Àâòîðèçàöèÿ
Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì
Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. — Chemistry of the Elements
Îáñóäèòå êíèãó íà íàó÷íîì ôîðóìå Íàøëè îïå÷àòêó?
Íàçâàíèå: Chemistry of the ElementsÀâòîðû: Greenwood N.N., Earnshaw A. Àííîòàöèÿ: When this innovative textbook first appeared in 1984 it rapidly became a great success throughout the world and has already been translated into several European and Asian languages. Now the authors have completely revised and updated the text, including more than 2000 new literature references to work published since the first edition. No page has been left unaltered but the novel features which proved so attractive have been retained. The book presents a balanced, coherent and comprehensive account of the chemistry of the elements for both undergraduate and postgraduate students. This crucial central area of chemistry is full of ingenious experiments, intriguing compounds and exciting new discoveries. The authors specifically avoid the term `inorganic chemistry' since this evokes an outmoded view of chemistry which is no longer appropriate in the final decade of the 20th century.
ßçûê: Ðóáðèêà: Õèìèÿ /Ñòàòóñ ïðåäìåòíîãî óêàçàòåëÿ: Ãîòîâ óêàçàòåëü ñ íîìåðàìè ñòðàíèö ed2k: ed2k stats Èçäàíèå: second editionÃîä èçäàíèÿ: 1997Êîëè÷åñòâî ñòðàíèö: 1340Äîáàâëåíà â êàòàëîã: 18.02.2007Îïåðàöèè: Ïîëîæèòü íà ïîëêó |
Ñêîïèðîâàòü ññûëêó äëÿ ôîðóìà | Ñêîïèðîâàòü ID
Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü
Donor-acceptor complexes of dithiolenes 674 Donor-acceptor complexes of Group 13 halides 237—239 Donor-acceptor complexes of NO see “Nitrosyls Donor-acceptor complexes of SO, 700—703 Donor-acceptor complexes, first 408 Donor-acceptor complexes, stability of 198 Double-helix structure of nucleic acids 474 Downs cell 72 73 Dry batteries 1204 Dubnium 1281—1282 Dysprosium 1229 see Dysprosium, +4 oxidation state 1244 e-Process in stars 8 Effective atomic number (BAN) rule 921 see Effective ionic radii, Table of 1295 Eighteen electron rule 1037 1104 1109 1112 1134 Einsteinium 1252 1262 see Eka-silicon, Mendeleev's predictions 29 Electric arc process of steelmaking 1072 Electrical properties, influence of H bonding 53 Electrofluorination 821 Electron affinity 75 82 800 Electron transfer reactions, mechanisms of 1124 Electron-counting rules for boranes 161 Electron-counting rules for carbonyl clusters 1107 1142 1169 Electron-counting rules for carhoranes 181 Electron-counting rules for gold-phosphine clusters 1197 Electron-counting rules for metal-halide clusters 966 1018 1022 Electron-counting rules for metallocarboranes 194 Electronegativity, definition of 26 Electronegativity, periodic trends in 26 Electronic structure and chemical periodicity 21—23 Electronic structure of atoms 21—23 Elements, abundance in crustal rocks 1294 Elements, bond dissociation energies of gaseous diatomic 584 Elements, cosmic abundance 3 l2 Elements, isolopic composition of 47 Elements, origin of 1 5 9 I2 Elements, periodic table of see “Inside front cover” Elements, periodicity in properties 20—31 Elements, table of atomic weights see “Inside back cover” Elements, Z=104-112 see “Transactinide” Ellingham diagram 308 307 369 Emerald 107 1003 Enstatite 349 Entropy and the chelate effect 910 Equilibrium process in stars (e-process) 8 Erbium 1229 see Ethene (ethylene) as a ligand 930 931 Europium 1229 see Europium, +2 oxidation stale 1239 1240 1241 1248 Europium, magnetic properties of 1243 Eutrophication 478 528 Exclusion principle (Pauli) 22 Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) 1036 f-block contraction 562 1234 Faraday's phosphide synthesis 489 Faujasite 358 Fehling's test 1181 Feldspars 354 358 414 Femanium ion 1109 Fenton's reagent 636 Fermi level, definition of 332 Fermium 1252 1262 see Ferredoxins 1035 1036 1098 1101—1103 Ferrites 1081 1209 Ferritin 1098 1104 Ferrocene, bonding 938—939 Ferrocene, historical importance of 924 1070 1109 Ferrocene, physical properties 937 Ferrocene, reactions 1109—1112 Ferrocene, structure 937 Ferrocene, synthesis 938 1109 Ferrochrome 1003 Ferroelectricity 57—58 386 571 Ferromanganese 1041 Ferromolybdenum 1003 Ferrophosphonis 480 492 525 Ferrosilicon alloys 330 Ferrovanadium 977 First short period, “anomalous” properties of 27 Fischer (Karl) reagent 628 Fischer — Tropsch process 309 1106 Fish population, relation to phosphate-rich waters 