|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Paeth A.W. (ed.) — Graphics gems (volume 5) |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Line, joining two with circular arc fillet 193 III.198 III.596
Line, segment, face connected, generation in  -dimensional space III.89 III.91 III.560 -dimensional space III.89 III.91 III.560
Line, subsegment III.189
Line, tangent, to circle I.5
Line, tangent, to circle and perpendicular to line I.8 I.9
Line, tangent, to two circles I.7-I.8
Line, vertical distance to point IV.7 IV.8
Line-edge intersections, uniform grid I.29-I.36
Linear color rendering III.343 III.348 III.583
Linear congruential generators I.67
Linear fccdback shift register I.222
Linear interpolation see Interpolation
Linear transformations II.335 II.337
Linear transformations, nonsingular, decomposing III.108 III.112
Linear transformations, singular, decomposing III.112 III.116
Lissajous figure III.166
Locally circular assumption IV.99-I.600
Logarithmic space, interpolation III.121
Lookup table (LUT) IV.424 IV.449 IV.468
Lookup table (LUT), color III.39
Lookup table (LUT), nonlinear pixel mappings I.253
Lorentz transformations, H IV.9-III.60
LU decomposition II.349
Luminaires, power from II.307
Luminance meter III.59 III.60
Luminance-color difference space III.57
M2 III.54
Mach band effect II.235-II.236
Magic square, as outer product II.74
Magic square, dither II.60-II.62
Magnification of image IV.449
Mailbox II.264
Mailbox technique III.285 III.286
Mailbox, algorithm II.268
Manhattan distance IV.32 II.258-II.259
map projections I.307-I.320
Map projections, Alber's I.321-I.325
Map projections, central (gnomonic) I.315 III.314
Map projections, cylindrical I.310 II.540 III.290
Map projections, equal area I.312 I.318 I.321
Map projections, Mercator's conformal I.313 II.545
Map projections, orthographic I.316
Map projections, Sanson's sinusoidal I.314
Map projections, stereographic I.316 II.385
Map-making IV.497
Mapping 3D I.306
Mapping, nonlinear pixels I.251-I.253
Mapping, original colors onto representatives I.291
Mapping, RGB triples II.143-III.56
Maps, cylindrical I.310-I.311
Marching Cubes IV.325 V.98
Marsden identities V.160 V.166
Martian panoramas III.291 III.293
Mass, superquadric III.139-III.140 III.152
Mathematician's tea V.37
Matrix groups II.344
Matrix groups, affine II.345
Matrix groups, angle-preserving II.345
Matrix groups, inverse II.348 II.349
Matrix groups, length-preserving II.344-II.345
Matrix groups, membership and privileges II.346 II.347
Matrix groups, nonsingular II.345
Matrix groups, nonsingular, inverse II.350
Matrix groups, window-to-viewport II.344
Matrix groups, window-to-viewport, inverse II.348
Matrix identities IV.53-IV.54
Matrix inversion IV.70-IV.71 II.342-II.350
Matrix inversion, elementary II.347
Matrix inversion, evaluation strategy II.347 II.348
Matrix inversion, problem statement II.342
Matrix multiplication, fast IV.60 IV.61
Matrix orthogonalization IV.64
Matrix techniques II.319
Matrix techniques, 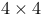 matrices II.351 II.354 matrices II.351 II.354
Matrix techniques, cross product II.333-II.334
Matrix techniques, data recovery from transformation matrix II.324-II.331
Matrix techniques, linear transformations II.335-II.337
Matrix techniques, notation II.338
Matrix techniques, pseudo-perspective II.340-II.341
Matrix techniques, quaternions II.351 II.354
Matrix techniques, random rotation matrices II.355 II.356
Matrix techniques, shear II.339 II.340
Matrix techniques, small sparse matrix classification II.357 II.361
Matrix techniques, tensor product II.333-II.334
Matrix techniques, transformations as exponentials II.332 II.337
Matrix, decomposition IV.207
Matrix, decomposition, into simple transformations II.320-II.323
Matrix, determinant IV.154 IV.167
Matrix, eigenvalues, 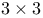 matrix IV.195 matrix IV.195
Matrix, eigenvalues, 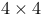 matrix IV.201 IV.209 matrix IV.201 IV.209
Matrix, exponential II.332 II.333
Matrix, inverse IV.199 IV.534
Matrix, of central moments IV.194
Matrix, subroutine library for 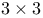 and and 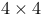 IV.534 IV.534
Matrix-vector II.360-II.361
Mechanical simulation, mass and spring model IV.506
Median cut algorithm I.288
Median finding, 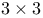 and and  grid II.71-II.75 grid II.71-II.75
Medical imaging, contrast enhancement IV.474
Medical imaging, contrast enhancement, volume data IV.324 IV.366 IV.521
Memory Allocator III.59 III.50 III.548
Menelaus' theorem 213
Menelaus's theorem II.524 II.527 V.213
Mensuration see Area and Volume
Mercator projection I.311 I.313
Meridians I.310 I.311
Mesh, computing normals for 3D IV.60
