|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Branden C., Tooze J. Ч Introduction to protein structure |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
GroEL-GroES complex, protein folding inside 104
GroES 100
GroES, binding to GroEL 101F 102
GroES, subunits and structure 102 103F
Growth hormone 37 38F 267Ч270
Growth hormone receptor 267
Growth hormone receptor as model for erythropoietin receptor agonist 364Ч365
Growth hormone receptor, 1:1 complex 268Ч269
Growth hormone receptor, 1:2 complex 268
Growth hormone receptor, C-terminal regions 267 268
Growth hormone receptor, dimerization, induced by growth hormone 267Ч268 269
Growth hormone receptor, dimerization, sequential process 268Ч269
Growth hormone receptor, extracellular domains 267 267F
Growth hormone receptor, ligand-binding site 268
Growth hormone, binding to prolactin receptor 269Ч270 269F 270F 271F
Growth hormone, dimerization of receptor induced by 267Ч268 269
Growth hormone, four-helix bundle structure 37 38F 267 267F
Growth hormone, receptor complex 268F 365
GTP hydrolysis 252
GTP hydrolysis by  259Ч260 260F 261F 259Ч260 260F 261F
GTP hydrolysis by Ras 260Ч261
GTP hydrolysis, mechanism 259Ч261 260F 261F
GTP hydrolysis, prevention by cholera toxin 254
GTP hydrolysis, rate, GAP and RGS effect 261
GTP hydrolysis, regulators (RGS) 252 261 266
GTP hydrolyzing enzymes 255 (see also УG proteins УGTPaseФ УRas
GTP, G protein activation 252
GTP, hydrolysis see УGTP hydrolysisФ
GTP, linking to Ras proteins 255 255F
GTP-binding proteins 254 (see also УG proteinsФ)
GTPase 254
GTPase, G proteins as 252 259Ч260
GTPase, mechanism of GTP hydrolysis 259Ч261 260F 261F
GTPase, transducin  256 256F 256 256F
GTPase-activating protein (GAP) 254 261
Guanine in DNA, hydrogen bonds 123F
Guanine, G proteins binding 252
Guanine, zinc finger motif binding 181
Guanyl cyclases, transmembrane 271
H subunit, photosynthetic reaction center 235 236Ч237
Haemophilus influenzae, genome 55
Hairpin  motif 26Ч27 26F motif 26Ч27 26F
Hairpin  motif, chymotrypsin 211 211F motif, chymotrypsin 211 211F
Hairpin  motif, complex motif arrangement 30Ч31 31F motif, complex motif arrangement 30Ч31 31F
Hairpin  motif, hemagglutinin and pH changes 82F motif, hemagglutinin and pH changes 82F
Hairpin loops 21 21F
Hairpin loops, reverse turns 21Ч22 21F
Halobacterium halobium 226
Handedness,  helix 16 285 helix 16 285
Handedness, 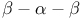 motif 28 48 49F 217 motif 28 48 49F 217
Handedness, amino acids 5
Handedness, polyproline type 11 (left-handed) 285
Hanging-drop method 375 376F
Haptens 308
Haptens, antigen-binding site 308Ч309 309F
Hardman, Karl 23
Harrison, Stephen 136 169 187 190 276 319 331 342
Hartl, Ulrich 104
Hck 275 276
Heat-shock proteins (Hsps) 100
Heavy chains see under УImmunoglobulin(s)Ф
Heavy metals, in x-ray diffraction 380Ч381
Helical wheel 17T
Helix,  see У see У helix (helices)Ф helix (helices)Ф
Helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif 24 39 196Ч197
Helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif, amino acid sequences 201F
Helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif, calcium binding 24 25F
Helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif, consensus sequence recognized 197 199 201
Helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif, homodimer and heterodimers 196Ч197 196F
Helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif, transcription factors see Уb/HLH transcription factorsФ
Helix-turn-helix motif 24 25F 129Ч149 133 134F 159
Helix-turn-helix motif, catabolite gene activating protein (CAP) 146 146F
Helix-turn-helix motif, Cro proteins 132 134F
Helix-turn-helix motif, DNA binding 133 134F
Helix-turn-helix motif, homeodomain similarity 160 161F
Helix-turn-helix motif, lac repressor 144 145F
Helix-turn-helix motif, lambda repressor 133 133F
Helix-turn-helix motif, phage 434 repressor and Cro protein 137
Helix-turn-helix motif, POU region binding to DNA 164Ч166 164F 165F
Helix-turn-helix motif, trp repressor 142 142F
Helix-turn-helix motif, two tandemly orientated in POU region 164Ч166 164F
Hemagglutinin 77
Hemagglutinin as membrane fusogen 80
Hemagglutinin as membrane fusogen, pH effect 82
Hemagglutinin,  and and 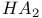 79 79F 79 79F
Hemagglutinin, inhibitors 80
Hemagglutinin, jelly roll motif 80 81F
Hemagglutinin, low and high pH forms 82Ч83 82F 83F
Hemagglutinin, polypeptide chains 78F 79
Hemagglutinin, sialic acid binding domain 80 81F
Hemagglutinin, subunit structure 79 79F
Hemagglutinin, subunit structure, pH change effect 81Ч84
Hemagglutinin, subunit structure, stem and tip 79Ч80 80F
Hemagglutinin, synthesis 79
Hemagglutinin, trimer molecule 79Ч80
Heme pocket 43
Heme pocket, evolutionary conservation 43
Hemoglobin, concentrations 43
Hemoglobin, globin fold in 40
Hemoglobin, polymerization in sickle-cell anemia 44
Hemoglobin, sickle-cell see УSickle-cell hemoglobinФ
Hemoglobin, structure 43 44F
Hen egg-white lysozyme, folding pathways 95Ч96 95F
Henderson, Richard 226
Hendrickson, Wayne 319 381
Heparin 113
Heptad repeats 36 36F 192 286
Heptad repeats in fibrous proteins 287
Herzberg, Osnat 26
Heterodimers, Fos-Jun 192Ч193
Heterodimers, HLH motif 196Ч197 196F
Heterodimers, leucine zippers 192Ч193 193F
Heterodimers, Myc with Max 199
Heterodimers, retinoid X receptor 185Ч186
Heterodimers, transcription factor binding to DNA 163 163F
Hexokinase 58F 293
Hinge helix, lac repressor 144
Hinge region, immunoglobulins 303 312 312F
Histidine in LH1 light-harvesting complex 242
Histidine in LH2 light-harvesting complex 241 241F
Histidine in serine proteinases 209
Histidine, barnase stabilization 357Ч358
Histidine, DNA binding domain of glucocorticoid receptor 181Ч182
Histidine, side chain in alcohol dehydrogenase 11 11F
Histidine, structure 7F
Histidine, substrate-assisted catalysis 218
Histidine, zinc finger motif 176 176F
Histidine, zinc finger motif, interaction with DNA 179 179F
HIV, CD4 receptor 319
HIV, Nef protein 275 276F
HIV-1 protease, L- and D- forms 9
HLA-A2 312 313 313F
HLH motif see УHelix-loop-helix (HLH) motifФ
Hogle, James 333
Hol, Wim 111
Holmes, Ken 255 292 296
Homeobox 159
Homeodomain proteins 159Ч160 160
Homeodomain proteins, definition 159
Homeodomain proteins, evolutionary role 159Ч160
Homeodomain proteins, monomer binding to DNA 160Ч162 161F
Homeodomains 160
Homeodomains, amino acid sequences 160 162 162F
Homeodomains, conserved residues 161
Homeodomains, engrailed 162F 165
Homeodomains, function in vivo 166
Homeodomains, helix-turn-helix motif comparison 160 161F
Homeodomains, recognition helix 161
Homeodomains, selectivity 162Ч164
Homeodomains, structure 160 160F
