|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Branden C., Tooze J. Ч Introduction to protein structure |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
NMR, homeodomain binding to DNA 162
NMR, interpretation of spectra 390
NMR, limitations 390 391
NMR, NOE 388 388F 389 389F
NMR, one-dimensional spectra 387F 388
NMR, radio frequency (RF) 387
NMR, SH2 domain 273
NMR, silk fibroins 290
NMR, two-dimensional spectra 388 388F 390F
NMR, two-dimensional spectra, sequential assignment 389Ч390
NMR, x-ray crystallography results comparisons 390Ч391
NOE (nuclear Overhauser effect) spectrum 388 388F 389 389F
NOE NMR 38h 388F 389 389F
Nuclear lamins 287F
Nuclear magnetic resonance see УNMRФ
Nuclear receptors 181 191 202
Nyborg, Jens 255
Oct-1 164F 165
Octylglucoside 224
Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis 359F
Omega loop 22
Operator regions (OR) 130
Operator regions (OR), bacteriophage 434 137T
Operator regions (OR), bacteriophage lambda 130 131Ч132 131T
Operator regions (OR), bacteriophage, overwinding 140Ч141
Operator regions (OR), bacteriophage, repressor recognition 135 136
Operator regions (OR), differential binding of Cro and repressor, DNA conformation changes 140Ч141
Operator regions (OR), differential binding of Cro and repressor, sequence-specific 138Ч139
Operator regions (OR), palindromic sequences 131Ч132 131T 135
Operator regions (OR), sequence-specific protein-DNA, interactions 138Ч139 139F
Ovalbumin 111 111F
Overwinding, operator region, phage 434 140Ч141
Oxidation, disulfide bridge formation 5
Oxidizing agents 98
Oxyanion hole 209
Oxyanion hole, chymotrypsin 211 211F
Oxyanion hole, subtilisin 216Ч217
Oxygen, binding to myoglobin 105
Oxygen, ion selectivity filter of 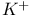 channel 234 channel 234
P hairpin see УHairpin  motifФ motifФ
P2 family 70
p21 166 254F
p21, transcription activation by p53 166
p53 166
p53, Arg mutations 170 170F 171
p53, DNA binding 169Ч170 169F
p53, DNA-binding domain 167 167F
p53, DNA-binding domain, antiparallel  barrel 168Ч169 168F barrel 168Ч169 168F
p53, DNA-binding domain, mutations 167 170Ч171 170F 171F
p53, DNA-binding domain, nucleotide sequence of DNA 169F
p53, domains 167 167F
p53, function 166
p53, loop regions 169Ч170 171 171F
p53, mutations, regions 170Ч171 170F 171F
p53, oligomerization domain 167Ч168 167F
p53, tetramers 167
p53, tetramers, formation 167Ч168 167F
Pabo, Carl 133 160 165 177 197
Palindromic sequences 131Ч132 131T 135
Palindromic sequences, glucocorticoid receptor binding 185 191
Palindromic sequences, MyoD recognition sequence 198F
Papain 304F
Papovavirus family 341
Paracelsus challenge 368Ч370 369F 369T
Parvalbumin, motif 24 25
Parvoviruses 326
Patterson maps 380 380F
Pauling, Linus 14 43 205 285
Pavletich, Nikola 107 167 177
Pectate lyase,  helix structure 84 84F 86F helix structure 84 84F 86F
Peptide bonds, cleavage by serine proteinases 208 208F
Peptide bonds, formation 4 4F
Peptide bonds, hydrolysis 208 208F
Peptide inhibitor, binding to chymotrypsin 211
Peptide units 8
Peptide units, dipole moment 16 16F
Peptide, binding to MHC molecules 314Ч315 315F 316
Peptidyl prolyl isomerases 98
Periplasmic space 228 231
Perutz, Max 14 44F 113 370F 379Ч381 380F
Petsko, Greg 54
PH domain 272
pH, hemagglutinin structural change 81Ч84
Phage see УBacteriophageФ
Phage display see УBacteriophage displayФ
Phage replicase 339
Phase determination, diffracted beams 370F 379Ч381 380F
PHD program 351
Phenylalanine, insertion in TATA box 156
Phenylalanine, structure 6F
Pheophytin 238 239
Phi ( ) angle 8 9 14 ) angle 8 9 14
Phi ( ) angle, Ramachandran plot 9 9F 10 ) angle, Ramachandran plot 9 9F 10
