|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Misner C.W., Thorne K.S., Wheeler J.A. — Gravitation |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
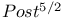 -Newtonian approximation and its relationship to radiation damping 1077 -Newtonian approximation and its relationship to radiation damping 1077
4-Force, Lorentz 73
Aberration formulas for 68
Aberration in light-deflection experiments 1101
Absolute space of Newtonian theory 19 40 291f
Absolute time of Newtonian theory 291f
Abundances of elements 765
Accelerated observer in curved spacetime 327—332 (see also “Proper reference frame”)
Accelerated observer in flat spacetime 163—175
Accelerated observer in flat spacetime constraints on size of frame 168—169
Accelerated observer in flat spacetime local coordinate system of 172—176
Accelerated observer in flat spacetime measuring equipment of 164—165
Accelerated observer in flat spacetime problems of principle in defining coordinate system of 168—169
Accelerated observer in flat spacetime tetrad Fermi-Walker transported with 169—172
Accelerated observer in flat spacetime with rotating tetrad 174f
Acceleration 4-acceleration always orthogonal to 4-velocity 166 (see also “Fermi — Walker transport”)
Acceleration constant in comoving frame, for hyperbolic motion 166—167
Acceleration equivalent to gravitational field see “Equivalence principle”
Acceleration gravity mocked up by 163ff
Acceleration of neutron in nucleus 163
Acceleration special relativity adequate to analyze 163ff
Acceleration, relative see “Geodesic deviation”
Acceleration, “absolute,” and the equivalence principle 17
Accretion of gas onto a black hole 885
action see “Dynamical path length”
Action at a distance, gravitational 4
Action at a distance, gravitational derived from local law 120
Action at a distance, gravitational Newton’s stricture against 41
Action principle see «Variational principle”
Active vs. passive transformations 1140
Adiabatic index defined 692
Advanced fields, and radiation reaction 474
Advanced potential 121
Affine connection see «Connection” “Covariant
Affine geometry characterized 191 242
Affine geometry characterized in extensor, Chap 10 (see also specific concepts such “Connection
Affine parameter, defined 211 244ff
Affine parameter, defined effect of changing, on geodesic deviation 269
Affine parameter, defined in geometric optics 575
Affine parameter, defined of geodesic 244—246
Affine parameter, defined variational principle adapted to 322—323
After, undefined term in quantum geometrodynamics 1183
Alternating symbol, in spinor analysis, defined 1152 (see also “Levi — Civita tensor “Permutation
Alternating tensor see “Permutation tensor”
Ampere’s law. from electromagnetic 4-potential 122
Angle-effective distance vs. redshift 795f
Angular integrals, useful formulas 1001
Angular momemum operators 240
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source as geometric object residing in asymptotically flat region 453
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source conservation laws for 455 468—471
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source contribution of interbody matter and fields to 468
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source defined by way metric approaches flatness in exienso, chapter 19
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source defined by way metric approaches flatness in general 453ff
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source defined by way metric approaches flatness in linearized theory 448—451
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source for Kerr — Newman black hole 891
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source Gaussian flux integral for 460—464
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source measured by frame dragging 451 457
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source measured by gyroscope precession 451 454 457
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source measured by satellite-orbit precession 451 454 457
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source no meaning of for closed universe 457ff
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source total unambiguous, despite contribution of pseudotensor to 470
Angular momentum in curved spacetime, for an isolated source volume integral for 460—466
Angular momentum in flat spacetime conservation of 156f
Angular momentum in flat spacetime decomposition of total into intrinsic and orbital 158f
Angular momentum in flat spacetime density of 151 156f