Mesh, generation for 2D region IV.47
Metric properties, transformations IV.43 IV.44
Metric tensor IV.43 IV.44
Microdot distribution V.297
Mirror image, transformation matrices IV.74
Mirror image, transformation matrices, data recovery from II.327
Mitchell filter III.15 III.16
Modeling IV.39 IV.42
Modified cylindrical equidistant projection I.311
Modified facet shading II.236 II.237
Moir patterns 300 patterns 300
Moire patterns III.339 III.340 V.300
Molecular graphics IV.193
Mollweide's Formula II.3
Monitor, white point, setting II.159-III.62
Monochromatic triples III.56
Monochrome enlargements, smoothing II.66 II.70
Monochrome enlargements, smoothing, pattern within rules II.69
Monochrome enlargements, smoothing, rules II.66 II.67
Monomial evaluation algorithm, B zier curves IV.90-IV.91 zier curves IV.90-IV.91
Monomial form, conversion, from B zier form IV.92-IV.93 zier form IV.92-IV.93
Monomial form, conversion, to B zier form IV.91-IV.92 zier form IV.91-IV.92
Monte - Carlo integration 359
Monte Carlo integration III.80 V.359
Monte Carlo integration, spectral radiance III.308
Monte Carlo label placement IV.498
Monte Carlo sampling IV.370
Morphing II.545
Motion blur, graphics workstation III.374 III.382
Motion blur, graphics workstation, code III.606
Motion blur, graphics workstation, combining spatial and temporal anti-aliasing III.376 III.378
Motion blur, graphics workstation, computing on fields III.375 III.376
Motion blur, graphics workstation, implementation tricks III.380-III.382
Motion blur, graphics workstation, interlace artifact reduction III.378-III.379
Motion blur, graphics workstation, pixel shifts III.380 III.381
Motion blur, graphics workstation, supersampling in time III.374 III.375
Multi-indices II.512
Multidimensional sum tables I.376 I.381
Multidimensional sum tables Superquadrics, review III.137 III.138
Multidimensional sum tables,  -dimensional I.380 I.381 -dimensional I.380 I.381
Multidimensional sum tables, three-dimensional I.378-I.380
Multidimensional sum tables, two-dimensional I.376 I.377
Multilinearity V.215
| Multiple output levels, halftoning to II.64-II.65
Multiple-angle relations II.7
Multivariate approximation, B zier curves and surfaces II.509 zier curves and surfaces II.509
Narrow domains, aliasing III.23-III.24
National Television Systems Committee, encoding basics II.148 III.52
Nearest neighbor V.30 V.65
Nearest neighbor 3D 65
Nearest-point-on-curve problem I.607-I.611
Nearest-point-on-curve problem, B zier form conversion I.609-I.611 zier form conversion I.609-I.611
Nearest-point-on-curve problem, problem statement I.608-I.609
Negative light III.367
Nesting IV.67-IV.68
Neumark's algorithm V.9
Neutral file format (NFF) V.398
Newell's method, plane equation of polygon III.231 III.232 III.517
Newton's formula II.5IV.96 IV.98
Newton-Raphson iteration, digitized curve fitting I.621-I.623
Nice numbers, for graph labels I.61 I.63
Nine-point circle IV.143
Noise function V.367; see Wave generators
Noise thresholding, edge images III.05-III.06
Nolid I.238
Nonhomogeneous coordinates IV.23
Nonlinear pixel mappings I.251 I.253
Nonlocality tension II.238
Nonsingular matrix group II.345
Nonsingular matrix group, inverse II.350
Nonuniform random point sets, via warping 80III.83
Normal buffer I.257 I.258
Normal coding I.257 I.264
Normal coding, encoding methods I.258 I.263
Normal coding, encoding methods, improving I.263-I.264
Normal coding, encoding methods, index number I.260
Normal coding, encoding methods, principles I.258 I.259
Normal coding, normal buffer I.257 I.258
Normal map I.260
Normal vector IV.39 IV.40
Normal vector,  -dimensional IV.156 -dimensional IV.156
Normal vector, in 2D IV.138
Normal vector, interpolation IV.404
Normal vector, of cylinder IV.359
Normal vector, of ellipsoid IV.113 IV.114
Normal vector, rotation IV.168
Normal vector, superquadrics III.148
Normal vector, vertex IV.60
Normals see Surface normal
NTSC encoding see Pixel encoding
Null transform II.96 II.97
Numerical and programming techniques II.365 47
Numerical and programming techniques, arctangent, approximation II.389 II.391
Numerical and programming techniques, bit picking II.366-II.367
Numerical and programming techniques, cross product, in four dimensions and beyond III.84 III.88
Numerical and programming techniques, face-connected line segment generation,  -dimensional space III.89 III.91 III.560 -dimensional space III.89 III.91 III.560
Numerical and programming techniques, fast generation of cyclic sequences III.67 III.76 III.558
Numerical and programming techniques, fast memory allocator III.59 III.50 III.548
Numerical and programming techniques, Fourier transform II.368-II.370
Numerical and programming techniques, generic pixel selection mechanism III.77 III.79
Numerical and programming techniques, half-angle identity II.381-II.386