Phillips, David 23F 95F
Phosducin 265Ч266
Phosducin, binding to 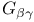 265Ч266 266F 265Ч266 266F
Phosducin, C-terminal domain 265 266
Phosducin, structure and domains 265Ч266 265F
Phosducin, thioredoxin homology 265Ч266
Phosphate in  helix 16F helix 16F
Phosphate, Ras and  binding to GTP 255 257 259 binding to GTP 255 257 259
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) 115 117
Phosphofructokinase (PFK) 114Ч117
Phosphofructokinase (PFK), allosteric properties 114Ч117
Phosphofructokinase (PFK), ami no acids 115Ч116
Phosphofructokinase (PFK), dimers and packing of 116
Phosphofructokinase (PFK), Escherichia coli 115Ч116 115F
Phosphofructokinase (PFK), quaternary structure 116F
Phosphofructokinase (PFK), R and T states 115 116Ч117 117F
Phosphofructokinase (PFK), reaction 114F
Phosphofructokinase (PFK), subunit structure 115
Phosphofructokinase (PFK), subunit structure, catalytic sites 116
Phosphoglycerate mutase 58F
Phosphoribosyl anthranilate (PRA) isomerase 52Ч53 53F
Phosphorylation, Src tyrosine kinase 275 276
Phosphorylcholine 308Ч309 309F
Phosphotyrosine (pTyr) 272Ч273
Phosphotyrosine (pTyr), binding to SH2 domain 273Ч274 278
Photoisomerization, retinal 227 228 229F
Photon absorption, photosynthesis 239Ч240 243
Photon absorption, rhodopsin 265
Photosynthesis, energy flow and mechanisms 243Ч244 244F
Photosynthesis, process 239Ч240
Photosynthetic pigments 234Ч236 235 236 236F
Photosynthetic pigments in photosynthetic reaction center 235 236 236F
Photosynthetic pigments, arrangement 238F
Photosynthetic pigments, bound to L and M subunits 237Ч239
Photosynthetic reaction center 234Ч236
Photosynthetic reaction center, amino acid sequences 247F
Photosynthetic reaction center, definition 235
Photosynthetic reaction center, Fe atom 236 238
Photosynthetic reaction center, hydropathy plots, correlation with crystal structure data 246
Photosynthetic reaction center, L, M and H subunits 235
Photosynthetic reaction center, L, M and H subunits, transmembrane  helices 236Ч237 237F helices 236Ч237 237F
Photosynthetic reaction center, light energy converted to electrical energy 239Ч240
Photosynthetic reaction center, light-harvesting (LH1 and LH2) complexes surrounding 240Ч241 243F
Photosynthetic reaction center, modeling 244
Photosynthetic reaction center, pigments see УPhotosynthetic pigmentsФ
Photosynthetic reaction center, polypeptide chains 234Ч236
Photosynthetic reaction center, three-dimensional structure 237F
Photosynthetic reaction center, transmembrane  helices 244Ч245 (see also УLight-harvesting complexesФ) helices 244Ч245 (see also УLight-harvesting complexesФ)
Picornaviruses 326 326F 333Ч335 333F
Picornaviruses, antibody binding sites 333
Picornaviruses, capsid 333
Picornaviruses, capsid, subunit arrangement 334Ч335 334F
Picornaviruses, jelly roll structure 335 336F
Picornaviruses, structural proteins (VP1-VP4) 334 336
Picornaviruses, T=3 plant virus relationship 337 (see also УHuman rhinovirusФ)
Pigments, photosynthetic see УPhotosynthetic pigmentsФ
Plasma membrane proteins 228
| Plasminogen 29F
Plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI) 111 113
Plastocyanin 24F
Plastocyanin, NMR and x-ray crystallography comparison 391
Pleated  sheets 19 19F sheets 19 19F
Pleckstrin 272
Pleckstrin-homology (PH) domain 272
Point mutations 366
Poliovirus 336F
Poljak, Roberto 304 309
Polyalanine repeats 290
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR), random mutagenesis method 359F
Polyomavirus 326 341Ч343
Polyomavirus, structure 342
Polypeptide chains (subunits) 4 29
