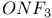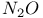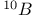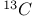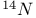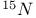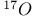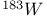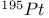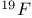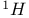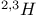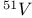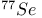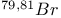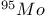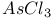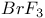јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. Ч Chemistry of the Elements
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Chemistry of the Elementsјвторы: Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. јннотаци€: When this innovative textbook first appeared in 1984 it rapidly became a great success throughout the world and has already been translated into several European and Asian languages. Now the authors have completely revised and updated the text, including more than 2000 new literature references to work published since the first edition. No page has been left unaltered but the novel features which proved so attractive have been retained. The book presents a balanced, coherent and comprehensive account of the chemistry of the elements for both undergraduate and postgraduate students. This crucial central area of chemistry is full of ingenious experiments, intriguing compounds and exciting new discoveries. The authors specifically avoid the term `inorganic chemistry' since this evokes an outmoded view of chemistry which is no longer appropriate in the final decade of the 20th century.
язык: –убрика: ’ими€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: second edition√од издани€: 1997 оличество страниц: 1340ƒобавлена в каталог: 18.02.2007ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Mercuration 1222 Mercury, +1 oxidation state 1213Ч1215 Mercury, +2 oxidation state 1413Ч1416 Mercury, abundance 1202 Mercury, alkyls and aryls 1222 Mercury, chalcogenides 1208 1211 Mercury, cyclopentadienyls 1223 Mercury, halides 1211Ч1213 Mercury, history 1173 Mercury, organometallic compounds 926 1222Ч1224 Mercury, oxide 1208Ч1209 Mercury, polycations 1214 1215 Mercury, production and uses 1203 Mercury, sulfide, solubility of 638 679 Mercury, toxicity 1225 Mesoperiodic acid see УPeriodic acidsФ Metal cations, amphoteric 52 Metal cations, hydrolysis of 51 Metalloboranes 172Ч174 178 Metallocarbohedrenes (met-cars) 300 Metallocarboranes 189Ч195 Metallocarboranes, bonding 188 190 194 Metallocarboranes, chemical reactions 195 Metallocarboranes, structures 188 Metallocarboranes, synthesis 189Ч191 Metallocenes see УFerroceneФ Metalloregulatory proteins 1226 Metaperiodic acid see УPeriodic acidsФ Metaphosphates see УChain polyphosphatesФ УCyclo-polyphosphatesФ Metaphosphimic acid tautomers 541 (see also УTetrametaphosphimatesФ) Metatelluric acid 781 methane 300 Methane as greenhouse gas 274 302 Methane in Habcr-Bosch 420 Methanides see УCarbidesФ Methyl bridges in 258 259 Methyl bridges in 127 Methyl bridges in 131 Methyl methacrylate 321 Methylene complexes see УCarbene ligandsФ Methylparathion 509 Meyer reaction 596 Meyer's periodic table 21 23 MICA 109 349 356Ч413 Millon's base 1218 1220 Mischmetall 946 1228 Mohorovicic discontinuity 358 Mohr's salt 1092 Molecular orbital theory of coordination compounds 922Ч924 Molecular sieves see УZeolitesФ Molybdates 1008Ч1016 Molybdenite, 649 1003 Molybdenum see also УGroup 6 elementsФ Molybdenum, abundance 1002 Molybdenum, benzene tricarbonyl 941 Molybdenum, biological activity 1035Ч1037 Molybdenum, blues 1008 Molybdenum, bronzes 1016 Molybdenum, carbonyls 928 1037 1038 Molybdenum, carbyne complexes 929 Molybdenum, chalcogenides 1017Ч1018 Molybdenum, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1031Ч1035 Molybdenum, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1027Ч1031 Molybdenum, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1025Ч1027 Molybdenum, complexes, +5 oxidation state 1024Ч1025 Molybdenum, complexes, +6 odixation state 1023Ч1024 Molybdenum, complexes, with 702 Molybdenum, complexes, with S 666Ч669 672 Molybdenum, compounds with quadruple metal-metal bonds 1032Ч1034 Molybdenum, cyclopentadienyl