|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Misner C.W., Thorne K.S., Wheeler J.A. — Gravitation |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
Conservation laws baryon number applied to collapsing stars 858
Conservation laws baryon number applied to pulsating stars 691f
Conservation laws baryon number in PPN formalism 1088
Conservation laws electric charge 369f
Conservation laws electric charge as consequence of dd = 0 118
Conservation laws electric charge differential formulation of 88 568 570
Conservation laws electric charge integral formulation from differential via Stokes theorem 98 156
Conservation laws energv –momentum  in flat spacetime 132 146 152—155 in flat spacetime 132 146 152—155
Conservation laws energv –momentum  in terms of generalized exterior derivative 362f in terms of generalized exterior derivative 362f
Conservation laws energv –momentum  integral formulation in flat spacetime 142—146 integral formulation in flat spacetime 142—146
Conservation laws energv –momentum  tested in elementary particle physics 19 tested in elementary particle physics 19
Conservation laws energv –momentum  to be interpreted as automatic, via “wiring up” to geometry 364 367f 371 404—407 to be interpreted as automatic, via “wiring up” to geometry 364 367f 371 404—407
Conservation laws energv –momentum  transition to curved spacetime 386f 390 transition to curved spacetime 386f 390
Conservation laws energv –momentum  various mathematical representations for 379 various mathematical representations for 379
Conservation laws equivalence of differential and integral formulations of 146
Conservation laws for test-particle motion in any spherical, static geometry 681
Conservation laws for test-particle motion in Kerr metric and electromagnetic field 898f
Conservation laws for test-particle motion in Schwarzschild geometry 655—658
Conservation laws for test-particle motion related to Hamilton’s principle 654
Conservation laws for test-particle motion related to Killing vector field 651
Conservation laws total mass-energy and 4-momentum of a gravitating source 455 468—471
Constants, fundamental limits on deviations from constancy 1061—1063
Constants, fundamental listed, endpapers 1061
Constraint, as signaling reduced number of degrees of freedom 528f
Constraints, first and second class, in Dirac’s formulation of geometrodynamics 486
Constructive interference as shortest leap from quantum to classical 1185
Constructive interference behind Hamilton — Jacobi formulation of mechanics and geometrodynamics 423f
Constructive interference in particle mechanics and in geometrodynamics, compared 1186f
Continuity, equation of 152ff 565
Contraction of tensor 82
Contravariant components 76 201—207 312
Controlled ignorance, philosophy of 452f 996
Convection, in supermassive stars 600
Coordinate patch, concept introduced 10—12
Coordinate singularities see “Singularities coordinate”
Coordinate systems asymptotically Minkowskiian 463
Coordinate systems Boyer — Lindquist 877—880
Coordinate systems comoving, for collapsing star 857
Coordinate systems comoving, for universe 715ff
Coordinate systems curvilinear, in linearized theory 441
Coordinate systems Eddington — Finklestein 828—831 849
Coordinate systems Euclidean 22f
Coordinate systems Fermi normal 332
Coordinate systems for any spherical system 616f
Coordinate systems Galilean 289 291—298 414
Coordinate systems isotropic, for Schwarzschild geometry 840
Coordinate systems isotropic, for static, spherical system 595
Coordinate systems Kerr 879f
Coordinate systems Kerr — Schild 903
Coordinate systems Kruskal — Szekeres 827 831—836
Coordinate systems local Lorentz 207
Coordinate systems Lorentz 22f
Coordinate systems Minkowski same as “Lorentz”
Coordinate systems nature of, deducible from metric 595f
Coordinate systems Novikov 826f
Coordinate systems of accelerated observers 172—176
Coordinate systems of post-Newtonian formalism 1073f 1082—1087 1089 1091 1097
Coordinate systems Regge — Wheeler, same as Tortoise Riemann normal 285ff 329—332
Coordinate systems Schwarzschild, for pulsating star 689
Coordinate systems Schwarzschild. for Schwarzschild geometry 607
Coordinate systems Schwarzschild. for static, spherical systems 597
Coordinate systems Tortoise, for Schwarzschild geometry 663 665—666
coordinates 5—10
Coordinates canonical, in context of differential forms and symplectic structure 125f
Coordinates must not be predicted by geometrodynamic law 409
Coordinates preferred, in Newton, Minkowskii, and Einstein spacetime 296
Coordinates rotation and translation of in Newton — Cartan theory 294f
Coplanarity, test for 281
Coriolis forces 165 175 294 327 332
Correspondence principles 412f
Correspondence, between 1-forms and vectors 310 (see also “Vectors”; “Forms differential”)
Cosmic censorship 937
Cosmic gravitational-wave background 712 736f 764f
Cosmic microwave radiation 712f 764ff
Cosmic microwave radiation existence of, refutes steady-state cosmological model 770
Cosmic microwave radiation incompatible with “turnaround universe” 751
Cosmic microwave radiation isotropy of 703
Cosmic microwave radiation prediction of by Gamow et ai 760
