|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Branden C., Tooze J. Ч Introduction to protein structure |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Domain-domain associations, immunoglobulin hypervariable region 307
domains 3F 29 29F
Domains from structural motifs 30
Domains, CDK2 107Ч108 107F
Domains, definition 29
Domains, GroEL see УGroELФ
Domains, interdomain movements 109Ч110
Domains, large polypeptide chains 29Ч30
Domains, lysozyme 95F
Domains, movements 89
Domains, thioredoxin 97
Domains, types 29F (see also У domainsФ У У У domainsФ У У У
Doolittle, D.F. 245
Drenth, Jan 215
Drosophila 159 160 162F 179
Drug design, for common cold 337Ч338 337F
DsbA 96 97 97F
DsbA as oxidizing agent 98
Dystrophin 36
Edmundson, Allen 304
EF motif (EF hand) 24 25F
EF motif (EF hand), amino acid sequences 26F
EF motif (EF hand), calmodulin 110
Eisenberg, David 353
Elastase 212Ч213 213F
Electron microscopy 374
Electron microscopy, membrane proteins 225Ч226 226F
Electron microscopy, myosin cross-bridges 292
Electron microscopy, transthyretin 288
Electron-density map 381Ч382 382F 384
Electron-transfer reactions 11
Electronic area detectors 377
Electrons, scattering 378
Electrons, transfer in photosynthesis 239
Electrons, x-ray interactions 381
Elongation factor, Tu 255
Emphysema 113
Endoplasmic reticulum, MHC molecule loading 316
Energy, folded and denatured state of proteins 90
Energy, light, conversion to electrical energy 239Ч240
Engelman, D.A. 245
Engrailed gene 160 162F
Engrailed homeodomain 162F 165
Enhancer elements, distal 151 151F 152
Enhancer elements, distal, distance from promoters 152
Enhancer elements, GAL4 zinc cluster, regions binding to 188Ч189 189F
Enteroviruses 333
Enthalpy, folded/denatured proteins 90
Entropy, cost of folding proteins 354
Entropy, native/denatured state of proteins 90
Enzyme(s), 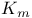 and and values 206 values 206
Enzyme(s),  barrels 48Ч49 barrels 48Ч49
Enzyme(s), activation energy of reactions decreased by 206Ч207 207F
Enzyme(s), antibodies as see УAntibodies catalyticФ
Enzyme(s), catalysis see УCatalysisФ
Enzyme(s), catalytic properties 206
Enzyme(s), evolution 54Ч55
Enzyme(s), in protein folding 89
Enzyme(s), multidomain subunits 51
Enzyme(s), R and T states 114Ч117
Enzyme(s), R and T states, phosphofructokinase 115 116Ч117 117F
Enzyme(s), reactions see УCatalysisФ
Enzyme(s), transition-state affinities 207 207F
Enzyme-linked receptors 251
Enzyme-linked receptors, classes 270Ч271
Enzyme-linked receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors 270Ч271
Enzyme-substrate (ES) complex 206
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) 29F
Epinephrine 253 254
Erabutoxin 26 26F
Erythropoietin 364
Erythropoietin receptor (EPOR), agonists, phage display of random peptide libraries 364Ч365
Erythropoietin receptor (EPOR), EMP1 peptide 364 365 365F
Erythropoietin receptor (EPOR), extracellular domain (EBP) 364 365 365F
Escherichia coli, arabinose-binding protein 62Ч63 62F
Escherichia coli, bacteriophage growth 129Ч130
Escherichia coli, DsbA structure 97 97F
Escherichia coli, heat-shock proteins see УGroELФ УGroESФ
Escherichia coli, lac operon 143Ч145
Escherichia coli, maltoporin 230
Escherichia coli, met repressor 175
Escherichia coli, phosphofructokinase 115Ч116 115F
Escherichia coli, porins 229
Escherichia coli, PRA isomerase and IGP synthase 53 53F
Escherichia coli, ribonucleotide reductase 11 11F
Estrogen receptor 181 181F 183
ethane 10F
Eucaryotic cells, disulfide bridge formation 96
Evans, Phil 50 115
Evolution,  -crystallin 76 -crystallin 76
Evolution, antibodies, T-cell receptor and MHC 300
Evolution, chymotrypsin 210 212
Evolution, combinatorial methods accelerating 358Ч359
Evolution, conservation of  domains 41Ч42 domains 41Ч42
Evolution, conservation of heme pocket 43
Evolution, directed, recombination and mutation in 365Ч366 366F
Evolution, DNA shuffling 365Ч366
Evolution, enzymes 54Ч55
Evolution, globin fold preservation 41Ч42
Evolution, homeodomain proteins role 159Ч160
Evolution, immunoglobulin domains 301
Evolution, jelly roll barrel structures of viruses 335Ч337 335F
Evolution, new enzyme activities and  barrels 54Ч55 barrels 54Ч55
Evolution, POU-specific domains 166
Evolution, proteinases 205
Evolution, serine proteinases 210
Evolution, subtilisin 210
Evolution, transcription factors 202
