|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Huggins E.R. Ч Physics 2000 |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
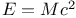 10Ч3 10Ч3
 , Uncertainty principle 40-19 , Uncertainty principle 40-19
 , Uncertainty principle 40-15 , Uncertainty principle 40-15
 zero, definition of 31-19 zero, definition of 31-19
 meson 40-23 meson 40-23
10 dimensions, String theory int-16
100 billion to one, Matter over anti matter int-30
13.6 eV, hydrogen spectrum 35-4
1836 times, proton/electron mass ratio int-17
1987 supernova 6-14 20-14
2.74 degrees, cosmic background radiation int-29
2D or 3D? equipotential plotting experiment 25-8
4 dimensions int-16
Absolute zero 17Ч9 17Ч21
Abundance of the elements 34Ч24
AC voltage generator 30Ч21
AC voltage generator, Gaussmeter 30Ч23
Accelerating field in electron gun 26Ч10
Acceleration versus time graphs 4Ч7
Acceleration, angular 12Ч3
Acceleration, Angular analogy 12Ч3
Acceleration, Calculus definition of 4Ч5 Cal-1Ч7
Acceleration, Calculus definition of Component equations Cal-1Ч8
Acceleration, Calculus definition of Vector equation Cal-1Ч7
Acceleration, Constant acceleration formulas in three dimensions 4Ч11 Cal-1Ч22
Acceleration, Constant acceleration formulas, Calculus derivation 4Ч9 Cal-1Ч20
Acceleration, Definition of 3Ч13
Acceleration, due to gravity 3Ч21
Acceleration, From a strobe photograph 3Ч15
Acceleration, Intuitive discussion 3Ч20
Acceleration, On inclined plane 9Ч11
Acceleration, radial 12Ч5
Acceleration, tangential 12Ч4
Acceleration, Uniform circular motion, Direction of 3Ч18
Acceleration, Uniform circular motion, Magnitude of 3Ч18
Acceleration, Vector, definition of 3Ч15
Accelerators, particle int-1 28Ч22
Accurate values of Fourier coefficients 16Ч32
Adding sines and cosines in Fourier analysis 16Ч28
Addition 2Ч3
Addition of charge 19Ч10
Addition of forces 9Ч2
Adiabatic expansion in Carnot cycle 18Ч11
Adiabatic expansion, Calculation of work 18Ч26
Adiabatic expansion, Introduction to 18Ч9
Air cart in impulse experiments 11Ч9
Air cart in recoil experiments 6Ч2
Air cart, Analysis of coupled carts 16Ч12
Air cart, Construction of 6Ч2
Air cart, Oscillating cart 14Ч5
Air cart, Speed detector 30Ч5 (see also Experiments II: Faraday's law air cart speed detector)
Air Resistance, Calculus analysis for projectile motion 4Ч12
Air Resistance, Computer analysis for projectile motion 5Ч24 8Ч3
Air Resistance, Strobe analysis for projectile motion 3Ч22
Airplane wing 23Ч13
Airplane wing, Bernoulli's equation 23Ч13
Allowed orbits, Bohr theory int8 35Ч1
Allowed projections, spin 39Ч3
Allowed standing wave patterns 37Ч1
Alpha particles 20Ч8
Amount of sin(3t) present in a wave 16Ч28
Ampere's law, Applied to a solenoid 29Ч15
Ampere's law, Chapter on 29Ч1
Ampere's law, Derivation of line integral 29Ч7
Ampere's law, Field of straight wire 29Ч11
Ampere's law, Final result 29Ч11
Ampere's law, Maxwell's correction to 32Ч4
Ampere, Definition of 27Ч2
Ampere, MKS units 24Ч2
Amplitude and intensity, Fourier analysis lecture 16Ч33
Amplitude and phase, Fourier analysis lecture 16Ч31