Cosmic neutrino background 712 736f 764f
Cosmic rays 757
Cosmic rays evolution of mean density of 798
Cosmic rays observations refute Klein — Alfven cosmological models 770
Cosmological constant 410ff
Cosmological constant Einstein’s invention and retraction of 410f 707 758
Cosmological constant influence on evolution of universe 747 771 774
Cosmological models anisotropic, Chap 30
Cosmological models Brans — Dicke 770
Cosmological models closure of universe as boundary condition 1181
Cosmological models closure of universe related to Mach’s principle 543 549
Cosmological models de Sitter 745 758
Cosmological models Einstein static universe 746f 750 758f
Cosmological models flat, closed, static 3-torus model 284
Cosmological models Friedmann 752
Cosmological models Friedmann arbitrariness in expansion factor 720ff
Cosmological models Friedmann assumed equation of state 713 726
Cosmological models Friedmann assumption of homogeneity and isotropy 703 713
Cosmological models Friedmann assumption that matter and radiation exchange negligible energy 726ff 765
Cosmological models Friedmann assumption that pressure of mafter can always be neglected 726 728
Cosmological models Friedmann coordinate system constructed 715ff
Cosmological models Friedmann critical density for closure of universe if  782 782
Cosmological models Friedmann curvature parameter  721 721
Cosmological models Friedmann density and pressure expressed in terms of expansion factor 727
Cosmological models Friedmann discovery of by Friedmann and Lemaitre 751 758
Cosmological models Friedmann dynamic equation (for  ) 729 ) 729
Cosmological models Friedmann dynamic equation derivable from initial-value equation plus first law of thermodynamics 729
Cosmological models Friedmann dynamics of early stage independent of k (unaffected by closure) 742f
Cosmological models Friedmann Einstein tensor for 728
Cosmological models Friedmann element, various forms for 721ff 731 759
Cosmological models Friedmann embedding diagrams 723 725
Cosmological models Friedmann expansion factor introduced 718
Cosmological models Friedmann expansion factor renormalized 721f
Cosmological models Friedmann first law of thermodynamics for 726ff
Cosmological models Friedmann Friedmann assumption of perfect-fluid stress-energy tensor 711f
Cosmological models Friedmann implications of homogeneity and isotropy 714f 720ff
Cosmological models Friedmann implications of parameter values for future of universe 747 771 773f
Cosmological models Friedmann initial-value equation (for  ) 744 ) 744
Cosmological models Friedmann isotropy implies homogeneity 715 723
Cosmological models Friedmann observer’s parameters vs. relativity parameters 771ff
Cosmological models Friedmann orthonormal frames attached to matter 728
Cosmological models Friedmann possible 3-geometries for homogeneous hypersurfaces 720—725
Cosmological models Friedmann small perturbations of 800f (see also “Hubble constant” “Density “Deceleration
Cosmological models Friedmann time parameters:  730—732 730—732
Cosmological models Friedmann topology not unique 725
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  in extenso 733—742 in extenso 733—742
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , causal isolation of various regions from each other 740ff , causal isolation of various regions from each other 740ff
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , compared with Newtonian cosmological models 707f , compared with Newtonian cosmological models 707f
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , concrete numbers for a typical model 738 , concrete numbers for a typical model 738
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , coordinate diagram for 741 , coordinate diagram for 741
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , critical density for closure 710 782 , critical density for closure 710 782
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , effective potential for evolution of 706 , effective potential for evolution of 706
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , Einstein’s arguments favoring closure 704 , Einstein’s arguments favoring closure 704
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , embedding diagram 723f , embedding diagram 723f
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , first law of thermodynamics applied to 705 726ff , first law of thermodynamics applied to 705 726ff
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , geometry of 3-sphere hypersurfaces 704 721 723f , geometry of 3-sphere hypersurfaces 704 721 723f
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , inevitability of recollapse 707 , inevitability of recollapse 707
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , initial-value equation for 537 705f 729 733 , initial-value equation for 537 705f 729 733
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , matter-dominated era 733ff 738—742 , matter-dominated era 733ff 738—742
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , mocked up by Schwarzschild-lattice universe 739f , mocked up by Schwarzschild-lattice universe 739f