Numerical and programming techniques, IEEE fast square root III.58 III.546
Numerical and programming techniques, integer square root algorithm II.387-II.388
Numerical and programming techniques, interval arithmetic III.61 III.66 III.554
Numerical and programming techniques, interval sampling II.394 II.395
Numerical and programming techniques, nonuniform random point sets, via warping III.80 III.83
Numerical and programming techniques, Perlin noise function, recursive implementation II.396-II.501
Numerical and programming techniques, rolling ball III.51 III.60 III.552
Numerical and programming techniques, sign of cross product calculation II.392-II.393
Numerical and programming techniques, using geometric constructions to interpolate orientation with quaternions II.377-II.380
NURBS see B-splines nonuniform
NURBS (nonuniform rational B-spline) IV.256 286 V.216
Object area II.26 II.27
Object space partitioning III.284 III.287
Object-space rendering II.26
Octahedral subdivision see Ellipsoid generation
Octahedron, dihedrals III.74-III.75
Octree I.288 IV.74
Octree quantization I.287-I.293
Octree quantization, algorithm I.289
Octree quantization, color table filling I.290-I.291
Octree quantization, evaluation of representatives I.289-I.290
Octree quantization, improvements I.291-I.292
Octree quantization, mapping onto representatives I.291
Octree quantization, memory and computational expense I.292-I.293
Octree quantization, principle I.288
Octree, bit interleaving IV.43-IV.47
Offset prints III.65
Opcode II.36
Optical character recognition (OCR) V.329
Optimal sampling patterns V.359
Ordered dithering II.76-II.78 V.297
Ordered dithering, color II.73 II.75
Ordered dithering, matrix II.58-II.60
Orientation control IV.175
Orientation control, mouse-driven, rolling ball III.51 III.60 III.552
Orientation, of triangle IV.144
Oriented lines V.50
Orthogonal loops II.05
Orthogonal projection, in 2D IV.142
Orthogonal projection, transformation matrices IV.75
Orthogonal transformations, normal vectors IV.42-IV.43
Orthogonalization, matrix IV.64
Orthographic projection I.309 I.316
Orthonormal base 3D viewing and rotation using IV.16 IV.21
Orthonormal base 3D viewing and rotation using, general rotations IV.20-IV.21
Orthonormal base 3D viewing and rotation using, new approach IV.17-IV.20
Orthonormal base 3D viewing and rotation using, UVN coordinate system IV.18 IV.19
Orthonormal base 3D viewing and rotation using, viewing transformation, pseudo-code IV.21
Orthonormal base, movement from one to another IV.08
Overcrossing correction III.179 III.180
Overlapping testing,  -dimensional extent 240 III.243 III.527 -dimensional extent 240 III.243 III.527
Packing, body centered cubic (bcc) V.68
Packing, circumspherical V.67 V.270
Packing, face centered cubic (fcc) V.68
Paint program IV.433
Painter's algorithm see Back to front polygon rendering
PAL encoding III.53 III.54
Panoramic virtual screen, ray tracing 288-III.294 III.551
Parallel connected stripes representation 203-II.204
Parallel projection, transformation matrices IV.75
Parallelepiped IV.155 IV.161
Parallelogram IV.140
Parallelogram approximation II.83 II.84
Parallelohedron V.67
Parametric continuity I.616 II.530-II.531
Parametric elliptical arc algorithm, code III.578
Parametric elliptical arc algorithm, conjugate diameters III.169-III.171
Parametric elliptical arc algorithm, digital generation of sinusoids III.167 III.169
Parametric elliptical arc algorithm, quarter ellipse III.164 III.165
Parametric elliptical arc algorithm, simplifying computation III.171-III.172
Parametric surface see Surfaces parametric
Parametric surface functions, superquadrics 146 III.147
Partitioning, object space III.284 III.287
Partitioning, three - D polygons III.219 III.222 III.502
Patch see Surfaces parametric
Patch visibility index II.313
Pattern mask II.57
PCS-to-boundary conversion II.205
Peano curve I.28 II.27-II.28
Peano curve, coherence of transversal sequences II.28 II.30
Peano curve, generation algorithm II.25 II.26
Perception of brightness IV.416
Perception of texture patterns IV.487
Perimeter, triangles I.20
Periodic plane tesselation II.29 II.30
Perlin noise function, recursive implementation II.396-II.501
Perp-dot product IV.139 V.400
Perpendicular bisector IV.139
Perpendicular bisector, intersection, triangles I.22-I.23
Perpendicular vector see Normal vector
Perspective projection, transformation matrices IV.75
Perspective,  -dimensional IV.153 -dimensional IV.153
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 -dimensional space
-dimensional space 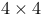 matrices
matrices 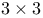 matrix
matrix  grid
grid  patterns
patterns 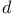 -dimensional
-dimensional