|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Riviere J.C. (ed.), Myhra S. (ed.) Ч Handbook of Surface and Interface Analysis |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Depth profiling, non-destructive, GaAs 264 265
Depth profiling, non-destructive, maximum analysable depth 264
Depth profiling, non-destructive, RBS 260Ч263
Depth profiling, non-destructive, summary 265
Depth profiling, optimum conditions 284Ч285 303
Depth profiling, recommendations 289Ч290 771Ч772
Depth profiling, sample preparation, optical examination 260
Depth profiling, sample preparation, polishing, electrochemical 260
Depth profiling, sample preparation, polishing, mechanical 260
Depth profiling, sample preparation, washing 260
Depth profiling, sample rotation 108 110 272Ч276 284 302Ч305
Depth profiling, SNMS 251 255 257 266 358
Depth profiling, sputtering 266 301 650
Depth profiling, SSIMS 229 251 266 358Ч359
Depth profiling, taper section 202 494 650Ч651 810Ч811
Depth profiling, typical profiles 255Ч257
Depth profiling, XPS 201Ч205 255 257 266Ч269 300 359 618Ч619 659-660
Depth resolution, constancy during sample rotation 284
Depth resolution, DCEMS 365
Depth resolution, DCEMS, data processing 365
Depth resolution, degradation during sputtering 108 269Ч271 300
Depth resolution, dependence on primary ion KE 108 270
Depth resolution, depth profiling 304 310
Depth resolution, depth profiling, charging problems 270
Depth resolution, depth profiling, definition 269
Depth resolution, depth profiling, limiting factors 270
Depth resolution, depth profiling, RBS 262Ч264
Depth resolution, depth profiling, sample rotation 110 273 302Ч303
Depth resolution, depth profiling, single interface between thick layers 306
Depth resolution, SPM (STM/STS) 401Ч402 404
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS) 360Ч368
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), characteristics 43
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), data processing 364Ч365
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), depth information 363
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), description 360
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), Eu implant in S/S 362Ч363 368
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), instrumentation 365Ч366
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), physical processes 361 364
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), sampling depth 360Ч361
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), spatial resolution 360
Depth-selective CEMS (DCEMS), theory 364
Differential scattering cross-sections, ISS 148Ч149
Differentiation, in SPCMA 98
Differentiation, in SPCMA, primary beam chopping 98
Disappearance cross-section and yield, SSIMS and SNMS 221
Documentary standards in surface analysis 906Ч926
Doniach Ч Sunjic line shape, XPS 168
DSIMS 212 257Ч259
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion 3ЧD images 678
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion, C map 457
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion, choice of primary ion 666
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion, damage effects 679
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion, depth profiling 666Ч667 677Ч678
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion, detection of H 666
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion, elemental images 670
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion, grain boundary segregation 457
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion, mapping 666 670 678
DSIMS problem-solving, corrosion, trace element sensitivity 666 668Ч669
DSIMS, characteristics 42 212 258Ч259 282
DSIMS, depth profiling 212 260 273 282Ч284 300 666Ч667
DSIMS, depth profiling, choice of ion 284
DSIMS, depth profiling, incident angle 284
DSIMS, depth profiling, ion energies 284Ч285
DSIMS, depth profiling, optimum conditions 284Ч285
DSIMS, depth profiling, sample rotation 273Ч276 284
DSIMS, elemental sensitivity 282Ч283
DSIMS, erosion rate 282