compounds 933 1038 Molybdenum, discovery 1002 Molybdenum, halides and oxohalides 1019 Molybdenum, heteropolyacids and salts 1014Ч1016 Molybdenum, isopolyacids and salts 1009Ч1014 Molybdenum, nitrogen fixation, role in 1035Ч1037 Molybdenum, nonstoichiometric oxides 1008 Molybdenum, organometallic compounds 1037Ч1039 Molybdenum, oxides 1007Ч1009 Molybdenum, production and uses 1003 1004 Molybdic acid 1010 Molybdocene 1038 Molybdoferredoxin 1035 1098 Monactin 96 Monazite 945 1230 1232 1254 Mond process 1146 Monel 1146 Montmorillonite 349 353 356 Mossbauer spectroscopy of nonstoichiometric oxides 642 Mossbauer spectroscopy with 371 Mossbauer spectroscopy with 753 Mossbauer spectroscopy with 802 838 841 Mossbauer spectroscopy with 898 Mossbauer spectroscopy with 1094 1095 1096 1101 Mossbauer spectroscopy with 1062 Mother-of-pearl 122 Muriatic acid 792 Muscovite see УMicaФ Myoglobin 1098Ч1101 n-p-n junction see УTransistorФ N-type semiconductor see УSemiconductorФ УTransistorФ Nacreous sulfur 655 NADP 125 Names of elements having Z >100 30 1252 1280Ч1283 Neodymium 1228 (see also УLanthanide elementsФ) Neodymium, +2 oxidation state 1237 1239 1241 Neodymium, +4 oxidation state 1244 Neon see also УNoble gasesФ Neon, atomic and physical properties 891 892 Neon, discovery 889 Neptunium 1252 1262 Neptunium, bis(cyclooctatetraene) 942 Neptunium, radioactive decay series 1254 Nernst equation (for electrode potentials) 435 Neso-silicates 347 348 Nessler's reagent 1218 Neutrons, fast 1256 Neutrons, slow, thermal 1256 Newnham process for roasting PbS 677 Niccolite (Kupfernickel) 1145 Nichrome 1146 Nickel arsenide 555 556 649 Nickel arsenide, relation to 556 697 Nickel arsenide, structure type 555 556 Nickel silver 1146 Nickel, 933 1172 Nickel, abundance 1145 Nickel, alkene and aklyne complexes 1170Ч1172 Nickel, aryls 1168 Nickel, atomic and physical properties 1148Ч1150 Nickel, biochemistry of 1167 Nickel, carbonyls 928 929 1168Ч1170 Nickel, chalocogenides 1152 Nickel, complexes with 702 Nickel, complexes, +1 oxidation state 1166 Nickel, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1156Ч1162 Nickel, complexes, +3 oxidation stale 1155 Nickel, complexes, +4 oxidation state 1154 Nickel, complexes, zero oxidation state 1166 1167 Nickel, coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1150 Nickel, cyclobutadiene complexes 936 Nickel, cyclopentadienyls 1170 Nickel, dithiolene complexes, redox series 675 Nickel, halides 1152 1153 Nickel, organometallic compounds 1167Ч1172 Nickel, oxidation states 1150 Nickel, oxides 1151 1152 Nickel, phosphides 489 Nickel, production and uses 1145Ч1148 Nickel, reactivity of elements 1149 Nickel, tetracarbonyl 928 929 1168 Nickel, УanomalousФ behaviour of 1160 1159 Nickelocene 939 1170 Nielsbohrium see УBohriumФ Niobates 987 (see also УGroup 5 elementsФ) Niobium, abundance 977 Niobium, alkyls and aryls 999 Niobium, bronzes 987 Niobium, carbonylate anions 980 1000 Niobium, chalcogenides 988 Niobium, complexes, +4 oxidation state 994Ч995 Niobium, complexes, +5 oxidation state 994 Niobium, compounds with oxoanions 993 Niobium, cyclopentadienyls 940 1000Ч1001 Niobium, discovery 976 Niobium, halides and oxohalides 988 Niobium, nonstoichiometric oxides 982 Niobium, organometallic compounds 999Ч1001 Niobium, oxides 982 983 Niobium, production and uses 977 Nitramide, 459 Nitrates 465 467Ч472 539Ч545 Nitrates, coordination modes 469Ч471 Nitrates, thermal stability 469 Nitric acid 422 456 457 459 465Ч468 Nitric acid, anhydrous 465 467 Nitric acid, hydrates 469 468 Nitric acid, industrial production 466 467 Nitric acid, industrial uses 467 Nitric acid, ionization in 711 Nitric oxide, bonding in paramagnetic molecule 446 Nitric oxide, catalytic production from 466 Nitric oxide, chemical reactions 446 Nitric oxide, colourless, not blue 446 Nitric oxide, complexes with transition metals see УNitrosyl complexesФ Nitric oxide, crystal structure 446 Nitric oxide, dimeric 446 Nitric oxide, NO 422 442 Nitric oxide, physical properties 446 Nitric oxide, preparation 445 Nitric oxide, reaction with atomic N 413 Nitride ion, 417 Nitride ion, 418Ч419 Nitrides 417Ч419 Nitrido complexes see УNitride ion as ligandФ Nitriles see УCyanidesФ Nitrite ion, 463 Nitrite ion, 463 464 920 Nitrites 422 461Ч465 Nitro-nitrito isomerism 463 464 920 Nitrogen see also УDinitrogenФ Nitrogen, abundance in atmosphere 406 407Ч409 Nitrogen, abundance in crustal rocks 407 Nitrogen, atomic properties 