Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Higham N.J. — Accuracy and Stability of Numerical Algorithms
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Accuracy and Stability of Numerical AlgorithmsАвтор: Higham N.J. Аннотация: What is the most accurate way to sum floating point numbers? What are the advantages of IEEE arithmetic? How accurate is Gaussian elimination and what were the key breakthroughs in the development of error analysis for the method? The answers to these and many related questions are included here.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Издание: 2Год издания: 2002Количество страниц: 680Добавлена в каталог: 19.06.2009Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
59 497—498 63 67 42 490 492 197 68 3M method 437—438 447—448 502 3M method, error analysis 444—446 Aasen's method 222—225 Aasen's method, growth factor 224 Aasen, Jan Ole 214 222 224 227 Abdelmalek, Nabih N. 376 403 Abramowitz, Milton 30 Absolute error 3 Absolute norm 107 Accuracy versus precision 6 28 ACRITH 483 Acton, Forman S. 30 195 283 486 Adams, Duane A. 103 Adjugate matrix 282 Aelfric xxi Aggarwal, Vijay B. 76 Ahac, Alan A. 190 Ahlberg, J.H. 154 Aitken extrapolation 91 Aitken, Alexander Craig 91 374 Albers, Donald J. 511 Alefeld, Goeltz 483 Alexopolous, Aristides G. 49 Allen, Jr., Richard C. 76 Almacany, Montaha 415 Alt, H. 447 Alternating directions method 474—475 Aluru, Srinivas 446 Alvarado, Fernando L. 153 Amato, James J. 317 Amodio, Pierluigi 190 Anda, Andrew A. 376 Anderson, Edward 287 397 404 Anderson, Iain J. 88 Anderson, T.W. 524 525 Ando, T. 188 Antonov, A.G. 285 Arioli, Mario 130 301 324 337 402—404 413 414 Arnold, William F. 318 Ashcraft, Cleve 188 219 227 Ashenhurst, R.L. 486 Asplund, Edgar 302 Atanasoff, John V. 139 Atlas 579 Augment precompiler 483 501 Augmented system 383 Augmented system, iterative refinement on 389 Augmented system, scaling and conditioning 391 Automatic Computing Engine (ACE) 53 185 188 337 Automatic differentiation 485 Automatic error analysis 471—487; see also “Interval analysis” “Running Automatic error analysis using direct search optimization 472—474 Automatic error analysis, condition estimation 477—478 Automatic error analysis, roots of a cubic 479—481 Automatic error analysis, Strassen's inversion method 478—479 Axelsson, Owe 337 Babuska, Ivo 90 Bachelis, Boris 50 Back substitution 140 Backward error 6—7 Backward error analysis in differential equations 29 Backward error analysis, development by Wilkinson 29—30 185—186 Backward error analysis, motivation 6 Backward error analysis, not a panacea 1 Backward error analysis, purpose 65 195 Backward error columnwise 122 Backward error linear system, Oettli — Prager theorem 122 Backward error linear system, Rigal — Gaches theorem 12 120 Backward error Lyapunov equation 311—312 Backward error, componentwise 122 128 Backward error, componentwise relative 122 Backward error, componentwise, evaluating 130 Backward error, definition 6 Backward error, least squares problem 392—395 406 Backward error, mixed forward-backward error 7 456 Backward error, normwise 120 Backward error, normwise relative 120 Backward error, preserving symmetric structure 394—395 Backward error, row-wise 122 Backward error, structured 129 Backward error, Sylvester equation 308—311 Backward error, symmetric structure, preserving 136 Backward error, underdetermined system 411 Backward stability, componentwise 129 Backward stability, definition 7 Backward stability, normwise 129 Backward stability, row-wise 130 Bai, Zhaojun 317 346 397 404 524 Bailey, David H. 436 446—448 457 478 489 501 502 Baksalary, J.K. 318 Balle, Susanne M. 448 Ballester, C. 429 Banded matrix, growth factor 173 Bank, Randolph E. 257 Bareiss, E.H. 49 189 Bargmann, V. 183 Barlow, Jesse L. 29 47 49 181 189 299 376 397 Barnett, S. 317 Barone, John L. 381 402 Barrett, Geoff 56 