Iridium, oxides 1117 1118 Iridium, production and uses 1114 Iridium, reactivity of element 1116 Iridium, relationship with other transition elements 1116Ч1117 Iridium, sulfides 1117 Iron age 1070 Iron pyrites, reserves of 651 Iron pyrites, source of S 759Ч649 Iron pyrites, structure 555 557 680 Iron, abundance 1071 Iron, allyls 933 Iron, alums 1088 Iron, atomic and physical properties 1074 Iron, biochemistry of 1098 Iron, bis (cyclopentadienyl) see УFerroceneФ Iron, carbidocarbonyls 1107Ч1108 Iron, carbonyl halides 1108 Iron, carbonyl hydrides and carbonylate 1107 Iron, carbonyls 928 1071 1104 Iron, chalcogenides 1080 1081 Iron, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1091Ч1095 Iron, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1088Ч1091 Iron, complexes, lower oxidation states 1098 Iron, complexes, with 702 Iron, complexes, with S 666 671 Iron, complexes, with SO 696 Iron, cyclooctatetraene complexes 945 Iron, cyclopentadienyls 1109Ч1112 (see also УFerroceneФ) Iron, dithiocarbamate complexes 673 1090 Iron, electronic spin states 1079 Iron, halides 1083Ч1085 Iron, history 1070 1072 Iron, mixed metal oxides (ferrites) 1081 Iron, organometallic compounds 937 1104Ч1112 Iron, oxidation states 1077 1078 Iron, oxides 1079 1080 Iron, oxoanions 1081 1121 Iron, production and uses 1071Ч1072 Iron, proteins 1098Ч1104 Iron, reactivity of element 1075 Iron, relationship with other transition elements 1077 Iron, standard reduction potentials 1077 1093 1101 Iron-sulfur proteins 1102Ч1104 Irving Ч Williams order 909 Isocyanates 319 322 Isocyanates as polyurethane intermediates 305 Isohypophosphoric acid [diphosphoric (III, 512 515 516 Isomerism 918 Isomerism, cis-trans 919 1128 Isomerism, conformational 918 Isomerism, coordination 920 Isomerism, fac-mer 919 Isomerism, geometrical 919 Isomerism, ionization 920 Isomerism, ligand 921 Isomerism, linkage 920 Isomerism, optical 919 Isomerism, polymerization 921 Isomerism, polytopal 918 Isomerism, syn-anti 935 Isomerism, Уclassical-nonclassicalФ in organoboron structures 186 Isopolymolybdates 1175Ч1183 Isopolyniobates 987 Isopolytantalates 987 Isopolytungstates 1175Ч1183 Isopolyvanadates 1146Ч1150 Isotopes, definition of 22 Jahn Ч Teller effect 1021 Jahn Ч Teller effect in 1190 Jahn Ч Teller effect in 970 Jahn Ч Teller effect in high-spin 1021 1032 Jahn Ч Teller effect in high-spin 1049 1057 Jahn Ч Teller effect in low-spin 1133 Jasper 342 Joliotium see УDubniumФ Kaolinite 349 352Ч354 357 Karl Fischer reagent 627 Keatite 342 343 Keggin structure 1014 1015 Keiselguhr 342 Kinetic inertness of chromium(lll) complexes 1027 Kinetic inertness of cobalt(III) complexes 1123 Kirsanov reactions 535 Kraft cheese process 524 Kraft paper process 89 Kroll process 955 956 Krypton see also УNoble gasesФ Krypton, atomic and physical properties 801 890 Krypton, clathrates 893 Krypton, compounds of 903 Krypton, discovery 889 Kupfernickel 1144 1145 Kurchatovium see УRutherfordiumФ Kurrol's salt 528Ч531 Landolt's chemical clock 864 Lanthanide contraction 27 1232 1234 Lanthanide elements see also УGroup 3 elementsФ Lanthanide elements as products of nuclear fission 1228 1251 1260 Lanthanide elements, +2 oxidation state 1240 1248 Lanthanide elements, +4 oxidation state 1240 1244 Lanthanide elements, abundance 1229 Lanthanide elements, alkyls and aryls 249 Lanthanide elements, aquo ions 1245 Lanthanide elements, arsenides 555 Lanthanide elements, atomic and physical properties 1232Ч1235 Lanthanide elements, carbonyls 1238 Lanthanide elements, chalcogenides 679 1238 1239 Lanthanide elements, complexes 1244Ч1248 