јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Dunford N., Schwartz J., Bade W.G. Ч Linear operators. Part 2
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Linear operators. Part 2јвторы: Dunford N., Schwartz J., Bade W.G.јннотаци€: In mathematics, a linear map (also called a linear mapping, linear transformation or, in some contexts, linear function) is a mapping V ↦ W between two modules (including vector spaces) that preserves (in the sense defined below) the operations of addition and scalar multiplication. An important special case is when V = W, in which case the map is called a linear operator, or an endomorphism of V. Sometimes the definition of a linear function coincides with that of a linear map, while in analytic geometry it does not.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1963 оличество страниц: 986ƒобавлена в каталог: 18.02.2014ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Characterizations, of (394Ч396) Characterizations, of Hilbert space (393Ч394) Characterizations, of the space of continuous functions (394Ч397) Charzynski, Z. 91 Chevalley, C. 79 Chiang, T.P. 928 Christian, R.R. 233 382 543 927 Clarkson, J.A. 235 384 393 396 397 473 Clifford, A.H. 82 Closed curve, positive orientation of (225) Closed graph theorem II.2.4 (57) Closed graph theorem, remarks on (83Ч85) Closed linear manifold spanned by a set II.1.4 (50) Closed operator, definition II.2.3 (57) Closed orthonormal system, definition IV.14.1 (357) Closed orthonormal system, study of IV.14 Closed set, definition I.4.3 (10) Closed set, definition, properties I.4.4Ч5 (10) Closed sphere II.4.1 (70) Closed unit sphere II.3.1 (59) Closure of a set, criterion to be in I.7.2 (27) Closure of a set, definition I.4.9 (11) Closure of a set, properties of the closure operation I.4.10Ч11 (11Ч12) Closure of a symmetric operator, definition XII.4.7 (1226) Closure theorems XI.4 (978Ч1001) Closure theorems, Wiener XI.4.7 (986) Closure theorems, Wiener XI.5.C (1003) Closure theorems, Wiener XI.4.21 (996) Cluster point, of a set I.7.8 (29) Coddington, E.A. 1433 1434 1498 1503 1587 1590 1591 1592 Cohen, I.S. 400 Cohen, L.W. 543 729 Collatz, L. 610 928 Collins, H.S. 466 Commutator of two operators, definition X.9 (934) Compact operator, criteria for and properties of VI.9.30Ч35 (515) Compact operator, definition VI.5.1 (485) Compact operator, elementary properties VI.5 Compact operator, ideals of (552Ч553) Compact operator, in VI.9.51Ч57 (517Ч519) Compact operator, in C VI.9.45 (516) Compact operator, remarks concerning (539) (609Ч611) Compact operator, representation of (547Ч551) Compact operator, representation of, into C(S) VI.7.1 (490) Compact operator, representation of, on VI.8.11 (507) Compact operator, representation of, on C(S) VI.7.7 (486) Compact operator, spectral theory of VII.4 VII.5.35 VII.8.2 Compact space, conditional compactness I.5.5 (17) Compact space, criteria for compactness I.5.6 (17) 1.7.9 1.7.12 Compact space, definition I.5.5 (17) Compact space, metric spaces I.6.13 (21Ч22) I.6.18Ч19 Compact space, properties I.5.6Ч10 (17Ч18) Compact space, sequential compactness, definition I.6.10 (21) Compact space, weak sequential compactness, conditions for in special B-spaces IV.15 Compact space, weak sequential compactness, definition II.3.25 (67) Compact space, weak sequential compactness, in reflexive spaces II.3.28 (68) Complement, and projections (553Ч554) Complement, of a set (2) Complement, orthocomplement IV.4.8 (249) Complement, orthogonal II.4.17 (72) Complemented lattice (43) Complete and (43) Complete metric space, compact I.6.15 (22) Complete metric space, definition I.6.5 (19) Complete metric space, properties I.6.7 (20) I.6.9 Complete normed linear space see "B-space" Complete orthonormal set, in Hilbert space IV.4.8 (250) Complete partially ordered space, definition I.3.9 (8) Completely regular space, compactification of IV.6.22 (276) IX.2.16 Completely regular space, definition IV.6.21 (276) IX.2.15 Completion of a normed linear space (89) Complex numbers, extended (3) Complex vector space (38) (49) Conditional compactness, definition I.5.5 (17) see Cone, definition V.9.9 (451) Confluent hypergeometric function XIII.8 (1526) Conjugate space, definition