|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Riviere J.C. (ed.), Myhra S. (ed.) Ч Handbook of Surface and Interface Analysis |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Ion sources, ion implantation, Уbucket 354
Ion sources, ISS 126Ч127
Ion sources, SSIMS, SNMS 212Ч213 215
Ion sources, SSIMS, SNMS,  bombardment 213 215 bombardment 213 215
Ion sources, SSIMS, SNMS, electron impact 212Ч213 215 267
Ion sources, SSIMS, SNMS, LMIG 213Ч215 267
Ion sputtering process 107 210Ч211 350Ч351
Ion sputtering process, artefacts introduced 107 300 306 325 664 772 808
Ion sputtering process, atom ejection 211 350
Ion sputtering process, atomic mixing 271 300Ч301 310Ч311 353
Ion sputtering process, atomic mixing, energy dependence 310Ч311
Ion sputtering process, collision cascade 210 227 240 350Ч351
Ion sputtering process, compound reduction 271Ч272 313 325Ч332 496 510 772
Ion sputtering process, compound reduction, database reference 772
Ion sputtering process, dependence on crystallinity 108 270
Ion sputtering process, dependence on primary ion energy 108 270 272 300 351Ч352 772
Ion sputtering process, depth resolution degradation 108 269Ч273 300
Ion sputtering process, induced microtopography 271 302 306Ч308 664
Ion sputtering process, induced segregation 271 310 772
Ion sputtering process, preferential sputtering 268Ч269 310
Ion sputtering process, recoil atoms 210Ч211 350
Ion sputtering process, Sigmund model 107 353
Ion sputtering process, statistical nature 107 350
Ion sputtering process, surface roughening 270Ч271 302 306Ч308 664
Ionization, post, in SNMS 211 216Ч217 221 224 285Ч286
Ionization, secondary, in SIMS 211 222
IPES, complement to STS 405
IPES, complement to UPS 405
IR spectroscopy 246 524
IR spectroscopy, corrosion 667
IR spectroscopy, Fourier Transform (FTIR) 552 739
IR spectroscopy, information 546Ч547
IR spectroscopy, tribology 707 738Ч739
Ir, reaction with Si, RBS 262Ч263
Isotopic data 877Ч883
ISS 121Ч152
ISS problem-solving, catalysis,  on on  776 776
ISS problem-solving, catalysis, applicability 749
ISS problem-solving, catalysis, charge compensation 751
ISS problem-solving, catalysis, combination with XPS 752
ISS problem-solving, catalysis, coverage plot 775Ч776
ISS problem-solving, catalysis, intensity/coverage relationship 775
ISS problem-solving, catalysis, surface specificity 751
ISS problem-solving, grain boundaries in minerals and ceramics 569
ISS problem-solving, surface sites on ceramics 579Ч580
ISS spectra,  , platinized 134 , platinized 134
ISS spectra, 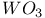 on on 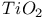 776 776
ISS spectra, Ag, cleaning treatments 143
ISS spectra, Ag, oxidation 144
ISS spectra, Ag/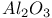 , catalyst 123 , catalyst 123
ISS spectra, Al oxidation 127
ISS spectra, Mg 129
ISS spectra, Ni/Cr 138
ISS spectra, Pd 139
ISS spectra, Zn/Cr/O spinel catalyst 152
ISS spectra, ZnS 126
ISS, 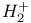 as primary ion 125 as primary ion 125
ISS, background intensity 133 148 150
ISS, characteristics 43 121Ч122 258Ч259
ISS, charging problems 130 751
ISS, choice of primary ion 136Ч138 144Ч145
ISS, comparison with AES and XPS 142Ч143
ISS, data processing 150Ч151
ISS, depth profiling 151Ч152 772
ISS, detection of C 140
ISS, detection of H 139Ч140
ISS, differential scattering cross-section 148Ч149
ISS, elemental sensitivity 141Ч142 614
ISS, energy analyzers 128Ч130
ISS, energy and mass resolution 144Ч146
ISS, energy relation 122
ISS, experimental geometry 122
ISS, history 121 124Ч125
ISS, influence of adsorbed H 139
ISS, information 546Ч547
ISS, instrumentation 126Ч130
ISS, intensity in inelastic tail 150
ISS, ion sources 126Ч127
ISS, isotopic effects 148