Angular momentum in flat spacetime intrinsic, sets lower limit to size 162
Angular momentum in flat spacetime parallel transport of and Thomas precession 175—176
Angular momentum in flat spacetime total 156—159
Angular momentum in Newtonian theory, flux integral for 470
Angular momentum, orbital, for test particles in Kerr — Newman geometry 898f
Angular momentum, orbital, for test particles in Schwarzshild geometry 656ff
Angular velocity extended to four dimensions 170f
Angular velocity in context of spinor analysis 1139 1142
Angular velocity of orbital motion in Kerr — Newman geometry 893ff
Angular velocity rotating tetrad, vs. Fermi — Walker tetrad 174f
Anholonomie basis 204 210 239
Anisotropy energy 802 807
Antisymmetrization. of tensor 83
Asymptotically flat spacetime geometry 453
Asymptotically flat spacetime geometry conformal treatment of infinity 917—921
Asymptotically flat spacetime geometry form of far from stationary fully relativistic source 456f
Asymptotically flat spacetime geometry form of in linearized theory 448ff
Asymptotically flat spacetime geometry in evaluation of Gaussian flux integral 462f
Asymptotically flat spacetime geometry key to defining mass and angular momentum 457ff
Asymptotically flat spacetime geometry “I weigh all that’s here” 475
Automatic conservation of source 404 408f 417
Background geometry defined by limiting procedure 479—480 (see also “Gravitational waves shortwave
Backscatter of waves off curvature 864f 869ff 957
Bar operation in linearized theory 436ff
Bar operation in shortwave formalism 967
Baryons conservation law for see under “Conservation laws”
Baryons mass density of 1069 1074
Baryons number density of 558
Base metric, in time-symmetric initial-value problem 535
Basis 1-forms as coordinate gradients 60ff
Basis 1-forms connection coefficients for 209 215 258f
Basis 1-forms dual to basis vectors 60f 202f 232 234
Basis 1-forms transformation laws for 68 203
Basis forms 2-forms and dual labeling thereof 151
Basis forms 3- and 4-forms for volume integrals 150
Basis vectors 50
Basis vectors as differential operators 229f
Basis vectors commutation coefficients for 204
Basis vectors connection coefficients for 209 258f
Basis vectors coordinate basis 230f (see also “Proper reference frame tetrad”)
Basis vectors coordinate vs. general basis 201—203
Basis vectors dual to basis 1-forms 60ff 232
Basis vectors in extenso 201—207
Basis vectors transformation laws for 68 201 203 230f
Bell bongs 55f 60 99 202 231
Bertotti — Robinson electromagnetic universe 845
Betti numbers, characterize connectivity 221
Bianchi identities applied to equations of motion 473
Bianchi identities as automatically fulfilled conservation law 405
Bianchi identities expressed in terms of curvature 2-form 362
Bianchi identities from coordinate-neutrality of Hilbert — Palatini variational principle 503
Bianchi identities in terms of boundary of a boundary, Chap 15
Bianchi identities model for, in geodesic identity 318
Bianchi identities proved 287
Bianchi identities required because geometrodynamic law-must not predict coordinates 409
Bianchi identities stated 221f 224 325f
Big Dipper, shape unaffected by velocity of observer 1160—1164
Binary generation of gravitational waves by 986 988ff 995
Binary star black holes as members of 886f
Binding eneray of orbits around black holes 885 911
Birkhoff’s theorem for Reissner — Nordstrem geometry 844ff
Birkhoff’s theorem for Schwarzschild geometry 843f
Bivector defined 83
Bivector in surface of Whitaker’s calumoid 125
Black body see under “Radiation”
Black hole 884—887
Black hole astrophysical aspects of 883—887
Black hole baryon number transcended by 876
Black hole brief summary of properties 620
Black hole dynamical processes 884ff
Black hole dynamical processes can never bifurcate 933
Black hole dynamical processes collision and coalescence of 886 924 939
Black hole dynamical processes gravitational waves from hole-hole collisions 886 939 982
Black hole experimental tests of general relativity using 1047 (see also “Black-hole dynamics laws gravitational”;
Black hole gravitational waves from collapse that forms 1041
Black hole history of knowledge of 620 623
Black hole in extenso, Chap 33
Black hole interactions with matter 885f
Black hole interactions with matter change of parameters of hole due to infall of particles 904—910 913
Black hole interactions with matter Cygnus X-I as an examplar of ix gravitational waves from matter falling into 885 904 982f 986
Black hole interactions with matter extraction of energy from 906 908
Black hole Kerr — Newman geometry as unique external field 863 875—877 esp
Black hole lepton number transcended by 640 876
