|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Rosenberg H.M. — Low temperature solid state physics. Some selected topics |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Dislocations, thermal activation over barriers 360 363 366 373 374
Dislocations, vibrating segments 384
Distortion of lattice, by impurity atoms 76
Distortion of lattice, by passage of electrons 190
Distortion of lattice, by point defects 82
Divalent metals see also Beryllium Cadmium Magnesium Mercury Zinc
Divalent metals, electrical conductivity 73
Divalent metals, electronic specific heat and axial ratio 18
Divalent metals, holes 108 216
Divalent metals, magneto-resistance 108
Divalent metals, specific heat 17
Divalent metals, zone structure 73
Divergence of point defect scattering formula 54
Division of Cu acceptors 239
Doidge, P. R. (1956), Phil Trans. A 248 553 187
Dominant lattice wavelength 10 92
Dominant phonon argument for thermal conductivity 54 56 57
Donor atoms and levels see Acceptor
Doping of semiconductors, effect on thermal conductivity 144
Double nitrates 292 305
Double resonance (ENDOR) 339
Double sulphates, susceptibility 295
Doyama, M., and Koehler, J. S. (1960), Phys. Rev. 119 939 82
Dresselhaus, G., Kip, A. F., and Kittel, C. (1953), Phys. Rev. 92 827 241
Dresselhaus, G., Kip, A. F., and Kittel, C. (1955), Phys. Rev. 98 368 $42
Drift mobility 228
du Pr , F. K. see Casimir , F. K. see Casimir
Ductile-brittle transition 363
Duffus, H. J. see Cooke
Dulong and Petit law 3
Easy glide 364
Edge dislocation 359
Edmonds, P. T. see Cooke
Effective area of Fermi surface 266
Effective electrons in anomalous skin effect 103
Effective mass of carriers 225 229 240 258
Effective mass of carriers, from cylotron resonance 241 243
Effective mass of carriers, from specific heat data 23
Effective mass of carriers, in divalent metals 108
Effective mass of carriers, influence on mobility in semiconductors 224
Effective mass of carriers, temperature dependence 243
Effective mass of carriers, transverse and longitudinal 229 230 242
Effective masses of carriers, Ge, Si, and InSb 242
Effective volume of a superconductor 174
Effectiveness of small angle scattering for thermal resistance 114
Egan, C. J. see Giauque
Einstein theory of specific heats 3
Einstein, A, (1907), Ann. Phys. (4) 22 180 800 4
Elastic coefficient, 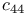 , Cu 361 , Cu 361
Elastic constants, adiabatic and isothermal 362
Elastic constants, bulk modulus 38
Elastic constants, calculations of Debye  13 13
Elastic constants, dependence on phonon velocity 93
Elastic constants, superconductors 162
Elastic constants, temperature dependence 360
Elastic constants, ultrasonic measurements 361
Elastic continuum, thermal conduction in 45
Elastic continuum, vibrational modes 5
Electric current see Current
Electrical conductivity of metals and alloys 68 ff.
Electrical conductivity of metals and alloys, alloys containing transition elements 77 79
Electrical conductivity of metals and alloys, anomalous skin effect 102 ff.
Electrical conductivity of metals and alloys, basic concepts 71
Electrical conductivity of metals and alloys, deformation, effect of 83 226
Electrical conductivity of metals and alloys, Fermi surface determination 104 357
Electrical conductivity of semiconductors see Semiconductors
Electrical conductivity, 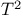 resistivity law for transition elements 98 resistivity law for transition elements 98
Electrical conductivity, 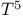 resistivity law 93 98 resistivity law 93 98
Electrical conductivity, activation energy from 86
Electrical conductivity, divalent metals 73
Electrical conductivity, electron-electron scattering 97
Electrical conductivity, Fermi surface determination 108
Electrical conductivity, Gr neisen — Bloch function 93 97 neisen — Bloch function 93 97
Electrical conductivity, high temperatures 94
Electrical conductivity, impurities, effect of 72 75 76 79
Electrical conductivity, insulators 73
Electrical conductivity, Kohler’s rule 106
Electrical conductivity, magneto -resistance size effect 100
Electrical conductivity, magneto -resistivity 105 ff.