Lanthanide elements, coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1236 1237 Lanthanide elements, cyclopentadienides 1238 Lanthanide elements, group trends 1232Ч1237 Lanthanide elements, halides 1240Ч1242 Lanthanide elements, history 1228 Lanthanide elements, magnetic properties 1242Ч1244 Lanthanide elements, organometallic compounds 1248 1249 Lanthanide elements, oxides 1238 1239 Lanthanide elements, production and uses 1230Ч1232 Lanthanide elements, separation of individual elements 1424 1426Ч1428 Lanthanide elements, spectroscopic properties 1242Ч1244 Lanthanoid see УLanthanide elementsФ Lanthanon see УLanthanide elementsФ Lanthanum see also УGroup 3 elementsФ УLanthanide Lanthanum, abundance 945 Lanthanum, complexes 950Ч953 Lanthanum, discovery 944 1228 Lanthanum, halides 949Ч950 Lanthanum, organometallic compounds 953 Lanthanum, oxide 949 Lanthanum, production and uses 945Ч946 Lanthanum, salts with oxoanions 949 Lapiz lazuli 359 Laser, ruby 1029 Lattice defects, nonstoichiometry 643 (see also УSpinels (inverse)Ф) Lattice energy see also УActinide elementsФ Lattice energy of hypothetical compounds 83 Lattice energy, calculation of 82 Lattice energy, Lawrencium 1252 1262 Lead chamber process for 646 Lead in antiquity 367 Lead, abundance 368 Lead, alloys 371 Lead, atomic properties 371 Lead, atomic weight variability 368 Lead, benzene complex with 405 Lead, bis(cyclopentadienyl) 395 404 Lead, chalcogenides 389 Lead, chemical reactivity and group trends 435 373 Lead, cluster anions 374 393 Lead, cluster complexes 387 395 Lead, dihalides 375 381 382 Lead, dinitrate 388 Lead, halogeno complexes 382 Lead, hydride 375 Lead, hydroxo cluster cation 395 Lead, isolation and purification 369Ч371 Lead, metal-metal bonded compounds 392 Lead, mixed dihalides 382 Lead, monomeric 390 Lead, monoxide 383 384 386 395 Lead, nitrate, thermolysis of 456 469 Lead, nonstoichiometric oxides 385Ч387 Lead, organohydrides 375 Lead, organometallic compounds 402Ч405 Lead, oxides, nonstoichiometric 384Ч387 Lead, oxides, uses of 386 Lead, oxoacid salts 388 Lead, Pb-S-O system 677 Lead, physical properties 371 372 Lead, pigments 386 388 Lead, production statistics 369 370 371 Lead, pseudohalogen derivatives 389 Lead, radiogenic origin 368 Lead, retrafluoride 388 Lead, sulfate 388 Lead, tetraacetate 388 Lead, tetrahalides 375 381 Lead, toxicity 367 368 Lead, uses 371 386 Leblanc process for NaOH 71 790 Lewis acid (acceptor) 905 (see also УDonor-acceptor complexesФ УClass-a Lewis base (donor) 198 905 УLigandsФ) Lifschitz salts 1156 1160 Ligand field theory 922 Ligand polyhedral model 1105 1140 Ligands see also УClass-a and class-b metalsФ УHapticityФ УLinkage УSynergic Ligands, ambidentate 907 920 Ligands, chelating 906 Ligands, classification as УhardФ and УsoftФ 326 909 Ligands, classification by number of donor atoms 906Ч907 Ligands, macrocyclic 907 Ligands, non-innocent 1055 Ligands, tripod 907 Ligands, УoctopusФ 99 Lime, production and uses of 119Ч121 Limestone, occurrence and uses 109 120Ч121 274 Limonite 1071 1146 Linde synthetic zeolites 358 359 Linkage isomerism of 702 Linkage isomerism of nitrite ion 463 464 920 Linkage isomerism of thiocyanate ion 326 920 Litharge see УLead monoxideФ Lithium see also УAlkali metalsФ Lithium compounds, industrial uses of 70 Lithium compounds, organometallics, synthesis of 102 103 Lithium compounds, organometallics, synthetic uses of 105Ч106 Lithium tetrahydroaluminate, synthetic reactions of 229 Lithium, abundance 69 Lithium, acetylide, synthetic use of 103 Lithium, alkyls and aryls 102Ч106 Lithium, aluminium