ISS, isotopic purity of primary ion 136
ISS, multiple scattering 126 134
ISS, multiply charged ion scattering 127 135
ISS, neutralization probability 132Ч133 136 150
ISS, peak shape, theory 147Ч148 150
ISS, potential damage 126Ч127 137
ISS, primary ion mass 137
ISS, quantification 148Ч150 751 775Ч776
ISS, scattering 123Ч125
ISS, scattering angle 128Ч130
ISS, shadowing, blocking 124
ISS, spectral interpretation 123 130Ч132 134
ISS, structural analysis of minerals, ceramics and glasses 550
ISS, surface specificity 121Ч123 142Ч144 751 775
ISS, typical spectrum 123
ISS, vacuum conditions 127
Josephson junctions, AES analysis 494Ч496
Josephson junctions, AES analysis, backscattering effects 495Ч496
Josephson junctions, aging behaviour 493
Josephson junctions, choice of analytical methods 493Ч494
Josephson junctions, depth profiles 495Ч496
Josephson junctions, description 486 493
Josephson junctions, protective role of In 503
Josephson junctions, surface analysis requirements 486
Josephson junctions, XPS analysis 496Ч499
Josephson junctions, XPS analysis, Nb/(Pb Ч In) junction 497
Josephson junctions, XPS analysis, Nb/Pb junction 497
Josephson junctions, XPS analysis, Pb lineshape during profiling 497
KEs, Auger, table 902Ч904
Kikuchi diffraction, in SEM 654
Kikuchi diffraction, in SEM, use in corrosion 654
KLL, Si, effect of ion bombardment 328Ч329 512Ч513 527
KLL, Si, effect of ion bombardment, peak energies 512Ч513
KLL, Si, effect of ion bombardment, peak width 517 521 523
Krytox, SSIMS spectrum 232
KVV, O, in  on Si depth profile 516 on Si depth profile 516
KVV, O, in InP on  compound indicator 530 compound indicator 530
Laser ablation assisted deposition (LAPVD) 298
LEED, application to mineral, ceramic and glass surfaces 549
LEED, application to mineral, ceramic and glass surfaces, surface sites 566
LEED, information 546Ч547
Lewis acids and bases, role in ceramic/polymer adhesion 804
Line scanning, SAM 491 527 531
Line scanning, scanning ELS (REELM) 491
Line widths, characteristics X-rays 65Ч66 625
LMIG, beam damage 614
LMIG, characteristics 267
LMIG, fine focussing 213 215
LMIG, high brightness 213
LMIG, spatial resolution 227Ч228 551 571
lnterferometry, tribology 712
lnterferometry, ultrathin film (UFI), measurement of boundary lubricant film thickness 714 716
Low angle electron diffraction (LAED) LRM 300
Low angle electron diffraction (LAED) LRM, characteristics 40
Lubricant, SSIMS spectrum 232
LVV,  , lineshape 524 , lineshape 524
LVV,  , surface specificity 524 527 , surface specificity 524 527
LVV, ion bombardment damage 527
LVV, Si, chemical shift 489
M ssbauer spectroscopy 359Ч368 ssbauer spectroscopy 359Ч368
M ssbauer spectroscopy, adhesion 810 ssbauer spectroscopy, adhesion 810
M ssbauer spectroscopy, catalysis, bimetallic systems 771 ssbauer spectroscopy, catalysis, bimetallic systems 771
M ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS) 359Ч368 ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS) 359Ч368
M ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), description 359Ч362 ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), description 359Ч362
M ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), isomer shift 361 ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), isomer shift 361
M ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), magnetic splitting 361 ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), magnetic splitting 361
M ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), measurement geometries 362 ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), measurement geometries 362
M ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), quadrupole splitting 361 ssbauer spectroscopy, conversion electron (CEMS), quadrupole splitting 361
