|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Branden C., Tooze J. Ч Introduction to protein structure |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Proteinase inhibitors, affinity and specificity optimization 361Ч363
Proteinase, families 205Ч206 (see also УSerine proteinasesФ)
Proteolytic degradation, loop regions 22
Protofibrils 283
Protofilaments 283
Proton abstraction 54 54F
Proton channel, bacteriorhodopsin 227 228F
Proton pump 227
Proton pump, light-driven, bacteriorhodopsin as 227Ч228 229F
Psi (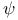 ) angle 8 9 14 ) angle 8 9 14
Psi (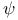 ) angle, Ramachandran plot 9 9F 10 ) angle, Ramachandran plot 9 9F 10
PSTAIRE helix 107F 108 108F 109F 278
Ptashne, Mark 135 190
Pulse amide hydrogen-deuterium exchange 95
PurR 143
PurR, repressor 144
pY+3 pocket 274 277
Pyrrol rings 238
Pyruvate kinase, domains and  barrel 51Ч52 51F barrel 51Ч52 51F
Quasi-equivalent packing, icosahedral subunits 330 343
Quasi-equivalent packing, T=3 plant viruses 331Ч332
Quaternary structure of proteins 3F 29
Quaternary structure of proteins, phosphofructokinase 116F
Quinone in photosynthetic reaction center 238 238F
Quinone in photosynthetic reaction center, 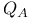 and and 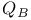 238 238F 239 238 238F 239
Quiocho, Florante 62 110
R (relaxed) state 113Ч114
R factors 383
Radio frequency (RF), in NMR 387
Ramachandran plot 9Ч10 9F 18 19 167
Random mutagenesis 359 359F
Ras protein 254Ч257
Ras protein,  comparison 256Ч257 comparison 256Ч257
Ras protein, diphosphate-binding loop (P-loop) 255Ч256
Ras protein, GTP hydrolysis mechanism 260Ч261
Ras protein, GTP linking via 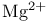 255 255F 255 255F
Ras protein, loop regions 255Ч256
Ras protein, mutants 254 261
Ras protein, switch regions 256
Ras protein, three-dimensional structure 254Ч257 254F
Rayment, Ivan 294 295 342
RecA 131
Receptor tyrosine kinases 270
Receptor tyrosine kinases in cell growth and differentiation 271 272F
Receptor tyrosine kinases, activation and signaling 271
Receptors, enzyme-linked see УEnzyme-linked receptorsФ
Receptors, extracellular domains 251 251F
Receptors, genes 252
Receptors, immunoglobulin-like domains 318Ч319
Receptors, organization 251F
Receptors, orientation importance 270
Receptors, peptide hormones 267
Receptors, transmembrane helices 252 (see also УSpecific typesФ)
Recognition  helix 134 helix 134
Recombinant DNA techniques 3 252 375
Recombinant DNA techniques, Multiwavelength Anomalous Diffraction method 381
Recombination 365Ч366
Recombination, immunoglobulin genes 302 302F 303F
Reflection angle 378 379F
Regan, Lynne 369
REL-homology region 169
Repressor proteins 125 129
Repressor proteins as activator for own synthesis 130F 131
Repressor proteins, action in genetic switch region 130Ч131 130F
Repressor proteins, actions/functions 130Ч131
Repressor proteins, differential binding to operator sites 140Ч141
Repressor proteins, dimerization 132Ч133 133F
Repressor proteins, dimers 131 132
Repressor proteins, DNA-binding domain 132Ч133 133F
Repressor proteins, DNA-binding, allosteric control 142
Repressor proteins, DNA-binding, Cro protein and DNA 134Ч135
Repressor proteins, DNA-binding, phage 434 136Ч137 137 137F
Repressor proteins, DNA-binding, phage 434 and P22 135 136F
Repressor proteins, lac see УLac repressorФ