Polypeptide chains (subunits) in hemagglutinin 78F 79 79F
Polypeptide chains (subunits), antibodies 300Ч301
Polypeptide chains (subunits), large, domains 29Ч30
Polypeptide chains (subunits), main-chains 4
Polypeptide chains (subunits), organization 29F
Polypeptide chains (subunits), unfolded and folded states 90F
Polypeptide chains (subunits), virus capsid 325
Polyproline type II helix 274
Porins 228Ч231
Porins, channels 230Ч231 231F
Porins, channels, eyelet 230 231F
Porins, channels, up and down  barrels 229Ч230 230F barrels 229Ч230 230F
Porins, transmembrane channels formed by  strands 228Ч229 strands 228Ч229
Positive control protein 146
Potassium 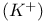 channels 232 channels 232
Potassium 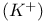 channels, ion pore 232F 233 channels, ion pore 232F 233
Potassium 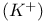 channels, ion selectivity filter mechanism 233Ч234 233F channels, ion selectivity filter mechanism 233Ч234 233F
Potassium 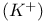 channels, selectivity filter structure 233F channels, selectivity filter structure 233F
Potassium 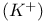 channels, tetrameric molecule 232Ч233 232F channels, tetrameric molecule 232Ч233 232F
POU homeodomain 162F
POU regions 164Ч166 175
POU regions, binding to DNA by helix-turn-helix motifs 164Ч166 164F 165F
POU regions, domains 164F
POU regions, structure 164 164F
PPR1 transcription factor 190Ч191 190F
PRA-isomerase, IGp-synthase, double barrels 52Ч53 52F
Prealbumin 69
Prediction of structure 348Ч354
Prediction of structure from amino acid sequences 352Ч353
Prediction of structure,  helix (helices) 352 helix (helices) 352
Prediction of structure, active sites in  barrels 57 59 barrels 57 59
Prediction of structure, CDR regions 350F
Prediction of structure, complementarity determining regions 350 350F
Prediction of structure, loop regions 21
Prediction of structure, secondary structure see УSecondary structure of proteinsФ
Prediction of structure, side chain conformation 349
Prediction of structure, tertiary structure, secondary structure, knowledge needed 350Ч351
Prediction of structure, threading methods 353Ч354
Prediction of structure, three-dimensional, in homologous proteins 349Ч350
Prediction of structure, transmembrane  helix from, amino acid sequence 244Ч245 helix from, amino acid sequence 244Ч245
Primary structure of proteins 3F 4 28 29
Prion diseases 283
Prion proteins 290
Prion proteins, model system for 370
Procollagen 284
Prolactin receptor 267
Prolactin receptor, extracellular domain 269
Prolactin receptor, growth hormone complex 269Ч270 269F 270F 271F
Proline  helix 16Ч17 helix 16Ч17
Proline  helix in collagen 284 helix in collagen 284
Proline  helix, cis-trans isomerization 98Ч99 98F helix, cis-trans isomerization 98Ч99 98F
Proline  helix, effect on protein stability 356Ч357 helix, effect on protein stability 356Ч357
Proline  helix, structure 7F helix, structure 7F
Proline-rich regions, binding to SH3 domain 273 274Ч275
Prolyl hydroxylase 284
Promoter elements 130
Promoter elements, core (basal) 151 151F
Promoter elements, enhancer element distance from 152
Promoter elements, proximal 151 151F
Pronase 71
Protein Data Bank 353
Protein design from first principles 367Ч368
Protein design,  structure conversion to a structure 368Ч370 369F 369T structure conversion to a structure 368Ч370 369F 369T
Protein design, definition 347
Protein design, zinc finger not stabilized by zinc 367Ч368 368F 368T
Protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) 96 97
Protein engineering 347Ч354