Barrlund, Anders 181 190 209 405 Bartels — Stewart method 307—308 Bartels, R.H. 307 Bartels, Sven G. 129 301 429 Base of floating point arithmetic 36 Bau III, David 169 337 Bauer's scaling theorem 127 133 Bauer, F.L. 53 76 107 114 127 133 135 177 281 547 Beam, Richard M. 525 Beaton, Albert E. 381 402 Bell, E.T. 279 Bellman, Richard 318 Benford, Frank 47 Benoit, Commandant 209 Benschop, N.F. 323 Berman, Abraham 133 152 Bhatia, Rajendra 317 374 Bilinear noncommutative matrix multiplication algorithm 436—437 Bilinear noncommutative matrix multiplication algorithm, error analysis 443—444 Binary-decimal conversion 57 Bini, Dario 429 443 444 Birkhoff, Garrett 279 479 Bischof, Christian H. 297—299 363 376 Bit 56 Bjoerck, Ake 76 241 353 371 375—377 379 380 386 388 389 391 391 392 399 402—405 413 414 423 423 425 429 565 Bjorstad, Petter 448 Blanch, G. 505 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms) 578 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms), Extended and Mixed Precision 64 241 462 503 579 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms), fast level 3 447 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms), Technical Forum Standard 503 579 BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms), xnrm2 (2-norm) 499—500 507 Bliss, B. 485 Block algorithm, advantages of 245 Block algorithm, definition 246 Block diagonal dominance 251—255 257 Block diagonal dominance and block LU factorization 252—255 Block diagonal dominance, definition 251 Block LDLl factorization (of skew-symmetric matrix) 225—226 Block LDLl factorization (of skew-symmetric matrix), growth factor 226 Block LDLT factorization (of symmetric matrix) 214—222 Block LDLT factorization (of symmetric matrix) for tridiagonal matrix 221—222 Block LDLT factorization (of symmetric matrix), complete pivoting and its stability 215—216 Block LDLT factorization (of symmetric matrix), growth factor, complete pivoting 216 Block LDLT factorization (of symmetric matrix), growth factor, partial pivoting 218 Block LDLT factorization (of symmetric matrix), growth factor, rook pivoting 221 Block LDLT factorization (of symmetric matrix), partial pivoting and its stability 216—219 Block LDLT factorization (of symmetric matrix), rook pivoting and its stability 219—221 Block LU factorization 246 247 Block LU factorization computation 247 Block LU factorization error analysis 250—256 Block LU factorization existence and uniqueness 247 Block LU factorization stability for (point) diagonally dominant matrix 254—255 Block LU factorization stability for block diagonally dominant matrix 251—255 Block LU factorization stability for block tridiagonal matrix 257 Block LU factorization stability for symmetric positive definite matrix 255—256 Blue, James L. 499 Bodewig, E. 185 Bohlender, Gerd 88 Bohte, Z. 173 Boley, Daniel 242 Bollen, Jo A.M. 323 Bondeli, S. 522 Boros, T. 429 Borwein, J.M. 489 Borwein, P.B. 48 Bowden, B.V. 19 Bowdler, H.J. 188 Boyd, David W. 289 291 301 Boyle, Jeff 47 Brent, Richard P. 47 150 151 436 439 440 447 483 501 505 Brezinski, Claude 209 Briggs, William L. 456 Brightman, Tom 56 Brown, W.S. 495 498 49 Brunet, Marie-Christine 485 486 Buchan, John 57 Buchanan, James L. 152 Buchholz, W. 56 Bukhberger, B. 302 Bulirsch, R. 76 187 Bunch — Kaufman partial pivoting strategy 216—219 Bunch — Parlett complete pivoting strategy 215—216 Bunch, James R. 129 133 136 213 215 216 221 225—227 231 Buoni, John J. 190 Burdakov, Oleg 282 Burgmeier, James W. 76 Businger, Peter A. 133 180 403 Butcher, J.C. 90 Byers, Ralph 302 315 318 319 346 562 BYTE 56 Caffney, John 518 Calculator, displaying words on 32 Calvetti, D. 428—430 Calvin (and Hobbes) 471 Campbell, S.L. 332 Campbell-Kelly, Martin 245 Cancellation 9—10 27 Cancellation in summation 83 539 Cancellation not a bad thing 10 Cancellation of rounding errors 19—22 Cao, Wei-Lu 302 Caprani, Ole 90 Cardano, Geronimo 