|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Riviere J.C. (ed.), Myhra S. (ed.) Ч Handbook of Surface and Interface Analysis |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
O(oxygen), Auger parameter  512 516 512 516
O(oxygen), chemical shifts 171 328Ч329
O(oxygen), chemical shifts, bonded to 172
O(oxygen), in C fibres, effect of electrochemical treatment 611
O(oxygen), in C fibres, effect of heat from X-ray source 621
O(oxygen), in C fibres, from coated fibre 618
O(oxygen), in C fibres, functionality contributions 620Ч621
O(oxygen), in Cr Ч O Ч Si cermet, 1s position 328Ч329
O(oxygen), in Cr Ч O Ч Si cermet, ion beam effect 328Ч329
O(oxygen), in InP on  , O KVV indicator 530 , O KVV indicator 530
O(oxygen), in PbO and 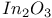 , peak positions 499 , peak positions 499
O(oxygen), in polymers, ion beam damage 338
O(oxygen), in polymers, peak positions 338
O(oxygen), in TiN, peak positions 318 320
Optical interferometry, measurement of crater depth 269
Optical microscopy, corrosion film 651 653
Optical microscopy, corrosion pit in Cu 652
Optical microscopy, information 546Ч547 648
Optical microscopy, usefulness 548 648 650
Organosilanes, adhesion promoters 811Ч814
Organosilanes, adhesion promoters, adsorption isotherms on Fe 811Ч812
Organosilanes, adhesion promoters, covalent bonding to hydrated oxide 811
Organosilanes, adhesion promoters, schematic of interaction with glass fibres 814
Organosilanes, adhesion promoters, surface organisation 812Ч814
Organosilicon polymers, C 1s spectra 340
Organosilicon polymers, fast atom treatment 339Ч340
Organosilicon polymers, permeability changes 339
Organosilicon polymers, properties 339
Organosilicon polymers, Si 2p spectra 340
Orientation imaging microscopy (OIM) 654
Orientation imaging microscopy (OIM), Kikuchi images 654
Orientation imaging microscopy (OIM), use in corrosion 654
Oxidation, InGaAsP, by 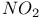 500Ч509 500Ч509
Oxidation, InGaAsP, O coverage 501Ч502
Oxidation, InGaAsP, oxide thickness 502
Oxidation, metals, growth law 478
Oxidation, Ni/Cr, AES 104Ч105
Oxidation, PbS, pH dependence 564
Oxidation, PbS, purging gas dependence 564
Oxidation, PbS, STM images 560Ч561 563
Oxide films, ion beam reduction 325Ч327 496
Oxide films, vapour deposited 324
Oxide films, vapour deposited, applications 324
Oxide films, vapour deposited, stoichiometry 324
Oxides, ion beam reduction 327 496
P (phosphorus), chemical shifts 171
P (phosphorus), KLL spectra 505
P (phosphorus), KLL spectra, peak positions 505
P (phosphorus), LVV spectra 504
P (phosphorus), LVV spectra, peak positions 504
Particle size effects, catalysis, bimetallic systems 770Ч771
Particle size effects, catalysis, EXAFS analysis 765
Particle size effects, catalysis, STM measurements 763 765
Particle size effects, catalysis, supported metal catalysts 763 765
Particle size effects, catalysis, XPS 763 765Ч766
Passivation, InGaAsP by 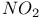 500Ч509 500Ч509
Passivation, InGaAsP by 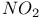 , AES quantification 502 , AES quantification 502
Passivation, InGaAsP by 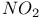 , AES spectra 504 507 , AES spectra 504 507
Passivation, InGaAsP by 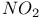 , description 500Ч501 , description 500Ч501
Passivation, InGaAsP by 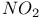 , ELS analysis 507Ч508 , ELS analysis 507Ч508
Passivation, InGaAsP by 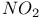 , interpretation 508Ч509 , interpretation 508Ч509
Passivation, InGaAsP by 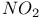 , O coverage 502 , O coverage 502
Passivation, InGaAsP by 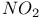 , O depth profile 503 , O depth profile 503
Passivation, InGaAsP by 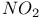 , SAM analysis 503Ч507 , SAM analysis 503Ч507
