јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Michael Baer, Gert D.Billing Ч Advances in Chemical Physics, The Role of Degenerate States in Chemistry, Vol. 124
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Advances in Chemical Physics, The Role of Degenerate States in Chemistry, Vol. 124јвторы: Michael Baer, Gert D.Billing јннотаци€: Edited by Nobel Prize-winner Ilya Prigogine and renowned authority Stuart A. Rice, the Advances in Chemical Physics series provides a forum for critical, authoritative evaluations in every area of the discipline. In a format that encourages the expression of individual points of view, experts in the field present comprehensive analyses of subjects of interest.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2002 оличество страниц: 824ƒобавлена в каталог: 05.08.2009ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Visicot, J.P. 434(5) 500 Vogel, W. 204(92) 208(92) 211(92) 213(92) 275 Volobuev, Y. 399(213 215) 403(213 215) 430 Von Busch, H. 248(310) 281 von Neumann, J. 5(19) 37 215(242) 226(255) 261(242) 280 558(3) 561(3) 580 von Niessen, W. 381(170) 393(170) 429 Voronin, A.I. 696(71) 719(88) 740Ч741 Vorontsov, Yu.I. 208(140 142) 277 Voter, A.F. 435Ч436(24) 447(39) 453(39) 455(24) 474(24) 493(39) 500Ч501 Voth, G. 360(75) 426 Vourdas, A. 207(132) 276 Vrakking, M.J.J. 212(200) 278 458(61Ч62) 460(61Ч62) 487(61Ч62) 501 Vreven, T. 360(80 86Ч87) 406(233) 408(80) 410(86) 411Ч412(87) 426 430 Vrtilek, J.M. 633Ч634(164) 658 Wagh, A.G. 207(123Ч124) 208(124) 248(123) 276 Walch, S.P. 571(28) 581 Walmsley, I.A. 204(88 92 96) 208(92) 211(88 92 96) 213(92) 275 Walsh, A.D. 617(70) 655 Walsworth, R.L. 249(316) 282 Walter, J. 499(140) 504 Walton, A. 380(157Ч158) 428 Wang, I. 360(66) 371(66) 425 Wang, J. 3(17) 20(17) 37 248(310) 281 Wang, L.C 118(129) 142 Wang, L.S. 625(136) 657 Wang, P.-R. 624(127) 657 Wang, W. 633Ч634(164) 658 Warhurst, E. 435(17) 447(17) 494(17) 500 Warshel, A. 359(61Ч62) 360(67) 371(67) 411(241) 425 430 Waschewsky, G.C.G 234(280) 281 Wash, P.W. 234(280) 281 Watson, G.N. 25(32) 34(32) 37 Watson, J.K.G. 610(41Ч42) 654 Wave function, conical intersection, anchors, molecules and independent quantum species 440Ч441 Wave function, conical intersection, two-state chemical reactions 437Ч438 Wave function, crude Born Ч Oppenheimer approximation, basic principles 507Ч512 Wave function, crude Born Ч Oppenheimer approximation, Coulomb potential derivatives 527Ч542 Wave function, crude Born Ч Oppenheimer approximation, Coulomb potential derivatives, first-order derivatives 529Ч535 Wave function, crude Born Ч Oppenheimer approximation, Coulomb potential derivatives, second-order derivatives 535Ч542 Wave function, degenerate states chemistry xiiЧxiii Wave function, direct molecular dynamics, propagation mechanisms 422Ч423 Wave function, direct molecular dynamics, vibronic coupling, diabatic representation 384Ч386 Wave function, electron nuclear dynamics (END), basic ansatz 330Ч333 Wave function, electron nuclear dynamics (END), molecular systems, final-state analysis 342Ч349 Wave function, electron nuclear dynamics (END), time-dependent variational principle (TDVP) 328Ч330 Wave function, electronic states, adiabatic-to-diabatic transformation, two-state system 303Ч309 Wave function, geometric phase theory, eigenvector evolution 11Ч17 Wave function, molecular