Black hole mechanisms of formation 883—884
Black hole why deserve their name 872—875
| Black hole “hair on” 43 863 876
Black-hole dynamics, laws of 887f (see also “Second law of black-hole dynamics”)
Boost 67ff
Boundary of a boundary is zero 364—370
Boundary of a boundary is zero automatically conserve’s Cartan’s moment of rotation 377—378
Boundary of a boundary, route to Bianchi identities, Chap 15
Boundary of the boundary of a 4-simplex 380—381
Boundary operator 96
Boyer — Lindquist coordinates 877—880
Brackets, round and square, define symmetry 126
Bragg reflection, related to 1-forms 232
Brans — Dicke theory of gravity see “Gravitation theories
Brill — Hartle averaging process 970
Brownian forces 1038
Bubble-time derivative 497
Buffer zone, in analysis of departures from geodesic motion 476—480
Buoyant force 606
Calumoid, Whitaker’s. related to flux integrals 125
Canonical structure, metric and symplectic structure 126
Canonical variables, in Hamiltonian mechanics 125
Cartan structure equations 359
Carter’s fourth constant 899
Causal relationships in flat spacetime 48 51
Causal structure of curved spacetime 922ff
Causal structure of curved spacetime future horizons 923—924
Causal structure of curved spacetime global structure of horizons, analysis of 926—931 (see also “Global techniques” “Horizons”)
Causal structure of curved spacetime global structure of horizons, theorems about 924—925
Causality, principle of and the mechanism of radiation 110
Caustics, of a horizon 925
Cavendish experiment 1121f
Cavendish gravitational constant 1121ff
Cavendish gravitational constant dependence on chemical composition of gravitating bodies 1125
Cavendish gravitational constant dependence on velocity relative to “preferred universal rest frame” 1123—1124
Cavendish gravitational constant variations in, cause deviations from geodesic motion 1127—1128
Center of mass 161
Centrifugal forces 294
Centrifuge, in idealized redshift experiment 63f
Centroid 161
Cepheid variable stars pulsation of 632
Cepheid variable stars pulsation of as distance indicators 786
Cepheid variable stars pulsation of confused with H II regions in Hubble’s work 709
Cepheid variable stars pulsation of confusion resolved by Baade 710 760
Cepheid variable stars pulsation of period-luminosity relation discovered 758
Chain rule abstract 314—315
Chain rule for covariant derivative 252 257f 260f
Chandrasekhar limit 619
Charge as lines of force trapped in the topology of space 221 368 1200f
Charge as measured by tubes of force, in 2-form representation 107
Charge conservation see “Conservation laws charge”
Charge density-current 3-form 113f 151
Charge density-current 4-vector, Lorentz transformation of 68
Charge density-current Dirac’s representation, for particle in arbitrary motion 120f
Charge density-current dual representations 88 97f
Charge evaluated from flux integral 98
Charge of closed universe, meaningless integral for 457—458
chemical potential see under “Thermodynamics”
Chinese historical records of Crab supernova 11
Classical mechanics, correspondence with quantum mechanics 413
Classical theory, conceives of geometry and fields as measureable 13
Clock “paradox” 167
Clocks as tools in parametrization of geodesies 246
Clocks bad vs. good 26—27
Clocks ideal built on geodesies 396—399
Clocks ideal defined 393
Clocks ideal in Newton — Cartan theory 301
Clocks infinite sequence of needed as one approaches a singularity 813f
Clocks influence of acceleration on 164f 327 396
Clocks influence of tidal forces on 396
Clocks specific types of 28 393—396
Clocks stability of 28 1048
Closed form 114 (see also “Forms differential”)
Closure of universe see “Cosmological models”)
Clusters of galaxies origin of 766 769f
Clusters Virgo as source of gravitational waves 1042
Cold, catalyzed matter 624—626
Collapse, gravitational in one and two dimensions 867f
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical shell of dust 555—556
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star analyzed by examining exterior geometry 846—850 857
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star comovins coordinates for 857
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star decay of luminosity of 847 850 872
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star Eddington — Finklestein diagram for 849 864 873
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star embedding diagrams for 855f
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star equations governing adiabatic collapse 858f
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star Kruskal diagram for 848 855