Repressor proteins, Mat 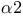 160 160
Repressor proteins, met 175
Repressor proteins, repression of Cro gene 130
Repressor proteins, summary 141Ч142
Repressor proteins, trp see Уtrp repressorФ (see also УBacteriophage lambdaФ)
Restriction enzymes 125
Retinal 226
Retinal, binding to bacteriorhodopsin 227
Retinal, isomerization 227F 228 229F
Retinal, trans state 228 229F
Retinoic acid receptor 181 181F
Retinoid X receptor 185Ч186
Retinol 68 69F
Retinol-binding protein (RBP), amino acid sequence 69Ч70 70F
Retinol-binding protein (RBP), binding site for retinol 69F
Retinol-binding protein (RBP), structure 68F
Retinol-binding protein (RBP), superfamily 70
Retinol-binding protein (RBP), synthesis 68Ч69
Retinol-binding protein (RBP), up-and-down  barrels 68Ч69 68F barrels 68Ч69 68F
RGS (Regulators of GTP hydrolysis) 252 261 266
Rhinovirus see УHuman rhinovirusФ
Rhinoviruses 333
Rhodobacter capsulatus. porins 229 230F
Rhodobacter sphaeroides 236 246F 247F
Rhodopsendomonas acidophila 240F 241
Rhodopsin 265
Rhodospirillum molischianum 241
Rhodospirillum rubrum 243F
Rhvdopseudomonas viridis 235 236
Ribonuclease inhibitor 47
Ribonuclease inhibitor, horseshoe folds 55 56F
Ribonuclease, barnase, folding 94Ч95 94F
Ribonucleotide reductase, iron in 11 11F
Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCo) see УRuBisCoФ
Rich, Alexander 285
Richardson, Jane 23 23F 25F
Richmond, Tim 196
Rigor mortis 295 296
RNA phage 339
RNA polymerase I 151
RNA polymerase II 151 152
RNA polymerase III 151
RNA polymerase, classes 151
RNA, bacteriophage MS2 packaging 339Ч340 340F
RNA, virus capsid units recognizing 332Ч333 333F
RNA-binding protein, ROP see УROPФ
Rod cells 265
Rod cells, light-adapted and dark-adapted 265
Rop protein 38Ч39 39F 196
Rop protein, amino acid sequence 369T
Rossman fold 47 115
Rossmann, Michael 47 333 337 341
Rotamers 11 349
Rotamers, libraries 11
Rotating anode x-ray generators 376
Rous sarcoma virus 271
RuBisCo, active site 53F
RuBisCo, crystals 374F
Rutter, William 213
Salt bridges 36 37F
Salt bridges,  activation 258F 259 activation 258F 259
Sander, Chris 351
Sarcomeres 291F
Satellite tobacco necrosis virus 326F 329 329F
Satellite tobacco necrosis virus, coat 336F
Satellite tobacco necrosis virus, jelly roll structure 336F
Satellite viruses 329
Scaffolds, structural, homologous proteins 349
Scaffolds, structural, Kunitz domains of LACI-D1 and APPI 362
Scaffolds, structural, size reduction with full function 363Ч364
Scattering of electrons 378
Scattering of x-rays, anomalous 381
Schematic diagrams 22Ч23
Schematic diagrams,  complex 264F complex 264F
Schematic diagrams, 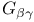 from transducin 262F from transducin 262F
Schematic diagrams,  and WD repeat 263F and WD repeat 263F
| Schematic diagrams,  domains 48F domains 48F
Schematic diagrams,  sheet, antiparallel 18F sheet, antiparallel 18F
Schematic diagrams,  sheet, parallel 19F sheet, parallel 19F
Schematic diagrams, 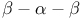 motif 28F motif 28F
Schematic diagrams,  -crystallin 74F 75F -crystallin 74F 75F
Schematic diagrams, Antennapedia homeodomains 160F
Schematic diagrams, arabinose-binding protein 62F 63F
Schematic diagrams, B-DNA 121F
Schematic diagrams, bacterial muramidase 39F
Schematic diagrams, bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPT1) 96F