DSIMS, quantification 282Ч283
DSIMS, quantification, detection limits 283
DSIMS, quantification, matrix effect 283
DSIMS, quantification, sensitivity factor 283
DSIMS, quantification, standards 283
DSNMS 212
ECM 400Ч401
EDS, accelerating voltage 654
EDS, characteristics 42
EDS, corrosion 650
EDS, corrosion, oxide film 654 657
EDS, grain boundary analysis 450 474Ч475
EDS, grain boundary analysis, Inconel 690 475
EDS, information 546Ч547
EDS, tribology 709
EDS, use alongside electron spectroscopies 161
EFM 400Ч401
Electrochemistry, corrosion of Monel 400, anodic polarisation measurements 680Ч681
Electrochemistry, corrosion of Monel 400, EIS measurements 679 681Ч682
Electrochemistry, corrosion of Monel 400, electrochemical parameters during oxide film growth 682 692
Electrochemistry, electrochemical techniques 671Ч674
Electrochemistry, electrochemical techniques, anodic polarisation 672Ч673
Electrochemistry, electrochemical techniques, impedance spectroscopy 673Ч674
Electrochemistry, electrochemical techniques, linear polarisation 672
Electrochemistry, electrode kinetics 671Ч672
Electrochemistry, Tafel slope 672
Electron beam effects, damage of C fibres 609
Electron beam effects, ESD during AES 891Ч892
Electron beam effects, ESD during AES, minimisation methods 894
Electron beam effects, in depth profiling 271
Electron beam effects, InP on  527 527
Electron beam effects, oxide reduction 325Ч327
Electron sources 473
Electron sources, AES 95
Electron sources, HREELS 899
Electron sources, SAM 118
Electron tunnelling, energy level scheme 402Ч406
Electron tunnelling, in STM/STS 402Ч404
Electronegativity, correlation with BE shifts 84
Electronegativity, Si 517
Electronegativity, transition metals 517
Electronic configuration of elements 873Ч876
Elemental data, configuration 873Ч876
Elemental data, density 873Ч876
Elemental data, isotopes 877Ч883
Elemental data, structure 873Ч876
Elemental sensitivity 488
Elemental sensitivity, AES 501
Elemental sensitivity, definition 489
Elemental sensitivity, ELS 489
Elemental sensitivity, SIMS 751
ELNES, tribology 708 718
ELS (low energy) 487 888Ч891
ELS (low energy), angular resolution 888Ч889
ELS (low energy), characteristics 41 488
ELS (low energy), description 888
ELS (low energy), elemental sensitivity 488 189
ELS (low energy), information 546Ч547
ELS (low energy), InP on  , as complement to SAM 526 , as complement to SAM 526
ELS (low energy), InP on  , electron backscattering contrast 534 , electron backscattering contrast 534
ELS (low energy), InP on  , loss spectra 532 , loss spectra 532
ELS (low energy), InP on  , scanning images 532Ч534 , scanning images 532Ч534
ELS (low energy), InP on  , surface specificity 534 , surface specificity 534
ELS (low energy), inter and intra-band transitions 888
ELS (low energy), passivation of InGaAsP by 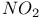 507Ч508 507Ч508
ELS (low energy), passivation of InGaAsP by 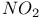 , comparison with SAM 509 535 , comparison with SAM 509 535
ELS (low energy), passivation of InGaAsP by 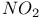 , interband transition 508 , interband transition 508
ELS (low energy), passivation of InGaAsP by 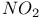 , interpretation 508Ч509 535 , interpretation 508Ч509 535
ELS (low energy), passivation of InGaAsP by 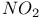 , plasmon features 508 , plasmon features 508
ELS (low energy), scanning mode (REELM) 509 526
ELS (low energy), scanning mode (REELM), image of GaAs 510
ELS (low energy), scanning mode (REELM), spatial resolution 491 494 501 535
ELS (low energy), semiconductors and microelectronics 487 501
ELS (low energy), Sn 888Ч889
ELS (low energy), Sn oxides 890Ч891
ELS (low energy), Sn, surface and plasmon losses 888Ч889
ELS (low energy), spectral interferences 493
Embrittlement, steel, time and temperature 451
Energies, Auger, calculation 94 100 178
Energy analysis, RBS 261Ч262
Energy calibration, AES, use of standards 161
Energy calibration, XPS, adventitious carbon 69 315
