|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ashcroft N.W., Mermin N.D. Ч Solid State Physics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Helium, solid, and neutron scattering (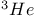 ) 470 ) 470
Helium, solid, and small oscillations assumption 488 490
Helium, solid, and theory of quantum solids 422
Helium, solid, pathological 376n
Helium, solid, solidification pressure (T = 0) 398n
Helmholtz free energy see "Free energy Helmholtz"
Hexagonal close-packed structure 76Ч79 see
Hexagonal close-packed structure and close-packed spheres 78
Hexagonal close-packed structure and nearly free electrons 167Ч168 299Ч300
Hexagonal close-packed structure vs. face-centered cubic Bravais lattice 78
Hexagonal close-packed structure, c/a ratio, ideal 78
Hexagonal close-packed structure, c/a ratio, table 77
Hexagonal close-packed structure, elements with 77
Hexagonal close-packed structure, spin-orbit coupling in 169 299
Hexagonal close-packed structure, structure factor 109
Hexagonal crystal system 119
Hole orbits 229
Hole orbits in noble metals 292
Hole surface 165
Hole surface in aluminum 301
Hole surface in lead 303Ч304
Holes 225Ч229 see "Semiconductors"
Holes and conduction in semiconductors 562
Holes and DC conductivity 251
Holes and Hall effect 235Ч236
Holes and thermopower 258
Holes, effective mass 227
Honeycomb network 66
Honeycomb network and hexagonal close-packed structure 79
Honeycomb network as lattice with basis 75
Horse, after cart 92
Hubbard model 685
Hubbard model of hydrogen molecule 689Ч691
Hund Ч Mulliken approximation 678n
Hund's rules 650Ч651
Hund's rules, applied to rare earth ions 657
Hund's rules, applied to transition metal ions 658
Hund's rules, formula for 667
Hund's rules, table 652
hybridization 181
Hydrogen bond 376n 379 391Ч392
Hydrogen bond and ice 392
hydrogen molecule 674Ч681
Hydrogen molecule in Hubbard model 689Ч691
Hyperfine (contact, Fermi) interaction 665n
Hysteresis (magnetic) 722
ICE 392
Ideal hexagonal close packed structure 78
Image charge and work function 360n
Improper operations 124
Impurities see also "Defects in crystals"
Impurities and electrical conductivity 216 315
Impurities and gapless superconductivity 727n
Impurities and Kondo effect 687Ч689
Impurities in semiconductors see also "Semiconductors"
Impurities in semiconductors and carrier densities 573 575Ч577 582Ч584 586Ч587
Impurities in semiconductors and resistivity (graph) 565
Impurities in semiconductors, Bohr radius 579
Impurities in semiconductors, donors and acceptors 577
Impurities in semiconductors, doping 590Ч591
Impurities in semiconductors, importance of 564
Impurities in semiconductors, impurity band conduction 584
Impurities in semiconductors, levels 586Ч587
Impurities in semiconductors, levels, table of binding energies 580
Impurities in semiconductors, population of levels in thermal equilibrium 581Ч582
Impurities, elastic scattering by 320Ч322
Impurities, magnetic 685Ч689
Independent electron approximation 4 60 132 192 see "Fermi "Hartree
Independent electron approximation vs. free electron approximation 4 60Ч61
Independent electron approximation, failure of, in low density electron gas 684
Independent electron approximation, failure of, in magnetic problems 673 676Ч679
Independent electron approximation, failure of, in partially filled tight-binding bands 186Ч187
Independent electron approximation, failure of, in rare earth metals 308
Independent electron approximation, failure of, in superconductors 726
Independent electron approximation, justification for 345Ч348
Independent electron approximation, representation of electron-electron interactions in 330Ч337
Index of refraction 534 see
Index of refraction, Kramers Ч Kronig relations 778
Indirect exchange 681Ч682
Indirect exchange and rare earth metals 685n
Indirect optical transitions 567
Inelastic scattering and Wiedemann Ч Franz law 322Ч323
Inert gas see "Noble gas"
Infrared absorption and reststrahl resonance 551
Infrared absorption and reststrahl resonance in superconductors 735Ч736
Inhomogeneous semiconductors see "Semiconductors"
Insulator-metal (Mott) transition 187 685
Insulators, distinguished from metals 60 223 562
Insulators, distinguished from semiconductors 562
Integer, convention on use of term 34
interactions see "Electron-electron interaction" "Electron-ion "Electron-phonon "Magnetic "Magnetic "Phonon-phonon
Interband transitions 218
Interband transitions and conductivity 253n
Interband transitions and dielectric constant 778Ч779
Interband transitions and recombination in semiconductors 603Ч604
Interband transitions, condition for absence in semiclassical motion 219Ч220 773Ч775
Interband transitions, direct 294n
Interband transitions, indirect 294n
Interband transitions, threshold 294
Intermediate state in superconductors 733n
International nomenclature for crystallographic point groups 123Ч125
International nomenclature for crystallographic point groups, tables 121 122
Interstitials 616 618 see
Intrinsic semiconductors 564 see
Inversion in a point 112 123