| Homeotic transformations 159
Homodimerization 202
Homologous proteins 29 348Ч350
Homologous proteins, conserved structural cores and variable loops 349Ч350 349F
Homologous proteins, definition 348
Homologous proteins, multiple alignment, secondary structure prediction 351Ч352
Homologous proteins, similar structure and function 348
Homology, definition 348
Hormone-response elements 181
Horseshoe folds 47 55
Horseshoe folds, leucine-rich motifs in 55Ч56
Horwich, Arthur 100
hsc70 293
Hsp 10 100
Hsp 60 100
Hsp 70 (DnaK) 100
Huber, Robert 26 26F 111 210 235
Human growth hormone see УGrowth hormoneФ
Human lymphocyte antigen (HLA), HLA-A2 312 313 313F
Human rhinovirus 333 336F
Human rhinovirus, antiviral drug design 337Ч338 337F 338F
Human rhinovirus, ICAM-1 receptor 338
Human rhinovirus, УcanyonsФ in VP1 337 337F 338
Huxley, A.F. 292
Huxley, H.E. 292 293
Hydrogen atoms, in NMR 387
Hydrogen bonds in  helix 15 helix 15
Hydrogen bonds in  strands 19 strands 19
Hydrogen bonds,  activation 257 259F activation 257 259F
Hydrogen bonds, acceptors and donors in DNA 125
Hydrogen bonds, B-DNA-protein interactions 124Ч125
Hydrogen bonds, jelly roll motif 78
Hydrogen bonds, mixed  sheet 20 20F sheet 20 20F
Hydrogen bonds, nonspecific protein-DNA interactions 139Ч140 140F
Hydrogen bonds, subtilisin 217
Hydrogen bonds, TATA box and TBP binding 157 158
Hydrogen bonds, triple helix collagen 286 286F
Hydrogen bonds, zinc finger motif 177
Hydropathy index 245
Hydropathy plots 245 246F
Hydropathy plots, photosynthetic reaction center 245 246 246F
Hydrophilic regions, membrane proteins 223 223F
Hydrophilic residues in  domains 35 domains 35
Hydrophilic residues in  helix 17 helix 17
Hydrophobic core 14
Hydrophobic core,  domains 35 42Ч43 domains 35 42Ч43
Hydrophobic core, formation 14
Hydrophobic core, T4 lysozyme 358
Hydrophobic interaaions, TATA box and TBP 157Ч158
Hydrophobic residues, in  helix 17 helix 17
Hydrophobic side chains see УSide chainsФ
Hydrophobicity, light-harvesting complex 242
Hydrophobicity, porins 231
Hydrophobicity, scales 245 245T
Hydrophobicity, transmembrane regions 223
Hydroxyproline, in collagen 284
Hypervariable regions, immunoglobulins 301 302F 305Ч306 349
Hypervariable regions, immunoglobulins, antigen-binding site 306Ч308 306F
Hypervariable regions, immunoglobulins, antigen-binding site, formation 306Ч308 306F 307F 308F
Hypervariable regions, immunoglobulins, conformations 305Ч306
Hypervariable regions, immunoglobulins, loop structure 305Ч306 306F
Hypervariable regions, immunoglobulins, modeling 349
Hypervariable regions, immunoglobulins, space-filling model 308F (see also УComplementarity determining regionsФ)
Hypervariable regions, T-cell receptor 316 317 318F
ICAMЧ1 338
Icosahedral symmetry 327Ч328 328F
Icosahedral symmetry, viruses 327 327F
icosahedron 327Ч328 328F
Icosahedron, asymmetric units 328 328F
Icosahedron, quasi-equivalent packing 330Ч331
Icosahedron, satellite tobacco necrosis virus 329
Icosahedron, symmetry 327Ч328
Icosahedron, triangulation numbers (T) 330
IgG see УImmunoglobulin G (IgG)Ф
IGP-synthase 52
Image plates 377
Immune system 299Ч323
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) 301F
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) 301F
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) 301F
Immunoglobulin fold 168 304 304Ч305
