|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Branden C., Tooze J. Ч Introduction to protein structure |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Cell cycle,  phase 106 phase 106
Cell cycle, Gap 1 ( phase) 105 phase) 105
Cell cycle, Gap 2 ( phase) 105Ч106 phase) 105Ч106
Cell cycle, M phase 105
Cell cycle, protein kinase conformational changes 105Ч109
Cell cycle, regulation by p21 166
Cell cycle, S phase 105
Cell growth/differentiation 271 272F
Cellulase, NMR 387F 390F
Cephalosporinase genes, DNA shuffling 366 366F 367F
ch see УImmunoglobins constant
cH-rasp21 254F
Chaperones 89
Chaperones, hsc70 293
Chaperonin, definition 100
Chaperonin, GroEL see УGroELФ
Chaperonin, protein folding/unfolding in 99Ч100
Chemical shifts, in NMR methods 387 387F 388
Chimeric protein 190
Chiral forms, amino acids 5
Chlorophyll, accessory molecules 238 238F 239
Chlorophyll, arrangement 238F
Chlorophyll, circular rings in light-harvesting complex LH2 241 241F 242F 243
Chlorophyll, photon absorption 239
Chlorophyll, Уspecial pairФ 236 238 238F 239 244
Cholera toxin 254
Chothia, Cyrus 31 32 42 311 317
Chymotrypsin 29F
Chymotrypsin, active site structure 211Ч212 211F 212F
Chymotrypsin, domains 211 211F
Chymotrypsin, evolution 210
Chymotrypsin, evolution, gene duplication 212
Chymotrypsin, preferential cleavage mechanism 212Ч213
Chymotrypsin, specificity mechanism 209
Chymotrypsin, specificity pockets 212Ч213 213F
Chymotrypsin, structure 210Ч211 210F
Chymotrypsin, subtilisin similarity 216Ч217
Chymotrypsin, superfamily 210 212
cis-peptide 98 98F
cis-retinoid acid receptor (RXR) 185
cis-retinoid acid receptor (RXR), heterodimer formation 186 186F
Citrate synthase 17T
Classification of protein structure, classes 31Ч32
Classification of protein structure, topology diagrams 23
Clonal selection theory 299F 300
Coagulation cascade 361
Cogdell, Richard 241
Coiled-coil  helix see У helix see У helixФ helixФ
Collagen 284Ч286
Collagen, alanine mutation 285 285F
Collagen, fibers 283
Collagen, polypeptide chains 284 284F 285
Collagen, superhelix of left-handed helices 284Ч286 284F
Collagen, superhelix of left-handed helices, hydrogen bonding 286 286F
Collagen, synthesis 284
Collectins 36
Colman, Peter 71
Combinatorial control, leucine zipper dimerization 193
Combinatorial design, FSDЧ1 peptide 368
Combinatorial joining 302 302F 303
Combinatorial libraries 358
Combinatorial methods in vitro selection see УBacteriophage displayФ
Combinatorial methods, definition 358
Combinatorial methods, protein engineering 358Ч359
Combinatorial screening, sequence recognition by SH3 274
Common cold, drugs 337Ч338
Complementarity determining regions (CDR) 301 302F
Complementarity determining regions (CDR), CDR1 305
Complementarity determining regions (CDR), CDR2 305 311
Complementarity determining regions (CDR), CDR3 302Ч303 305 310 311
Complementarity determining regions (CDR), CDR3, loop conformations and sequences 350
Complementarity determining regions (CDR), conformation prediction 350 350F
Complementarity determining regions (CDR), conformational changes 311Ч312
Complementarity determining regions (CDR), conformational changes, limited range 311Ч312 350
Complementarity determining regions (CDR), lysozyme and Fab binding 309Ч310 310F
Complementarity determining regions (CDR), T-cell receptor 317F (see also УHypervariable regions immunoglobulinsФ)
Computer-generated diagrams,  -crystallin structure 74 74F -crystallin structure 74 74F
Computer-generated diagrams, myoglobin 22F
Computer-generated models 23
Computer-generated models, building from x-ray diffraction data 382 382F 384
Concanavalin A 77
Concerted model 113Ч114
Conformational changes 105
Conformational changes, calmodulin and peptide binding 109Ч110 110F
Conformational changes, complementarity determining regions 311Ч312
Conformational changes, ligand-induced 142Ч143
Conformational changes, protein kinase 105Ч109
Conformational changes, R and T states of allosteric proteins 113Ч114
Conformational changes, R and T states of allosteric proteins, phosphofructokinase 114Ч117 117F
Conformational changes, serpins 111Ч113 112F
Conformational changes, switch regions in  257Ч259 257Ч259
Conformational changes, trp repressor 142Ч143
Consensus motif, sequence recognition by SH3 274
Consensus sequence,  -horseshoe fold 55 -horseshoe fold 55
Consensus sequence, b/HLH transcription factors binding to 197 199 201
Consensus sequence, TATA box 154F
Continuous lipidic cubic phase 225
control module 151
Cooperative binding 113
