|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Huggins E.R. Ч Physics 2000 |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Measuring short times using uncertainty principle 40Ч22
Measuring time constant from graph Cal-1Ч34
Mechanics, Classical H atom 35Ч3
Mechanics, Newton's second law 8Ч4
Mechanics, Newton's Third Law 11Ч6
Mechanics, Newtonian, Chapter on 8Ч1
Mechanics, Photon mechanics 34Ч12
Mechanics, relativistic int-12
Mechanics, The role of mass in 8Ч3
Medical imaging Optics 15
Megabit, fiber optics communication Optics 14
Meiners, Harry, electron scattering apparatus 36Ч1
Meniscus-concave lens Optics 27
Meniscus-convex lens Optics 27
Mercury barometer, pressure measurement 17Ч22
Meter, definition of int-2
Microscope int-1 0
Microscope, Atomic 17Ч1
Microscope, Ptics 50
Microscope, Scanning tunneling microscope Optics 51
Microwave polarizer 32Ч24
Microwave polarizer, Center of our galaxy Optics 47
Microwave polarizer, Milky Way int-2
Microwave polarizer, Photon energies 34Ч11
Microwaves, Electromagnetic spectrum int-7 32Ч20
Millikan oil drop experiment 26Ч17
Mirror images, General discussion Optics 6
Mirror images, Reversing front to back Optics 7
Mirror images, Right-hand rule Optics 6
Mirror, parabolic, Focusing properties of Optics 4 Optics
MKS units, Ampere, volt, watt 24Ч2
MKS units, Coulomb's law in 24Ч2
MOD command, computer 5Ч10
Model Atom 37Ч4
Model Atom, Energy levels in 37Ч4
Model showing equipotential and field lines 25Ч10
Modulus, bulk 15Ч8
Modulus, Definition of 15Ч8
Modulus, Young's 15Ч8
Molar heat capacity 17Ч26
Molar specific heat of helium gas 17Ч27
Mole, Avogadro's number 17Ч24
Mole, Volume of 17Ч25
Molecular forces int-6 14Ч20 17Ч12
Molecular forces, A classical analysis 19Ч18
Molecular forces, A classical analysis, The bon ding region 19Ч19
Molecular forces, A more quantitative look 19Ч18
Molecular forces, Binding energy 17Ч13
Molecular forces, Electric interaction 19Ч1
Molecular forces, Four basic interactions 19Ч2
Molecular forces, Introduction to 19Ч15
Molecular forces, Represented by springs 17Ч13
Molecular weight 17Ч24
Molecules 17Ч2
Molecules, Cholera 17Ч2
Molecules, Hydrogen molecule ion 19Ч16
Molecules, Hydrogen, electric forces in 19Ч16
Molecules, Myoglobin 17Ч3
Molecules, water 17Ч2
Moment, magnetic and angular momentum 31Ч24
Moment, magnetic, Calculating 12Ч8
Moment, magnetic, definition of 31Ч21
Moment, magnetic, Moment of inertia, Angular mass 12Ч7
Moment, magnetic, Of charge in circular orbit 31Ч24
Moment, magnetic, Rotational kinetic energy 12Ч22
Moment, magnetic, Summary of equations 31Ч24
Momentum of photon, Compton scattering. 34Ч15
Momentum of photon, Formula for 34Ч13
Momentum version of Newton's second law 11Ч8
Momentum, Uncertainty principle, position-momentum form 40Ч15
Mormon Tabernacle, ellipse Optics 3
Mormon Tabernacle, focusing of sound waves 8Ч26
Motion in radiation belts 28Ч32
Motion, Angular acceleration 12Ч3
Motion, Angular analogy 12Ч3
Motion, Angular velocity 12Ч2
Motion, Computer program for 14Ч30
Motion, Damped harmonic motion 14Ч21