Immunoglobulin fold in transcription factors 168Ч169
Immunoglobulin fold, antiparallel  sheets 304Ч305 304F sheets 304Ч305 304F
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) 301 302
Immunoglobulin G (IgG), cleavage 304F
Immunoglobulin G (IgG), crystallization 312
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) 302
Immunoglobulin M (IgM), structure 301F
Immunoglobulin(s) 299
Immunoglobulin(s), antigen recognition 315
Immunoglobulin(s), antigen-binding site see УAntigen-binding siteФ
Immunoglobulin(s), class-switching 302
Immunoglobulin(s), conformational flexibility 312 312F
Immunoglobulin(s), constant domains 301 301F 302
Immunoglobulin(s), constant domains, association in antigen-binding site 307 307F
Immunoglobulin(s), constant domains, comparison with variant domains 305 305F
Immunoglobulin(s), constant domains, globular units 306 306F
Immunoglobulin(s), constant domains, structure 304 304F
Immunoglobulin(s), diversity 302Ч303
Immunoglobulin(s), domains 301 301F 302 302F
Immunoglobulin(s), domains, classification 318Ч319
Immunoglobulin(s), evolution 301
Immunoglobulin(s), genetic recombination 302 302F 303F
Immunoglobulin(s), heavy chain 300Ч301
Immunoglobulin(s), heavy chain, antigen-binding site formation 306Ч308 306F
Immunoglobulin(s), heavy chain, CDR3 and CDR2 311
Immunoglobulin(s), heavy chain, diversity generation 302
Immunoglobulin(s), heavy chain, genes 302
Immunoglobulin(s), hinge region 303 312 312F
Immunoglobulin(s), hypervariable regions see УHypervariable regionsФ
Immunoglobulin(s), light chain 300Ч301
Immunoglobulin(s), light chain, antigen-binding site formation 306Ч308 306F
Immunoglobulin(s), light chain, CDR2 311
Immunoglobulin(s), light chain, diversity generation 302Ч303
Immunoglobulin(s), structure 301F
Immunoglobulin(s), V-D-J joining process 302 303F
Immunoglobulin(s), variable domains 301 301F 302F 305 305F
Immunoglobulin(s), variable domains, association in antigen-binding site 307Ч308 307F
Immunoglobulin(s), variable domains, globular units 306 306F
Immunoglobulin(s), variable domains, hypervariable regions in loops 305Ч306
Immunoglobulin-like domain 300
Immunosuppression, peptidyl, prolylisomerases in 98
Indoleglycerol phosphate (IGP) synthase 52Ч53 53F
Induced fit, ligand binding theory 114
Influenza virus 70
Influenza virus, binding site 80
Influenza virus, drug design targets 80
Influenza virus, hemagglutinin see УHemagglutininФ
Influenza virus, infection initiation 80 82
Influenza virus, neuraminidase see УNeuraminidaseФ
Influenza virus, progeny and release 79
Influenza virus, protease treatment 79
Insulin, disulfide bridges 8
Interdomain movements 109Ч110
Intermediate filaments 287 287F
Intermediate filaments, construction model 287F
Inverse folding problem 353
ion channels 232Ч234 251
Ion channels, definition 232 (see also УPotassium channelsФ)
Iron atom, in photosynthetic reaction center 236 238
Iron in ribonucleotide reductase 11 11F
Iron, functions 11
Isaacs, Neil 241
Isoleucine, binding to SH2 domain 274
Isoleucine, Nef binding to SH3 domain 275
Isoleucine, structure 6F
Isoleucine, x-ray diffraction data 382
Isomerization 227F
Isomerization, proline residues 98Ч99 99F
Isomerization, retinal 227F 228 229F
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте




 motif
motif  helix
helix 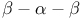 motif
motif  and
and