Coreceptors, CD4 319
Corepressor 142Ч143 143F
COSY (correlation spectroscopy) NMR experiments 388 388F 389
COSY (correlation spectroscopy) NMR experiments, cross-peaks (ТfingerprintsТ) 388F 389
Covalent bonds, , peptide units 8
Covalent bonds, native/denatured state of proteins 90
Craik, Craig 213
Creighton, Thomas 96
Creutzfeldt Ч Jacob disease 113
Crick, Francis 13 35 36 121 285 387
Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP) 353
Cro gene, repression by repressor protein 130
Cro protein 129
Cro protein as dimer 132 132F
Cro protein as repressor 131
Cro protein, action in genetic switch region 130Ч131 130F
Cro protein, differential binding to operator sites 140Ч141
Cro protein, dimerization 132
Cro protein, DNA interactions 134Ч135
Cro protein, helix-turn-helix motif 132 134F
Cro protein, lambda see УBacteriophage lambdaФ
Cro protein, phage 434 see УBacteriophage 434Ф
Cro protein, phage P22 135 136F
Cro protein, summary 141Ч142
Cro protein, synthesis 131
Cross-bridges see Уwider MyosinФ
Cross-peaks, in COSY spectra 388F 389
Cryocooling 377
Cryoelectron microscopy, alphaviruses 340Ч341
Cryoprotectants 377
Crystallites 384 385F
Crystallization 375
Crystallization, hanging-drop method 375 376F
Crystallization, membrane proteins 224Ч225
Crystals, protein, channels in 374Ч375 375F
Crystals, protein, cooling 377
Crystals, protein, difficulties in obtaining 374 375 384
Crystals, protein, growth 375
Crystals, protein, isomorphous 380
Crystals, protein, structure 373F
Crystals, protein, unit cell 374
Cyclic AMP 253
Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase 277Ч278
Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase 265
Cyclin 106 166
Cyclin A 106
Cyclin A, binding to CDK2 107 107F 108F 109F
Cyclin A, structure 107F
Cyclin box 108
Cyclin fold 108 159
Cyclin, half-life 106
| Cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs) 106 272
Cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs) as relay of switches 106
Cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs), CDK2 106Ч108 107F 272
Cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs), CDK2, cyclin A binding and conformational change 107Ч108 107F 108F 109F
Cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs), CDK2, domains 107Ч108 107F
Cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs), CDK2, T-loop 108 109F
Cyclophilin 98Ч99 99F
Cyclophilin, cis-trans isomerization enhancement 99
Cyclophilin, structure 99 99F
Cyclosporin A 98Ч99
Cys-X-X-Cys motif 97
Cysteine proteinase 205
Cysteine, disulfide bridge formation 5Ч8
Cysteine, DNA-binding domain of GAL4 187 188F
Cysteine, loop length between, effect of stability 355Ч356
Cysteine, side chain in alcohol dehydrogenase 11 11F
Cysteine, structure 6F
Cysteine, zinc finger motif 176 176F
Cysteine, zinc finger motif, DNA-binding domain of glucocorticoid receptor 181Ч182 183 184
Cytochrome  37 38F 37 38F
Cytochrome c oxidase, crystallization 225
Cytochrome c' 37
Cytochrome, in photosynthetic reaction center 235 236 240
Cytosine, in DNA, hydrogen bonds 123F
D-form of amino acids 5 9
D-form, of amino acids 5 9
Dahiyat, Bassil 367
Database on World Wide Web 393 394
Database, homologous proteins 348
Database, protein folds 353
Davies, David 304 309
Deacylation 208 209F
Dehydration, ion selectivity filter mechanism 234
Deisenhofer, Hans 235
Deisenhofer, Johann 55 102
Denatured state of proteins 90
Dennis, Mark 362
Detergents, membrane protein solubilization 224 225F
Dictyostelium myosin 295
Diffraction patterns see also УX-ray diffractionФ
Diffraction spot 379 386
Dijkstra, Bauke 39
Dimeric proteins, bacteriophage MS2 339Ч340 339F 340F
Dimeric proteins, glucocorticoid receptor 183Ч184
Dimeric proteins, lambda Cro protein 132 132F
Dimeric proteins, lambda repressor 132 132F
Dimeric proteins, phosphofructokinase (PFK) 116 (see also УHeterodimersФ)
Dipole moment,  helix 16 16F 357Ч358 357F helix 16 16F 357Ч358 357F
Dipole moment, peptide unit 16 16F
Distance constraints, NMR methods 390Ч391
Disulfide bonds/bridges 5
Disulfide bonds/bridges in 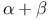 domains 32 domains 32
Disulfide bonds/bridges, chymotrypsin 210
Disulfide bonds/bridges, collagen 285
Disulfide bonds/bridges, formation 5Ч8
Disulfide bonds/bridges, formation, during protein folding 96Ч98
Disulfide bonds/bridges, insulin 8
Disulfide bonds/bridges, protein stability increased 354Ч356
Disulfide bonds/bridges, stability 97Ч98
Disulfide bridge-forming enzymes (Dsb) 96 97 97F
DNA 121
DNA in control module 151
DNA recognition 129