Electrical conductivity, minima and maxima 80 87
Electrical conductivity, Nordhehn’s rule 78 79
Electrical conductivity, of dislocations and stacking faults 75 86
Electrical conductivity, of free electron metal 108
Electrical conductivity, open and closed orbits 109 110
Electrical conductivity, ordering and phase transition 80
Electrical conductivity, phonon scattering 72 75 76 80 91
Electrical conductivity, purity determination 80
Electrical conductivity, recovery of resistivity 85 91
Electrical conductivity, residual resistivity 75 76 80 91 100 111 122
Electrical conductivity, resistivity mechanisms 72 74
Electrical conductivity, resistivity of lattice imperfections 81 ff.
Electrical conductivity, resistivity ratio 81
Electrical conductivity, Rutherford scattering 77
Electrical conductivity, small angle scattering 92
Electrical conductivity, temperature dependence 75
Electrical conductivity, temperature dependent 91 ff.
Electrical conductivity, thin films and rods 98 ff.
Electrical conductivity, transition elements 97
Electrical conductivity, umklapp-processes 73 92 94 96
Electrical conductivity, valency rule 76
Electrical conductivity, Wiedemann — Frartz law 112 115 120 122 142
Electrical conductivity, zone boundary, effect of 73
Electrical resistivity see Electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity of semiconductors see Semiconductors
Electrical resistivity, Au and AuMn alloys minima and maxima 90
Electrical resistivity, Bloch — Gruneisen function 94
Electrical resistivity, characteristic temperature, 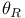 , for alkalis 95 , for alkalis 95
Electrical resistivity, Cu alloys, 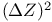 rule 77 rule 77
Electrical resistivity, Cu, deformed, S 3
Electrical resistivity, Cu, recovery after deformation 88
Electrical resistivity, Cu, recovery after irradiation 86 87
Electrical resistivity, CuAu alloys, ordered and disordered 79
Electrical resistivity, CuFe alloy, minimum 89
Electrical resistivity, CuZn alloys deformed 85
Electrical resistivity, Ge,  -type 234 -type 234
Electrical resistivity, Ge,  -type, impurity conduction range 239 -type, impurity conduction range 239
Electrical resistivity, Ge, 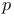 -type, impurity conduction range 238 -type, impurity conduction range 238
Electrical resistivity, high frequency, Sn 170
Electrical resistivity, Sn foils 101
Electrical resistivity, transition group metals 98; see Magneto-resistivity
Electron coherence in superconductors 189
Electron correlation, superconductors 185
Electron current flow 72
Electron energy levels in a metal 13 14
Electron irradiation, paramagnetic resonance 336
Electron irradiation, paramagnetic resonance, recovery of resistivity 85
Electron microscopy of thin films 84 139
electron pairs 190 193 198
Electron spin 285
Electron tunnelling experiments with superconductors 199 ff.
Electron-electron scattering 97
Electron-phonon interaction constant in semiconductors 224
Electron-phonon interaction in metals see Scattering of electrons
Electron-phonon interaction, superconducting state 186 188 189 197
Electron-photon interaction, carrier absorption in semiconductors 248
Electronic contribution to expansion 41
Electronic contribution to thermal expansion 40
Electronic heat conduction 43 111
Electronic specific heat 13 ff. 40 70 112 115
Electronic specific heat coefficient,  , Be, Mg, Zn, Cd 18 , Be, Mg, Zn, Cd 18
Electronic specific heat coefficient,  , elements, table 8 , elements, table 8
Electronic specific heat coefficient,  , first transition group 20 , first transition group 20
Electronic specific heat, classical theory 13
Electronic specific heat, Fermi — Dirac statistics 13
Electrons see Carrier
Electropolished surfaces of superconductors 171
ENDOB, (double resonance) 339
Energy distribution of electrons during electrical and thermal transport 114 115
Energy gap in semiconductors 74 210 216 219 220 222 232 245
Energy gap in semiconductors, for shallow states, optical and Hall data compared 250 251
| Energy gap in semiconductors, table 211
Energy gap in semiconductors, temperature dependence 245
Energy gap in superconductors 161 188 189 194 195 196
Energy gap in superconductors, experimental determination 198 ff.
