Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Higham N.J. — Accuracy and Stability of Numerical Algorithms
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Accuracy and Stability of Numerical AlgorithmsАвтор: Higham N.J. Аннотация: What is the most accurate way to sum floating point numbers? What are the advantages of IEEE arithmetic? How accurate is Gaussian elimination and what were the key breakthroughs in the development of error analysis for the method? The answers to these and many related questions are included here.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Издание: 2Год издания: 2002Количество страниц: 680Добавлена в каталог: 19.06.2009Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Ng, Michael K. 457 Nickel, Karl 85 482 483 Nilson, E.N. 154 Nocedal, Jorge 226 468 Nonsymmetric positive definite matrix 208 Nonsymmetric positive definite matrix, LU factorization, stability of 208—209 Nordio, Marcelo 189 Norm 105—117 Norm 116 Norm consistent 108 Norm, 2-norm, evaluation without overflow 499—500 Norm, absolute 107 Norm, dual 107 Norm, Hoelder inequality 106 Norm, matrix 107—112 Norm, matrix norm equivalence constants 109 Norm, matrix p-norm 112—114 Norm, matrix p-norm of magic square matrix 115 Norm, monotone 107 Norm, Probenius 107 Norm, subordinate matrix 108 109 Norm, unitarily invariant 108 Norm, vector 106—107 Norm, vector norm equivalence constants 109 Normal distribution 3 Normal equations 382 405 Normal equations error analysis 386—388 Notation, explanation of 2—3 67—69 Notay, Yvan 324 NPSOL 189 Numerical analysis, definition 5—6 Numerical radius 343 Numerical stability definition 7 29 Numerical stability for linear equation solvers 129—130 O'Cinneide, Colm Art 133 O'Leary, Dianne Prost 302 Oberaigner, W. 88 Oettli — Prager backward error theorem 122 Oettli, W. 122 132 Ofman, Yu. 447 Olesky, D.D. 190 Oliver, J. 103 428 Olkin, Ingram 524 525 Olshevsky, V. 428 429 Olver, F.W.J. 49 69 77 102 187 Omladic, Matjaz 210 Opfer, Gerhard 429 Ordinary differential equations accuracy of mesh point formation 92 Ordinary differential equations, backward error in 29 Ordinary differential equations, Euler's method with compensated summation 86 Ortega, James M. 376 Osborne, M.R. 413 Ostrowski, A.M. 344 543 Outer product, error analysis 64—65 Overflow 16 38 Overflow, avoiding 499—501 Overton, Michael L. 35 P-norm power method 289—291 301—302 Paige, Christopher C. 190 209 371 376 377 380 386 397 403 404 407 413 414 565 Pair wise elimination 180 189 Pairwise (fan-in) summation 80 Palmer, John 522 Palmer, Kenneth J. 29 Pan, Ching-Tsuan 183 Pan, Victor Y. 278 282 429 436 437 446 Papadimitriou, Pythagoras 377 Papadopoulos, Philip M. 318 Parallel prefix operation 103 152 Paranoia code 495 Parhami, Behrooz 56 Park, Haesun 376 Parlett, Beresford N. xxviii xxx 24 30 55 76 79 184 215 226 353 375 376 Partial pivoting 158 162 Partial pivoting for skew-symmetric matrices 225 Partial pivoting for symmetric indefinite matrices 216—219 Partial pivoting growth factor 166—173 Partial pivoting growth factor, large growth in practical problems 167 Partial pivoting, early use of 188 Partial pivoting, threshold pivoting 193 Partitioned algorithm, definition 246 Partitioned LU factorization 246 Partitioned LU factorization, error analysis 249—250 Pascal matrix 518—521 Pascal matrix, Cholesky factor 519 Pascal matrix, eigenvalue reciprocity 519 Pascal matrix, inverse 520 Pascal matrix, total positivity 520 Pasternak, Mary E. 485 Patashnik, Oren 79 518 Paterson, Michael S. 102 Patrick, Merrell L. 227 Patriot missile software problem 503—504 Patterson, David A. 35 53 Paxson, Vern 57 Pei matrix 284 