systems, component amplitude analysis, cyclic wave functions 224Ч228 Wave function, molecular systems, phase factors 205Ч214 Wave function, non-adiabatic coupling, Born Ч Oppenheimer approximation 187Ч191 Wave function, non-adiabatic coupling, semiclassical calculation, 164Ч167 Wave function, permutational symmetry, electronic wave function 680Ч682 Wave function, permutational symmetry, rotational wave function 683Ч687 Wave function, permutational symmetry, rovibronic/vibronic wave functions 682Ч683 Wave function, permutational symmetry, total molecular wave function 661Ч668 674Ч678 Wave function, permutational symmetry, vibrational wave function 687Ч692 Wave function, phase-change rule, loop construction, coordinate properties 443Ч446 Wave function, quantum theory 199Ч205 Wave function, Renner Ч Teller effect, triatomic molecules 587Ч598 Wavepacket reconstruction, direct molecular dynamics, adiabatic systems, initial conditions 373Ч377 Wavepacket reconstruction, direct molecular dynamics, nuclear motion Schroedinger equation 366Ч373 Wavepacket reconstruction, direct molecular dynamics, propagation mechanisms 422Ч423 Wavepacket reconstruction, direct molecular dynamics, theoretical background 357Ч361 Wavepacket reconstruction, molecular systems, component amplitude analysis, expanding waves 230Ч232 Wavepacket reconstruction, molecular systems, component amplitude analysis, frozen Gaussian approximation 229Ч230 Wavepacket reconstruction, molecular systems, component amplitude analysis, one-dimensional free particles 229 Wavepacket reconstruction, molecular systems, component amplitude analysis, reciprocal relations 216Ч217 Wavepacket reconstruction, techniques 211Ч212 Weber, T. 200(21) 273 Wei, H. 611(46) 654 Weide, K. 366(117) 427 Weinacht, T.G 200(19) 204(19 95) 211(95) 273 275 Weinberg, S. 203Ч204(70) 213(70) 250(70) 275 Weiner, B. 337(25) 352 Weingart, O. 411(242) 430 Weis, B. 621(88) 622(88 96) 655Ч656 Weiss, R. 359(61Ч62) 425 Welge, K.H. 167(80 82 84Ч85 87) 196 Welsch, D.-G. 204(92) 208(92) 211(92) 213(92) 275 Wensmann, A. 402Ч403(222) 430 Wenzel, W. 491(121) 503 Werner, H.-J. 41(6) 41(49) 82(49) 138 140 285(39 41) 321 363(98) 381(173) 385(184) 393(173) 405(231) 427 429Ч430 481(93) 502 506(1) 555 621(88) 622(88 92) 655Ч656 Weyl, H. 204(103) 276 Wheeler, J.A. 339(32) 352 Whetten, R. 381(162) 428 Whetton, R.L.K. 3(16) 20(16) 32(16) 37 White, L.S. 458(60) 487(60) 501 Whiteley, T.W.J. 285(40) 321 Whitesides, T.H. 481(94) 502 Whitham, G.B. 265(325) 282 Whitney, R.S. 210(176) 278 Whittaker, E.T. 25(32) 34(32) 37 Whitten, R.C. 106(123) 142 661(31) 739 Widmark, P.-O. 363(97) 427 Wiener, N. 219(248) 280 Wienkoop, M. 624(126) 656 Wigner function, direct molecular dynamics, adiabatic systems 375Ч377 Wigner function, direct molecular dynamics, Gaussian wavepackets and multiple spawning 402 Wigner function, direct molecular dynamics, recent studies 415 Wigner function, permutational symmetry, dynamic Jahn Ч Teller and geometric phase effects 708Ч711 Wigner rotation matrix, non-adiabatic coupling, adiabatic-to-diabatic transformation matrix 89Ч92 Wigner, E.P. 5(19) 37 89(108) 141 199(5) 213(224) 226(255) 273 279Ч280 374(137) 375(137 140) 428 558(3) 561(3) 580 661(30) 669(30) 720(93) 739 741 Wilczek, F. 204(77Ч79) 209(78) 250(77Ч79) 253(79) 270(78) 275 Wilhelm, T. 410(240) 430 Williams, B.A. 472(79) 502 