Energy gap parameter 196 198
Energy gap parameter, BCS theory 196
Energy gap parameter, BCS theory, values from infra-red reflectivity 148
Energy gaps of semiconductors 211
Energy level splittings, iron group salts 299
Energy level splittings, rare earth group salts 299
Energy levels in semiconductors 211 ff.
Energy levels of electrons in metal 13
Energy of electrons at Fermi surface 14 70 112
Energy of magnetic dipole in field 290
Energy surface for semiconductor 228 241 243
Energy surface for simple cubic metal 71 75
Entropy diagram for adiabatic demagnetization 346
Entropy difference 3
Entropy: co-operative transition 33
Entropy: normal and superconducting states 156 157
Entropy: Schottky specific heat anomaly 26 27 343
Equalization of populations 329 339 340 341
Equilibrium, during heat flow 114
Equilibrium, dynamic, during current flow 72 113 114
Equilibrium, for thermo-electricity 265
Equilibrium, of carriers with the lattice 257 ff. 269
Equilibrium, of electron distribution, no current flow 72
Equipartition of energy 3
Ergmsoy, C. (1950), Phys. Rev. 79 1013:
Erickson, R. A., and Heer, C. Y. (1957), Phys. Rev. 108 896 32
Ethyl sulphates 305
Euken, A. (1911), Ann. Phys. (4) 34 185
Euken, A. (1911), Phys. Z. 12 1005
Euken, A. (1911), Verh. der Deutschen Phys. Oesellschaft 13 829 44
Europium, susceptibility 296 297 299
Evans, D. F.. see Cooke
exchange interaction 192 288 304 307 319
Exchange interaction, in ferro- and anti-ferromagnetism 309 ff.
Exchange interaction, super-exchange 308
Excitation of carriers in semiconductors see Carrier excitation
Excited state of a superconductor 194
Exclusion principle 288
Exhaustion region for semiconductors 234
Exhaustion theory of creep 374
expansion see Thermal expansion
Expansion coefficient, gold 39
Expansion coefficient, metals, table 41
Experimental observation of intermediate state of a superconductor 177
Exponential rise in thermal conductivity 52 55 58 62 63
Exponential specific heat of superconductors 161 188 197
Extended zone scheme 69
Extreme orbits 353
Extrinsic properties of semiconductors 232
Faber, T. E. (1952), Proc. Boy. Soc. A 214 392 179
Faber, T. E., and Pippard, A. B. (1955), Prog. in Low Temp. Phys. 1 159 180
Fan, H. Y. see Kaiser Ray
Fan, H. Y. (1958), Repts. on Progr. in Phys. 19 107 244 247 249 252
Fan, H. Y., and Fisher, P. (1959), J. Phys. Chem. Solids 8 270 251
Faraday effect technique to show intermediate state 178 180
Fatigue 378 ff.
Fatigue, Al 379
Fatigue, correspondence with tensile strength 380
Fatigue, corrosion 378 381
Fatigue, crack propagation 381
Fatigue, Cu 379
Fatigue, metals which exhibit brittle fracture 380
Fatigue, microcracks 378 379
Fatigue, over-ageing 382
Fatigue, processes activated by 381 382
Fatigue, ratio tensile/fatigue strengths, Ag, Au, Cd, Cu 380
Fatigue, softening 381
Faulkner, E. A. see Croft
Feher, G. (1956), Phys. Rev. 103 834 339
Fereday, R. A., and Wiersma, E. C. (1935), Physica 2 575 306
Fermi energy, metal 14 70
Fermi energy, semiconductor 221 233
Fermi surface 73 74 78 90 92 96 108 146
Fermi surface investigations, by anomalous skin effect 104 110 357
Fermi surface investigations, by de Haas — van Alphen effect 110 349 353 354 355 356
Fermi surface investigations, by magneto-resistance 108 357
Fermi surface, Au 356
Fermi surface, contact with zone boundary 71 104 105 109 266 267 357
Fermi surface, copper 104 105 356 357
Fermi surface, Cu 105
Fermi surface, effective area 266
Fermi surface, Ge and Si, conduction bands 229
Fermi surface, in electrical and thermal conduction 114 118 222 223
Fermi surface, multiply-connected 109
Fermi surface, non-spherical 96 108 118
Fermi surface, open and closed orbits 109 110
Fermi surface, radius of curvature 104
Fermi surface, simple cubic metal 70 71
Fermi surface, thermo-electricity 265 266 271 272
Fermi — Dirac statistics 70 216 233
Fermi — Dirac statistics, for donors 221
Ferric methylammonium sulphate, Shottky specific heat 29
Ferric methylammonium sulphate, specific heat 29
Ferrimagnetism 314 ff. 320
Ferrimagnetism, compensation point 317
Ferrites 314 ff.