DNA recognition by helix-turn-helix motifs 129Ч149 (see also УCro proteinsФ УHelix-turn-helix УRepressor
DNA recognition by transcription factors 151Ч174
DNA recognition, sequence-specific 124Ч125 125F
DNA recognition, sequence-specific for restriction enzymes 125
DNA recognition, sequence-specific, recognition pattern 124Ч125 125F
DNA shuffling 359F 365Ч366
DNA shuffling, cephalosporinase genes 366 366F 367F
DNA shuffling, process 366 366F
DNA,  -crystallin sequence 76 -crystallin sequence 76
DNA, A-DNA 121 122F
DNA, A-DNA, diffraction patterns 386 386F
DNA, A-DNA, major groove 123 123F
DNA, B-DNA 121 121F 122F
DNA, B-DNA as preferred conformation 124
DNA, B-DNA, base pairs in turn 135
DNA, B-DNA, base sequences 124Ч125 124F
DNA, B-DNA, deformation after TBP binding 155Ч157
DNA, B-DNA, diffraction patterns 386 386F
DNA, B-DNA, distortions due to protein binding 138 138F 145
DNA, B-DNA, helix-turn-helix motif binding 134
DNA, B-DNA, hydrogen bonds with protein side chains 124Ч125
DNA, B-DNA, major and minor grooves 122Ч123 123F
DNA, base pairs, in major and minor grooves 123F 124F
DNA, bending, CAP-induced 146Ч147 156
DNA, bending, energy 147
DNA, bending, functional implications 158
DNA, bending, TATA box-binding protein inducing 155Ч157 156F 158
DNA, conformational changes, differential binding of repressors and Cro 140Ч141
DNA, conformational changes, glucocorticoid receptor binding 182F 183
DNA, conformational changes, protein-DNA backbone interactions 139Ч140
DNA, diffraction patterns 386Ч387 386F
DNA, distortion, p53 binding 170
DNA, hairpin, in TATA box 154
DNA, helix regularity, fiber formation 384
DNA, helix structure 121Ч122 122F
DNA, helix structure, major and minor grooves 122Ч123 122F 123F
DNA, homeodomain complex 161 161F
DNA, homeodomain protein monomer binding 160Ч162 161F
DNA, kinks 156 156F
DNA, major groove, b/HLH motif binding 198Ч199 198F
DNA, major groove, classic zinc fingers binding 177Ч178
DNA, major groove, Cro protein binding 134Ч135
DNA, major groove, GCN4 binding 196
DNA, major groove, homeodomain binding 161 161F
DNA, major groove, hydrophilic protein-DNA interactions 157
DNA, major groove, lac repressor binding 143Ч145 145F
DNA, major groove, p53 binding 169Ч170 169F 171
DNA, major groove, sequence-specific recognition 124Ч125 125F
DNA, major groove, zinc cluster of GAL4 binding 188 189F
DNA, major groove, zinc finger of glucocorticoid receptor binding 184
DNA, Mat 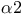 -Mat al complex binding 163 163F -Mat al complex binding 163 163F
DNA, minor groove, homeodomain recognition 161
DNA, minor groove, lac repressor binding 143Ч145 145F
DNA, minor groove, p53 binding 169Ч170 169F 171
DNA, minor groove, TATA box-binding protein binding 155Ч157 156F
DNA, palindromic sequences 131Ч132 131T 135
DNA, POU region binding 165Ч166 165F
DNA, protein interactions see УProtein-DNA interactionsФ
DNA, protein linked to 359Ч361
DNA, recognition see УDNA recognitionФ
DNA, sequence-specific interactions, operator regions and repressors 139 139F
DNA, sequence-specific recognition pattern 124Ч125 125F
DNA, site-directed mutagenesis 354
DNA, structural change after TBP binding 155Ч157
DNA, structures 121Ч126
DNA, sugar-phosphate backbone 139 141
DNA, synthesis, cell cycle 105 106
DNA, twist angles 121
DNA, unwinding, TATA box-binding protein binding 156 156F
DNA, Z-DNA see УZ-DNAФ
DNA-binding domain 129
DNA-binding domain, cis-retinoic acid receptor (RXR) 186 186F
DNA-binding domain, GCN4 194 195F
DNA-binding domain, glucocorticoid receptor 181Ч183
DNA-binding domain, MyoD 197F
DNA-binding domain, p53 167 167F 168Ч169 168F
DNA-binding motifs, helix-turn-helix 133 134F
DNA-binding motifs, lambda Cro and repressor proteins 133Ч134
DNA-binding motifs, zinc in 175
DNA-binding proteins 121 152
DNA-binding proteins, catabolite gene activating protein (CAP) 146
DNA-binding proteins, procaryotic, homeodomain differences 160
DNA-binding proteins, transcription factors see УTranscription factorsФ (see also УCro proteinФ УRepressor
DnaK (Hsp 70) 100
dodecahedron 327F
Dodson, Christopher 95
Dodson, Guy 94
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 phase
phase  phase)
phase) 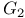 phase)
phase)  helix
helix  -crystallin structure
-crystallin structure 
 -horseshoe fold
-horseshoe fold 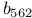
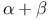 domains
domains 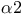 -Mat al complex binding
-Mat al complex binding