|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Knuth D.E. Ч The art of computer programming (vol. 2 Seminumerical Algorithms) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
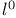 -chain 479 483 485 -chain 479 483 485
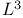 algorithm 118 417 453 algorithm 118 417 453
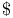 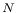 170 170
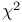 42 56 42 56
 (Euler's constant) 359 379 726Ч727 733 (Euler's constant) 359 379 726Ч727 733
 , representation of 225 244Ч245 332 , representation of 225 244Ч245 332
 -distributed sequence 151Ч161 177 180Ч182 -distributed sequence 151Ч161 177 180Ч182
 (golden ratio) 164 283 359 360 514 652 726Ч727 733 (golden ratio) 164 283 359 360 514 652 726Ч727 733
 (golden ratio), logarithm of 283 (golden ratio), logarithm of 283
 (golden ratio), number system 209 (golden ratio), number system 209
 (circle ratio) 41 151 158 161 198 200 279Ч280 284 358 726Ч727 733 (circle ratio) 41 151 158 161 198 200 279Ч280 284 358 726Ч727 733
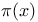 (prime count) 381Ч382 416 (prime count) 381Ч382 416
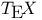 iv vi 762 iv vi 762
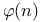 (totient function) 19Ч20 289 369 376 583 646 (totient function) 19Ч20 289 369 376 583 646
0-origin indexing 444 512
10-adic numbers 632
1009 vi 188 413 661
2-adic numbers 213
69069 75 106 108
A priori tests 80
abacus 196
Abacus, binary 200
Abel, Niels Henrik, binomial theorem 58 535
Abramowitz, Milton 44
Absolute error 240 309 312Ч313
Absorption laws 694
Abuse of probability 433
Abuse of theory 88
ACC: Floating point accumulator 218Ч219 248Ч249
Acceptance-rejection method 125Ч126 128Ч129 134 138 139 591
Accuracy of floating point arithmetic 222 229Ч245 253 329 438 485
Accuracy of random number generation 27 95 105 185
adaptation of 490Ч494 516Ч517
Adaptation of coefficients 490Ч494 516Ч517
Add-with-carry sequence 23 35 72 108 547
Addition 194 207 210 213 265Ч267
Addition chains 465Ч485 494 519
Addition chains, 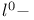 479 483 485 479 483 485
Addition chains, ascending 467
Addition chains, dual 481 485
Addition chains, star 473Ч477 480 482 467
Addition, complex 487
Addition, continued fractions 649
Addition, double-precision 247Ч249 251
Addition, floating point 215Ч220 227Ч228 230Ч231 235Ч238 253Ч254 602
Addition, fractions 330Ч331
Addition, left to right 281
Addition, mixed-radix 281
Addition, mod m 12 15 203 287Ч288
Addition, modular 285Ч286 293
Addition, multiprecision 266Ч267 276Ч278 281 283
Addition, polynomial 418Ч420
Addition, power series 525
Addition, sideways 463
Addition-subtraction chains 484
Additive random number generation 27Ч29 39Ч40 186Ч188 193
Adleman, Leonard Max 396 403 405 414 417 671
Admissible numbers 177
Ahrens, Joachim Heinrich Ludecke 119 129Ч130 133 134 136 137 140 141 588
Ahrens, Wilhelm Ernst Martin Georg 208
Akushsky, Izrail Yakovlevich (јкушский, »зраиль яковлевич) 292
al-Biruni, Abu al-Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad 461
al-Kashi, Jamshid ibn Mas'ud 198 326 462
al-Khwarizmi, Abu 'Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Musa 197 280