Amplitude and phase, Wave motion 15Ч17
Amplitude of a sine wave Cal 1Ч37
Amplitude, Diffraction pattern by Fourier analysis 16Ч33
Amplitude, Fourier coefficients 16Ч32
Analysis, Fourier 16Ч6
Analysis, Of coupled air carts 16Ч12
Analysis, Of path 1 for electromagnetic pulse 32Ч14
Analysis, Of path 2 for electromagnetic pulse 32Ч16
Analytic solution, Of the RC circuit 27Ч22
Analytic solution, Oscillation of mass on spring 14Ч7
Analytic solution, Projectile motion with air resistance 4Ч12
Anderson, C., positrons int13
Andromeda galaxy int2 int-3 1Ч22
Angle of reflection (scattering of light) 36Ч3 Optics 1
Angles of incidence and reflection Optics3
Angular acceleration 12Ч3
Angular analogy 12Ч3
Angular analogy for Newton's second law 12Ч14
Angular analogy, Torque (angular force) 12Ч15
Angular frequency, Definition of 14Ч4
Angular frequency, Wave motion 15Ч14
Angular magnification of magnifier Optics39
Angular mass, Moment of inertia 12Ч7
Angular mass, Rotational kinetic energy 12Ч22
Angular momentum as a Vector 7Ч14 12Ч7
Angular momentum as a Vector, Movie 7Ч15
Angular momentum, Bohr model 35Ч1 35Ч8
Angular momentum, conservation of 7Ч9 12Ч16
Angular momentum, Conservation of, angular momentum, Definition of 7Ч10
Angular momentum, Definition of, cross product 12Ч11
Angular momentum, Definition of, more general 7Ч12
Angular momentum, Definition of, still more general 12Ч6
Angular momentum, Derivation from F = ma 12Ч16 (see also Experiments)
Angular momentum, Formation of planets 7Ч17
Angular momentum, Gyroscopes 12Ч18
Angular momentum, Kepler's second law 8Ч32
Angular momentum, Magnetic moment 31Ч24
Angular momentum, Movie on vector nature 7Ч15 12Ч6 12Ч17
Angular momentum, Of bicycle wheel 12Ч6
Angular momentum, Planck's constant 35Ч8
Angular momentum, Projections of classical 7Ч14
Angular momentum, Projections of electron spin 39Ч3
Angular momentum, Quantized int9
Angular momentum, Quantized projections 38Ч5
Angular momentum, Quantum number 38Ч7
Angular velocity as a vector 12Ч7
Angular velocity, Definition of 12Ч2
Angular velocity, Mass on spring 14Ч9
Angular velocity, Oscillating cart 14Ч5
Annihilation of 34Ч17
Annihilation of antimatter 34Ч17
Annihilation of Excess of matter over in early universe 34Ч17 34Ч29
Annihilation of Introduction to int12 34Ч16
Annihilation of Neutrino int22
Annihilation of Neutron int13
Annihilation of Positron int13
Annihilation of Positron electron pair 34Ч17
Annihilation of Proton int13
Annihilation of Wave equation for 15Ч2
Antielectron int13
Antielectron type neutrino int22
Antimatter 34Ч16
Antiparticle int-13
Antiparticle, Created by photon 34Ч17
Applications of BernoulliТs equation 23Ч12
Applications of FaradayТs law 30Ч21
Applications of NewtonТs Second Law 9Ч1
Applications of the second law of thermodynamics 18Ч17
Arbitrary wave, Fourier analysis 16Ч28
Area as a vector 24Ч22
Area, Negative or positive 16Ч29
Area, Related to integration Cal 1Ч11
Area, Under the curve Cal 1Ч12
Arecibo radio telescope int15
Arecibo radio telescope, Optics 48
Arithmetic of vectors (see also Vector)