Ferromagnetic metals, nuclear specific heat 31
Ferromagnetic powder patterns to show intermediate state 178
Ferromagnetic superconductors 183
ferromagnetism 32 34 285 307 309 320
Ferromagnetism, effect on electronic specific heat 20
Films, electrical resistivity 98 ff.
Finn, C. B. P., Orbach, R., and Wolf, W. P. (1961), Proc. Phys. Soc. 77 261 325 326
Fisher, P. see FaN
Flaws, nucleation of superconductivity at 179
Fluosilicates 305
Foner, S. see Keyes
Force-distance curves from strain rate experiments, Al, Cu, Ag 369
Forest dislocations 360 365
Foster, E. L. see Berman
Fracture strength 369 381
Frank, J. P., Manchester, F. D., and Martin, D. L. (1961), Proc. Roy. Soc. A 263 494 90
Fraser, D. B., and Hollis Hallett, A. C., (University of Toronto Press) 39
Fraser, D. B., and Hollis Hallett, A. C., Proc. 7th Int. Conf. Low Temp. Phys. p. 689
Frederikse, H. P. R. (1953), Phys. Rev. 92 248 279
Frederikse, H. P. R., and Mielczarek, E. V. (1955), Phys. Rev. 99 1889 280
Free atoms, paramagnetism 288
Free carriers in semiconductors, determination of effective mass from specific heat data 23
Free carriers in semiconductors, specific heat 22
Free electron model of a metal 68 228
Free electron model of a metal, magneto-resistance 108
Free electron model of a metal, thermopower 266
Free energy, intermediate state 176
Free energy, of electrons, variation with volume 40
Free energy, of superconductor 156 173 174 189 197
Free energy, thermal expansion derivation 37
Frequency of atomic vibrations 4
Fritzsche, H. (1955), Phys. Rev. 99 406 238
Fritzsche, H. (1958), J. Phys. Chem. Solids 6 69:
Fritzsche, H., and Cuevas, M. (1960), Phys. Rev. 119 1238 240
Fritzsche, H., and Lark-Horovitz, K. (1955), Phys. Rev. 99 400:261
Frohlich, H. (1950), Phys. Rev. 79 845 186
Frozen-in fiux 133 152 153 154
Gaffney, J. see Overton
Gallium, anisotropy of electrical and thermal conductivity 145
Gallium, de Haas — van Alphen effect 355
Gamma (electronic specific heat coefficient) 8 16
Gamma irradiation, effect on thermal conductivity of non-metals 67
Gamma irradiation, paramagnetic resonance investigations 336
Gap see Energy gap
Garnets 316
Garnets, rare earth, magnetization 317
Gases, magnetic susceptibility of NO and 318
GdRu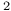 in ThBu in ThBu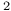 , transition and Curie temperatures 184 , transition and Curie temperatures 184
Geballe, T. H. see Carruthers Hein Herring Matthias
Geballe, T. H., and Hull, G. W. (1954), Phys. Rev. 94 1134 279 283
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 , F. K.
, F. K. 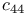 , Cu
, Cu 
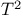 resistivity law for transition elements
resistivity law for transition elements 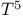 resistivity law
resistivity law  neisen — Bloch function
neisen — Bloch function 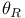 , for alkalis
, for alkalis 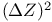 rule
rule  -type
-type 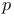 -type, impurity conduction range
-type, impurity conduction range  , Be, Mg, Zn, Cd
, Be, Mg, Zn, Cd 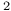 in ThBu
in ThBu