al-Samaw'al (= as-Samaw'al), ibn Yahya ibn Yahuda al-Maghribi 198
al-Uqlidisi, Abu al-Hasan Ahmad ibn Ibrahim 198 280Ч281 461
Ala-Nissila, Tapio 75 570
Alanen, Jack David 30
Aldous, David John 145
Alekseev, Boris Vasilievich (јлексеев, Ѕорис ¬асильевич) 117
Alekseyev, Valery Borisovich (јлексеев, ¬алерий Ѕорисович) 699
Alexi, Werner 669
Alford, William Robert 659
Algebra, free associative 437
Algebraic dependence 496 518
Algebraic functions 533
Algebraic integers 396
Algebraic number fields 331 333 345 403 674
Algebraic system: A set of elements together with operations defined on them see УFieldФ УRingФ УUnique
Algol 279
Algorithm 439Ч447
Algorithms: Precise rules for transforming specified inputs into specified outputs in a finite number of steps, analysis of 7Ч9 76 140 147 276Ч278 281 301Ч302 348Ч356 360Ч373 377Ч378 382Ч384 399Ч400 435 445Ч447 455Ч456 530Ч532 658 714
Algorithms: Precise rules for transforming specified inputs into specified outputs in a finite number of steps, complexity of 138 178Ч179 280 294Ч318 396 401Ч402 416 453 465Ч485 494Ч498 516Ч524 720
Algorithms: Precise rules for transforming specified inputs into specified outputs in a finite number of steps, discovery of 99
Algorithms: Precise rules for transforming specified inputs into specified outputs in a finite number of steps, historical development of 335 461Ч462
Algorithms: Precise rules for transforming specified inputs into specified outputs in a finite number of steps, proof of 281Ч282 336Ч337 592
Alias method 120 127 139
Allouche, Jean-Paul 656
ALPAK 419
Alt, Franz Leopold 706
American National Standards Institute 226 246 600 602
Amplification of guesses 172Ч174 416Ч417
Analysis of Algorithms 7Ч9 76 140 147 276Ч278 281 301Ч302 348Ч356 360Ч373 377Ч378 382Ч384 399Ч400 435 445Ч447 455Ч456 530Ч532 658 714
Analysis of algorithms, history 360
Analytical engine 189 201
Ananthanarayanan, Kasi 128
AND (bitwise and) 140 188 322 328Ч329 389Ч390 453 671
Anderson, Stanley F. 312
ANSI: The American National Standards Institute 226 246 600 602
Antanairesis 335Ч336 378
Apollonius of Perga 225
Apparently random numbers 3Ч4 170Ч171
Apparition, rank of 410Ч411
Approximate associative law 232Ч233 239Ч240 244
Approximate equality 224 233Ч235 239 242Ч243 245
Approximately linear density 126
Approximation, by rational functions 438Ч439 534
Approximation, by rational numbers 331Ч332 378Ч379 617
Arabic mathematics 197 280Ч281 326 461Ч462
Arazi, Benjamin 396
Arbitrary precision 279 283 331 416
Arbogast, Louis Francois Antoine 722
Archibald, Raymond Clare 201
Arctangent 313 628
Aristotle of Stagira, son of Nicomachus 335
Arithmetic 194Ч537 (see УAdditionФ УComparisonФ УDivisionФ УDoublingФ УExponentiationФ УGreatest УHalvingФ УMultiplicationФ УReciprocalФ УSquare УSubtractionФ)
Arithmetic chains see УQuolynomial chainsФ
Arithmetic, complex 205 228 283 292 307Ч310 487 501 506 519 700 706
Arithmetic, floating point 214Ч264
Arithmetic, fractions 330Ч333 420 526
Arithmetic, fundamental theorem of 334 422 483
Arithmetic, mod m 12Ч16 185Ч186 203 284 287Ч288
Arithmetic, modular 284Ч294 302Ч305 450 454 499
Arithmetic, multiprecision 265Ч318
Arithmetic, polynomial 418Ч524
Arithmetic, power series 525Ч537