304 Pelz, Richard 502 Pena, J.M. 152 179 180 189 190 Pentium chip, division bug 55 Penzl, Thilo 317 Percival, Colin 457 Pereyra, Victor 423 423 425 429 Performance profile, for LAPACK norm estimator 294 Perturbation theory by calculus 132 Perturbation theory, linear systems 119—137 Perturbation theory, statistical 133 136 Perturbation theory, Sylvester equation 313—315 Peters, G. 103 188 275 281 282 404 Peterson, Brian 189 Philippe, Bernard 376 pi ( 489 Pichat, M. 88 Pierce, Daniel J. 299 Pinkus, Allan 186 188 Plemmons, Robert J. 133 152 180 190 299 332 404 413 Polar decomposition 377 380 Poljak, Svatopluk 128 Polman, Ben 257 Polynomials 93—104; see also “Horner's method” Polynomials, divided differences 99—101 Polynomials, fast evaluation schemes 103—104 Polynomials, matrix, evaluation of 102 Polynomials, Newton form 99—101 Ponceleon, Dulce B. 227 Poole, George 188 Poromaa, Peter 302 315 318 PORT library, machine constants 497 Portability of software 496—499 Positive definite matrix see “Nonsymmetric positive definite matrix” “Symmetric Pothen, Alex 153 Powell, M.J.D. 210 362 375 395 404 472 474 Power method 22 Power method for matrix 1 Power method for matrix p-norm estimation 289—291 301—302 Power method, norm estimation 292—295 Power, Stephen 209 Powers of a matrix 339—352 Powers of a matrix in exact arithmetic 340—346 Powers of a matrix in finite precision arithmetic 346—350 Powers of a matrix, behaviour of stationary iteration 351 Powers of a matrix, departure from normality 344—345 Powers of a matrix, hump 342—343 Powers of a matrix, pseudospectrum 345—346 349—350 Powers of a matrix, role of spectral radius 340—342 Prager, W. 122 132 Precise 486 Precision effect of increasing 17—19 Precision versus accuracy 6 28 Preparata, F.P. 282 Press, William H. 476 487 505 Priest, Douglas M. 28 29 54 87—89 92 499 501 529 Program verification, applied to error analysis 485 Pryce, J.D. 69 241 Pseudo-inverse 382 402 405 408 Pseudospectral radius 345 Pseudospectrum 345—346 349—350 Pseudospectrum of companion matrix 523 Puglisi, Chiara 365 Pukelsheim, Friedrich 317 Puschmann, Heinrich 189 Pythagorean sum 500 507—509 QR factorization 355 QR factorization column pivoting 362 378 QR factorization iterative refinement for linear system 368—369 QR factorization perturbation theory 373—374 QR factorization rank-revealing 377 QR factorization row pivoting 362 QR factorization row sorting 362 QR factorization, generalized 397—398 QR factorization, Givens 365—366 QR factorization, Givens, cancellation of errors in 21—22 QR factorization, Givens, error analysis 366—368 QR factorization, Householder 355—357 QR factorization, Householder, error analysis 359—363 QR factorization, Householder, error analysis for application to LS problem 384—385 QR factorization, Householder, error analysis for partitioned (WY representation) 363—365 Quadratic equation, solving 10—11 29 Quadrature accuracy of grid formation 92 Quadrature error bound for evaluation of rule 78 Quasidefinite matrix see “Symmetric quasidefinite matrix” Quinlan, Gerald D. 87 Quinn, Thomas R. 87 Quintana, Enrique S. 282 Quintana, Gregorio 282 Rabinowitz, Philip 90 Rail, Louis B. 402 483 485 Raimi, Ralph A. 48 Ramos, George U. 456 Random matrices 515—518 Random matrices with given singular values 517—518 Random matrices, 2-norm of 516 Random matrices, condition number of 516 Random matrices, correlation matrices 525 Random matrices, expected number of real eigenvalues 516—517 Random matrices, orthogonal 517 524 Random matrices, spectral radius of 516 Random matrices, tend to be well conditioned 516 Randsvd matrix 517—518 524 525 Range reduction 51 Rath, Wolfgang 