|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Branden C., Tooze J. Ч Introduction to protein structure |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Amino acid sequence in interpretation of NMR spectra 390
Amino acid sequence,  -crystallin 76 -crystallin 76
Amino acid sequence, assignment to three-dimensional folds 353Ч354
Amino acid sequence, calcium-binding motif 26F
Amino acid sequence, calculation of possible number 352
Amino acid sequence, DNA binding domain of glucocorticoid receptor 182F
Amino acid sequence, Fos and Jun 192F
Amino acid sequence, GCN4 192F 193 194F
Amino acid sequence, heptad, in coiled-coil  helix 35Ч37 36F helix 35Ч37 36F
Amino acid sequence, HLH region 201F
Amino acid sequence, homeodomains 160 162 162F
Amino acid sequence, homologous from different species 21
Amino acid sequence, homologous proteins 348
Amino acid sequence, Max protein 192F
Amino acid sequence, photosynthetic reaction center 247F
Amino acid sequence, protein structure prediction from 352Ч353
Amino acid sequence, retinol-binding protein (RBP) 69Ч70 70F
Amino acid sequence, Rop 369T
Amino acid sequence, similar three-dimensional structures 352
Amino acid sequence, TATA box-binding protein 153
Amino acid sequence, transmembrane a helices prediction 244Ч245
Amino acid sequence, Zif 268 protein 177F 368T
Amino acids in  barrels 48 50T barrels 48 50T
Amino acids, basic, in helix-loop-helix region 196
Amino acids, classes 5
Amino acids, D- and L- forms 5 9
Amino acids, handedness 5
Amino acids, nomenclature 7F
Amino acids, preferred in a helix 16Ч18
Amino acids, role of individual residues 391
Amino acids, side chains see УSide chainsФ
Amino acids, structures 4 4F
Amino groups 4 4F
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, domains 59Ч60 59F 60F
Ammonium ions 211 213
Amplitude, diffracted beams 370F 379 380 380F
Amyloid  -protein precursor inhibitor, AlzheimerТs (APPI) 361 362 362T -protein precursor inhibitor, AlzheimerТs (APPI) 361 362 362T
Amyloid fibers 289 297
Amyloid fibrils 288Ч289
Amyloidosis 288
Antenna pigment proteins 235 240Ч241
Antenna pigment proteins, ring in LH1 light-harvesting complex 242Ч244 243F
Antennapedia 159 160 162 162F
Antibodies 299
Antibodies, antigen-binding sites see УAntigen-binding sitesФ
Antibodies, catalytic 207 309
Antibodies, catalytic, production 309
Antibodies, chimeric 306
Antibodies, diversity 302Ч303
Antibodies, membrane protein solubilization 224Ч225
Antibodies, polypeptide chains 300Ч301 (see also УImmunoglobulin(s)Ф)
Antigen, recognition in MHC molecules 314Ч315 315F 316
Antigen-binding sites 21
Antigen-binding sites for antigens 308Ч311
Antigen-binding sites for haptens 308Ч309 309F
Antigen-binding sites for lysozyme 309Ч310 310F
Antigen-binding sites of immunoglobulins 21 306Ч308 306F 308Ч311
Antigen-binding sites of immunoglobulins, modeling 349Ч350
Antigen-binding sites of MHC class I molecule 314
Antigen-binding sites of T-cell receptors (TCR) 317F
Antigen-presenting cells 315
Antigenic determinants 299
Antiparallel  barrels, chymotrypsin 210Ч211 210F barrels, chymotrypsin 210Ч211 210F
Antiparallel  barrels, cyclophilin 99 99F barrels, cyclophilin 99 99F
Antiparallel  barrels, GroES 102 barrels, GroES 102
Antiparallel  barrels, p53 DNA-binding domain 168Ч169 168F barrels, p53 DNA-binding domain 168Ч169 168F
Antiparallel  barrels, porins 229Ч230 230F barrels, porins 229Ч230 230F
Antiparallel  barrels, viruses 335 335F barrels, viruses 335 335F
Antiparallel  hairpin see УHairpin hairpin see УHairpin  motifФ motifФ
Antiparallel  sandwich, TFIIA 159 sandwich, TFIIA 159
Antiparallel  sheets 18F 19 67 67F sheets 18F 19 67 67F
Antiparallel  sheets in sheets in  domains 31 domains 31