Arithmetic, rational 330Ч333 420 526
Armengaud, Joel 409
Arrival time 132
Arwin, Axel 687
Aryabhata 343
ASCII: The American Standard Code for Information Interchange 417
Ashenhurst, Robert Lovett 240 242 327
Associative law 229Ч233 242 341 418 694
Associative law, approximate 232Ч233 239Ч240 244
Asymptotic values: functions that express the limiting behavior approached by numerical quantities 59Ч60 79 263Ч264 355 372Ч373 377Ч378 415 472 525 541Ч542 659 686 722
Atanasoff, John Vincent 202
Atkin, Arthur Oliver Lonsdale 681
Atrubin, Allan Joseph 315
Automata (plural of Automaton) 313Ч317 329 416
Automorphic numbers 293Ч294
Avogadro di Quaregna e Cerreto, Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo, number 214 227 238 240
Axioms for floating point arithmetic 230Ч231 242Ч245
b-ary number 151
b-ary sequence 151Ч153 177
Babbage, Charles 201
Babenko, Konstantin Ivanovich (Ѕабенко, онстантин »ванович) 366 376
Babington-Smith, Bernard 3 74 76
Babylonian mathematics 196 225 335
Bach, Carl Eric 396 661 663 689
| Bachet, Claude Gaspard, sieur de Meziriac 208
Bag 694
Bailey, David Harold 284 634
Baker, Kirby Alan 316
Balanced binary number system 213
Balanced decimal number system 211
Balanced mixedЧradix number system 103 293 631
Balanced ternary number system 207Ч208 209 227 283 353
Ballantine, John Perry 278
Bareiss, Erwin Hans 262 292 434
Barlow, Jesse Louis 262
Barnard, Robert 292
Barnsley, Michael Fielding 206
Barton, David Elliott 74 566
Barycentric coordinates 567
Base of representation 195
Base of representation, floating point 214Ч215 254 263
BASEBALL 378
Bauer, Friedrich Ludwig 241Ч242 327
Baum, Ulrich 701
Baur, Walter 718
Bays, John Carter 34
Beauzamy, Bernard 452 461 683 684
Beckenbach, Edwin Ford 135
Becker, Oskar Joachim 359
Bejian, Robert 164
Belaga, Edward Grigorievich (Ѕелага, Ёдуард √ригорьевич) 496
Bell Telephone Laboratories Model V 225
Bellman, Richard Ernest ix.
Ben-Or, Michael 669
Benford, Frank 255
Bentley, Jon Louis 141
Bergman, George Mark 676
Berkowitz, Stuart J. 718
Berlekamp, Elwyn Ralph 439 449 456 681
Bernoulli, Jacques (= Jakob = James) 200
Bernoulli, numbers 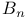 355 569 355 569
Bernoulli, numbers, table 728
Bernoulli, sequences 177
Bernstein, Daniel Julius 724
Besicovitch, Abram Samoilovitch (Ѕезикович, јбрам —амойлович) 178
Beta distribution 134Ч135
Beyer, William Aaron 115
Bharati Krishna Tirthaji Maharaja, Jagadguru Swami Sri, Shankaracharya of Goverdhana Matha 208
Bhaskara Acharya I 343
Bienayme, Irenee Jules 74
Bilinear forms 506Ч514 520Ч524
Billingsley, Patrick Paul 384 661
Bin-packing problem 585
Binary abacus 200
Binary basis 212
Binary computer: A computer that manipulates numbers primarily in the binary (radix 2) number system 30Ч32 201Ч202 276 328 339 389Ч390
Binary digit 195 200
Binary gcd algorithms 338Ч341 348Ч356 435
Binary gcd algorithms, compared to Euclid's 341
Binary gcd algorithms, extended 356
Binary method for exponentiation 461Ч463 466 482 696
Binary number systems 195 198Ч206 209Ч213 419 461 483
Binary point 195
Binary recurrences 318 634 714
Binary search 324
Binary shift 322 339 481 637 686
Binary trees 378 527 696 723
Binary-coded decimal 202 322 328Ч329
Binary-decimal conversion 319Ч329
BINEG 205
