|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Riviere J.C. (ed.), Myhra S. (ed.) Ч Handbook of Surface and Interface Analysis |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Analyzers, electron energy, magnetic toroidal 365Ч366
Analyzers, electron energy, magnetic toroidal, in DCEMS 366Ч368
Analyzers, electron energy, RFA 95
Analyzers, electron energy, SPCMA, differentiation 99
Analyzers, electron energy, SPCMA, phase sensitive detection 95 99
Analyzers, electron energy, SPCMA, primary beam chopping 99
Analyzers, electron energy, SPCMA, specimen position sensitivity 98
Analyzers, ion energy, CHA 129Ч130
Analyzers, ion energy, double toroidal 130Ч131
Analyzers, ion energy, DPCMA 129Ч130
Analyzers, ion energy, SPCMA 129
Analyzers, mass, choice for SSIMS and SNMS 214Ч215
Analyzers, mass, double focussing 214Ч215
Analyzers, mass, ion cyclotron resonance 214 215
Analyzers, mass, quadrupole 214 215
Analyzers, mass, time-of-flight (ToF) 214 215
Angular distribution, secondary ions 222
Angular resolution, AES (ARAES) 104 111Ч113 204Ч205 260 263Ч265 487
Angular resolution, mounting of fibres 607
Angular resolution, UPS (ARUPS) 887
Angular resolution, UPS (ARUPS), band structure mapping 887
Angular resolution, XPS (ARXPS) 77 111Ч112 260 263Ч265 487 511 513 566 619 750 794
Anodes, X-ray sources 63Ч65
Anodes, X-ray sources, contamination 63
Anodes, X-ray sources, Ti 65
Anodes, X-ray sources, Zr 66
Anodes, X-ray sources, Уcross-over" radiation 63
ARAES 104 111Ч113 260 263Ч265 487
ARAES, advantages and disadvantages 266
ARAES, angle/depth relation 263
ARAES, calculation of layer-by-layer, contribution to Auger signal 112Ч114
ARAES, characteristics 258
ARAES, comparison with ISS 143Ч144
ARAES, instrumentation 112Ч113
ARAES, maximum analysable depth 264
ARAES, summary of capabilities 265
Archaeomaterials, choice of techniques, bulk 836
Archaeomaterials, choice of techniques, surface 836Ч837
Archaeomaterials, introduction 835
Archaeomaterials, relative destructiveness of XPS and SAM 837
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes 837Ч868
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, Auger parameter  , Cu and Pb 839 857Ч858 860 , Cu and Pb 839 857Ч858 860
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, Auger spectra 841Ч844 853Ч855
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, backscattering effects 842 866
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, depth profiles 842Ч846 849Ч850 860-861
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, descriptions 837 857
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, lateral inhomogeneities 841Ч842 847 860Ч866
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, Pb Auger and BEs 839 842Ч843 856Ч857
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, SAM images 841Ч842 848 851 855Ч856
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, SAM point analyses 838 840Ч841 847
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, SEM images 840 847 862 864Ч865
Archaeomaterials, Roman lead pipe and leaded bronzes, XPS spectra 842 844 859
Archaeomaterials, specimen preparation 838
ARUPS, band structure mapping 887
ARXPS 77 111Ч112 260 263Ч265 487 513 566Ч567 619 794
ARXPS,  on Si 78 513Ч514 on Si 78 513Ч514
ARXPS,  on Si, average escape depths 514 on Si, average escape depths 514
ARXPS, advantages and disadvantages 266
ARXPS, angle/depth relation 263 513Ч514
ARXPS, characteristics 258
ARXPS, GaAs 264Ч265
ARXPS, maximum analysable depths 264
ARXPS, summary of capabilities 265
Asymmetry parameter, XPS 190Ч191
Asymmetry parameter, XPS, magic angle 191
Atom probe (time of flight) 477Ч478
Atom probe (time of flight), atomic resolution 477
Atom probe (time of flight), characteristics 43
Atom probe (time of flight), grain boundary analysis Astroloy 477Ч478
Atom probe (time of flight), position sensitive detection 478
Atomic mixing, during sputtering, effect on depth resolution 300Ч301
Atomic mixing, during sputtering, ion energy dependence 300 310