Energy calibration, XPS, Fermi level measurement 70
| Energy calibration, XPS, noble metal deposit 70
Energy calibration, XPS, spectral self-consistency 70
Energy calibration, XPS, use of standards 161
Energy calibration, XPS, work function measurement 69
Energy conversion factors 872
Energy distribution, secondary electrons 92Ч93
Energy distribution, secondary ions 222
Energy resolution, SRPS 491
Energy resolution, XPS 63Ч65 165 491
EPMA, analytical range 550
EPMA, characteristics 41
EPMA, corrosion film cross-sections 651
EPMA, elemental sensitivity 836
EPMA, information 546Ч547
EPMA, Roman leaded bronzes 848
EPMA, sampling depth 836
EPMA, use alongside electron spectroscopies 161
EPMA, Z limitation 836
ERDA, characteristics 43
ERDA, ion implanted layers 358
ESCA-300(Scienta) 90
Escape depth, average 61 264 308 462Ч463
ESCASCOPE (VG) 90Ч91
ESD 891Ч896
ESD, as surface analytical technique 894Ч896
ESD, as surface analytical technique, bonding of H on Si(100) 895
ESD, as surface analytical technique, detection of H 895
ESD, as surface analytical technique, ion energy analysis (ESDIED) 895
ESD, description, electron beam effects 891Ч894
ESD, description, mass analysis of desorbed ions 893
ESD, desorption cross-section 894
ESD, expression for desorbed current 892
ESD, in SAM 118
ESD, ion angular distribution (ESDIAD) 896
Eu implant in S/S, DCEMS phase analysis 362Ч363
Eu implant in S/S, stress induced transformation 363
EXAFS, catalysis, atomic environment in bimetallic systems 770Ч771
EXAFS, catalysis, Pt Ч Re and Pt Ч Sn reforming catalysts 771
EXAFS, characteristics 40
EXAFS, derivation of local atomic order 708Ч709 717Ч718 771
EXAFS, description 550 708Ч709
EXAFS, information 546Ч547 707
EXAFS, radial distribution function (RDF) 708Ч709 717Ч718
EXAFS, tribology, environment of Fe and Zn atoms in wear debris 717Ч719
EXAFS, tribology, location of shearing process 710
EXAFS, use in analysis of minerals 556Ч558
EXAFS, use in analysis of minerals, surface sites 566 568
EXELFS, characteristics 42
EXELFS, tribology 708
F (fluorine), Auger parameter  762 762
F (fluorine), XAES spectrum 163
FABMS, catalysis 749
FABMS, catalysis, association of Pt and Sn on 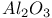 767 769 767 769
FABMS, catalysis, avoidance of charging problems 751
FABMS, catalysis, support-related clusters 769
FABMS, characteristics 43
Factor analysis, AES 180 277Ч278
Factor analysis, AES, W/N system 277Ч278
Fibres, C 1s spectra 609Ч611 618 620Ч632
Fibres, C 1s spectra,  -carbon atoms 629Ч631 -carbon atoms 629Ч631
Fibres, C 1s spectra, component peaks 618 620Ч632
Fibres, C 1s spectra, curve-fitting 622Ч632
Fibres, C 1s spectra, from various fibres 623
Fibres, C 1s spectra, line-width variation 623
Fibres, conducting, problems inside instrumentation 607
Fibres, conducting, removal from instrumentation 607
Fibres, decomposition during analysis 609
Fibres, decomposition during analysis, electron beam damage 609
Fibres, decomposition during analysis, sputtering damage 609Ч610
Fibres, decomposition during analysis, use of monochromatisation 628Ч631
Fibres, decomposition during analysis, X-irradiation damage 609
Fibres, depth profiling 618Ч619
Fibres, depth profiling, ion bombardment damage 618
Fibres, depth profiling, non-destructive 618Ч619
Fibres, depth profiling, sample mounting 608 619
Fibres, in composites 605Ч606
Fibres, interfaces 636Ч639 804
Fibres, interfaces, methods of examination 636Ч638 804
Fibres, mounting for surface analysis 606Ч608
Fibres, mounting for surface analysis, multiple fibres 606Ч608
Fibres, mounting for surface analysis, orientation 607Ч608
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, AFM 612Ч613 788
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, FTIR and Raman spectroscopies 611Ч612
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, ISS 614
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, SEM 612
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, SIMS 614
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, surface free energy 613