Passivation, InGaAsP by 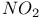 , surface analysis requirements 501 , surface analysis requirements 501
Pb, in Josephson junction electrode, depth profiles 495Ч496
Pb, in Josephson junction electrode, surface analysis 494Ч496
Pb, in Roman lead pipe, Auger chemical shift 839 854 856Ч857
Pb4 XPS spectra, lineshape during profiling 497
Pb4 XPS spectra, Nb/(Pb Ч In) junction 497
Pb4 XPS spectra, Nb/Pb junction 497
Pb4 XPS spectra, peak positions 499
PbS, STM images, clean 559 561
PbS, STM images, deposition of Pb hydroxide 565
PbS, STM images, oxidized 560Ч561
PbS, STM images, water treated 563
Pd, ISS spectra 139
PE16 superalloy, grain boundary segregation, irradiation effects 471Ч472
PE16 superalloy, grain boundary segregation, reversal by annealing 471Ч472
PEELS, characteristics 42
PEELS, grain boundary analysis 450 473Ч474
PEELS, tribology 707Ч708
Phase analysis, CEMS, implanted layers 360
Phase analysis, DCEMS, Eu implant in S/S 362Ч363
Photoelectron emission, theory 57Ч58 161 267
Physical constants 871
PIXE information 546Ч547
Plasmon excitation, AES 92 888Ч889
Plasmon excitation, C, graphitic,  electrons 166Ч167 electrons 166Ч167
Plasmon excitation, ELS 507Ч508 888Ч889
Plasmon excitation, polymers 166
Plasmon excitation, surface 166 508 888Ч889
Plasmon excitation, theory 166Ч167 888
Plasmon excitation, XPS 86 166Ч167
Point analysis, SAM 491 503Ч507 509 520 525Ч528 531
Point analysis, scanning ELS 491
Polymers, air oxidation 333
Polymers, applications 332
Polymers, damage during analysis 333Ч334 752Ч753
Polymers, ion beam damage 333Ч340
Polymers, ion irradiated 368Ч369
Polymers, SSIMS spectra 218 237 245 248Ч249
Polymers, thin films, applications 332
Polymers, thin films, preparation 332Ч333
Polymers, thin films, recommended analysis procedures 333Ч334 752Ч753
Polymers, XPS damage index 752
Polymers, XPS spectra 335Ч337 340
Polymers, Уhydrophobic recovery 333
Post-ionization. SNMS, laser 216Ч217 221
Post-ionization. SNMS, probability 224
Preferential sputtering 268Ч269 310
Preferential sputtering, 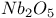 79 79
Preferential sputtering, correction to profile 269
Preferential sputtering, during profiling 310 496
Preferential sputtering, SIMS quantification 282Ч283
Preferential sputtering, SNMS quantification 282Ч283
Pressure conversion factors 872
Profilometry, information 546Ч547
Profilometry, oxide film thickness 677
Promoters, adhesion, organosilanes 811Ч814
Pt, (III), surface, Auger emission contour map 118
Pt4 XPS spectra 83
PTFE, XPS spectrum 163
Quadrupole mass spectrometer 213Ч214
Quantification, AES 183Ч185 195Ч198 267-269
Quantification, AES, depth profiling 201 308Ч309
Quantification, AES, Si and Ge signals 308Ч309
Quantification, GDOES 279Ч280
Quantification, general considerations 160Ч161
Quantification, ISS 148Ч150 751 775Ч776
Quantification, ISS, coverage of 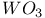 on on 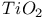 775Ч776 775Ч776
Quantification, multi-technique approach 161
Quantification, SIMS 212 614
Quantification, SNMS 282Ч283 287Ч288
Quantification, SSIMS 232Ч239 282Ч283
Quantification, XPS 179 182Ч186 189Ч195 268Ч269 490 683Ч684 772-775
Quantification, XPS, catalyst crystallite growth and sintering 774
Quantification, XPS, catalysts 772Ч775
Quantification, XPS, corroded Monel 400 683Ч684 688Ч689
Quantification, XPS, errors and pitfalls in heterogeneous systems 772 775
Quantification, XPS, extended layer catalytic models 774
Quantification, XPS, intensity related to catalyst atomic ratio 773Ч774
Quantification, XPS, layer model of catalytic system 773Ч774
Quantification, XPS, procedure 659 683Ч684
Quasimolecular ions 231
Quinone standards, C 1s spectra 624
RAIRS 897Ч898
RAIRS, adhesion 812Ч813
RAIRS, comparison with HREELS 900Ч901
RAIRS, cyclohexane on Cu( III) spectrum 901
| RAIRS, description 897Ч898
RAIRS, FT Ч RAIRS 898