Atomic mixing, during sputtering, surface modification 300Ч301
ATR, and the electron spectroscopies 160
ATR, characteristics 41
ATR, description 897
ATR, sampling depth 897
ATR, surface coverage on PbS 573
ATR, use in analysis of minerals, ceramics and glasses 552
Attenuation length (AL) 61 104 113 190Ч192 204 487 511 517 519Ч520 523 584 597 856Ч857
Attenuation length (AL), dependence on KE 62 203
Attenuation length (AL), measurement 584 585
Auger kinetic energies, table 902Ч904
Auger parameter  902Ч904 902Ч904
Auger parameter  , advantages 81 181 490 492 586 760 799Ч800 , advantages 81 181 490 492 586 760 799Ч800
Auger parameter  , Ag + oxides 81 , Ag + oxides 81
Auger parameter  , Al 762 , Al 762
Auger parameter  , avoidance of charging problems 181 331 492 760 800 , avoidance of charging problems 181 331 492 760 800
Auger parameter  , chemical sensitivity 760 , chemical sensitivity 760
Auger parameter  , chemical state plot 181Ч182 760Ч762 , chemical state plot 181Ч182 760Ч762
Auger parameter  , Cr 763 , Cr 763
Auger parameter  , Cu 766 858 860 , Cu 766 858 860
Auger parameter  , database reference 179 904 , database reference 179 904
Auger parameter  , definition 81 180Ч181 331 492 586 760 799 , definition 81 180Ч181 331 492 586 760 799
Auger parameter  , extra-atomic relaxation energy 760 , extra-atomic relaxation energy 760
Auger parameter  , F 762 , F 762
Auger parameter  , O 512 516 , O 512 516
Auger parameter  , Pb 839 , Pb 839
Auger parameter  , Si 331 512Ч513 516 585Ч587 760 , Si 331 512Ч513 516 585Ч587 760
Auger parameter  , Zn 799Ч800 , Zn 799Ч800
Auger parameter  181 181
Autoradiography 458
Average escape depths 61 63 264 308 462Ч463 513Ч514 517 519Ч520
Background, AES 93 187Ч189 316
Background, XPS 161Ч163 185Ч186 316
Background, XPS, subtraction 72 185Ч186 616 625Ч629
Backscattering, factor, AES 195 197Ч198 267 462 490Ч492 495Ч196 661
Backscattering, factor, peak shape effect 490
Backscattering, factor, substrate effect 198 463 495Ч496 842 860 866
Ball-cratering, AES depth-profiling 810
BE shifts, correlation with electronegativity 84
Benzene, adsorption on Ni(III), UPS spectrum 886
BEs, elemental 78 79
BEs, elemental, table 902Ч904
Bimetallic catalyst systems, cluster formation 770
Bimetallic catalyst systems, effects of alloying, XPS BEs 770
Bimetallic catalyst systems, effects of alloying, XPS peak widths 770
Brass adhesion to rubber 789Ч791
Brass adhesion to rubber, formation of sulphides 789
Brass adhesion to rubber, model compounds 789Ч790
Brass adhesion to rubber, schematic of chemical situation at interface 790
Bremsstrahlung background. X-ray sources 65
Bremsstrahlung use in XAES 181 492 511Ч512
BSE images, acquisition details 554 555
BSE images, atomic number dependence 554Ч555
BSE images, ceramic surface 554
BSE images, composite mineral 555
C (carbon), 1s energy as reference 172 315 628 758 763
C (carbon), 1s peak energy 69 166 172 315 627 758
C (carbon), 1s XPS spectrum, curve-fitted 180
C (carbon), 1s XPS spectrum, epoxy resin 628Ч629
C (carbon), 1s XPS spectrum, ethyl irifluoroacetate 61
C (carbon), 1s XPS spectrum, fibres 609Ч611 618Ч621 620-632
C (carbon), 1s XPS spectrum, hexafluoropropylene vinylidene fluoride 174
C (carbon), atomic mass standard 230
C (carbon), Auger spectra 103
C (carbon), graphitie 166 628
C (carbon), graphitie, line shape 166
C (carbon), graphitie, plasmon losses,  electrons 166Ч167 electrons 166Ч167
C (carbon), in implantation profile 355
C (carbon), in polymers 172Ч173 336
C (carbon), in TiN, energetic positions 320
C (carbon), surface contaminant 166 175 313 659 758 783
C (carbon), surface contaminant, as energy reference 69 315
C (carbon), surface contaminant, line shape 166Ч167 625Ч626
C (carbon), XAES spectrum 163 172
C fibres, in composites 605Ч606
C fibres, in composites, 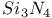 coating 617 coating 617
C fibres, in composites, AFM 613 788
C fibres, in composites, electron beam damage 609
| C fibres, in composites, FTIR and Raman spectroscopies 611Ч612
C fibres, in composites, ISS 614
