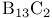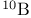јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. Ч Chemistry of the Elements
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Chemistry of the Elementsјвторы: Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. јннотаци€: When this innovative textbook first appeared in 1984 it rapidly became a great success throughout the world and has already been translated into several European and Asian languages. Now the authors have completely revised and updated the text, including more than 2000 new literature references to work published since the first edition. No page has been left unaltered but the novel features which proved so attractive have been retained. The book presents a balanced, coherent and comprehensive account of the chemistry of the elements for both undergraduate and postgraduate students. This crucial central area of chemistry is full of ingenious experiments, intriguing compounds and exciting new discoveries. The authors specifically avoid the term `inorganic chemistry' since this evokes an outmoded view of chemistry which is no longer appropriate in the final decade of the 20th century.
язык: –убрика: ’ими€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: second edition√од издани€: 1997 оличество страниц: 1340ƒобавлена в каталог: 18.02.2007ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Argon, production and uses 889 Arsenates 577 Arsenic, abundance and distribution 548 549 Arsenic, allotropes 551 Arsenic, alloys 549 554 Arsenic, amino derivatives 561 Arsenic, atomic properties 550 Arsenic, catenation 583Ч590 Arsenic, chalcogenide cluster cations 579 Arsenic, chalcogenides 578Ч583 Arsenic, chemical reactivity 552Ч554 577 Arsenic, cluster anions 553 588Ч591 Arsenic, coordination geometries 553 Arsenic, diiodide 564 Arsenic, encapsulated 554 Arsenic, extraction and production 548 549 Arsenic, halide complexes 564Ч569 Arsenic, halides 558Ч566 see trihalidesФ УArsenic pentahalidesФ УArsenic diiodideФ УArsenic oxide УArsenic mixed УArsenic halide Arsenic, halogenoorganoarsenic compounds 593Ч596 Arsenic, history 547 Arsenic, hydrides 557 558 583 679 Arsenic, intermetaUic compounds see УArsenides Arsenic, metal-metal bonded species 583Ч590 Arsenic, mixed halides 563 Arsenic, organic compounds 553 Arsenic, organoarsenic(I) compounds 597 Arsenic, organoarsenic(III) compounds 583Ч587 592Ч594 596 Arsenic, organoarsenic(III) compounds, arsabenzene 593 Arsenic, organoarsenic(III) compounds, arsanaphthalene 593 Arsenic, organoarsenic(III) compounds, physiological activity 596 Arsenic, organoarsenic(III) compounds, preparation of 593 595 Arsenic, organoarsenic(III) compounds, reactions of 593 595 Arsenic, organoarsenic(V) compounds 594 596 Arsenic, oxidation state diagram 578 Arsenic, oxide 549 572Ч575 Arsenic, oxide 574 Arsenic, oxide 573 Arsenic, oxide 549 574 Arsenic, oxide halides 570Ч572 Arsenic, oxides and oxocompounds 570Ч578 Arsenic, oxoacid salts of 591 Arsenic, pentahatides 561. 664 Arsenic, physical properties 551 552 Arsenic, selenides 581 Arsenic, sulfide, 547 548 578 579 648 Arsenic, sulfide, 580 581 Arsenic, sulfide, 578 579 Arsenic, sulfide, 548 578Ч581 649 Arsenic, sulfides, 578Ч580 Arsenic, triangular species 583 586Ч589 Arsenic, trichloride solvent system 560 Arsenic, trihalides 558Ч561 564 566 Arsenic, uses 549 Arsenic, volt-equivalent diagram 578 Arsenicals, therapeutic uses 593 see Arsenides 554Ч558 Arsenides, stoichiometries 554 Arsenides, structures 554Ч557 Arsenidine complexes 597 Arsenious acid 574 Arsenite 575 575 577 Arsenite esters 561 Arsenopyrite 649 Arsine 558 Arsinic acids 594 Arsinous acids 594 Arsonic acids RAsO(OH) 596 Arsonous acids 594 Asbestos 109 351 Asbestos minerals 349 351 Astatate ion, 886 Astatide ion 886 Astatine see УHalogensФ Astatine, abundance 796 Astatine, atomic properties 800 Astatine, chemistry 885. 