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , propagation of signals around universe 741 750 , propagation of signals around universe 741 750
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , radiation-dominated era 733—737 740ff , radiation-dominated era 733—737 740ff
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , radius of defined 704 , radius of defined 704
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , radius of maximum expansion 705 , radius of maximum expansion 705
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , solutions of field equations for 734f , solutions of field equations for 734f
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , topology not unique 725 , topology not unique 725
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , track-1 overview 704—711 , track-1 overview 704—711
Cosmological models Friedmann, closed  , volume of 724 , volume of 724
Cosmological models Friedmann, flat and open  , embedding diagram 724f , embedding diagram 724f
Cosmological models Friedmann, flat and open  , geometry of homogeneous hypersurfaces 721 724f , geometry of homogeneous hypersurfaces 721 724f
Cosmological models Friedmann, flat and open  , matter-dominated era 743f , matter-dominated era 743f
Cosmological models Friedmann, flat and open  , radiation-dominated era 742f , radiation-dominated era 742f
| Cosmological models Friedmann, flat and open  , Solutions of field equations for 742 , Solutions of field equations for 742
Cosmological models Friedmann, flat and open  , topology not unique 725 , topology not unique 725
Cosmological models Friedmann, plus cosmological constant  , dynamical evolution of 744—747 , dynamical evolution of 744—747
Cosmological models Friedmann, plus cosmological constant  , effective potential for evolution of 744 746 748f , effective potential for evolution of 744 746 748f
Cosmological models Friedmann, plus cosmological constant  , initial-value equation (for , initial-value equation (for  ) 744 ) 744
Cosmological models Friedmann, plus cosmological constant  , special cases of 745ff 750f , special cases of 745ff 750f
Cosmological models hesitation universe 750
Cosmological models hierarchic (island) universe 748f 770
Cosmological models inhomogeneous but spherical models 804
Cosmological models inhomogeneous Gowdy models 804
Cosmological models inhomogeneous, Chap 30
Cosmological models Kasner model 801 805ff
Cosmological models Klein — Alfven model 748 770
Cosmological models mixmaster 805—814
Cosmological models Newtonian 707f 759
Cosmological models primordial chaos in big-bang models 769 802ff
Cosmological models primordial chaos in big-bang models in extenso, Chap 30
Cosmological models primordial chaos in big-bang models primordial black holes produced by 884 (see also “Isotropy and homogeneity of universe possible
Cosmological models Schwarzschild lattice universe 739f
Cosmological models steady-state universe 745 750 770
Cosmological models turnaround universe 750f (see also “Cosmology: history of universe according to “standard big-bang model””)
Cosmology, expansion of universe, discovery of by Hubble 759 792—794
Cosmology, expansion of universe, prediction of by Friedmann, de Sitter, and Weyl 758 776
Cosmology, expansion of universe, removed motive for cosmological term 410—411
Cosmology, expansion of universe, was greatest prediction of Einstein’s theory 411
Cosmology, expansion of universe, what expands and what does not 719 739
Cosmology, expansion of universe, will Universe recontract 747 771 774
Cosmology, expansion of universe, “Where is the new space added?” 719 739
Cosmology, history of man’s ideas and knowledge of the universe 752—762
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” complete thermal equilibrium at  second 736 763f second 736 763f
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” condensation of stars, galaxies, and clusters of galaxies 766 769 800
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” decoupling of gravitational waves and neutrinos 736 764
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” expansion forever vs. recontraction 747 771 774
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” in extenso, Chap 28
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” initial singularity 769f
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” past history not much affected by k (by geometry of hypersurfaces) 742f 763
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” possible roles of primordial chaos 769 803f 816
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” recombination of pairs 736f 764
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” thermal interaction of matter and radiation during expansion 765f
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” transition from matter dominance to radiation dominance 74If 765f
Cosmology, history of the universe according to the “standard big-bang model,” what “preceded” initial singularity? 769
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model 780—798
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, abundances of elements 765