hydride 228Ч229 Lithium, compounds with oxygen 84 85 Lithium, coordination chemistry of 90Ч94 Lithium, diagonal relationship with Mg 76 102 Lithium, discovery of 68 Lithium, methyl, bonding in 103 Lithium, methyl, structure of tetrameric cluster 103 104 113 Lithium, organometallic compounds 102Ч106 Lithium, production of metal 71 73 Lithium, reduction potential of 75 76 Lithium, stereochemistry of 91 Lithium, terrestrial distribution of 69 Lithium, variable atomic weight of 18 Lithium, УanomalousФ properties of 75Ч76 Lithophile elements 648 Lodestone 1080 lodic acid, 863 864 866 Loellingite structure 557 Lone pair, stereochemical influence 377 772 775Ч777 Lonsdaleite 274 276 Low-spin complexes of octahedral, 1087 Lutetium 1228 (see also УLanthanide elementsФ) Macrocyclic effect 911 Macrocyclic polyethers see УCrown ethersФ Maddrell's salt 528Ч531 Madelung constant 83 Magma, crystallization of silicates from 329 Magneli-type phases of titanium oxides 959 Magneli-type phases of vanadium oxides 952 Magnesium see also УAlkaline earth metalsФ Magnesium in biochemical processes 125 Magnesium, alkyl alkoxides 133 136 Magnesium, complexes of 123Ч126 Magnesium, cyclopentadienyl 136 Magnesium, diagonal relationship with Li 76 102 Magnesium, dialkyls and diaryls 131Ч133 Magnesium, history of 108 Magnesium, organometallic compounds 131 (see also УGrignard reagentsФ) Magnesium, porphyrin complexes of see УChlorophylФ Magnesium, production and uses of 110 111 magnetic moment see also УSpin equilibriaФ Magnetic moment of low-spin, octahedral, 1087 Magnetic moment, orbital contribution to 1132 1158 Magnetic quantum number m 22 Magnetite, 1071 Magnetite, 249 1080 Magnus's salt 1163 Malachite 1174 Malathion 509 Manganates 1050 1051 1222 Manganese see also УGroup 7 elementsФ Manganese, abundance 1040 Manganese, allyl complexes 934 Manganese, biochemistry of 1061Ч1062 Manganese, carbonyls 928 1062Ч1064 Manganese, chalocogenides 1049 Manganese, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1058Ч1061 Manganese, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1057Ч1058 Manganese, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1056 Manganese, complexes, lower oxidation states 1061 Manganese, complexes, with 702 Manganese, complexes, with S 667Ч669 Manganese, cyclooctatetraene complex 943 Manganese, cyclopentadienyls 1065Ч1067 Manganese, dioxides 1045Ч1048 Manganese, dioxides, uses of 1048 Manganese, halides and oxohalides 1051 Manganese, nodules 1041 Manganese, organometallic compounds 935 943 1062Ч1069 Manganese, oxides 1045 Manganese, production and uses 1041Ч1043 Manganin 1042 Marcasite structure 555Ч557 680 Marcasite structure, mineral 648 Marine acid 793 Marsh's test for As 558 Martensite 1075 Mass number of atom 22 Masurium 1040 (see also УTechnetiumФ) Matches 474 509 Meitnerium 1281 1283 Melamine 323 Mellitic acid 289 Melting points, influence of H bonding 54 Mendeleev's periodic table 20 Mendeleev, prediction of new elements 29 217 Mendelevium 1252 1262 Mercaptans, origin of name 1220
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



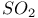
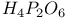 )]
)]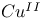
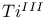
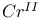
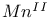
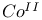
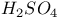
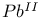
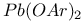
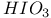
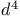 ions
ions