Motion, Description of, chapter on 3Ч3
Motion, Differential equation for 14Ч21
Motion, Forced harmonic motion, Differential equation for 14Ч25 14Ч28
Motion, Harmonic motion 14Ч12
Motion, Motion of electrons in a magnetic field, Of light through a medium Optics 8
Motion, Of charged particles in magnetic fields 28Ч19
Motion, Oscillatory motion 14Ч2
Motion, Oscillatory motion of various kinds, Prediction of motion 5Ч12
Motion, Particles in magnetic field 28Ч20
Motion, Radian measure 12Ч2
Motion, Rotational motion 12Ч1
Motion, Tacoma Narrows bridge 14Ч24
Motion, Translation and rotation 12Ч24
Motion, Uniform circular motion 3Ч17 8Ч2
Motion, Wave motion, amplitude and phase 15Ч17
Movie, Angular momentum as a Vector 7Ч15
Movie, Brownian motion 17Ч7
Movie, Circular motion of particles in magnetic field 28Ч20
Movie, Diver 11Ч1
Movie, Magnetic deflection 28Ч9
Movie, Magnetic focusing 28Ч30
Movie, Muon Lifetime 1Ч21
Movie, Standing De Broglie like waves 35Ч11
Movie, Time reversed dive, second law of thermodynam, ics 18Ч1
Mt. Hopkins telescope Optics 43
Mt. Palomar telescope Optics 43
Mu ( ) zero, definition of 31Ч19 ) zero, definition of 31Ч19
Multi Electron Atoms 38Ч9
Multiple lens systems Optics 28
Multiple slit grating 16Ч33
Multiple slit interference patterns 33Ч12
Multiplication notation, computer 5Ч6
Multiplication of vectors, By a number 2Ч5
Multiplication of vectors, Scalar or dot product 2Ч12
Multiplication of vectors, Vector cross product 2Ч15 12Ч9
Muon and Mt. Washington, Lorentz contraction 1Ч29
Muon type neutrino int-21
Muon, Discovery of int-23
Muon, Half life used as clock 1Ч20
Muon, Lepton family int-22
Muon, Lifetime, exponential decay Cal-1Ч32
Muon, Movie on lifetime 1Ч21
Muon, Movie on lifetime, Cerenkov radiation Optics 10
Muscle injuries lifting weights 13Ч11
Muscle, ciliary in the eye Optics 31
Myoglobin molecule 17Ч3
Myopia, nearsightedness Optics 32
NatureТs speed limit int-12 6Ч11
Nearsightedness Optics-32
Nebula, Crab, neutron star 20Ч16
Nebula, Eagle 7Ч16 7Ч18
Nebula, Orion 7Ч17
Negative and positive charge 19Ч10
Negative focal length, diverging lenses Optics-26
Negative image distance Optics-26
Negative object distance Optics-27
negative slope Cal-1Ч31
Neon bulb oscillator 27Ч28
Neon bulb oscillator, Experimental setup 27Ч31
Neon, up to, periodic table 38Ч13
Nerve fibers, Cones Optics-31
Nerve fibers, human eye Optics-31
Nerve fibers, Rods Optics-31
Net area (Fourier analysis) 16Ч29
Neutrino astronomy 6Ч14 11Ч21
Neutrinos 6Ч13 11Ч20 1987
Neutrinos in nuclear structure 20Ч7
Neutrinos in stellar evolution 20Ч15
Neutrinos in supernova explosions 20Ч16
Neutrinos, 1987 Supernova 6Ч14
Neutrinos, Beta 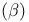 decay reactions 20Ч6 decay reactions 20Ч6
Neutrinos, cosmic background int-30
| Neutrinos, Created in the weak interaction 20Ч6
Neutrinos, Electron type int-21
Neutrinos, From the sun 6Ч13 11Ч21
Neutrinos, Muon type int-21
Neutrinos, Passing through matter int-22
Neutrinos, Pauli's prediction of int-21 20Ч6
Neutrinos, Rest mass 20Ч6
Neutrinos, Stability of 19Ч14
Neutrinos, Tau type int-21