Aspirator 23Ч16
Aspirator, Bernoulli's equation 23Ч16
Aspirator, Hydrostatics 23Ч12
| Aspirator, Leaky tank 23Ч12
Aspirator, Sailboat 23Ч14
Aspirator, Venturi meter 23Ч15
Associative law 2Ч4
Associative law, Commutative law 2Ч4
Associative law, Exercise 2Ч7
Associative law, Multiplication by number 2Ч5
Associative law, Negative of 2Ч5
Associative law, Scalar or dot product 2Ч12 10Ч13
Associative law, Subtraction of 2Ч5
Associative law, Vector cross product 2Ч15 12Ч9
Astigmatism Optics21
Astronomy, 1987 supernova int-19 6Ч14 20Ч14
Astronomy, Abundance of the elements 34Ч24
Astronomy, Big bang model of universe 33Ч25 34Ч26
Astronomy, Binary stars int-2
Astronomy, Black dwarf star int-19
Astronomy, Black holes 10Ч29
Astronomy, Black holes, Introduction to int-19
Astronomy, Blackbody radiation, color of stars 34Ч2
Astronomy, Copernicus 8Ч25
Astronomy, Crab nebula 20Ч16
Astronomy, Decoupling of light and matter 34Ч31
Astronomy, Doppler effect 33Ч23
Astronomy, Eagle nebula 7Ч18 Optics 44
Astronomy, Early universe int27 34Ч29
Astronomy, Escape velocity 10Ч28
Astronomy, Evolution of the universe 34Ч21
Astronomy, Excess of matter over antimatter 34Ч29
Astronomy, Expanding universe, Hubble int-3
Astronomy, Formation of planets 7Ч17
Astronomy, Galaxy, Andromeda int-2
Astronomy, Galaxy, Introduction to int-2
Astronomy, Galaxy, Most distant int-3
Astronomy, Galaxy, Sombrero int-2
Astronomy, General relativity 8Ч29
Astronomy, Globular cluster 11Ч2
Astronomy, Gravitational tensing 34Ч20
Astronomy, Helium abundance in universe 34Ч26
Astronomy, Helium core of massive star 20Ч15
Astronomy, Hubble rule for expanding universe int-3
Astronomy, Iron core of massive star 20Ч15
Astronomy, Kepler's laws 8Ч24
Astronomy, Light years int-2
Astronomy, Magnetic field of the earth 28Ч11
Astronomy, Models of the universe 34Ч23
Astronomy, Neutrino 6Ч14 11Ч21
Astronomy, Neutron star and black holes 20Ч18
Astronomy, Neutron star in Crab nebula 20Ч17
Astronomy, Neutron star, Introduction to int-19
Astronomy, Nuclear fusion and stellar evolution 20Ч12
Astronomy, Orion nebula 7Ч17
Astronomy, Penzias and Wilson, cosmic radiation 34Ч27
Astronomy, Powering the sun 34Ч23
Astronomy, Ptolemy, epicycle in Greek astronomy 8Ч25
Astronomy, Quantum fluctuations in space 40Ч25
Astronomy, Quasar, gravitational lens 34Ч20
Astronomy, Radio galaxy Optics 48
Astronomy, Radio images of variable star Optics 49
Astronomy, Radio telescope (see Radio telescope)
Astronomy, Radio telescope, three degree radiation int30 34Ч27
Astronomy, Radio telescopes Optics 48
Astronomy, Red shift and expanding universe int-3 33Ч24 34Ч21
Astronomy, Red supergiant star 20Ч15
Astronomy, Retrograde motion of Mars 8Ч24
Astronomy, Space travel and time dilation 1Ч22
Astronomy, Star, blackbody spectrum 34Ч3
Astronomy, Steady state model of the universe 34Ч25
Astronomy, Stellar evolution int19
Astronomy, Telescopes Optics 40
Astronomy, Telescopes, Arecibo radio telescope Optics 48
Astronomy, Telescopes, Galileo's Optics 41
Astronomy, Telescopes, Hubbel Space Telescope Optics 44
Astronomy, Telescopes, Issac Newton's Optics 42