C fibres, in composites, problems with conducting fibres in instrumentation 607
C fibres, in composites, SEM 612
C fibres, in composites, SIMS 614 788 804
C fibres, in composites, sputtering damage 609Ч610
C fibres, in composites, surface free energy 613
C fibres, in composites, TPD 614
C fibres, in composites, treatment for strong adhesion 787
C fibres, in composites, WDS 612
C fibres, in composites, XPS 614Ч638 787Ч788 802
C fibres, in composites, XRD (grazing incidence) 610Ч611
Catalysis, acid-base properties 769Ч770
Catalysis, acid-base properties, chemical shifts in XPS 769Ч770
Catalysis, acid-base properties, molecular probes 769Ч770
Catalysis, acid-base properties, N 1s shifts in pyridine as probe 769
Catalysis, acid-base properties, OH groups on supports 770
Catalysis, AES, charging problems 750
Catalysis, AES, damage problems 750 752
Catalysis, AES, poor quantification 750
Catalysis, AES, usefulness in model systems 750
Catalysis, applicability of surface techniques 749Ч752
Catalysis, applicability of surface techniques, usefulness of XPS 749
Catalysis, best practice references 749
Catalysis, bimetallic systems 770Ч771
Catalysis, bimetallic systems, cluster formation 770
Catalysis, bimetallic systems, multi-technique approach 771
Catalysis, bimetallic systems, particle size effects 770
Catalysis, bimetallic systems, Pt Ч Re and Pt Ч Sn reforming catalysts 771
Catalysis, bimetallic systems, use of EXAFS 770Ч771
Catalysis, bimetallic systems, use of XAS 771
Catalysis, bimetallic systems, use of XRD 771
Catalysis, catalyst parameters and appropriate techniques 748
Catalysis, charging problems 756Ч757
Catalysis, charging problems, ASTM guide 757
Catalysis, charging problems, elimination by use of  760 760
Catalysis, charging problems, methods of control 757
Catalysis, damage during analysis 752Ч753
Catalysis, damage during analysis, chemical reduction 752Ч753
Catalysis, damage during analysis, degradation index 752
Catalysis, damage during analysis, minimization of heat load from X-ray source 752
Catalysis, depth profiling 771Ч772
Catalysis, depth profiling, altered surface layers 772
Catalysis, depth profiling, chemical reduction 772
Catalysis, depth profiling, risk of misinterpretation 771Ч772
Catalysis, FABMS, association of Pt and Sn on 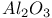 767 769 767 769
Catalysis, FABMS, support-related clusters 769
Catalysis, introduction 747Ч749
Catalysis, ISS, charge compensation 751
Catalysis, ISS, combination with XPS 752
Catalysis, ISS, surface specificity 751
Catalysis, multiple technique approach 748
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis 772Ч776
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, coverage by ISS 775Ч776
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, crystallite growth 774
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, dispersion and coverage 773Ч775
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, errors in XPS intensity interpretation 775
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, extended layer models 774
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, heterogeneity of catalysts 772 775
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, homogeneity assumption 772 775
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, information sought 772
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, ISS intensities 775Ч776
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, layer model for XPS interpretation 773Ч774
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, sampling depths 750 772
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, sintering 774
Catalysis, quantitative surface analysis, XPS intensities 772Ч775
Catalysis, sample condition 749Ч750
Catalysis, sample condition, activated 749
Catalysis, sample condition, aged 749
Catalysis, sample condition, calcined 749
Catalysis, sample condition, deactivated 749
Catalysis, sample condition, poisoned 749
Catalysis, sample condition, precursor 749
Catalysis, sample condition, reduced 749