Evolutionary relatedness, primary structure of proteins 29
F-actin 293
Fab fragments 303 304 306 307F 308F
Fab fragments, lysozyme complex 309Ч310 310F
Factor IX 29F
Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy 288
Fatty acids, synthesis 30
Fc fragment 303 312
Fe atom, in photosynthetic reaction center 236 238
Feedback inhibition 113
Feedback, negative loop 142
Feher, G. 246F
Fersht, Alan 60 93 357
Fiber diffraction methods 384Ч385 385F
Fiber diffraction methods, biopolymers 386Ч387
Fiber diffraction methods, diffraction patterns 385F
Fiber diffraction methods, diffraction patterns, DNA 386Ч387 386F
Fiber diffraction methods, diffraction patterns, transthyretin 288
Fibers, symmetry 384
Fibers, x-ray diffraction see УFiber diffraction methodsФ
Fibrils 283 285
Fibrinogen, heptad repeats 36
Fibronectin type III domain 267 319 319F
Fibrous proteins 283Ч298
Fibrous proteins, amyloid and transthyretin 288Ч289
Fibrous proteins, coiled-coil  helix 35 helix 35
Fibrous proteins, oligomers, coiled coil  helices 286Ч287 helices 286Ч287
Fibrous proteins, silk fibroins 289Ч290 (see also УActinФ УCollagenФ УMyosinФ)
Filamentous bacteriophage 359Ч361 360F
Filaments 283
Flavodoxin 24F 58F 59
Fletterick, Robert 213
Flexibility of proteins 91
Flexibility of proteins, folded proteins 104Ч105
FMN-binding redox protein 58F 59
Fold recognition (threading) 353Ч354
Folding of proteins see УProtein foldingФ
Foot-and-mouth disease virus 333
Fos 191 192 199
fos gene 199
Fos, amino acid sequence 192 192F
Fos-Jun heterodimer 192Ч193
| Four-helix bundle 37Ч39 38F
Fourier transform 379
Fourier, Jean Baptiste Joseph 379
Franklin, Rosalind 121 387
Free energy 90 92 93
Freeman, Hans 24F
Frog muscle 292Ч293
FructoseЧ6-phosphate (F6P) 114F 115 116 117
FSD-1 peptide 368 368F 368T
Functions of proteins 3
Fusogen, hemagglutinin as 80
fyn 274 275
G protein-linked receptors 251
G proteins 252Ч264
G proteins as GTPases 252 259Ч260
G proteins as molecular amplifiers 252Ч254
G proteins,  252 252
G proteins,  , , 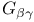 binding blocked by phosducin 265Ч266 binding blocked by phosducin 265Ч266
G proteins,  , activation by switch region change 257Ч259 , activation by switch region change 257Ч259
G proteins,  , GTP complex structure 256 , GTP complex structure 256
G proteins,  , GTP hydrolysis mechanism 260 260F 261F , GTP hydrolysis mechanism 260 260F 261F
G proteins,  , GTPase domain binding to , GTPase domain binding to  263Ч264 263Ч264
G proteins,  , inactive and active forms 258F , inactive and active forms 258F
G proteins,  , Ras comparison 256Ч257 , Ras comparison 256Ч257
G proteins,  , RGS regulating via 252 261 266 , RGS regulating via 252 261 266
G proteins,  , switch regions 257Ч259 258F , switch regions 257Ч259 258F
G proteins,  , three-dimensional structure 254Ч257 264 , three-dimensional structure 254Ч257 264
G proteins,  253 253
G proteins,  , binding to GTPase domain of , binding to GTPase domain of  263Ч264 263Ч264
G proteins,  , seven-blade propeller fold and WD units 261Ч263 , seven-blade propeller fold and WD units 261Ч263
G proteins,  252 252
G proteins,  , structure 263 , structure 263
G proteins, activated ( -GTP) 253 254 256 -GTP) 253 254 256
G proteins, activated ( -GTP), structure 253 253F -GTP), structure 253 253F
G proteins, activation 252 264
G proteins, activation by rhodopsin 265
G proteins, adenylate cyclase activation 253 253F
G proteins, definition 252
G proteins, genes 252
G proteins, heterodimer (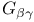 ) 253 ) 253
G proteins, heterodimer (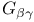 ), phosducin binding in rod cells 265Ч266 266F ), phosducin binding in rod cells 265Ч266 266F
G proteins, heterodimer (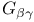 ), regulation by phosducin 265 266 ), regulation by phosducin 265 266
G proteins, heterodimer (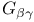 ), structure 262 262F 263 263F 264 ), structure 262 262F 263 263F 264
G proteins, heterotrimer ( ) 252 253 253F ) 252 253 253F
G proteins, heterotrimer ( ), ),  binding to binding to  263Ч264 263Ч264
G proteins, heterotrimer ( ), regulators 266 ), regulators 266
G proteins, heterotrimer ( ), structure 262Ч263 ), structure 262Ч263
G proteins, inactive ( ) 253 253F ) 253 253F
G proteins, physiological processed mediated by 252T
G proteins, signal transduction 254Ч264
G proteins, subunits 252