Mass analyzers, choice for SSIMS and SNMS 214
Mass analyzers, ion cyclotron resonance 214Ч215
Mass analyzers, magnetic sector 214Ч215
| Mass analyzers, quadrupole 214Ч215
Mass analyzers, time-of-flight 214Ч216 226 228 766
Mass peak assignment, SSIMS 230Ч232
Matrix assisted laser desorption (MALDI) 246
Matrix effect, in SIMS 211 223 232Ч233 282Ч284 761
Matrix effect, in SNMS 285
Medical prostheses, polyethylene 369
Medical prostheses, Ti6Al4V alloy 369
Medical prostheses, wear improvement by ion implantation 369Ч376
Metals, failure mechanisms 449
Metals, grain boundaries 447Ч449
Metals, grain boundaries, particle formation 448 449
Metals, grain boundaries, segregation 448Ч455
Metals, grain boundaries, strength 448 449
Metals, grain size 449
Metals, grain size, effect of aging 449
MFM 400Ч401 427
MFM, probe materia] 427
Mg, ISS spectra 129
Microelectronics, surface analysis, small area requirement 485
Minerals, adsorption 570Ч573
Minerals, adsorption of ethyl xanthate 564
Minerals, adsorption, information from combined techniques 573
Minerals, adsorption, information from STM and AFM 571
Minerals, adsorption, information from ToF-SIMS 572
Minerals, adsorption, surface coverage 573
Minerals, analysis strategy 545Ч549
Minerals, analysis strategy, chemical analysis 550
Minerals, analysis strategy, physical imaging 548
Minerals, analysis strategy, structural analysis 548Ч550
Minerals, combined techniques 545 570
Minerals, depth profiles 570
Minerals, depth profiles, ARXPS 570
Minerals, depth profiles, combined techniques 570
Minerals, depth profiles, labradorite, by SIMS 570Ч571
Minerals, depth profiles, sputtering 570
Minerals, grain boundaries 568Ч570
Minerals, grain boundaries, C on faces of ground sulphide ore 569
Minerals, grain boundaries, exposure by fracture 569
Minerals, grain boundaries, information from TEM techniques 569
Minerals, grain boundaries, information from XPS, SAM, SSIMS, and ISS 569
Minerals, grain boundaries, layer thickness 569
Minerals, grain boundaries, microinclusions 569
Minerals, grain boundaries, segregation and segregation factor 569
Minerals, growth of oxidation products on PbS 561Ч562
Minerals, information from AFM 561Ч565
Minerals, information from STM and STS 558Ч566
Minerals, information from XPS 560Ч562
Minerals, information requirement 543Ч547
Minerals, oxidised PbS STM image 560
Minerals, PbS(001)STM image 560Ч561
Minerals, pH dependence 564
Minerals, phase structures 552Ч558
Minerals, phase structures, analysis by EDS 556Ч557
Minerals, phase structures, analysis by XRF 557
Minerals, phase structures, identification by 556Ч557
Minerals, phase structures, identification by SEM, BSE 553Ч555
Minerals, phase structures, information from XRD and neutron diffraction 553
Minerals, phase structures, lattice imaging 556
Minerals, phase structures, optical microscopy 552
Minerals, phase structures, phase contrast imaging 556
Minerals, purging gas dependence 564
Minerals, STM-deposition of Pb(OH) 565
Minerals, surface characterisation requirements 543Ч544
Minerals, surface features 543Ч544
Minerals, surface modification 574Ч576
Minerals, surface modification, bauxite ore particles 575Ч576
Minerals, surface modification, calcination 575Ч576
Minerals, surface modification, catalytic properties 575Ч576
Minerals, surface modification, information from combined techniques 575
Minerals, surface modification, information from FTIR 575
Minerals, surface modification, information from SEM and 575
Minerals, surface modification, information from XPS 575
Minerals, surface modification, Kuolinite 575
Minerals, surface modification, molecular modelling 575
Minerals, surface modification, SIMS depth profiles 575Ч576
Minerals, surface modification, water vapour plasma 575
Minerals, surface reactions 573Ч574