Neutron in alpha particles 20Ч8
Neutron in isotopes int-17 19Ч6
Neutron in nuclear matter 20Ч1
Neutron star and black holes int-20 20Ч18
Neutron star in Crab nebula 20Ч17
Neutron star, Binary int-15
Neutron star, Pulsars 20Ч17
Neutron star, Stellar evolution int-19
Neutron, Decay, Beta decay reactions 20Ч7
Neutron, Decay, Charge conservation in int-21
Neutron, Decay, Energy problems int-21
Neutron, Decay, Weak interaction 20Ч6
Neutron, Formation of deuterium in early universe 34Ч30
Neutron, Neutron proton balance in early universe 34Ч30
Neutron, Neutron proton mass difference in early universe 34Ч30
Neutron, Nuclear binding energies 20Ч9
Neutron, Quark structure of int-24
Neutron, Rest mass energy int-22 20Ч9
Neutron, Role in nuclear structure 20Ч7
New functions, obtained from integration Cal-1Ч15
Newton, Particle nature of light 34Ч1 Optics-1
Newtonian mechanics 8Ч1
Newtonian mechanics, Classical H atom 35Ч3
Newtonian mechanics, Failure of in specific heats 17Ч31
Newtonian mechanics, Failure of in the classical hydrogen atom 35Ч3
Newtonian mechanics, The role of mass 8Ч3
NewtonТs laws, Chapter on 8Ч1
NewtonТs laws, Classical physics int-7
NewtonТs laws, Gravity int-15 8Ч5
NewtonТs laws, second law 8Ч4
NewtonТs laws, Second law and Newton's law of gravity 8Ч5
NewtonТs laws, Second law, Angular analogy 12Ч14
NewtonТs laws, Second law, Applications of, chapter on 9Ч1
NewtonТs laws, Second law, Atwood's machine 9Ч16
NewtonТs laws, Second law, Inclined plane 9Ч10
NewtonТs laws, Second law, Momentum version of 11Ч8
NewtonТs laws, Second law, Satellite motion 8Ч8
NewtonТs laws, Second law, String forces 9Ч15
NewtonТs laws, Second law, Vector addition of forces 9Ч6
NewtonТs laws, third law 11Ч6
NewtonТs reflecting telescope Optics-22 Optics-42
NMR experiment, the hydrogen-deuterium molecule 39Ч12
Nonlinear restoring forces 14Ч19
Nonrelativistic wave equation int-12 15Ч2 34Ч16
Normal modes, Degrees of freedom 17Ч29
Normal modes, Fourier analysis of coupled air cart system 16Ч12
Normal modes, Modes of oscillation 16Ч4 (see Experiments I: Ч11Ч Normal modes of oscillation)
Nuclear, binding energy 20Ч9
Nuclear, Charge, effective in periodic table 38Ч12
Nuclear, Energy well, binding energies 20Ч10
Nuclear, fission int-18 20Ч3
Nuclear, Fission, Energy from 20Ч4
Nuclear, Force int-18 20Ч2
Nuclear, Force, Four basic interactions 19Ч2
Nuclear, Force, Meson, Yukawa theory int-22
Nuclear, Force, Range of 20Ч3
Nuclear, Force, Range vs. electric force int-18
Nuclear, fusion int-18 20Ч12
Nuclear, Fusion, Binding energies, stellar evolution 20Ч13
Nuclear, Nuclear interaction int-14
Nuclear, Nuclear interaction, Alpha particles 20Ч8
Nuclear, Nuclear interaction, Binding energy 20Ч9
Nuclear, Nuclear interaction, Neutron stars 20Ч17
Nuclear, Nuclear magnetic moment 39Ч6
Nuclear, Nuclear matter, chapter on 20Ч1
Nuclear, Nuclear reactions, element creation int-4
Nuclear, Nuclear stability, binding energy 20Ч10
Nuclear, Nuclear structure int-22 20Ч7
Nucleon int-17
Nucleus int-17
Nucleus, Discovery of, Rutherford 35Ч1
Nucleus, Hydrogen int-6