Antiparallel  sheets, bacteriophage MS2 subunits 339 sheets, bacteriophage MS2 subunits 339
Antiparallel  sheets, DNA-binding site of TATA box-binding protein 154 sheets, DNA-binding site of TATA box-binding protein 154
Antiparallel  sheets, Greek key motifs 27 sheets, Greek key motifs 27
Antiparallel  sheets, immunoglobulin fold 304Ч305 3041" sheets, immunoglobulin fold 304Ч305 3041"
Antiparallel  sheets, lambda Cro protein 132 sheets, lambda Cro protein 132
Antiparallel  sheets, MHC class I molecule 314 sheets, MHC class I molecule 314
Antiparallel  sheets, neuraminidase 71Ч72 71F sheets, neuraminidase 71Ч72 71F
Antiparallel  sheets, p53 domain 167 sheets, p53 domain 167
Antiparallel  sheets, serpin fold 111 sheets, serpin fold 111
Antiparallel  sheets, SH2 domain 273 sheets, SH2 domain 273
Antiparallel  sheets, topology diagram 24F sheets, topology diagram 24F
Antiparallel  strands in up-and-down strands in up-and-down  barrel 68F 69Ч70 70F barrel 68F 69Ч70 70F
Antiparallel  strands, active site of carboxypeptidase 62 strands, active site of carboxypeptidase 62
Antiparallel  strands, GroEL 102 strands, GroEL 102
Antiparallel  strands, jelly roll barrel formation 77Ч78 77F strands, jelly roll barrel formation 77Ч78 77F
Antiparallel  strands, variable domain of immunoglobulin 306 308 strands, variable domain of immunoglobulin 306 308
Antiparallel  structures 67Ч84 structures 67Ч84
Antiparallel  structures, structures,  -crystallin 74 74F -crystallin 74 74F
Antiparallel  structures, Greek key motifs 72Ч74 (see also УGreek key motif proteinsФ structures, Greek key motifs 72Ч74 (see also УGreek key motif proteinsФ
Antiparallel  structures, included 67 structures, included 67
Antiparallel  structures, SH3 domain 274 275F structures, SH3 domain 274 275F
Antiparallel  structures, up-and-down structures, up-and-down  barrels (sheets) see УUp-and-down barrels (sheets) see УUp-and-down  barrelsФ УUp-and-down barrelsФ УUp-and-down
Antithrombin 111 112 113
Antiviral compounds, design for common cold 337Ч338 337F 338F
AP1 complex 192
AP1 complex, pseudo-symmetric binding site 194 194F 196
Aphthoviruses 333
APPI (AlzheimerТs amyloid P-protein precursor inhibitor) 361 362 362T
Arabidopsis thaliana 154
Arabinose 63F
Arabinose, transport 62
Arabinose-binding protein,  domains 62Ч63 62F domains 62Ч63 62F
Area detectors 377
Arginine, p53 binding to DNA 170 170F 171
Arginine, recognition helix of glucocorticoid receptor 184Ч185
Arginine, structure 7F
Arginine, zinc finger interaction with DNA 179 179F 181
Aromatic residues, hydrophobicity in porins 231
Asparagine, structure 6F
Asparagine, TATA box and TBP binding 157Ч158
Aspartate transcarbamoylase 24F
Aspartic acid in Gp subunit 263
Aspartic acid in parvalbumin calcium-binding motif 25
Aspartic acid in serine proteinases 209
Aspartic acid, mutation in trypsin 215
Aspartic acid, structure 6F
Aspartic acid, substrate-assisted catalysis 218
Aspartic proteinases 205
Asymmetric units, definition 328
Asymmetric units, icosahedron 328 328F
AT sequence, p53 binding to DNA 170
ATP, binding to phosphofructokinase 116
ATP, cyclin A and CDK2 binding 108 109F
ATP, depletion in rigor mortis 295 296
ATP, GroEL-GroES complex 101F 103
ATP, hydrolysis, GroEL-GroES binding 103
ATP, hydrolysis, swinging cross-bridge model 292F
ATP, role in muscular contraction 296Ч297
B cells (B lymphocytes) 299
B cells (B lymphocytes), antibody formation 300
B cells (B lymphocytes), numbers produced 302
B-DNA see УDNAФ
b/HLH transcription factors 175 196F 197 202
b/HLH transcription factors, amino acid sequences 201F
b/HLH transcription factors, consensus sequence recognized 197 199 201
b/HLH transcription factors, homodimer and heterodimers 196Ч197 196F