Catalysis, sample handling, ASTM guide 754
Catalysis, sample handling, protective atmosphere 754
Catalysis, sample mounting, deposition from solvent suspension 754
Catalysis, sample mounting, double-sided adhesive tape 754
Catalysis, sample mounting, pressed into grids or foils 754
Catalysis, sample mounting, wafers 754
Catalysis, sample preparation, 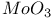 on on  755 755
Catalysis, sample preparation, outgassing problems 754
Catalysis, sample preparation, pellet grinding 754
Catalysis, sample preparation, spectral interference from binder 754
Catalysis, sample preparation, thin oxide film supports 755
Catalysis, sample preparation, treatment in preparation chamber 754
Catalysis, spatial resolution needs 750
Catalysis, SSIMS 766Ч769
Catalysis, SSIMS, cluster ions 766
Catalysis, SSIMS, high sensitivity requirement 766
Catalysis, SSIMS, model systems 769
Catalysis, SSIMS, nearest-neighbour information 766
Catalysis, SSIMS, recombination ambiguity 766
Catalysis, SSIMS, reference materials 766
Catalysis, SSIMS, Rh on 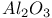 767Ч768 767Ч768
Catalysis, SSIMS, spectra databases 766
Catalysis, SSIMS, surface fragmentation 766
Catalysis, standardization 749
Catalysis, XPS, 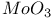 on on  755 755
Catalysis, XPS, activation of  -alumina 762 -alumina 762
Catalysis, XPS, Auger parameter  760Ч763 760Ч763
Catalysis, XPS, BE particle size dependence 763
Catalysis, XPS, C 1s reference difficulties 758Ч759
Catalysis, XPS, chemical state plots 762
Catalysis, XPS, differential charging 756Ч757
Catalysis, XPS, noble metal particle references 758Ч759
Catalysis, XPS, particle size effects 763 765
Catalysis, XPS, support peaks as references 758
Catalysis, XPS, supported metal catalysts 763
Catalysis, XPS, use of transition metal shake-up peaks 761 763
Ceramics 543 576Ч586
Ceramics, adsorption 582 584Ч585
Ceramics, adsorption, ARXPS 585
Ceramics, adsorption, contact angle 582
Ceramics, adsorption, film thickness from XPS 585
Ceramics, adsorption, information from combined techniques 582
Ceramics, adsorption, organic molecules 582 584 585
Ceramics, analysis strategy 549 552
Ceramics, analysis strategy, chemical analysis 550
Ceramics, analysis strategy, physical imaging 548
Ceramics, analysis strategy, structural analysis 548Ч550
Ceramics, combined techniques 545
Ceramics, depth profiles 581
Ceramics, depth profiles, information from nuclear techniques 581
Ceramics, depth profiles, information from XPS 584
Ceramics, grain boundaries 580Ч581
Ceramics, grain boundaries, information from SAM 581 583
Ceramics, grain boundaries, information from SSIMS 581 583
Ceramics, grain boundaries, intergranular films 580
Ceramics, grain boundaries, TEM images 580Ч582
Ceramics, information requirements 543Ч547
Ceramics, ion implanted 368
Ceramics, phase structures 576Ч578
Ceramics, phase structures, characterisation by combined techniques 576Ч578
Ceramics, phase structures, information from diffraction techniques 576
Ceramics, phase structures, information from nuclear methods 576
Ceramics, phase structures, information from STM and AFM 576
Ceramics, phase structures, ion beam damage 577
Ceramics, phase structures, schematic distribution 576Ч577
Ceramics, phase structures, TEM image 576 578
Ceramics, surface characterisation requirements 543Ч544
Ceramics, surface modification 585Ч586
Ceramics, surface modification, Auger parameter  585Ч586 585Ч586
Ceramics, surface modification, silicates 585Ч586
Ceramics, surface modification, water vapour plasma 585
Ceramics, surface sites 579Ч580
Ceramics, surface sites, information from ISS 579Ч580
Ceramics, surface sites, modelling theory 580
Ceramics, surface sites, oxides 580
Ceramics, surface structures 578Ч579
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 , Cu and Pb
, Cu and Pb  on Si
on Si 
 electrons
electrons 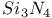 coating
coating 
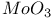 on
on  -alumina
-alumina