Williams, R.M. 204(89) 208(89) 211(89) 275 Wilsey, S. 459(65) 490(65) 502 Wilson, E.B. 610(39Ч40) 654 Wilson, K. 374(135) 428 Windus, T. 363(96) 426 Winnewisser, B.P. 626(160) 657 Winterstetter, M. 506(4) 555 WKB formula, electron nuclear dynamics (END), molecular systems 340Ч342 WKB formula, electronic states, triatomic quantum reaction dynamics 318 WKB formula, molecular systems, component amplitude analysis, phase-modulus relations 218 Woeste, L. 3(16) 20(16) 32(16) 37 707(78) 740 Wolf, E. 200Ч201(28) 206(28) 208(28) 211(28) 264(28) 274 Wolf, J.-P. 707(78) 740 Wolfrum, J. 365(111) 427 Wolicox, C.F. 458(59) 501 Wond, M.E. 363(95) 426 Woodward Ч Hoffman method, conical intersection research 494Ч496 Woodward Ч Hoffman method, phase-change rule, pericyclic reactions 450 Woodward Ч Hoffman method, phase-change rule, pi bond reactions 453 Woodward, R.B. 450(52) 479(52) 493Ч494(52) 501 Worth, G.A. 357(20) 364(20) 365(109Ч110) 381(109) 390(109) 393(109 190 192 195) 423(20) 424 427 429 487(100) 491(100) 503 Woywod, C: 285(38) 321 381(173Ч174) 385(187) 393(173Ч174) 429 479Ч480(92) 502 506(1) 555 Wrede, E. 167(80 82Ч87) 196 Wright, E.M. 210(171) 214(171) 278 Wright, S.C. 448(50) 501 Wright, T.G. 467(77) 469Ч470(77) 502 Wu, G.S. 326(7) 352 Wu, T.T. 43(76) 140 209(156) 234(156) 277 506(10) 555 Wu, T.Y. 212(211) 248(211) 279 Wu, X. 145(47) 150(47) 164(47) 195 Wu, Y.-S.M. 41(45) 106(121Ч122) 140 142 145(44Ч46) 150(44Ч46) 164(44Ч46) 167(46) 195 242(289) 281 285(33Ч37) 290(33) 310(33Ч37) 315Ч319(33) 320 668(48Ч49) 716(83) 739Ч740 Wurzer, A.J. 410(240) 430 Wyatt, R.E. 144(12) 145(47) 150(47) 164(47) 167(80) 194Ч196 207(128) 276 285(29) 320 364(106Ч107) 427 Xantheas, S. 388(189) 410(189) 429 438(33) 487(33) 500 558(5) 576(35) 580Ч581 Xiao, L. 397(205) 399(205) 403(205) 429 Xing, X. 484(99) 503 Xu, H. 145(51Ч52) 195 Xu, R. 82(96) 118(96) 141 Xu, Z. 359(56) 425 Xu, Z.-R. 13(25) 28(25) 37 41(11) 42Ч43(11) 73(11) 104(11) 107(11) 109(11) 139 145(34) 195 233(271Ч272) 280 Xu, Z.R. 660(4Ч8 11Ч12) 668(4Ч5 11Ч12) 693(5) 701Ч703(11) 704(12) 705(11Ч12) 706(11 77) 708(12) 709(11) 713(4Ч5 7Ч8) 715(4) 716(5) 717(6 8) 719Ч721(4Ч5) 738 740 Yahalom, A. 13(26) 28(26) 37 41(12 24 28) 42Ч43(12) 71(12) 73(12) 80(24) 99(12) 102(12) 104(12) 109(12) 111(12) 117(12) 118(126) 139 142 200(29Ч35 37Ч38) 202(61) 203(73) 204(34) 206(30Ч32) 210(30Ч32) 213(34) 222(29) 229(29) 242(29Ч32) 248(61) 264(31 33) 271(33) 274Ч275 359(57) 425 Yamaguchi, M. 455(56) 501 506(9) 555 Yamamoto, N. 406(233) 430 Yamanaka, T. 381(171) 429 Yamashita, K. 622(96) 656 Yamazaki, I. 381(171) 429 Yan, F. 210(167) 277 Yang Ч Mills fields, degenerate states chemistry xiЧxiii Yang Ч Mills fields, molecular systems, alternative derivation 254Ч255 Yang Ч Mills fields, molecular systems, curl condition 252Ч253 Yang Ч Mills fields, molecular systems, future implications 255Ч257 Yang Ч Mills fields, molecular systems, Hamiltonian formalism, observability in 259Ч261 Yang Ч Mills fields, molecular systems, nuclear Lagrangean equation 249Ч250 Yang Ч Mills fields, molecular systems, pure vs. tensorial gauge fields 251Ч252 Yang Ч Mills fields, molecular systems, tensorial field vanishing criteria 257Ч259 Yang Ч Mills fields, molecular systems, untruncated Hilbert space 253Ч254 Yang Ч Mills fields, non-adiabatic coupling 42Ч44 Yang Ч Mills fields, non-adiabatic coupling, curl condition 92Ч97 