Schematic diagrams, carboxypepudase 61F
Schematic diagrams, CDK2 106
Schematic diagrams, chymotrypsin 210F
Schematic diagrams, coiled-coil  helix 35F 36F helix 35F 36F
Schematic diagrams, DNA-binding domain of glucocorticoid receptor 182F
Schematic diagrams, four-helix bundle 38F
Schematic diagrams, globin fold 40F
Schematic diagrams, GroEL 100F 101F
Schematic diagrams, GroES 103F
Schematic diagrams, hemagglutinin 78F 82F
Schematic diagrams, hydrogen bonding in collagen 286F
Schematic diagrams, immunoglobulins 301F 308F
Schematic diagrams, immunoglobulins, constant and variable domains 307F 308F
Schematic diagrams, ion pore of 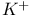 channel 233F channel 233F
Schematic diagrams, major and minor grooves of DNA 122F 123F
Schematic diagrams, Max binding to DNA 200F
Schematic diagrams, MHC molecules 313F
Schematic diagrams, MyoD binding to DNA 198F
Schematic diagrams, myosin 294F
Schematic diagrams, neuraminidase 71F 72F
Schematic diagrams, open twisted  structures 58F structures 58F
Schematic diagrams, ovalbumin 111F
Schematic diagrams, P helix 84F 85F 86F
Schematic diagrams, p53 DNA-binding domain 168F
Schematic diagrams, p53 oligomerization domain 167
Schematic diagrams, phosphofructokinase 115F
Schematic diagrams, Ras proteins 254F
Schematic diagrams, representations in 23
Schematic diagrams, Rop molecule 39F
Schematic diagrams, serpin fold 111F
Schematic diagrams, SH2 domain 273F
Schematic diagrams, SH3 domain 275F
Schematic diagrams, specificity pockets of serine proteinases 213F
Schematic diagrams, subtilisin 216F
Schematic diagrams, SV40 343F
Schematic diagrams, TATA box-binding protein 155F
Schematic diagrams, transducin  256F 256F
Schematic diagrams, up-and-down  barrels 68F barrels 68F
Schematic diagrams, virus jelly roll barrels 336F
Schematic diagrams, zinc finger motif 176F
Schematic diagrams, zinc fingers of Zif 268 178F
Schematic diagrams, Уknobs in holesФ model 37F
Schematic model, transcriptional activation 152F
Schiff base 227 228 229F
Schulz, Georg 58F 229
Scissile bonds 209 213F
Scrapie 113
Second messengers 253
Secondary structure of proteins 3F 14 28 29 89
Secondary structure of proteins in prediction of tertiary structure 350Ч351
Secondary structure of proteins, formation during folding process 93
Secondary structure of proteins, local, imposed by tertiary structure 351
Secondary structure of proteins, motif formation 24Ч26
Secondary structure of proteins, prediction from amino acid sequences 352Ч353
Secondary structure of proteins, prediction from homologous proteins 351Ч352
Secondary structure of proteins, prediction,  helix (helices) 352 helix (helices) 352
Secondary structure of proteins, x-ray crystallography and NMR 374Ч392 (see also У helix (helices)Ф У helix (helices)Ф У
Secretory pathway, proteins 5
Selenomethionine 381
Semliki Forest virus 340
Sequences see УAmino acid sequenceФ
Sequential assignment, two-dimensional NMR 389Ч390
Sequential model 113
Serine in serine proteinases 209
Serine proteinases 205Ч221
Serine proteinases, active sites 211Ч212 211F 212F 361
Serine proteinases, domains 29F 210F 211F
Serine proteinases, essential structural features 209
Serine proteinases, evolution 210
Serine proteinases, inhibition by serpins 110Ч113
Serine proteinases, reaction mechanisms 208 208F УSubtilisinФ)
Serine, structure 6F
Serine/threonine kinases 271
Serpell, Louise 288
Serpin fold 111 111F