886 Astatine, nuclear synthesis 791 795 Astatine, radioactivity of isotopes 795 885 Astatine, redox systematks 885 Astatine, trihalide ions 886 Atactic polymer 972 Atmophile elements 648 Atmosphere, composition 409 603 Atmosphere, industrial production of gases from 409 604 Atmosphere, origin of 602 Atom-at-a-time chemistry 1282 Atomic energy 1256 Atomic orbitals 1285Ч1289 Atomic piles 1256 see Atomic properties, periodic trends in 23Ч27 Atomic volume curve, periodicity of 23 24 Atomic weight, definition 15 Atomic weights, history of 15 601 Atomic weights, precision of 15Ч19 Atomic weights, Table of see УFront end paperФ Atomic weights, variability of 17Ч19 368 ATP see УAdenosine triphosphateФ Autoprotolysis constants of anhydrous acids 710 Azides 433 Azoferredoxin 1036 1098 Azotobacter 999 1036 Azotobacter vinetandii 1036 Back ( 923 926 927 931 1166 Baddeleyite 955 Baddeleyite, structure of 955 Baking powders 524 525 Barium see УAlkaline earth metalsФ Barium, history of 108 Barium, organometallic compounds 136 Barium, polysulfides 681 Bart reaction 596 Basic oxygen steel process 120 1072 Bastnaesite 945 1229 1232 Batteries, dry 1204 Batteries, lead 371 549 Batteries, sodium-sulfur 678 Bauxite 243 Bauxite in Al production 219 Bauxite, production statistics 218 Bayer process 167 Bayerite 243 245 Belousov Ч Zhabotinskii oscillating reactions 865 Bentonite see УMontmorilloniteФ Benzene as ligand 940Ч941 Berkelium 1252 1262 see Berry pseudorotation 474 499 914 see Beryl 107 108 349 Beryllia see УBeryllium oxideФ Beryllium see УAlkaline earth metalsФ Beryllium compounds, toxicity of 107 Beryllium ion, hydration number of 605 Beryllium, alkoxides etc 122 129 Beryllium, alkyls 126Ч130 Beryllium, borohydridc 115 116 Beryllium, chloride 116 117 Beryllium, complexes of 122Ч125 Beryllium, cyclopentadienyl complexes 130 Beryllium, discovery 107 108 Beryllium, fluoride 116 Beryllium, hydride 115 115 128 Beryllium, oxide 107 119Ч120 Beryllium, salts, hydrolysis of 121 Beryllium, uses of metal and alloys 110 Beryllium, СanomalousТ properties of 114 122 Beryllium, Сbasic acetateТ 122 123 Beryllium, Сbasic nitrateТ 122 Bessemer process 1072 BHB bridge bond, comparison with H bond 64 70 see Biotite see УMicasУ Bismuth, abundance and distribution 548 549 550 Bismuth, allotropes 551 551 Bismuth, alloys 549 554 Bismuth, atomic properties 550 Bismuth, Bi+cation 564 591 Bismuth, catenation 582 Bismuth, chalcogenides 581 582 Bismuth, chemical reactivity 552 553. Bismuth, cluster cations 564 565 583 588Ч591 Bismuth, extraction and production 549 550 Bismuth, halide complexes 564Ч567 Bismuth, halides 558Ч564 see trihalides УBismuth pentahalidesФ УBismuth oxide УBismuth lower УBismuth mixed УBismuth halide Bismuth, history 547 Bismuth, hydride 557 558 Bismuth, hydroxide, 575 Bismuth, hydroxo cluster cation, 575 591 592 Bismuth, intermetallic compounds see УBismuthidesФ Bismuth, lower halides 564 Bismuth, metal-metal bonded clusters 583 583Ч591 Bismuth, mixed halides 564 Bismuth, nitrate and related complexes 591. 592 Bismuth, organometallic compounds 592 596 599 Bismuth, oxidation state diagram 578 Bismuth, oxide halides 572 572 Bismuth, oxide, 573 574 Bismuth, oxides and oxo compounds 573Ч575 Bismuth, oxoacid salts of 591 Bismuth, pentafluoride 561 Bismuth, physical properties 550 552 Bismuth, trihalides 558Ч561 564 566 Bismuth, uses 549 Bismuth, volt-equivalent diagram 578 Bismuthates 577 Bismuthides 554 Bismuthine 557 Biuret 305 1191 Blast furnace 1073 Bleaching powder 790 860 Blue vitriol 1190 Boehmite 243 Bohrium 1281 1283 Boiiing points, influence of H bonding 54 Bom Ч Haber cycle 94Ч96 79 82Ч83 Borane adducts, 165 Borane adducts, amine-boranes 208Ч209 Borane anions 151 