b/HLH transcription factors, structure 197 200
b/HLH/zip transcription factors 196F 199Ч200
b/HLH/zip transcription factors, amino acid sequences 201F
b/HLH/zip transcription factors, motif structure 200
b/HLH/zip transcription factors, Myc 199
b/zip family, Fos and Jun 199
b/zip transcription factor 196F 197
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 215
Bacillus subtilis, PRA-isomerase and IGP-synthase 52
Bactenophage, filamentous 359Ч361 360F
Bactenophage, gene control 129Ч130
Bactenophage, helper 360
| Bactenophage, lytic-lysogeniccycle switch 130Ч131 130F 133
Bactenophage, repressors see УRepressor proteinsФ УSpecific
Bactenophage, T-even 326F
Bactenophage, temperate 130
Bacteria, antibody-tagged 299 300
Bacteria, antibody-tagged, disulfide bridge formation 96
Bacteria, antibody-tagged, lysogenic strains 129Ч130
Bacteria, antibody-tagged, lytic strains 130
Bacteria, antibody-tagged, outer membrane proteins see УPorinsФ
Bacteria, antibody-tagged, photosynthetic reaction center see УPhoto synthetic reaction centerФ
Bacteria, antibody-tagged, protein A 363 363F
Bacteria, antibody-tagged, purple 242 (see also УSpecific generaФ)
Bacteriochlorophyll 236 236F
Bacteriochlorophyll, LH2 light-harvesting complex 241 242F
Bacteriophage 434
Bacteriophage display 359Ч363
Bacteriophage display, applications 361Ч365
Bacteriophage display, binding specificity of proteinase inhibitors 362Ч363
Bacteriophage display, DNA shuffled libraries 366
Bacteriophage display, Kunitz domains 362 362T
Bacteriophage display, libraries of erythropoietin receptor agonists 364Ч365
Bacteriophage display, procedures 360
Bacteriophage display, protein linked to DNA by 359Ч361
Bacteriophage display, proteinase inhibitor optimization 361Ч363
Bacteriophage display, sorting of libraries 360F
Bacteriophage lambda, Cro protein 129
Bacteriophage lambda, Cro protein, dimer 132 132F
Bacteriophage lambda, Cro protein, DNA-binding motif 133Ч134 134F
Bacteriophage lambda, Cro protein, structure 131Ч132
Bacteriophage lambda, Cro-DNA interactions model 134Ч135
Bacteriophage lambda, Cro-DNA interactions model, genetic studies supporting 135
Bacteriophage lambda, dimers 132 132F 133 133F
Bacteriophage lambda, DNA-binding domain 132Ч133 133F
Bacteriophage lambda, DNA-binding motif 133Ч134
Bacteriophage lambda, genetic switch region 130Ч131 130F
Bacteriophage lambda, N-terminal domain 133F
Bacteriophage lambda, operator regions, nucleotide sequences 130 131Ч132 131T
Bacteriophage lambda, POU region structure similarity 164
Bacteriophage lambda, repressor 129 161F
Bacteriophage M13 359Ч361
Bacteriophage MS2 339Ч340
Bacteriophage MS2, dimer recognizing RNA packaging signal 339Ч340 339F 340F
Bacteriophage MS2, polypeptide chain fold 339
Bacteriophage MS2, subunit structure 339 339F
Bacteriophage P22 130Ч131 130F
Bacteriophage P22, repressor, DNA-binding surface 135 136F
Bacteriophage P22, tailspike protein 84Ч85
Bacteriophage replicase 339
Bacteriophage T4 325
Bacteriophage T4, lysozyme 354
Bacteriophage T4, lysozyme,  type 355F type 355F
Bacteriophage T4, lysozyme, cavities in hydrophobic core 358
Bacteriophage T4, lysozyme, dipoles of  helices 357 357F helices 357 357F
Bacteriophage T4, lysozyme, glycine and proline effect on stability 356Ч357
Bacteriophage T4, lysozyme, melting temperatures 356F
Bacteriophage T4, lysozyme, mutations to increase proline 356Ч357
Bacteriophage T4, lysozyme, polypeptide chain 355F
Bacteriophage T4, lysozyme, stability increased by disulfide bridges 355Ч356
Bacteriophage, Cro protein, DNA complex structure 136Ч137
Bacteriophage, Cro protein, DNA distortion after binding 138 138F
Bacteriophage, Cro protein, operator region binding 138Ч139 138F 139F