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, TPD 614
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, WDS 612
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, XPS 614Ч634
Fibres, surface analytical techniques, XRD (grazing incidence) 610Ч611
Fibres, surface functionality, advantages of monochromatisation 621
Fibres, surface functionality, curve-fitting of C 1s and O 1s 622Ч631
Fibres, surface functionality, decomposition by heat from X-ray source 619Ч621
Fibres, surface functionality, from valence band features 620Ч621
Fibres, valence band 632Ч636
Fibres, valence band, chemical information 633Ч636
Fibres, valence band, modelling 633
Fibres, valence band, spectra 634 637
Field emission gun STEM (FEGSTEM) 450 473Ч474 476Ч477 683 687
Field emission gun STEM (FEGSTEM), characteristics 42
Field emission gun STEM (FEGSTEM), comparison with AES 476Ч477
Field emission gun STEM (FEGSTEM), grain boundary analysis 450 474 476
Field emission gun STEM (FEGSTEM), spatial resolution 476
Flood guns, electron, charge neutralisation 757
Flotation, mineral separation 550
Flotation, mineral separation, adsorption of ethyl xanthate 566
Flotation, mineral separation, implications from STM images 562Ч565
Flotation, mineral separation, surface analytical requirements 550Ч551
Flotation, ToF Ч SIMS analysis of activating species 571Ч573
Force-distance spectroscopy, in AFM 407Ч410
Fracture, ceramics, intergranular, transfer vessel 569
Fracture, ceramics, intergranular, vacuum conditions 569
Fracture, metals, intergranular 449 459Ч464
Fracture, metals, intergranular, AES analysis 460Ч464 471
Fracture, metals, intergranular, AES analysis, SAM image 464
Fracture, metals, intergranular, carbide particles 459 463
Fracture, metals, intergranular, ductile/brittle transition temperature 459
Fracture, metals, intergranular, grain boundary segregation 459
Fracture, metals, intergranular, hydrogen charging 465 467Ч469
Fracture, metals, intergranular, hydrogen charging, cathodic in acid 467
Fracture, metals, intergranular, hydrogen charging, molten salts 468
Fracture, metals, intergranular, impact (fast) 459Ч64
Fracture, metals, intergranular, impact (fast), fracture stage 459Ч460
Fracture, metals, intergranular, impact (fast), fracture surface 461
Fracture, metals, intergranular, impact (fast), specimen preparation 459
Fracture, metals, intergranular, impact (fast), vacuum conditions 459
Fracture, metals, intergranular, irradiation effects 471Ч472
Fracture, metals, intergranular, irradiation effects, annealing reversal 472
Fracture, metals, intergranular, SAM images, P and Sn 463Ч464
Fracture, metals, intergranular, SEM images 463Ч464 470
Fracture, metals, intergranular, TEM analysis 471 473Ч477
Fracture, metals, intergranular, TEM analysis, EDS 474Ч476
Fracture, metals, intergranular, TEM analysis, FEGSTEM 473Ч477
Fracture, metals, intergranular, TEM analysis, grain boundary composition 475
Fracture, metals, intergranular, TEM analysis, PEELS 473Ч474
Fracture, metals, intergranular, TEM analysis, sample preparation 471 473
Fracture, metals, intergranular, tensile (slow), fracture stage 468Ч470
Fracture, metals, intergranular, tensile (slow), SEM images 470
Fracture, metals, intergranular, XPS analysis 465Ч466
Fracture, metals, intergranular, XPS analysis, Sn image 466
Fracture, metals, intergranular, XPS analysis, Sn spectrum 467
Fragment ions. SSIMS 219Ч220
FTIR, adsorption of long-chain alcohols on glass 590
FTIR, characteristics 40
FTIR, composites and fibres 611
FTIR, reaction of Kaolinite with water 575
FTIR, surface functionality of glasses 589
FTIR, use in analysis of minerals, ceramics, and glasses 552
Fullerene (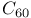 ), tribochemistry of thin films 740Ч741 ), tribochemistry of thin films 740Ч741
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте




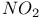

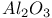
 -carbon atoms
-carbon atoms 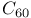 ), tribochemistry of thin films
), tribochemistry of thin films