166 178 181 590 see Boranes, arachno-structures 152 154 159 Boranes, as ligands 177 Boranes, bonding 157Ч162 590 Boranes, classification 151 Boranes, closo-structures 152 153 161 Boranes, conjuncto-structures 152 155Ч157 Boranes, hypno-strucuires 152 153 172 Boranes, nido- structures 152 154 161 Boranes, nomenclature 157 Boranes, optical resolution of 670 Boranes, physical properties 162 163 Boranes, preparation 162 Boranes, topology 158Ч160 175 see УPetaboraneФ УDecaboraneФ УMetalloboranesФ УCarboranesФ etc. Borate minerals, occurrence 140 Borate minerals, production and uses 140 see Borates 205Ч207 Borates, B-O distances in 206 Borates, industrial uses 207 Borates, structural principles 205 Borax 139 see Borazanes 209 Borazine 210 408 Bordeaux mixture (fungicide) 1190 Boric acids, 203 Boric acids, 204 Borides, bonding 151 Borides, catenation in 148 Borides, preparation 146 Borides, properties and uses 146 Borides, stoichiometry 145 147 Borides, structure 147Ч151 Borohydrides see УBorane anionsФ УTetrahydro-boratesФ Boron 167 see Boron carbide 149 Boron carbide 149 Boron carbide 143 Boron halides 195Ч202 Boron halides, 200 202 Boron halides, 200 Boron halides, lower halides 199Ч202 see Boron nitride, $\mathrm{B_{50}N_2} 143 Boron trifluoride see УBoron trihalidesФ Boron trihalides, adducts 198Ч199 Boron trihalides, bonding 196 Boron trihalides, physical properties 196 Boron trihalides, preparation 196 Boron trihalides, scrambling reactions 197 198 Boron, abundance 139 Boron, allotropes 141Ч144 Boron, atomic properties 144 222 Boron, chemical properties 144 145 Boron, crystal structures of allotropes 141 Boron, hydrides see УBoranesФ Boron, isolation 139Ч140 144 Boron, neutron capture therapy using 179 Boron, nitride 208 208 Boron, nuclear properties 144 Boron, oxide 203 Boron, physical properties 144 222 Boron, sulfides 213Ч214 Boron, variables atomic weight of 17 Boron-nitrogen compounds 207Ч211 Boron-oxygen compounds 203Ч207 Boron-oxygen compounds, organic derivatives 207 brass 1175 1178 1178 1201 1203 1397 Brimstone 645 646 Bromates, 862Ч864 Bromates, 866 Bromates, 853Ч856 Bromic acid, 863 Bromides, synthesis of 821 822 see Bromine see УHalogensФ Bromine, abundance and distribution 795 Bromine, atomic and physical properties 800Ч804 Bromine, cations 842Ч844 Bromine, history 790 790 792. 925 Bromine, monochloride 824 825 833 Bromine, monofboride 825 833 Bromine, oxide fluorides 880Ч881 Bromine, oxides 850 851 Bromine, oxides, nomenclature 853 Bromine, oxides, redox properties 853Ч855 see oxides individual УBromine oxides bromic УBromine oxides bromatesФ УBromine oxides perbromatesФ etc. Bromine, pentafluoride 832Ч834 Bromine, production and uses 798 800 Bromine, radioactive isotopes 801 802 Bromine, reactivity 805 Bromine, standard reduction potentials 854 Bromine, stereochemistry 806 Bromine, trifluoride 827Ч831 832 Bromine, volt-equivalent diagram 855 Bronsted's acid-base theory 32 48 Bronsted's acid-base theory in aqueous solutions 628 Bronsted's acid-base theory in non-aqueous solutions 51 Bronze 1173 1175 Bronzes, molybdenum 1016 Bronzes, titanium 964 Bronzes, tungsten 1016 Bronzes, vanadium 987 Brucite 121 352 385 Buffer solutions 48 49 521 524 Bulky tertiary phosphine ligands, special properties of 494 Butadiene as a fj4 ligand 935Ч936 Cadmium chloride structure 1211 Cadmium iodide structure type 556 680 680 1211 Cadmium iodide structure type, nonstoinchiometry in 679
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



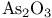
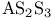
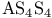



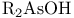
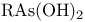
 "
" 
 in
in  ) bonding
) bonding 
![$\mathrm{[Bi_6(OH)_12]^{6+}}$](/math_tex/80e0ee6dc34d7960239e6a68f95c6b2382.gif)