Yang Ч Mills fields, non-adiabatic coupling, future research applications 118Ч119 Yang Ч Mills fields, theoretical background 203Ч205 Yang, B. 625(146) 639(146) 657 Yang, C.N. 42(58) 43(76) 93(58) 140 203(66) 209(156) 213(66) 234(156) 250(66) 275 277 Yang, L. 210(167) 277 Yang, X. 211(186) 248(186) 278 Yang, X.F. 211(186) 248(186) 278 Yarkony, D.R. 10(23) 37 41(46) 42Ч43(64Ч71) 71(66) 97(64Ч71) 104(64Ч71) 109(64) 118(64Ч71) 140 202(50 53) 233(270 273) 234(273 277 283) 236(285) 242(273 283) 246Ч247(270) 274 280Ч281 285(43 54) 290(43 65Ч68) 297(43) 301(54 77Ч82) 303(84) 308(84) 321Ч322 359(55) 382(176Ч178) 385(55) 405(232) 406(232 234) 425 429Ч430 434(11) 471(11) 488(108Ч109) 500 503 558(1 4 7) 559(8Ч10 12) 560(17) 561(8) 563(12) 564(7) 565(7 17) 567(18Ч21) 568(10) 569(20 23) 570(10) 571(8 26Ч27 29Ч30) 572(30Ч32) 573(33) 576(23) 580Ч581 660(22Ч23) 715Ч716(81) 739Ч740 Yoshihara, K. 381(171) 429 Yu, H.G. 233(271) 280 285(30) 320 660(1Ч2 4Ч8 11 27) 661(2) 668(2 11) 699(27) 701Ч703(11) 705Ч706(11) 709(11) 713(2) 716(1) 738Ч739 Zakrzewski, V.G. 363(95) 426 Zare, R.N. 145(49Ч52) 195 286(56Ч59) 321 341(39Ч40) 348(52) 353 613(59) 655 Zeh, H.D. 204(101) 212(101) 276 Zeidler, D. 211(183) 278 Zeilinger, A. 206(119) 207(129) 276 Zener, C. 67(88) 141 284(4 7) 320 397(209) 430 Zeroth-order approximation, crude Born Ч Oppenheimer approximation, basic principles 510Ч512 Zeroth-order approximation, crude Born Ч Oppenheimer approximation, hydrogen molecule, minimum basis set calculation 547Ч550 Zeroth-order approximation, Renner Ч Teller effect, tetraatomic molecules 629Ч631 Zeroth-order approximation, Renner Ч Teller effect, tetraatomic molecules, perturbative handling, delta electronic states 647Ч653 Zeroth-order approximation, Renner Ч Teller effect, tetraatomic molecules, perturbative handling, pi electronic states 644Ч646 Zeroth-order approximation, Renner Ч Teller effect, triatomic molecules 596Ч598 Zewail, A.H. 211(179) 278 326(5) 352 434(4) 458(64) 487(64) 500Ч501 Zhang, D. 361(94) 426 Zhang, D.H. 660(15) 739 Zhang, J.Z.H. 285(29 31) 320 660(15) 739 Zhang, W.M. 212(207) 279 Zhu, C. 667(90) 141 Zhu, W. 285(31) 320 Zhu, Y.F. 625(135) 657 Zigmund, A. 224(254) 280 Zilberg, S. 211(192) 248(192) 278 435(25) 436(27Ч28) 438(28) 447(25 40Ч41) 448(27Ч28 40 48Ч49) 449(28 51) 453(49) 483(28 49 98) 492(40Ч41) 496(138) 500Ч501 503Ч504 Zimmerman, H. 357(12) 424 435(20Ч21) 448(21) 450(21) 453(20) 494(20) 500 Zimmermann, H.E. 459(66) 482(97) 502 Zubairy, M.S. 201(41) 206Ч207(41) 274 Zuber, J.-B. 203(68) 204(68) 250(68) 275 Zucchetti, A. 204(92) 208(92) 211(92) 213(92) 275 Zucchini, G.L. 481Ч482(95) 502 Zulicke, L. 664(40) 739 Zuniga, J. 661(35) 739 Zurek, W.H. 212(216) 279 Zwanziger Ч Grant effect, phase-change rule, cyclopentadienyl cation (CPDC) 471Ч472 Zwanziger, J.W. 3(16) 20(16) 22(30) 32(16) 37 41(22) 68(22) 71(22) 117(22) 139 228(256) 232(265) 233(256) 245(256) 280 471(78) 502 Zygelman, B. 203(75) 204(80) 250(80) 275 УIsomorfic HamiltonianФ, Renner Ч Teller effect, triatomic molecules 618 УTracingФ techniques, molecular systems, multidegenerate nonlinear coupling, continuous tracing, component phase 236Ч241 УTracingФ techniques, molecular systems, multidegenerate nonlinear coupling, research background 234
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



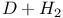 reaction
reaction