Astronomy, Telescopes, Mt. Hopkins Optics 43
Astronomy, Telescopes, Mt. Palomar Optics 43
Astronomy, Telescopes, Very Large Array, radio telescopes Optics 48
Astronomy, Telescopes, Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) Optics 49
Astronomy, Telescopes, William Hershel's Optics 43
Astronomy, Telescopes, WorldТs Largest Optical, Keck Optics 45
Astronomy, Telescopes, Yerkes Optics 41
Astronomy, Thermal equilibrium of the universe 34Ч28
Astronomy, Three degree cosmic radiation int-29 34Ч27
Astronomy, Tycho Brahe 8Ч25
Astronomy, Van Allen radiation belts 28Ч32
Astronomy, Visible universe int3
Astronomy, White dwarf star 20Ч15
Atmospheric pressure 17Ч23
Atomic and molecular forces, electric interaction 19Ч1
Atomic, Clocks 1Ч21
Atomic, Microscopes 17Ч1
Atomic, Processes 17Ч4
Atomic, Scanning Tunneling Microscope Optics 51
Atomic, Spectra 33Ч16
Atomic, Structure 19Ч3
Atomic, Units 19Ч22
Atoms, Angular momentum quantum number 38Ч7
Atoms, Atomic nucleus, chapter on 20Ч1
Atoms, Atomic processes 17Ч4
Atoms, Avogadro's law 17Ч24
Atoms, BASIC program, hydrogen molecule ion 19Ч24
Atoms, Beryllium in periodic table 38Ч13
Atoms, Bohr model int-8
Atoms, Boron in periodic table 38Ч13
Atoms, Brownian motion 17Ч7
Atoms, Chapter on 17Ч1 38Ч1
Atoms, Classical hydrogen atom 35Ч2
Atoms, Discovery of 11Ч19
Atoms, Effective nuclear charge 38Ч12
Atoms, Electron binding energy 19Ч20 38Ч11
Atoms, Electron energy in hydrogen molecule ion 19Ч21
Atoms, Electron spin 38Ч9
Atoms, Equipartition of energy 17Ч28
Atoms, Expanded energy level diagram 38Ч8
Atoms, Failure of classical physics 17Ч31
Atoms, Freezing out of degrees of freedom 17Ч32
Atoms, Heat capacity 17Ч26
Atoms, Hydrogen molecule 19Ч16
Atoms, Introductory view of int16
Atoms, Ionic bonding 38Ч15
Atoms, L=0 Patterns in hydrogen 38Ч4
Atoms, Lithium 38Ч12
Atoms, Model atom 37Ч4
Atoms, Molecular and atomic processes 17Ч1
Atoms, Molecular forces 19Ч15
Atoms, Multi electron 38Ч9
Atoms, Nuclear matter, chapter on 20Ч1
Atoms, nucleus (see also Nuclear)
Atoms, Particle-wave nature of matter int-10
Atoms, Pauli exclusion principle 38Ч9
Atoms, Periodic table 38Ч10
Atoms, Potassium to krypton 38Ч14
Atoms, Precession of in magnetic field 39Ч15
Atoms, Quantized projections of angular momentum 38Ч5
Atoms, Schroedinger's equation for hydrogen 38Ч2
Atoms, Silicon, surface (111 plane) of Optics 51
Atoms, Sodium to argon 38Ч13
Atoms, Standing wave patterns in hydrogen 38Ч3
Atoms, Table of 19Ч5
Atoms, Thermal motion of 17Ч6
Atoms, Up to neon 38Ч13
Atoms, Xenon, photograph of 17Ч1
AtwoodТs machine 9Ч16
Avogadro's number, the mole 17Ч24
AvogadroТs law 17Ч24
Balancing weights, equilibrium 13Ч2
Ball Spring Pendulum (see Pendulum: Spring)
Balmer series, Energy level diagram for 35Ч6
Balmer series, Formula from Bohr theory 35Ч5
Balmer series, hydrogen spectrum 35Ч4
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



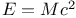
 , Uncertainty principle
, Uncertainty principle  , Uncertainty principle
, Uncertainty principle  zero, definition of
zero, definition of  meson
meson