II.3.7 (61) Conjugate space, representation for special spaces IV.15 Conjugations, in groups (85) Conjugations, in Hilbert space XII.4.17 (1231) Connected set in n-space (230) Connected space I.4.12 (12) Continuity of functionals and topology V.3.8Ч9 (420Ч421) V.3.11Ч12 Continuity of functionals and topology, criteria for existence of continuous linear functionals V.7.3 (430) Continuity of functionals and topology, in bounded V.5.6 (428) Continuity of functionals and topology, non-existence in V.7.37 (438) Continuous (or III.14.13 (181) Continuous (or III.4.12 (131) Continuous (or III.12.6 (214) Continuous (or (338) Continuous (or III.10 Continuous functions see also "Absolutely continuous functions" Continuous functions, as a B-space, additional properties IV.15 Continuous functions, as a B-space, definition IV.2.14 (240) Continuous functions, as a B-space, remarks concerning (373Ч386) Continuous functions, as a B-space, study of IV.6 Continuous functions, characterizations of C-space (396Ч397) Continuous functions, criteria and properties I.4.16Ч18 (13Ч14) I.6.8 I.7.4 Continuous functions, criteria for the limit to be continuous I.7.7 (29) IV.6.11 Continuous functions, definition I.4.15 (18) Continuous functions, density in TM and III.9.14 (170) IV.8.19 Continuous functions, existence of non-differentiable continuous functions I.9.6 (33) Continuous functions, existence on a normal space I.5.2 (15) Continuous functions, extension of I.5.3Ч4 (15Ч17) 1.6.17 Continuous functions, on a compact space I.5.8 (18) I.5.10 Continuous functions, representation as a C-space, almost periodic functions IV.7.6 (285) Continuous functions, representation as a C-space, bounded functions IV.6.18Ч22 (274Ч277) Continuous functions, special C-spaces (397Ч398) Continuous functions, uniform continuity I.6.16Ч18 (23Ч24) Continuous functions, uniform continuity, of almost periodic functions IV.7.4 (283) Convergence of filters I.7.10 (30) Convergence of functions IV.15 Convergence of functions, III.6.2Ч3 (145) III.6.12 Convergence of functions, (145) Convergence of functions, almost everywhere, criteria for III.6.12Ч13 (149Ч150) Convergence of functions, almost everywhere, definition III.1.11 (100) Convergence of functions, almost everywhere, properties III.6.14-17 (150-151) Convergence of functions, in III.3.6Ч7 (122Ч124) III.6.15 III.9.5 IV.8.12Ч14 (388) Convergence of functions, in measure (or in III.9.4 (169) III.9.33 Convergence of functions, in measure (or in III.2.6 (104) Convergence of functions, in measure (or in III.2.7Ч8 (104Ч105) III.6.2Ч3 III.6.13 Convergence of functions, quasi-uniform, definition IV.6.10 (268) Convergence of functions, quasi-uniform, properties IV.6.11Ч12 (268Ч269) IV.6.30Ч31 Convergence of functions, uniform, definition I.7.1 (26) Convergence of functions, uniform, properties I.7.6 7 (28Ч29) Convergence of sequences, generalized I.7.1Ч7 (26Ч29) Convergence of sequences, in a metric space I.6.5 (19) Convergence of sequences, in special spaces IV.15 Convergence of sequences, weak convergence in a B-space II.3.25 (67) Convergence of series in a B-space, absolute (93) Convergence of series in a B-space, unconditional (92) Convergence of sets, definition (126Ч127) Convergence of sets, measurable sets in III.7.1 (158) Convergence of sets, properties III.9.48 (174) Convergence of sets, remarks on (389Ч392) Convergence of sets, set functions III.7.2Ч4 (158Ч160) IV.8.8 IV.9.4Ч5 IV.9.15 IV.10.6 IV.15 Convergence theorems IV.15 Convergence theorems, Alexandroff theorem on convergence of measures IV.9.15 (316) Convergence theorems, Arzela theorem on continuous limits IV.6.11 (268) Convergence theorems, Banach theorem for operators into space of measurable functions IV.11.2Ч3 (332Ч333) Convergence theorems, Egoroff theorem on a.e. and III.6.12 (149) Convergence theorems, Fatou theorem on limits of integrals III.6.19 (152) III.9.35 Convergence theorems, for functions of an operator, by inverting sequences VIII.2.12 (650) Convergence theorems, for functions of an operator, examples of VII.8 Convergence theorems, for functions of an operator, in finite dimensional spaces VII.1.9 (559) see Convergence theorems, for functions of an operator, in general spaces VII.3.13 (571) VII.3.23 