Minerals, surface reactions, information from combined techniques 573
Minerals, surface reactions, information from XRD and XPS 574
Minerals, surface reactions, leaching, dissolution, precipitation 574
Minerals, surface reactions, oxidation of sulphides 573
Minerals, surface reactions, solution analysis 574
Minerals, surface reactions, sulphur oxidation products 573
Minerals, surface reactions, surface phase transformation 574
Minerals, surface sites 566Ч568
Minerals, surface sites, AES depth profile 566
Minerals, surface sites, ARXPS 566Ч567
Minerals, surface sites, Fe(III) on  566 566
Minerals, surface sites, information from EXAFS 568
Minerals, surface sites, information from structural techniques 566
Minerals, surface sites, information from XPS 566Ч568
Minerals, surface sites, modelling theory 568
Minerals, surface sites, oxidation of  566Ч568 566Ч568
Minerals, surface sites, water adsorption 567Ч568
Minerals, surface structures 558Ч566
Minerals, water-treated PbS 563
molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) 298
Molecular modelling, adhesion 823Ч827
Molecular modelling, adhesion, introduction 823
Molecular modelling, adhesion, molecular dynamics approximation 824Ч827
Molecular modelling, adhesion, simulation of arrangement, of organosilane molecules on FeOOH 824Ч827
Monel 400, composition 669
Monel 400, corrosion 668Ч696
Monel 400, corrosion, background 668Ч669
Monel 400, corrosion, experimental strategy 669Ч671
Monel 400, corrosion, grain boundary segregation 668Ч670
Monel 400, corrosion, SIMS images 670
Monel 400, corrosion, specimen preparation 669Ч671
Monochromatisation, X-rays 65 165 513 628Ч630 805
Multilayer structures 360
Multilayer structures, depth profiles 305
Multilayer structures, depth profiles, oscillatory behaviour, ion energy dependence 304 306
Multiplet splitting, XPS 85Ч87 566Ч567 763
Multiplet splitting, XPS, Cr 3s 87
Multiplet splitting, XPS, rare earths 4 86
N (nitrogen), in polymers, 1s spectra 337
N (nitrogen), in polymers, BEs 337
N (nitrogen), in polymers, ion beam damage 336Ч337
N (nitrogen), in TiN, new  phase 323Ч324 phase 323Ч324
N (nitrogen), in TiN, oxynitride phase 324
N, 1s, BE in Al/epoxy joint 802
N, 1s, BE in TiN 316Ч317 320Ч324
N, 1s, BEs 631Ч632
N, 1s, chemical shift in pyridine as probe of acid-base properties 769Ч770
N, 1s, chemical shifts 171 173 316Ч317 321 324 769
N, 1s, coating on fibre 618
N, 1s, curve-fitting 316Ч317 631Ч632
N, 1s, curve-fitting, effects of ion bombardment of TiN 320
N, 1s, curve-fitting, loss peaks 317
N, 1s, shifts on C fibres 787
N-methyl pyrrolidone, use in removal of polymers to expose buried interface 808Ч809
NaCl, Na 1s spectra 756
Nb 3d BEs 499
Neutralization probability. ISS 132Ч133 136 150
NEXAFS, use in analysis of minerals 556
Ni, adsorption of benzene. UPS 886
Ni/Cr, Auger KEs 105
Ni/Cr, cleaning by H atoms 73Ч74
Ni/Cr, ISS spectra 138
Ni/Cr, oxidation. AES spectra 105
NMR, informaiion 546Ч547
Noble meial substrates in SSIMS and SNMS 224Ч225
NRA, characteristics 43 358
NRA, description 734
NRA, ion implanted layers 358
NRA, tribology 734Ч735
O(oxygen), 1s spectrum, component peaks 611 613 621Ч622
O(oxygen), 1s spectrum, curve fitting 611 618 620Ч621 630Ч631
O(oxygen), 1s spectrum, peak positions 512 516 630Ч631
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



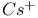 bombardment
bombardment 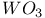 on
on 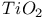
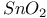 , platinized
, platinized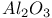 , catalyst
, catalyst 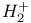 as primary ion
as primary ion  on Si depth profile
on Si depth profile  ssbauer spectroscopy
ssbauer spectroscopy
 phase
phase