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star models with zero pressure 859
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star models with zero pressure and uniform density 851—856 859
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star redshift of radiation from 847 849f 872
Collapse, gravitational of a spherical star surface of last influence 873f
Collapse, gravitational realistic 862f 883f
Collapse, gravitational realistic, at three levels: universe, black hole, quantum fluctuations 1201
Collapse, gravitational realistic, black box model of 1209 1213—1217
Collapse, gravitational realistic, collapse, pursuit, and plunge scenario 629
Collapse, gravitational realistic, creation of Kerr — Newman black hole by 882—883
Collapse, gravitational realistic, evolution of small perturbations from spherical symmetry 864—866
Collapse, gravitational realistic, gravitational waves emitted during 1041
Collapse, gravitational realistic, importance of and philosophical implications of 437 1196f
Collapse, gravitational realistic, in a dense star cluster 884
Collapse, gravitational realistic, inevitability of for massive stars 819
Collapse, gravitational realistic, issue of the final state 940 1196f
Collapse, gravitational realistic, Price’s theorem 866
Collapse, gravitational realistic, triggering of in late stages of stellar evolution 627 862
Collapsed star see “Neutron star Black
Collisions of particles in flat spacetime 19 69f
Comma-goes-to-semicolon rule 387—392 (see also “Equivalence principle”)
Commutation coefficients of basis vectors 204 243 314
Commutation coefficients of basis vectors calculated by exterior derivative of basis 1-forms 358f
Commutation coefficients of basis vectors for rotation group 243
Commutation, of observables on spacelike hypersurface 554
Commutator as closer of quadrilaterals 236 278
Commutator for normal and tangent to spacelike slice 517
Commutator for rotation group 332
Commutator Jacobi identity for 240
Commutator of covariant derivatives 276 389ff
Commutator of tangent vectors 204 206f 235—240
Commutator pictorial representation of 236—237
Compatibility of metric and covariant derivative 313ff 353f
Complexion, of electromagnetic field 108 482
Component manipulations see “Index manipulations”
Component notation, to remove ambiguity of slots 84
Components of 1-forms. introduced 61
Components of curvature tensor, introduced 34 37 40 42
Components of tensors, introduced 75
Components of vectors, introduced 8—10 50—51
Concepts of physics, defined by theory itself 71f
Conduction of heat 567
Conformal curvature tensor see under “Curvature formalism
Conformal part of 3-geometry, in York’s formulation of initial-value problem 540—541
Conformal transformation of infinity See under “Infinity”
Connection coefficients as components of covariant derivative 208f 256 261—262
Connection coefficients calculated from metric and commutators 210 216 314
Connection coefficients illustrated by great-circle navigation 212
Connection coefficients specialized to a coordinate basis called “Christoffel symbols” 210
Connection coefficients specialized to a coordinate basis contraction of in terms of metric 222
Connection coefficients specialized to a coordinate basis formula for, from Palatini variational principle 502
Connection coefficients specific cases of for 2-sphere 341 345
Connection coefficients specific cases of for flat 3-geometry, polar coordinates 213
Connection coefficients specific cases of for Newton — Cartan spacetime 291f 294 298
Connection coefficients specific cases of for plane, in polar coordinates 213 263
Connection coefficients specific cases of for proper reference frame of accelerated observer 330f
Connection coefficients specific cases of for Riemann normal coordinates 286f
Connection coefficients specific cases of for rotation group 264
Connection coefficients summarized 223
Connection coefficients symmetries of 213—214
Connection coefficients transformation law for 262
Connection coefficients unique, to make geodesies agree with straight lines of local Lorentz geometry 314f
Connection, measured by light signals and free particles 324 (see also “Covariant derivative”)
Connectivity at small distances 221
Connectivity charge as trapped lines of force 221 368 1200f
Connectivity of spacetime, in classical differential geometry 1204—1205
Conservation laws baryon number 558f 563ff
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



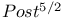 -Newtonian approximation and its relationship to radiation damping
-Newtonian approximation and its relationship to radiation damping