RAIRS, model catalysts 898
RAIRS, sample requirements 898
RAIRS, vibrational losses 897
Raman spectroscopy, characteristics 40
Raman spectroscopy, corrosion 667
Raman spectroscopy, information 546Ч547
Raman spectroscopy, spatial resolution 740
Raman spectroscopy, tribology 709
Raman spectroscopy, tribology,  thin films 740Ч741 thin films 740Ч741
Raman spectroscopy, tribology, instrumentation 709
Raman spectroscopy, use in analysis of minerals, ceramics, and glass 552
RBS, analysis of TiN 315
RBS, channelling conditions 358Ч359
RBS, characteristics 43 258Ч259 358
RBS, depth resolution 262 264
RBS, elemental identification 261 358
RBS, energy relation 261
RBS, information 546Ч547
RBS, interdiffusion study 263
RBS, ion implanted layers 358Ч359
RBS, operation 260Ч261
RBS, simulated spectrum 262
RBS, stopping cross-section 262 358
RBS, summary of strengths and weaknesses 264
Reduction, electron beam 490Ч491 752
Reduction, ion beam 107 271 752
Reduction, ion beam, oxides 2 72 325Ч332 496 499
Reduction, photon beam,  752Ч753 752Ч753
Reduction, photon beam, PbO 498 499
Reference materials, XPS, 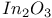 496 496
Reference materials, XPS, AgO 81Ч82
Reference materials, XPS, Au 315
Reference materials, XPS, C 315 758
Reference materials, XPS, C, difficulties with C Is as reference 172 758Ч759
Reference materials, XPS, noble metal particles 758Ч760
Reference materials, XPS, PbO 496 498
Reference materials, XPS, peaks from catalyst supports 758
Relative sensitivity factors, AES 184 189 267
Relative sensitivity factors, definition 184 193Ч194
Relative sensitivity factors, SIMS 283
Relative sensitivity factors, XPS 194 268
Relaxation energy, AES 179Ч181 184 331 491 750 772
Resolving power, AES 490
Resolving power, SRPS 489
Retarding field analyser (RFA) 95
Rh on 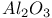 catalyst 767 catalyst 767
Rh on 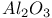 catalyst, SSIMS 767Ч768 catalyst, SSIMS 767Ч768
RHEED, information 546Ч547
Roughening, surface, at interface 306Ч308
Roughening, surface, effect on depth profile 306Ч308
S (sulphur), chemical shifts 171
SAM images, fracture surface, P and Sn 463Ч464
SAM images, InP on  , In 530 , In 530
SAM images, InP on  , O 530Ч533 , O 530Ч533
SAM images, InP on  , P 533Ч534 536 , P 533Ч534 536
SAM images, O in crack tip on FeCrMoV steel 479 481
SAM images, Roman lead pipe 848
SAM images, Roman leaded bronzes, Cu and Pb 866Ч867
SAM images, Roman leaded bronzes, Cu and Sn 864Ч865
SAM problem-solving,  on Si 520 on Si 520
SAM problem-solving, corrosion, general strategy 650
SAM problem-solving, Cs maps of fracture faces 583
SAM problem-solving, fibre analysis 606
SAM problem-solving, grain boundaries in minerals and ceramics 569
SAM problem-solving, InP on  527Ч529 527Ч529
SAM problem-solving, passivation of InGaAsP by 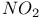 503Ч507 503Ч507
SAM problem-solving, passivation of InGaAsP by 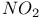 , point analyses 504Ч507 , point analyses 504Ч507
SAM problem-solving, semiconductors 487
SAM, beam damage 95 118Ч119 508 894
SAM, characteristics 41
SAM, charging problems 118 516 551
SAM, chemical contrast 492
SAM, description 118 463 488
SAM, imaging procedure 491
SAM, imaging procedure, minimization of topographic effects 863
SAM, imaging procedure, MULSAM approach 866
SAM, information 546Ч547
SAM, line scanning 491 527 531
SAM, point analysis 491 503Ч507 509 520 525Ч528 531
SAM, scatter diagrams 201
SAM, spatial resolution 118 201 463 491 494 525 534 551 606 750 837 864Ч865
SAM, topographical effects and correction 463 492 863 866
Sample (in)homogeneity 75
Sample configuration 72
Sample configuration, avoidance of charging 72Ч73
Sample configuration, mounting methods 72
Sample rotation (Zalar), depth profiling 108 110 272Ч276 284 302Ч305
Sample rotation (Zalar), depth profiling, multilayer profile 305