479 Flint 328 342 Fluorapatite see “Apatites” Fluoridation and dental caries 447 525 791 792 Fluorides 820—821 Fluorides, solubility in HF 817 Fluorides, synthesis 820—821 Fluorinated peimo compounds 639 640 Fluorinating agents 820—821 Fluorinating agents, 560 Fluorinating agents, 562 563 Fluorine see “Halogens” Fluorine, abundance and distribution 795 Fluorine, atomic and physical properties 800—804 Fluorine, chemical synthesis of 821 Fluorine, history 789—792 Fluorine, isolation 789 791 Fluorine, oxides see “Oxygen fluorides” Fluorine, oxoacid, HOF 789 853 856 Fluorine, preparation of fluorides using 820 Fluorine, production and uses 796—798 Fluorine, radioactive isotopes 801 802 936 Fluorine, reactivity 804—806 Fluorine, stereochemistry 806 Fluorine, toxicity 792 810 Fluorite, 109 Fluorite, 117 Fluorosulfuric acid 689 Fluorspar 789 790 see Fluorspar, fluorescence 789 790 Fluxional hehaviour see “Stereochemical non-rigidity” Francium see “Alkali metals” Francium, abundance 68 Francium, discovery 68 Frasch process for sulfur 646 Freons (eg 304 791 Friedel — Crafts catalysis, 171 176 186 235 236 338 Friedel — Crafts catalysis, 199 Friedel — Crafts catalysis, 385 Fuller's earth see “Montmorillonite” Fullerenes, chemical properties 282—287 Fullerenes, discovery 279 Fullerenes, incorporation of heteroatoms 287—9 Fullerenes, structure 280 Fullerides 285 Fullerols 284 Fulminate ion 319 433 g (gerade), definition 938 Gabbro rock 358 Gadolinium 1229 (see also “Lanthanide elements”) Gadolinium, diiodide 1242 Galena (Pb glance) 649 (see also “Lead sulfide”) Galena, roasting reactions 677 Gallane 231 Gallium see also “Group 13 elements” Gallium, abundance 218 Gallium, arsenide, semiconductor 221 Gallium, as eka-aluminium 216 Gallium, chalcogenides 252 253 Gallium, discovery 216 Gallium, hydride 231 Gallium, hydride halides 232 Gallium, III—V compounds 256 Gallium, ion, hydration number of 605 Gallium, lower halides 240 Gallium, organometallic compounds 262—266 Gallium, oxides 246 Gallium, production and uses 219 Gallium, sulfides 285 286 Gallium, trihalides 237 Garnets 348 Garnets, magnetic properties of 946 1081 Garnierite 1145 German silver 1146 Germanes see “Germanium hydrides” Germanium, abundance 368 Germanium, atomic properties 371 372 Germanium, chalcogenides 389 390 Germanium, chemical reactivity and group trends 373 375 Germanium, cluster anions 393 Germanium, dihalides 376 Germanium, dihydroxide 382 Germanium, dioxide 383 Germanium, discovery 367 Germanium, halogeno complexes 376 Germanium, hydrides 374 373 Germanium, hydrohalides 375 Germanium, isolation from flue dust 369 Germanium, monomeric 390 Germanium, monoxide 376 382 Germanium, organo compounds 376 396 404 Germanium, physical properties 371 372 Germanium, silicate analogues 383 Germanium, sulfate 387 Germanium, tetraacetate 387 Germanium, tetrahalides 375 377 Germanium, uses 369 Germanocene 398 Germenes 397 Germylenes 397 Gibbs' phase rule 676 Gibbsite 243 245 352 Girbotol process 311 Glassmaker's soap 1048 Gold see also “Group 11 elements” Gold, abundance 1174 Gold, alkyls 1180 1200 Gold, chalcogenides 1181—1182 Gold, cluster compounds 1197 1198 Gold, complexes, +1 oxidation state 1196 Gold, complexes, +2 oxidation state 1189 Gold, complexes, +3 oxidation state 1188—1189 Gold, complexes, lower oxidation states 1197 Gold, complexes, with S 666 Gold, halides 1183—1184 Gold, history 1173 Gold, nitrato complexes 469 471 Gold, organometallic compounds 925 1199—1200 Gold, oxide 1181 Gold, production and uses 1367 1174 Graham's salt 528—531 Graphite, alkali metal intercalates 293 Graphite, chemical properties 289—292 Graphite, halide intercalates 295 295 Graphite, intercalation compounds 293—294 Graphite, monofluoride 289 Graphite, occurrence and distribution 270 Graphite, oxide 289 290 Graphite, oxide intercalates 296 Graphite, physical properties 278 Graphite, production and uses 271 Graphite, structure 275 Graphite, subfluoride 289—290 Greek alphabet see “Back end paper” Greenhouse effect 273 687 Grignard reagents 131—136 Grignard reagents, allyl 933 Grignard reagents, constitution of 131 132 Grignard reagents, crystalline adducts of 133 Grignard reagents, preparation of 132 Grignard reagents, Schlenk equilibrium 131 132 Grignard reagents, synthetic uses of 134 135 151 Group 0 elements see “Noble gases” Group 1 elements see “Alkali metals” Group 10 elements see “Nickel” “Palladium” “Platinum” Group 11 elements (Cu, Ag, Au) see also “Copper” “Silver” “Goid” Group 11 elements (Cu, Ag, Au), atomic and physical properties 1176 1177 Group 11 elements (Cu, Ag, Au), coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1179 1180 Group 11 elements (Cu, Ag, Au), group trends 1177—1180 Group 11 elements (Cu, Ag, Au), oxidation states 1179 Group 12 elements (Zn, Cd, Hg) see also “Zinc” “Cadmium” “Mercury” “Element Group 12 elements (Zn, Cd, Hg), atomic and physical properties 1203 1205 Group 12 elements (Zn, Cd, Hg), coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1207 Group 12 elements (Zn, Cd, Hg), group trends 1205—1208 Group 13 elements (B, Al, Ga, In, Tl), + 1 oxidation state 224 227 Group 13 elements (B, Al, Ga, In, Tl), amphoteric behaviour of Al, Ga 225 Group 13 elements (B, Al, Ga, In, Tl), atomic properties 222 Group 13 elements (B, Al, Ga, In, Tl), chemical reactivity 224—227 Group 13 elements (B, Al, Ga, In, Tl), group trends 223—227 237 Group 13 elements (B, Al, Ga, In, Tl), physical properties 222 224 Group 13 elements (B, Al, Ga, In, Tl), trihalide complexes, stability of 237—239 Group 13 elements (B, Al, Ga, In, Tl), unusual sterochemistries 256 Group 14 elements see “Carbon” “Silicon” “Germanium” “Tin” “Lead” Group 15 elements see “Nitrogen” “Phosphorus” “Arsenic” “Antimony” “Bismuth” Group 16 elements see “Oxygen” “Sulfur” “Selenium” “Tellurium” “Polonium” Group 17 elements see “Halogens” Group 2 elements see “Alkaline earth metals” Group 3 elements (Sc, Y, La; Ac) see also “Lanthanide elements” Group 3 elements (Sc, Y, La; Ac), atomic and physical properties 946 947 Group 3 elements (Sc, Y, La; Ac), chemical reactivity 948—949 Group 3 elements (Sc, Y, La; Ac), group trends 948—949 Group 3 elements (Sc, Y, La; Ac), high coordination, numbers 952 Group 3 elements (Sc, Y, La; Ac), oxidation states lower than +3 949 950 Group 4 elements (Ti, Zr, Hf) see also “Titanium” “Zirconium” “Hafnium” “Rutherfordium” Group 4 elements (Ti, Zr, Hf), atomic and physical properties 957—958 Group 4 elements (Ti, Zr, Hf), coordination numbers and stereochemistries 960 Group 4 elements (Ti, Zr, Hf), group trends 957—960 Group 4 elements (Ti, Zr, HO, oxidation states 960 Group 5 elements (V, Nb, Ta) see also “Vanadium” “Niobium” “Tantalum” “Dubnium” Group 5 elements (V, Nb, Ta), atomic and physical properties 978 Group 5 elements (V, Nb, Ta), coordination numbers and stereochemistries 980 Group 5 elements (V, Nb, Ta), group trends 979 980 Group 5 elements (V, Nb, Ta), oxidation states 980 Group 6 elements (Cr, Mo, W) see also “Chromium” “Molybdenum” “Tungsten” Group 6 elements (Cr, Mo, W), atomic and physical properties 1004 1008 Group 6 elements (Cr, Mo, W), coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1006 Group 6 elements (Cr, Mo, W), group trends 1005 Group 6 elements (Cr, Mo, W), oxidation states 1006 Group 7 elements (Mn, Tc, Re) see also “Manganese” “Technetium” “Rhenium” Group 7 elements (Mn, Tc, Re), atomic and physical properties 1043 Group 7 elements (Mn, Tc, Re), coordination numbers and stereochemistries 1046 Group 7 elements (Mn, Tc, Re), group trends 1044 1045 Group 7 elements (Mn, Tc, Re), oxidation states 1046 Group 7 elements (Mn, Tc, Re), oxoanions 1049 1050 Group 7 elements (Mn, Tc, Re), redox properties 1044 1045 Group 8 elements see “Iron” “Ruthenium” “Osmium” Group 9 elements see “Cobalt” “Rhodium” “Indium” Guanidine 305 Guanine 61 62 Guano 408 Gunpowder 645 646 Gypsum 109 122 Gypsum, diluent in superphosphate fertilizer 525 Gypsum, occurrence in evaporites 647 Gypsum, process for 521 522 Gypsum, S recovery from 651 652 H bridge-bond in boranes and carboranes 154 Haber — Bosch ammonia synthesis 408 409 Haber — Bosch ammonia synthesis, historical development 421 Haber — Bosch ammonia synthesis, production statistics 421 Haber — Bosch ammonia synthesis, technical details 421 Haem 126 1099 Haematin 1099 Haematite 1071 Haemocyanin 1199 Haemoglobin 1098—1101 Hafnates 964
Ðåêëàìà
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



 ,
, 
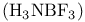

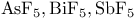

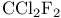 )
) 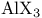 complexes
complexes 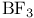 complexes
complexes 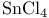

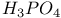 manufacture
manufacture