Protein engineering, combinatorial methods 358Ч359
Protein engineering, definition 347
Protein engineering, goal 367
Protein engineering, protein folding studies 93Ч95
Protein engineering, specificity pockets 213Ч215
Protein engineering, stability increased 354Ч358
Protein engineering, stability increased, disulfide bridges 354Ч356
Protein engineering, stability increased, increasing proline residues 356Ч357
Protein engineering, stability increased, stabilizing dipoles of  helices 357Ч358 387F lysozymeФ) helices 357Ч358 387F lysozymeФ)
Protein engineering, subtilisin 215 217 219
Protein fold assignments (threading) 353Ч354
Protein fold, database 353
Protein folding 4 89Ч120
Protein folding in GroEL-GroES complex 104
Protein folding, assignment of amino acid sequences (threading) 353Ч354
Protein folding, blocked, prevention 91
Protein folding, definition 89
Protein folding, disulfide bond formation 96Ч98
Protein folding, enzymes role in 89 96Ч98
Protein folding, hydrophobic side chain burying 93
Protein folding, inside chaperonins 99Ч100
Protein folding, intermediates 93 94
Protein folding, intermediates, accumulation 113
Protein folding, intermediates, disulfide-bonded 96Ч97
Protein folding, intermediates, unstable 91
Protein folding, inverse folding problem 353
Protein folding, isomerization of proline residues 98Ч99 98F
Protein folding, kinetic factors 91Ч92
Protein folding, molten globule as intermediate 93 94
Protein folding, multiple pathways 95F
Protein folding, problem in protein engineering 348
Protein folding, rate limiting step 98Ч99 98F
Protein folding, single pathway 93Ч95
Protein folding, single-site mutations and energetics 93Ч95
Protein folding, temperature-dependent fluctuations 104Ч105 (see also УConformational changesФ)
Protein G 369Ч370 369F
Protein kinase 106
Protein kinase, conformational changes 105Ч109
Protein kinase, cyclin-dependent (CDKs) see УCyclin-dependent protein kinases (CKDs)Ф
Protein kinase, domains of enzyme-linked receptors 271
Protein structure see УSpecific entriesФ
Protein(s), aggregation 99
Protein(s), breathing 105
Protein(s), classes 283
Protein(s), conformational state changes see УConformational changesФ
Protein(s), denatured state 90
Protein(s), folded 90F 92F
Protein(s), folded, flexible structure 104Ч105
Protein(s), folding see УProtein foldingФ
Protein(s), functions 3
Protein(s), homologous see УHomologous proteinsФ
Protein(s), membrane see УMembrane proteinsФ
Protein(s), molten globules see УMolten globular proteinsФ
Protein(s), native state 89 90
Protein(s), native state, secondary structure 92
Protein(s), native state, stability 90
Protein(s), techniques to determine structure 373Ч392 (see also Уx-ray crystallographyФ УNMRФ)
Protein(s), unfolded 90F 92F
Protein(s), unfolded as ensemble of interconverting structures 92 94F
Protein(s), unfolding, in chaperonins 99Ч100
Protein-DNA interactions, carbonyl groups of GAL4 in 188Ч189 189F
Protein-DNA interactions, glucocorticoid receptor 184
Protein-DNA interactions, Max and MyoD 201 201F
Protein-DNA interactions, water mediating 162 (see also УOther specific proteinsФ)
Protein-protein interactions, cytochrome subunit of photosynthetic reaction center 236
Protein-protein interactions, Mat  2-Mat al binding 163Ч164 2-Mat al binding 163Ч164
Protein-protein interactions, transcription activation 152Ч153 159
Proteinase inhibitors 110Ч111
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



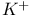 channel
channel  motifФ
motifФ ) angle
) angle 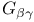
 helix
helix  binding to GTP
binding to GTP  channels
channels  barrels
barrels