Serpins 110Ч113
Serpins, active, cleaved and latent forms 112 112F
Serpins, serine proteinase inhibition mechanism 110Ч113
Serpins, structure 111Ч112 111F
SH2 domain 272 273Ч274
SH2 domain in Src tyrosine kinase 273F 275Ч277
SH2 domain, phosphotyrosine-containing regions binding 272 273Ч274 278
SH2 domain, pY+3 pocket 274 277
SH2 domain, structure 273F
SH3 domain 272 274Ч275 285
SH3 domain in Src tyrosine kinase 275Ч277
SH3 domain, Nef binding 275 275F 276F
SH3 domain, proline-rich regions binding 273 274Ч275
SH3 domain, structure 274 275F
Sialic acid, binding domain of hemagglutinin 80 81F
Sialic acid, chemical formula 80F
Sialic acid, hemagglutinin binding 80
Sialic acid, neuraminidase role 70Ч71
Sickle-cell anemia 43Ч45
Sickle-cell anemia, malaria resistance 44Ч45
Sickle-cell hemoglobin 43Ч45 44F
Sickle-cell hemoglobin, hydrophobic patch on surface 43 44F
Sickle-cell hemoglobin, mutation in 44F
Side chains 4 4F
Side chains,  helix 17 helix 17
Side chains, alcohol dehydrogenase 11 11F
Side chains, antigen recognition in MHC molecules 314Ч315 316
Side chains, branched hydrophobic, in  barrels 49Ч51 barrels 49Ч51
Side chains, charged 5 6F
Side chains, conformation prediction 349
Side chains, energetically favourable 10Ч11
Side chains, hydrophobic 5 6F 14
Side chains, hydrophobic,  barrels 49Ч51 barrels 49Ч51
Side chains, hydrophobic, antiparallel  structures 67 structures 67
Side chains, hydrophobic, burying as event in protein folding 93
Side chains, hydrophobic, coiled-coil  helix 36 36F helix 36 36F
Side chains, hydrophobicity scales 245
Side chains, interactions in leucine zippers 192 193F
Side chains, mutations,  helix movements accommodating 43 helix movements accommodating 43
Side chains, number 4Ч5
Side chains, pectate lyase  helix 85 helix 85
Side chains, polar 5 6F
Side chains, polar in Xfin 177
Side chains, polar, porins 231
Side chains, ribonucleotide reductase 11 11F
Side chains, serine proteinase specificity 209
Side chains, staggered conformations 10Ч11 10F
Side chains, TATA box-binding protein 154 157
Side chains, tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase 61F
Sigler, Paul 100 154 159 169 183 185 256 262
Signal transduction 251Ч281
Signal transduction by G proteins 254Ч264 (see also УG proteinsФ)
Signal transduction, amplification by rhodopsin 265
Signal transduction, phosducin system 265Ч266
Signal transduction, protein modules as adaptors 272Ч273 (see also УSH2 domainФ УSH3
Signal transduction, receptor tyrosine kinases 271
Signal transduction, tyrosine kinases 271
Signal-transducing receptors 251
Signal-transducing receptors, G proteins see УG proteinsФ
Silk fibroins 289 290F
Silk fibroins, genes 289
Sindbis virus 340
Sindbis virus, core protein 341 341F
Sippl, Manfred 354
SLH (strand-loop-helix) motif 168F 171
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



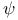 ) angle
) angle  barrel
barrel 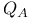 and
and 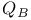
 comparison
comparison 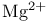
 helix
helix 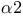
 barrels
barrels  complex
complex 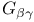 from transducin
from transducin  and WD repeat
and WD repeat 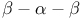 motif
motif  -crystallin
-crystallin 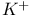 channel
channel