376 Ratz, H.C. 323 Razaz, M. 102 RCOND condition estimator (LAPACK, LINPACK, MATLAB) 302 477—478 Recursively partitioned LU factorization 248 Reese, M.S. 298 Reichel, Lothar 103 350 428—430 525 Reichelt, Mark W. 524 Reid, John K. 180 181 186 190 193 227 362 375 395 400 404 Reinsch, C. xxix 281 57 Reiser, John F. 54 Relative error 3 4 Relative error counter, <k> 68 Relative error, componentwise 4 Relative precision 69 Relative residual 12 Ren, Huan 56 Renaut, R.E. 180 Research problems 92 104 193 212 229 242 304 319 352 406 430 449 469 487 525 Residual, relative 12 Rew, R.K. 287 297 Rheinboldt, Werner C. 467 467 Riccati equation, algebraic 316 Rice, John R. 29 376 Rigal — Gaches backward error theorem 120 Rigal, J.L. 120 132 Robertazzi, T.G. 89 Roberts, J.D. 317 Rohn, Jiff 116 128 135 Romani, Francesco 324 Rook pivoting 159—160 188 Rook pivoting for symmetric indefinite matrices 219—221 Rook pivoting, average number of comparisons 160 220 Rook pivoting, growth factor 170 Rose, Donald J. 257 Rosenthal, Peter 317 Ross, D.R. 88 Rounding 4 38 Rounding dealing with ties 38 54 Rounding error analysis model, standard 40 Rounding error analysis model, with underflow 56—57 Rounding error analysis model, without guard digit 44 Rounding error analysis notation 67—69 Rounding error analysis ordering of operations, effect of 70 141 142 Rounding error analysis purpose of 65 195 Rounding error analysis statistical approach 48—49 Rounding error analysis, automatic 471—487 Rounding error analysis, demystified 74—76 Rounding error analysis, graphs in 76 Rounding errors are not random 25—26 48 Rounding errors in subtraction 45 Rounding errors, accumulation of 14 Rounding errors, beneficial effects of 22—24 Rounding errors, cancellation of 19—22 Rounding errors, statistical assumptions on 48—49 Rounding modes in IEEE arithmetic 41 Rounding to even versus to odd 54 Rounding, monotonicity of 38 Rowan, Thomas Harvey 485 486 Rubin, Donald B. 381 402 Ruhe, Axel 376 Ruiz, Daniel 337 Rules of thumb condition for computed powers of matrix to converge to zero 350 Rules of thumb forward error related to backward error and condition number 9 Rules of thumb relative speed of floating point operations 56 Rules of thumb square root of constants in error bound 48 Rump, Siegfried M. 127—129 191 482 483 Runge — Kutta method 83 90 Running error analysis 66 486 Running error analysis for continued fraction 77 Running error analysis for Horner's method 95—96 103 Running error analysis for inner product 65—67 RussinofT, David M. 56 Rust, B.W. 132 Rutishauser, Heinz 512 518 Sadkane, Miloud 404 Sameh, Ahmed H. 150 151 180 485 Samelson, Klaus 53 Sample variance see “Variance” Sande, G. 456 Sanz-Serna, J.M. 29 Saunders, Michael A. 226 227 229 257 413 Sautter, Werner 186 Scalapack 580 Scaling a linear system before Gaussian elimination 177—179 190 Scaling to minimize the condition number 123 125—127 178 Scarborough, James B. 28 54 Schatzman, James C. 456 Schaumburg, Kjeld 302 Schelin, Charles W. 50 Scherer, R. 76 Schneider, Hans 112 115 352 Schonfelder, J.L. 102 Schreiber, Robert S. 153 168 180 245 250—253 256 257 278 365 375 571 Schryer, N.L. 496 Schulz iteration 183 278 Schulz, Giinther 183 278 Schur complement 203 209 215 246 252 Schur complement, perturbation bounds for symmetric positive semidefinite matrix 203—208 Schwartz, S.C. 89 Schwetlick, Hubert 77 393 404 410 414 Searle, Shayle R. 317 487
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



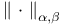 , explicit formulae for
, explicit formulae for  ), high-precision calculation as computer test
), high-precision calculation as computer test