Bacteriophage, Cro protein, repressor DNA-binding domain similarity 137
Bacteriophage, genetic switch region 130Ч131 130F
Bacteriophage, operator regions 137T
Bacteriophage, operator regions, base pair 4 140
Bacteriophage, operator regions, central region and overwinding 140Ч141
Bacteriophage, repressor 137 137F
Bacteriophage, repressor, DNA complex structure 136Ч137
Bacteriophage, repressor, DNA distortion after binding 138 138F
Bacteriophage, repressor, DNA-binding surface 135 136F
Bacteriophage, repressor, sequence-specific OR interactions 138Ч139 138F 139F 140
Bacteriorhodopsin, light-driven proton pump 227Ч228 229F
Bacteriorhodopsin, retinal binding site 227
Bacteriorhodopsin, transmembrane  helices 226Ч227 226F helices 226Ч227 226F
Ball-and-stick diagram 22
Ball-and-stick diagram, antiparallel  sheet 18F sheet 18F
Ball-and-stick diagram, collagen model 284F
Ball-and-stick diagram, parallel  sheet 19F sheet 19F
Banner, David 39
Barnase 357Ч358
Barnase, destabilizing mutants 358
Barnase, folding 94Ч95 94F
Barnase, stability increased by histidine 357Ч358
Bax, Ad 110
Bence Ч Jones protein 304
Benzoate, mandelate conversion to 54Ч55 54F
Berman, Helen 285
Biliverdin 70
Biochemical studies 391
Biopolymers, fiber diffraction 386Ч387
Bjorkman, Pamela 312
Blake, Colin 288
Blow, David 59 210
Bluetongue virus 326
Blundell, Tom 74 76
Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) 26 26F 96Ч97 96F
Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI), folding pathway 96Ч97 96F
Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI), NMR and x-ray crystallography comparison 390Ч391
Bragg, Lawrence 378
Bragg, W.L. 13
BraggТs law 378 379F
Braisted, Andrew 363
Branden, Carl 20F 49F 53F 59 97
Breathing, proteins 105
Brennan, Richard 143
Bugg, Charles 109
Burley, Stephen 154 159 199Ч200
Calcium 25F
Calcium-binding domain 29F
Calcium-binding motif 24 25F
Calcium-binding motif, amino acid sequences 26F
Calcium-binding proteins 25
Calmodulin 24 26 109Ч110
Calmodulin, calcium binding 26
Calmodulin, domains and structure 110 110F
Calmodulin, peptide binding 109Ч110 110F
Campbell, Ian 274
Canonical loop structures 311
CAP see УCatabolite gene activating protein (CAP)Ф
Capsid 325 326
Capsid, bacteriophage MS2 339Ч340 (see also УSpecific virusesФ)
Carbon atoms 4
Carbonyl groups, GAL4 binding to DNA 188 189F
Carboxyl groups 4 4F
Carboxypeptidase,  protein with mixed protein with mixed  sheet 60Ч62 61F sheet 60Ч62 61F
Carboxypeptidase, active site 62F
Carboxypeptidase, zinc environment 62F
Cardioviruses 333
Carrel, Robin 111
Caspar, Don 330 342
Catabolite gene activating protein (CAP) 132
Catabolite gene activating protein (CAP), cAMP-DNA complex 146 146F
Catabolite gene activating protein (CAP), DNA bending 146Ч147 156
Catabolite gene activating protein (CAP), helix-turn-helix motif 146 146F
Catalysis 205
Catalysis without catalytic triad in subtilisin 217Ч218 (see also УSerine proteinasesФ)
Catalysis, reactions,  barrels in 51 barrels in 51
Catalysis, substrate-assisted 218Ч219 218F
Catalytic triad 209
Catalytic triad, alphavirus coat protein protease 341
Catalytic triad, catalysis without 217Ч218
Catalytic triad, chymotrypsin 211 211F 212F
Catalytic triad, subtilisin 216 217
CCG triplets 191
CCG triplets, GAL4 binding 188 189
CCG triplets, zinc-containing motifs binding to 190 191
CD4 168 319 319F
Cdk see УCyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs)Ф
CDR see УComplementarity determining regionsФ
Cell cycle 105Ч106 106F
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -crystallin
-crystallin  helix
helix  barrels
barrels  -protein precursor inhibitor, AlzheimerТs (APPI)
-protein precursor inhibitor, AlzheimerТs (APPI) 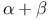 type
type