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, angle-effective distance vs. redshift (“lens effect of universe”) 795f
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, comparison of ages deduced by various methods 797f
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, comparison of temperature, redshift and emission times for cosmic background radiations 737
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, distance-redshift relation, derivation of 780f
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, distance-redshift relation, observational data 781 785—788 792ff
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, evolution of quasar population 767f 770
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, experimental tests of general relativity using cosmological observations 1047
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, magnitude-redshift relation, derivations of 782—785 794
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, magnitude-redshift relation, observational data 788—791
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, mean mass density of universe 710ff 796f
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe abundances of elements 765
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe age deduced from expansion rate 709f 797
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe ages of oldest stars 709 797f
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe ages of rocks and meteorites 759 761 798
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe cosmological expansion 772 775f 785—788 793f
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe deceleration parameter 785 788—791
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe density parameter 796f
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe energy and pressure in kinetic motions of galaxies and stars 711
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe entropy per baryon 766
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe homogeneity on large scales 703 815
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe isotropy on large scale 703 801 815
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe mean density in electromagnetic radiation 712
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe mean density of cosmic rays 712 757 798
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe mean density of intergalactic matter 712 761f 797
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe mean density of luminous matter 710f 761
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe quasar population, evolution of 767f 770
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe rotation, observational limits on 939
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, observed properties of universe “fine-scale” structure 703 (see also “Cosmic microwave radiation” “Hubble
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, source counts (number-flux relation) 798
Cosmology, observational probes of standard model, summary of 797f
Cosmology, speculations about initial and final states of universe 707 1209 1213—1217
Coulomb field, “pancaking” of for fast charged particle 124
Coulomb force, from electromagnetic 4-potential 122
Coupling of fields to matter, direct vs. indirect 1063f
Covariance, general see «General covariance”
Covariant components of a tensor 76 201—207 312
Covariant derivative additivity of 252
Covariant derivative algebra of 250—261
Covariant derivative as a machine with slots 253ff
Covariant derivative chain rule for 214 250 252 257f 260f
Covariant derivative commutes with contraction 214
Covariant derivative compatibility with metric 215f 313ff 353f
Covariant derivative component calculations of 215
Covariant derivative connection coefficients as its components 210 256 261f
Covariant derivative defined by parallel transport 208 249
Covariant derivative fundamental equations summarized 223—224
Covariant derivative in a hypersurface 510
Covariant derivative is not a tensor 253 255f
Covariant derivative noncommutation of two covariant derivatives 389ff
Covariant derivative of tensor densilies 501f
Covariant derivative pictorialized 209 212
Covariant derivative regarded as a gravitational field 387 (see also “Connection coefficients”; “Parallel transport”; “Rotation coefficients”
Covariant derivative rotation 1-forms constructed from 349ff 359f
Covariant derivative semicolon notation for, introduced 210
Covariant derivative symmetry of (“no torsion”) 250 252 353f
Crab nebula, ii 619f 760
Cross section collisional 69
Cross section Lorentz transformation of 70
Crystallography, related to 1-forms 232
Current 4-vector see “Charge density-current”
Curvature (see also “Bianchi identities”; “Gauss — Weingarten equations”; “Gauss — Codazzi equations”
Curvature of spacetime can be great locally even if average is near zero 220 (see also “Geodesic deviation” “Tidal “Spacetime
Curvature of spacetime coupling to moments of a macroscopic object 391f 476—480 1120f
Curvature of spacetime coupling to physics in equivalence principle 389—392
Curvature of spacetime generation of by mass-energy 37—44 Chap.