Binet, identity: 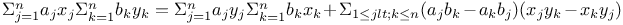 564 564
Binet, Jacques Philippe Marie 653
Bini, Dario Andrea 500 505 515 714 715 721
Binomial coefficients 416 516 622
Binomial distribution 136Ч138 141 401 559
Binomial distribution, tail of 167
Binomial number system see УCombinatorial number systemФ
Binomial theorem 526 534
Birnbaum, Zygmunt Wilhelm 57
Birthday spacings 34 71Ч72 78Ч79 188
Bit: "Binary digit", either zero or unity 195 200
Bit: "Binary digit", random 12 30Ч32 35Ч36 38 48 119Ч120 170Ч176
Bitwise operations see УBoolean operationsФ
Bjork, Johan Harry 244
Blachman, Nelson Merle 205
Black Box 455
Bleichenbacher, Daniel 478
Blinn, James Frederick 630
Blote, Hendrik Willem Jan 29
Blouin, Francois Joseph Raymond Marcel 582
Bluestein, Leo Isaac 634
Blum, Bruce Ivan 279
Blum, Fred 433 518
Blum, integer 174 416
Blum, Lenore Carol 36 599
Blum, Manuel 36 174 179 599
Bofinger, Eve 563
Bofinger, Victor John 563
Bohlender, Gerd 242 616
Bojaniczyk, Adam Wojciech 646
Bombieri, Enrico 683
Bombieri, norm 458 684
Boolean operations 30Ч31 140 202 328Ч329 389Ч390 459 605
Boolean operations, and 140 188 322 328Ч329 389Ч390 453 671
Boolean operations, exclusive or 31 32 193 419
Boolean operations, or 140 686 695
Boolean operations, shifts 322 339 481 637 686
Border rank 522Ч523
Borel, Emile Felix Edouard Justin 177
Borodin, Allan Bertram 498 505 515 707
Borosh, Itzhak 106Ч107 117 291 584
Borrow: A negative carry 267 273 281 545
Borwein, Peter Benjamin 284
Bosma, Wiebren 665
Bouyer, Martine 280
Bowden, Joseph 201
Box, George Edward Pelham 122
Boyar, Joan 599
Boyd, David William 691
Bradley, Gordon Hoover 343 378
Brakke, Kenneth Allen 608
Bramhall, Janet Natalie 530
Brauer, Alfred Theodor 470 478 483 690
Bray, Thomas Arthur 33 128 544
Brent, Richard Peirce 8 28 40 130 136 139 141 241 279 280 313 348 352Ч353 355 356 382 386 403 501 529Ч534 539Ч540 556 590 600 643 644 646 657 695 719Ч721
Brezinski, Claude 357 721
Brillhart, John David 29 394 396 400 660
Brockett, Roger Ware 712
Brocot, Achille 655
Bronte, Emily Jane 292
Brooks, Frederick Phillips, Jr. 226
Brouwer, Luitzen Egbertus Jan 179
Brown, David see УSpencer BrownФ
Brown, George William 135
Brown, Mark Robbin 712
Brown, Robert see УBrownian motionФ
Brown, William Stanley 419 428 438 454 686
Brownian motion 559
Bruijn, cycle 38Ч40
Brute force 642
Bshouty, Nader Hanna 700
Buchholz, Werner 202 226
Bunch, James Raymond 500
Buneman, Oscar 706
Burgisser, Peter 515
Burks, Arthur Walter 202
Burrus, Charles Sidney 701
Butler, James Preston 77
Butler, Michael Charles Richard 442
C language 185Ч188 193 327 556
Cahen, Eugene 676
Calculating prodigies 279 295
Camion, Paul Frederic Roger 449
Campbell, Edward Fay, Jr. vii.
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -chain
-chain  algorithm
algorithm 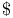
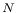
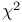
 (Euler's constant)
(Euler's constant)  , representation of
, representation of  (golden ratio)
(golden ratio)  (circle ratio)
(circle ratio) 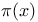 (prime count)
(prime count) 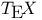
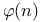 (totient function)
(totient function)