479 Carr III, John W. 53 Carter, Russell 493 494 Cauchy matrix 514—515 Cauchy matrix determinant 515 Cauchy matrix inverse 515 Cauchy matrix LU factors 515 Cauchy — Schwarz inequality 106 Cauchy, August in-Louis 515 Cayley, Arthur 434 CELEFUNT package 496 CESTAC 486 Chaitin-Chatelin, Francoise 351 468 485 486 Chan, N.N. 524 Chan, Raymond H. 457 Chan, Tony F. 11 29 133 134 189 377 Chandrasekaran, Shivkumar 123 129 377 Chang, Xiao-Wen 190 209 377 Chartres, Bruce A. 186 Chatelin, Francoise see “Chaitin-Chatelin Frangoise” Chebyshev spectral differentiation matrix 340 348 Cheng, Sheung Hun 219 221 224 227 295 Cho, Choong Yun 515 Choi, Man-Duen 511 523 Cholesky factorization 196 Cholesky factorization conditions for success in floating point 200 Cholesky factorization error analysis 197—200 Cholesky factorization existence and uniqueness 196 Cholesky factorization perturbation bounds 201 Cholesky factorization semidefinite matrix, complete pivoting 202 Cholesky factorization semidefinite matrix, computation of 202 Cholesky factorization semidefinite matrix, error analysis 205—208 Cholesky factorization semidefinite matrix, existence and uniqueness 201 Cholesky factorization semidefinite matrix, perturbation theory 203—205 Cholesky factorization semidefinite matrix, termination criteria 207—208 Cholesky factorization, computation of 197 Cholesky, Andre-Louis 209 Chopping 54 Christiansen, Soren 133 Chu, Eleanor 181 Chu, King-wah Eric 318 Chu, Moody T. 525 Circulant matrix 454 Circulant system, error analysis for solution by FFT 454—456 Clasen, B.-L. 281 Clenshaw, C.W. 49 102 Cline, Alan K. 287 295 297 404 Cline, R.E. 413 Clinger, William D. 57 Codenotti, B. 282 Cody, Jr., William J. 51 55 56 493 495 496 501 Cohen, A.M. 169 170 520 Colon notation 2 Commutation matrix 317 Companion matrix 522—523 Companion matrix, singular values 523 Comparison matrix 145 Compensated summation 83—88 Complete pivoting 158 Complete pivoting for symmetric indefinite matrices 215—216 Complete pivoting growth factor 169—170 189 Complete pivoting growth factor, conjecture proved false 170 Complete pivoting, early use of 188 Complete pivoting, fallacious criticism of 193 Complete pivoting, use of, in practice 188 562 Complex arithmetic, error analysis 71—73 77 Complex number division without overflow 500 506 Complex number, square root of 32 Componentwise relative error 4 Concus, P. 257 Condition number minimizing by scaling 123 125—127 133 Condition number of function 8 Condition number of linear system componentwise 123 Condition number of linear system normwise 121 Condition number of matrix (rectangular) 382 Condition number of matrix (square) 109 110 114 Condition number of nonlinear system 464—467 Condition number of summation 91 Condition number, distance to singularity and 111 114 127 Condition number, estimation 287—304 Condition number, estimation for tridiagonal matrices 299—301 Condition number, estimation, asymptotic cost 288 Condition number, estimation, block 1-norm estimator 294—295 Condition number, estimation, counterexamples 287 288 292—294 297 302 Condition number, estimation, counterexamples by direct search 477—478 Condition number, estimation, incremental 298 Condition number, estimation, LAPACK estimator 292—294 477—478 Condition number, estimation, LINPACK estimator 295—297 Condition number, estimation, probabilistic methods 297—298 Condition number, general theory 29
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



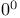 definition
definition 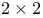 problems, reliable solution of
problems, reliable solution of 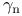 (error constant) definition
(error constant) definition  (IEEE arithmetic)
(IEEE arithmetic) 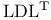 factorization
factorization  (error constant)
(error constant)