Curvature of spacetime implied by gravitational red shift 187ff
Curvature of spacetime measured by geodesic deviation 29—37 195f 270—275
Curvature of spacetime measured by gravity gradiometer 400—403
Curvature of spacetime modeled by surface of apple 4f
Curvature of spacetime procedure-in-principle to measure 72
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds 2-hyperboloid 334
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds 2-sphere 30 341
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds 2-surface of revolution 339f
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds 3-hyperboloid 343 721
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds 3-sphere 343 721
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds 3-surface of “constant curvature” 721
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds Friedmann cosmology 345 348 355ff 537 728
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds gravitational wave, exact, plane 346f 444
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds gravitational wave, linearized 948
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds linearized theory, any metric 438
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds Newton — Cartan spacetime 290
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds Newtonian sphere of uniform density 39f
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds Newtonian spherical vacuum field 37
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds Schwarzschild metric 821ff
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds spherical, dynamic line element 361f
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds spherical, static line element in Schwarzschild coordinates 360f
Curvature tensors for specific manifolds world tube of a collapsing star’s surface 853
Curvature, constant 3-geometries of 720—725
Curvature, formalism of Bel — Robinson (tidal) tensor 381f
Curvature, formalism of conformal (Weyl) tensor in Nordstrom — Einstein — Fokker theory of gravity 429 431
Curvature, formalism of conformal (Weyl) tensor introduced 325 327
Curvature, formalism of conformal (Weyl) tensor Petrov — Pirani algebraic classification of 1165
Curvature, formalism of conformal (Weyl) tensor principal null congruences of 902
Curvature, formalism of conformal (Weyl) tensor spinor representation of 1154f
Curvature, formalism of conformal (Weyl) tensor vanishes in 3 dimensions 550
Curvature, formalism of curvature 2-form 348—363
Curvature, formalism of curvature 2-form picture of, for 2-sphere 337
Curvature, formalism of curvature 2-form picture of, for pith helmet 338
Curvature, formalism of curvature operator 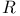 as machine-with-slots 351f as machine-with-slots 351f
Curvature, formalism of curvature operator 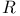 as twice-applied exterior derivative 351 as twice-applied exterior derivative 351
Curvature, formalism of curvature operator 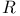 in context of Newton — Cartan theory 299 in context of Newton — Cartan theory 299
Curvature, formalism of curvature operator 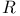 introduced 271 introduced 271
Curvature, formalism of curvature operator 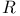 regarded as bivector-valued 2-form 376—380 regarded as bivector-valued 2-form 376—380
Curvature, formalism of Einstein tensor as trace of double dual of Riemann 325f 376
Curvature, formalism of Einstein tensor conservation of, from boundary of a boundary 377ff
Curvature, formalism of Einstein tensor contracted Bianchi identity (“conservation of Einstein”) 325 377ff
Curvature, formalism of Einstein tensor formula for mixed components in terms of Riemann components 343f
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



 in flat spacetime
in flat spacetime 

 )
)  )
) 
 in extenso
in extenso  , embedding diagram
, embedding diagram  , dynamical evolution of
, dynamical evolution of  second
second as machine-with-slots
as machine-with-slots