Sample treatment and cleaning 73Ч74
Sample treatment and cleaning, ex situ 73Ч74
Sample treatment and cleaning, film deposition 73
Sample treatment and cleaning, fracture 73
Sample treatment and cleaning, H atom cleaning 73
Sample treatment and cleaning, in situ 73Ч74
Sample treatment and cleaning, ion bombardment 73
Sample treatment and cleaning, sequential 74
Sampling depth, SEXAFS 709
Sampling depth, UFI 714 716
Sampling depth, XPS 75 103 200Ч201 359 517 519Ч520 615Ч616 624 636 656 750
Satellites, X-ray 63Ч65 164Ч165 625
SAX characteristics 40
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), AFM 398 400Ч401
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), conducting materials 405
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), electron tunnelling 402Ч405
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), family tree 398 400
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), history 398
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), information 401 546Ч547 712
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), instrumentation 410Ч417 712
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), instrumentation, piezoelectric drives 412Ч414
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), instrumentation, rastering 414Ч415
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), instrumentation, spatial control 412Ч415
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), interaction volume 401Ч402
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), introduction 395Ч397
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), physical principles 402Ч410
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), problem-solving, areas of application 440Ч441 667
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), problem-solving, C fibre topography 788
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), problem-solving, nanomanipulation 442
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), problem-solving, nanowriting 442
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), spatial resolution 401Ч402
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), STM 398Ч401
Scanned Probe Microscopy (SPM), vacuum conditions 405 416
SCM 400Ч401
Segregation, grain boundary 448Ч481
Segregation, grain boundary, analysis sequence 454Ч455
Segregation, grain boundary, atomic solubility and size 452Ч454
Segregation, grain boundary, diffusion theory 450Ч452
Segregation, grain boundary, impact fracture exposure 459Ч461
Segregation, grain boundary, intergranular fracture 449
Segregation, grain boundary, ion profiling 452Ч453
Segregation, grain boundary, quantification by AES 461Ч463
Segregation, grain boundary, segregating elements 450 452 153
Segregation, grain boundary, specimen preparation 455 157
Segregation, grain boundary, use of AES 450
Segregation, grain boundary, use of atom probe 477 178
Segregation, grain boundary, use of autoradiography 458
Segregation, grain boundary, use of SEM 463 164
Segregation, grain boundary, use of SIMS 457
SEM, Ag/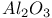 catalyst 76 catalyst 76
SEM, ceramic fracture surface 583
SEM, ceramic surface 554
SEM, characteristics 41
SEM, composite 612
SEM, correlation with SAM 120 463Ч464 522 527Ч528
SEM, corrosion 650 654 656 661Ч663 676 687
SEM, crack tip 479
SEM, fracture surfaces 463Ч464 470
SEM, information 546Ч547 653Ч656
SEM, InP on  525 528 533 525 528 533
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте




 , O KVV indicator
, O KVV indicator 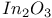 , peak positions
, peak positions 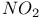
 electrons
electrons 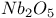
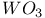 on
on 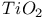
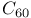 thin films
thin films 
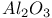 catalyst
catalyst