G proteins, subunits, amino acid residues 261 (see also УTransducinФ)
G-actin 293 293F
GAL4 187Ч189
GAL4, amino acids 187
GAL4, dimerization regions 187 190
GAL4, DNA binding, linker region role 189
GAL4, DNA-binding domain 187F
GAL4, DNA-binding domain, binuclear zinc cluster 187Ч188 188F
GAL4, domain swapping with PPR1 190 190F
GAL4, upstream-activating sequence (UAS) 188
GAL4, zinc cluster regions 187Ч188 188F
GAL4, zinc cluster regions, binding to enhancer (CCG triplet) 188Ч189 189F 191
GAP (GTPase-activating protein) 254 261
GCN4 36 175 191
GCN4, amino acid sequence 192F 193 194F
GCN4, DNA binding, nucleotide sequence 194 194F
GCN4, DNA binding, specific and nonspecific contacts 194Ч196
GCN4, DNA recognition sites 194 194F
GCN4, DNA-binding domain 194 195F
GCN4, leucine zipper binding to DNA 193Ч194
GDP, GTP hydrolysis to 252 260
Gelatin 285
Gene control, lysogeny and lytic cycle 129Ч130
Gene duplication,  -crystallin Greek key motifs and 76 -crystallin Greek key motifs and 76
Gene duplication, antibodies, T-cell receptor and MHC 300
Gene duplication, chymotrypsin evolution 212
Gene duplication, enzyme evolution 55
Gene duplication, immunoglobulin evolution 301
Gene expression, regulation 151
Gene expression, regulation, eucaryotes 159
Gene expression, regulation, procaryotes 159
Gene fusion, double  barrel formation 52Ч53 52F barrel formation 52Ч53 52F
Genetic code, amino acid side chains 4Ч5
Genetic economy, viruses 327 330
Genome organization, enzyme differences and 53
Gilbert, Walter 76
GLI 179 180F
Globin family 42
Globin fold 22F 35 40 401
Globin fold, conservation during evolution 41Ч42
Globin, hydrophobic interior 42Ч43
Globin, low sequence homology between 42Ч43
Globular proteins 90Ч91
Globular proteins,  helix 15 helix 15
Globular proteins, coiled coils in 287
Globular proteins, turnover and flexibility 91
Glucagon, NMR and x-ray crystallography comparison 391
Glucocorticoid receptor 181Ч183 182F
Glucocorticoid receptor,  helix in zinc motif 184Ч185 helix in zinc motif 184Ч185
Glucocorticoid receptor, dimer binding to DNA 183Ч184
Glucocorticoid receptor, DNA-binding domain 181Ч183 181F
Glucocorticoid receptor, DNA-binding domain, amino acid sequence 182F
Glucocorticoid receptor, DNA-binding domain, sequence-specific interactions 184Ч185 185F
Glucocorticoid receptor, function of two zinc ions 185
Glucocorticoid receptor, recognition helix 184Ч185
Glucocorticoid receptor, structure 182F 183 183F
Glucocorticoid response element (GRE) 183
Glutamic acid, side chain in ribonucleotide reductase 11 11F
Glutamic acid, structure 6F
Glutamine, GTP hydrolysis mechanism 260 260F
Glutamine, lysozyme-antilysozyme complex 310F
Glutamine, parvalbumin calcium-binding motif 25
Glutamine, recognition helix of repressor and Cro 139 141
Glutamine, structure 6F
Gly-Gly-X repeats 289 290
Glycine in silk fibroins 289
Glycine, collagen 285 286
Glycine, conformations 9Ч10
Glycine, conformations in folded structures 356
Glycine, effect on protein stability 356Ч357
Glycine, p53 mutations 167Ч168
Glycine, side chain 5 7F
Glycine, specificity of serine proteinases 213
Glycine, structure 7F
Glycolysis 114
Glycolytic enzymes 47
Goldman, A. 245
Goldsmith, Elizabeth 111
Greek key motif 27 27F 73F
Greek key motif in antiparallel  structures 72Ч74 structures 72Ч74
Greek key motif,  -crystallin 74Ч75 75F 76 -crystallin 74Ч75 75F 76
Greek key motif,  -crystallin, evolution 76 -crystallin, evolution 76
Greek key motif, alphaviruses core proteins 341
Greek key motif, chymotrypsin 211 211F
Greek key motif, complex arrangements 31 31F
Greek key motif, constant domain of immunoglobulin 304 304F
Greek key motif, jelly roll barrel formation 77 (see also УJelly roll motifsФ)
GroEL 100Ч102
GroEL, ATP complex 103
GroEL, cylindrical structure 100Ч102 100F
GroEL, cylindrical structure, model 101F
GroEL, domains 100Ч101 101F
GroEL, domains, apical 100 101F 102
GroEL, domains, equatorial 100 101F
GroEL, domains, intermediate 101F 102
GroEL, GroES binding 101F 102Ч104
GroEL, model 101F
GroEL-GroES complex 102Ч104
GroEL-GroES complex, functional cycle 104F
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 domainsФ
domainsФ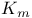 and
and values
values  barrels
barrels  -crystallin
-crystallin 
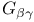 binding blocked by phosducin
binding blocked by phosducin 

 )
)  structures
structures