VII.5.32 Convergence theorems, for functions of an operator, study of VII.7 Convergence theorems, for kernels III.12.10Ч12 (219Ч222) Convergence theorems, for linear operators in F- and B-spaces II.1.17Ч18 (54Ч55) 11.3.6 (80Ч82) Convergence theorems, Lebesgue dominated convergence theorem III.3.7 (124) III.6.16 IV.10.10 Convergence theorems, Moore theorem on interchange of limits I.7.6 (28) Convergence theorems, Vitali theorem for integrals III.8.6 (122) III.6.15 III.9.45 IV.10.9 Convergence theorems, Vitali Ч Hahn Ч Saks theorem for measures III.7.2Ч4 (158Ч160) Convergence theorems, Weierstrass theorem on analytic functions (228) Convex combination V.2.2 (414) see "Convex "Convex Convex function, definition VI.10.I (520) Convex function, study of VI.10 Convex hull V.2.2 (414) Convex set II.4.1 (70) Convex set, definition V.1.1 (410) Convex set, study of V.1Ч2 Convex space, locally V.2.9 (417) (471) Convex space, strictly V.11.7 (458) Convex space, uniformly, defined II.4.27 (74) Convex space, uniformly, remarks on (471Ч474) Convexity theorem of M. Riesz VI.10.11 (525) Convexity theorem of M. Riesz, applications of VI.11 Convolution of functions, as an operator in XI.3.3 (954) Convolution of functions, definition VIII.1.23 (633) Convolution of functions, inequalities concerning VI.11.6Ч12 (528Ч529) Convolution of functions, properties VIII.1.24Ч25 (634Ч635) XI.3.1 Convolution of measures VIII.2.3 (643) Cooke, R.G. 80 926 927 Cooper, J.L.B. 927 932 1258 1273 Correspondence see "Function" Coset, definition (35) Countably additive set function see also "Set function" Countably additive set function, countable additivity of the integral III.6.18 (152) IV.10.8 Countably additive set function, definition III.4.1 (126) Countably additive set function, extension of III.5 Countably additive set function, integration with respect to III.6 IV.10 Countably additive set function, properties IV.9 IV.15 Countably additive set function, spaces of III.7 IV.2.16Ч17 Countably additive set function, study of III.4 Countably additive set function, uniform countable additivity III.7.2 (158) III.7.4 IV.8.8Ч9 IV.9.1 Countably additive set function, weak countable additivity, definition (318) Countably additive set function, weak countable additivity, equivalence with strong IV.10 (818) Covering of a topological space, definition I.5.5 (17) Covering of a topological space, Heine Ч Borel covering theorem (17) Covering of a topological space, in the sense of Vitali, definition III.12.2 (212) Covering of a topological space, in the sense of Vitali, Vitali covering theorem III.12.3 (212) Covering of a topological space, Lindeloef covering theorem (12) Cronin, J. 92 Cross product see "Product" Curve see "Jordan curve" "Rectifiable D'Alembert, J. 1582 da Silvas Dias, C.L. 399 Daniell, P.J. 381Ч382 Darboux, G. 1588 Davis, H.T. 80 Day, M.M. 82 233 393Ч394 398 463 729 Dcrwker, Y.N. 723Ч724 729 De Morgan, rules of (2) Decomposition of measures and spaces, Hahn decomposition III.4Ч10 (129) Decomposition of measures and spaces, Jordan decomposition, for finitely additive set functions III.1.7 (98) Decomposition of measures and spaces, Jordan decomposition, for measures III.4.7 (128) III.4.11 Decomposition of measures and spaces, Lebesgue decomposition III.4.14 (132) Decomposition of measures and spaces, Saks decomposition IV.9.7 (308) Decomposition of measures and spaces, Yosida Ч Hewitt decomposition (293) Deficiency indices and spaces, definition XII.4.9 (1226) Delsarte, J. 1626 Dense convex sets V.7.27 (437) Dense linear manifolds V.7.40Ч41 (438Ч439) Dense set, definition I.6.11 (21) Dense set, density of continuous functions in TM and III.9.17 (170) IV.8.19 Dense set, density of simple functions in III.3.8 (125) Dense set, nowhere dense set I.6.11 (21) Density of the natural embedding of a B-space V.4.5Ч6 (424Ч425) Derivative, chain rule for III.13.1 (222) Derivative, existence of III.12.6 (214) Derivative, of a set function III.12.4 (212) Derivative, of functions III.12.7Ч8 (216Ч217) III.13.3 III.18.6 Derivative, of Radon Ч Nicodym (132) Derivative, properties IV.15 Derivative, references for differentiation (233) Derivative, space of differentiable functions IV.2.23 (242) Determinant, definition (44Ч45) Determinant, elementary properties of I.13 Diagonal process (23) Diameter of a set, definition, I.0.1 (19) Diametral point V.11.14 (459) Dieudonne, J.A. 82 84 94 235 387Ч388 389 391 395 399Ч400 402 460 462Ч463 465 466 539 541 Differentiability of the norm, remarks on (471Ч473) (474) Differential calculus see also "Derivative" Differential calculus, Frechet differential (92) Differential calculus, in a B-space (92Ч93) Differential equations, solutions of systems of (561) VII.2.19 VII.5.16 VII.5.27 Differential equations, stability of VII.2.20Ч29 (564Ч565) Differential operator, boundary condition at an end point for XIII.2.29 (1304) Differential operator, boundary condition for XIII.2.17 (1297) Differential operator, boundary form for XIII.2.1 (1287) Differential operator, boundary matrix for XIII.2.1 (1287) Differential operator, boundary value for XIII.2.17 (1297) Differential operator, bounded below XIII.7.20 (1451) XIII.9.c Differential operator, branching point of XIII.7.62 (1490) Differential operator, characteristic equation of, at iofinity XIII.8 (1527) Differential operator, complete set of boundary values for XIII.2.17 (1297) Differential operator, determining set for XIII.5.22 (1374) Differential operator, essential spectrum of XIII.10.E (1607) Differential operator, finite below XIII.7.25 (1455) Differential operator, first characteristics of XIII.8 (1527) Differential operator, formal XIII.1.1 (1280) Differential operator, formal adjoint of XIII.2.1 (1287) Differential operator, formally positive XIII.7.6 (1439) Differential operator, formally selfadjoint XIII.2.1 (1287) Differential operator, Green's formula for XIII.2.4 (1288) Differential operator, in XIII.9.E (1549) Differential operator, indicial equation of XIII.8 (1504) Differential operator, irregular formal XIII.1 (1280) Differential operator, mixed boundary condition XIII.2.29 (1304) Differential operator, nonselfadjoint XIII.9.13 (1540) Differential operator, real boundary value for XIII.2.29 (1304) Differential operator, regular formal, XIII.1 (1280) Differential operator, regular, irregular, singular points for XIII.8 (1504) Differential operator, separated boundary conditions XIII.2.29 (1304) Differential operator, singular boundary value of second order for XIII.10.D (1604) Differential operator, Stokes lines of XIII.8 (1527) Differential operator, Sturm Ч Liouville XIII.2 (1291) XIII.9.F Differentiation theorems VIII.9.13Ч14 (719Ч720) see Dimension of a Hilbert space, as a criterion for Isometric isomorphism IV.4.16 (254) Dimension of a Hilbert space, definition IV.4.15 (254) Dimension of a Hilbert space, invariance of IV.4.14 (258) Dimension of a linear space, definition (36) Dimension of a linear space, invariance of I.14.2 (44) Dimension of a linear space, of a B-space (91Ч92) Dines, L.L. 466 Dini, U. 360 383 1583 Dirac, P.A.M. 402 1585 1648 1680 Direct product, of B-spaces (89Ч90) Direct sum, of B-spaces (89Ч90) Direct sum, of Hilbert spaces IV.4.17 (256) Direct sum, of linear manifolds in a linear space (87) Direct sum, of linear spaces (87) Directed set, definition I.7.1 (26) Disconnected, extremally (398) Disconnected, totally (41) see Disjoint family of sets, definition (2) Distinguish between points, definition IV.6.15 (272) Distributions XIV.8 Distributions, carrier or support of XIV.8.11 (1650) Distributions, definition XIV.3.2 (1645) Ditkin, V.A. 1161 Divisor of zero IX.1.27 (861) Dixmier, J. 94 398 538 886 935 Dixon, A.C. 1588 Doeblin, W. 730 Domain, in complex variables (224) Domain, of a function (2) Dominated Convergence Theorem III.8.7 (124) III.6.16 IV.10.10 Dominated ergodic theorem, k-parameter continuous case in VIII.7.10 (694)
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



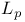
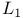
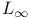
 -complete lattice
-complete lattice 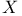 -topology
-topology  -continuous set functions), criterion for
-continuous set functions), criterion for 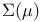
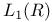

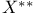 in the
in the 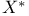 topology
topology