Nucleus, Isotopes of 19Ч6
Nucleus, Large int-22
Nucleus, Lithium int-6
Odd harmonics in a square wave 16Ч28
Odor of violets 17Ч6
Oersted, Hans Christian 28Ч12
Off axis rays, parabolic mirror Optics-4
OhmТs Law 27Ч7
One cycle of a square wave 16Ч28
One dimensional wave motion 15Ч1
Optical properties, Parabolic reflectors Optics-4
Optical properties, Spherical surface Optics-19
Optics of a simple microscope Optics-50
Optics, fiber, Introduction to Optics-14
Optics, fiber, Medical imaging Optics-15
Optics, geometrical, Chapter on Optics-1
Optics, geometrical, Definition of Optics-2
Orbitals 19Ч15 (see also Hydrogen atom: Standing wave
Orbits, Allowed, Bohr theory int-8
Orbits, Bohr, radii of 35Ч7
Orbits, Classical hydrogen atom 35Ч2
Orbits, Orbit-1 Program 8Ч21
Orbits, Precession of, general relativity 8Ч30
Orbits, satellite (see Satellite motion)
Order and disorder, Direction of time 18Ч25
Order and disorder, Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics 18Ч4
Order and disorder, Formula for entropy 18Ч24
Orion Nebula 7Ч17
Oscillation 14Ч1
Oscillation, Critical damping 14Ч23
Oscillation, Damped, Computer approach 14Ч21
Oscillation, Damped, Differential equation for 14Ч21
Oscillation, LC circuit 31Ч10
Oscillation, LC circuit, Intuitive picture of 31Ч12
Oscillation, Mass on a spring, Analytic solution 14Ч7
Oscillation, Mass on a spring, Computer solution 14Ч30
Oscillation, Mass on a spring, Differential equation for 14Ч8
Oscillation, Non linear restoring forces 14Ч19
Oscillation, Normal modes 16Ч4 (see also Experiments I: Ч11Ч Normal modes of oscillation)
Oscillation, period of 14Ч4
Oscillation, phase of 14Ч6
Oscillation, Resonance, Analytic solution for 14Ч26 14Ч28
Oscillation, Resonance, Differential equation for 14Ч25
Oscillation, Resonance, Introduction to 14Ч24
Oscillation, Small oscillation, Molecular forces 14Ч20
Oscillation, Small oscillation, Simple pendulum 14Ч16
Oscillation, Torsion pendulum 14Ч12
Oscillation, Transients 14Ч27
Oscillator, harmonic oscillator 14Ч12
Oscillator, Harmonic oscillator, Differential equation for 14Ч14
Oscillator, Harmonic oscillator, Forced 14Ч28
Oscillator, Neon bulb oscillator 27Ч28
Oscillator, Neon bulb oscillator, Period of oscillation 27Ч30 (see also Experiments II: Ч4Ч The neon bulb oscillator)
Oscillatory motion 14Ч2 (see also Experiments I: Ч10Ч Oscillatory motion of various kinds)
Osmotic pressure 17Ч34
Overview of physics int-1
Parabola, How to make one Optics-4
Parabolic mirror, f number Optics-5
Parabolic mirror, Focusing properties of Optics-4 Optics-42
Parabolic mirror, Off axis rays Optics-4
Parallel currents attract 28Ч14
parallel plate capacitor 26Ч14
Parallel plate capacitor, Capacitance of 27Ч16
Parallel plate capacitor, Voltage in 26Ч15
Parallel resistors 27Ч12
Particle int-14
Particle accelerators 28Ч22
Particle decays and four basic interactions int-23
Particle nature of light 34Ч1
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 ) zero, definition of
) zero, definition of 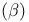 decay reactions
decay reactions