411 412 550 Nitrogen, atomic, production and reactivity of 412 413 Nitrogen, atypical group properties 416 550 Nitrogen, chemical reactivity 412Ч416 Nitrogen, comparison with C and O 416 Nitrogen, comparison with heavier Group 15 elements 416 551 577 Nitrogen, cycle in nature 406 408 410 Nitrogen, dinitrogen tetrafluoride 439 440 Nitrogen, dioxide 444 455 612 Nitrogen, discovery 406 Nitrogen, fixation, industrial 466 (see also УHaber Ч Bosch ammonia synthesisФ) Nitrogen, fixation, natural 999 1035Ч1037 1098 1102 Nitrogen, halides 438Ч441 Nitrogen, history 407 408 Nitrogen, hydrides of 426Ч433 (see also УAmmoniaФ УHydrazineФ УHydroxylamineФ) Nitrogen, industrial uses 409 Nitrogen, industrial uses, isotopes, discovery of 408 Nitrogen, isotopes, separation of 142 Nitrogen, ligand 408 Nitrogen, monoxide see УNitric oxideФ Nitrogen, multiple bond formation 416 417 Nitrogen, oxidation states 434 437 Nitrogen, oxides 443Ч458 Nitrogen, oxoacids 459Ч466 Nitrogen, oxoanion salts see УNitrosyl halidesФ УNitryl Nitrogen, physical properties 412 Nitrogen, production 411 Nitrogen, standard reduction potential for N species 434 Nitrogen, stereochemistry 413 Nitrogen, synthesis of pure 409 Nitrogen, tribromide 441 Nitrogen, trichloride 441 Nitrogen, trifluoride 438Ч439 Nitrogen, triiodide, ammonia adduct 441 Nitrogen, trioxide 444 458 Nitrogenase 1035 1098 Nitronium ion 458 712 Nitroprusside ion 1094 1095 Nitrosyl azide 433 443 Nitrosyl complexes 447Ч453 Nitrosyl complexes, coordination modes 450 450Ч452 Nitrosyl complexes, electronic structure of 450 451 Nitrosyl complexes, preparation 448 449 Nitrosyl halides 441 442 Nitrosyl trifluoride, 438 439 Nitrous acid 459 461Ч462 Nitrous acid, reaction with hydrazine 432 Nitrous oxide, 443Ч445 Nitrous oxide, 443 445 Nitrous oxide, 443 Nitrous oxide, 442 445 Nitrous oxide, 443 Nitrous oxide, 445 Nitroxyl 459 461 Nitroxylic acid 459 Nitryl halides, 441 Nmr spectroscopy with: 144 Nmr spectroscopy with: 371 Nmr spectroscopy with: 762 Nmr spectroscopy with: 802 803 Nmr spectroscopy with: 276 326 914 995 1104 1105 Nmr spectroscopy with: 326 408 411 1025 Nmr spectroscopy with: 408 411 Nmr spectroscopy with: 601 604 605 630 984 1012 Nmr spectroscopy with: 1012 Nmr spectroscopy with: 1165 Nmr spectroscopy with: 197 499 562 563 684 739 791 802Ч803 817 841 904 1022 Nmr spectroscopy with: 34 56 230 532 933 935 940 973 1111 1129 1135 1165 1223 Nmr spectroscopy with: 34 Nmr spectroscopy with: 330 Nmr spectroscopy with: 474 482 516 1165 Nmr spectroscopy with: 662 Nmr spectroscopy with: 791 802 803 Nmr spectroscopy with: 985 Nmr spectroscopy with: 762 769 Nmr spectroscopy with: 802 803 Nmr spectroscopy with: 1025 Nmr spectroscopy with: 144 197 NO see УNitric oxideФ Nobel prize for Chemistry, list of laureates 1296Ч1299 Nobel prize for Physics, list of laureates 1300Ч1304 Nobelium 1252 1463 Noble gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn) 888Ч904 Noble gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn), atomic and physical properties 890Ч891 Noble gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn), bonding in compounds of 897 Noble gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn), chemical properties 892Ч904 Noble gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn), clathrates 893 Noble gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn), discovery 888 889 Noble gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn), production and uses 889 890 1044 Nomenclature of elements having Z > 100 30 1252 1280Ч1283 Non-haem iron proteins (NHIP) 1102 1103 Nonactin 96 Nonaqueous solvent systems, 561 Nonaqueous solvent systems, 830 831 Nonaqueous solvent systems, 829 Nonaqueous solvent systems, 710Ч712 759 Nonaqueous solvent systems, 834 Nonaqueous solvent systems, 77Ч79 424Ч426
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте




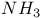 synthesis
synthesis 

 and
and 
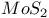
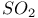
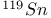
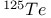
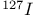 ,
, 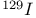
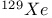
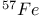
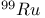

 -allylic complexes
-allylic complexes 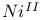

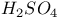

 , coordination modes
, coordination modes