Inversion symmetry and Fourier coefficients of periodic potential 137
Ion cores 374n see "Core
Ion, convention on use of term 416n
Ion-ion interactions, "bare" and "dressed," 513
ionic bond 379 388
Ionic conduction 621Ч622
Ionic crystals 377Ч379 see "Color "Ionic
Ionic crystals, cohesive energy 402Ч407
Ionic crystals, color centers in 622Ч626
Ionic crystals, compared with covalent 388
Ionic crystals, conductivity of 621
Ionic crystals, I-VII (alkali halides) 380Ч385
Ionic crystals, II-VI, 385Ч387
Ionic crystals, III-V (mixed ionic-covalent) 387Ч389
Ionic crystals, Madelung energy 403Ч405
Ionic crystals, optical modes in 547Ч552
Ionic crystals, optical properties 549Ч552
Ionic crystals, reflectivity 551
Ionic crystals, reststrahl 551
Ionic crystals, shell model of 425n 546 549
Ionic crystals, stability of crystal structure 413
Ionic displacement variables 423
Ionic plasma frequency in metals 512
Ionic radii 382Ч387
Ionic radii in alkali halides 382Ч385
Ionic radii in alkali halides, table 385
Ionic radii in II-VI compounds 385Ч387
Ionic radii in II-VI compounds, table 386
Ionic radii, compared with half nearest-neighbor distances in metals 391
Ionization energies of alkali metal and hydrogen atoms 391
Ionization energies of copper compared with potassium 289n
Ising model 712Ч713
Ising model and order-disorder transition 309n
Isotope effect 739
Itinerant exchange 681Ч682
Jahn Ч Teller theorem 659
Jones Zone 167
Josephson effects 751Ч753
Joule heating 26 253n
Junction 590Ч591
Junction, abrupt 590
Junction, biased 592
Junction, biased, sign convention 597
Junction, graded 591
Junction, p-n 590
| k-space 34
k-space, density of levels 35 136
Kelvin's method 361Ч362
Kilocalories per mole to eV/molecule conversion 396n
Kinetic theory of gases, applied to metals 2Ч27
Kinetic theory of gases, applied to phonons 499Ч501 506Ч508
KKR see "Korringa Kohn Rostoker
Knight shift 666
Kohler's rule 262
Kohn anomalies 515
Kondo theory 687Ч689
Korringa, Kohn, and Rostoker method (KKR) 202Ч206
Korringa, Kohn, and Rostoker method (KKR), compared with augmented plane-wave (APW) method 205
Kramers degeneracy 659
Kramers Ч Kronig relations 778
Kronecker delta 87
Kronig Ч Penney model 149
LA (longitudinal acoustic) phonons see "Acoustic modes"
Landau diamagnetism 664Ч665
Landau levels for free electrons 270Ч271
Landau theory of a Fermi liquid see "Fermi liquid theory"
Landau tube 273
Lande g-factor 654
Lande g-factor, evaluation of 797
Langevin function 559
Langevin susceptibility 649n see
Large zone 167
Larmor diamagnetism 648Ч652 see
Lasers and measurement of phonon spectrum 481
Lattice 61Ч62 76n
Lattice conductivity see "Thermal conductivity"
Lattice constant 73
Lattice constant, table, cesium chloride structure 81
Lattice constant, table, diamond structure 76
Lattice constant, table, fee monatomic Bravais lattice 70
Lattice constant, table, hexagonal close-packed structure 77
Lattice constant, table, orthorhombic crystals 128
Lattice constant, table, rhombohedral (trigonal) crystals 127
Lattice constant, table, sodium chloride structure 80
Lattice constant, table, tetragonal crystals 127
Lattice dynamics see "Lattice vibrations"
Lattice planes 89Ч93
Lattice planes, convention for specifying 92Ч93
Lattice planes, correspondence with reciprocal lattice vectors 90Ч91
Lattice planes, families of 90
Lattice planes, Miller indices 91Ч92
Lattice potential see "Periodic potential"
Lattice specific heat see "Specific heat (lattice)"
Lattice sums of inverse powers, table 400
Lattice sums of inverse powers, table, for Coulomb potentials 403Ч405
Lattice sums of inverse powers, table, for Coulomb potentials, table 405
Lattice vibrations see also "Anharmonic terms" "Crystal "Debye "Harmonic "Phonons" "Polarization"
Lattice vibrations and anharmonic effects 422 487Ч509
Lattice vibrations and dielectric constant of metals 515Ч518
Lattice vibrations and elasticity theory 443Ч447
Lattice vibrations and electrical resistivity 315 418 523Ч528
Lattice vibrations and long range interactions 443n 440n 448
Lattice vibrations and scattering of electrons 216 315 524Ч526
Lattice vibrations and specific heat 426Ч429 453Ч464
Lattice vibrations and superconductivity 739Ч740
Lattice vibrations and thermal conductivity 495 505
Lattice vibrations and thermal expansion 490Ч492 495
Lattice vibrations and thermopower 258
Lattice vibrations and X-ray diffraction 96n 794Ч795
Lattice vibrations in metals 512Ч531
Lattice vibrations in metals, Bohm Ч Staver relation 514
Lattice vibrations in metals, detailed dispersion relation 529
Lattice vibrations of one-dimensional lattice with basis 433Ч437 448
Lattice vibrations of one-dimensional monatomic Bravais lattice 430Ч433 448
Lattice vibrations of three-dimensional lattice with basis 442Ч443
Lattice vibrations of three-dimensional monatomic Bravais lattice 437Ч442 449Ч450
Lattice vibrations, acoustic branch 435 437 442
Lattice vibrations, adiabatic approximation 425Ч426
Lattice vibrations, classical theory of 422Ч450
Lattice vibrations, crystal momentum 482Ч486 784Ч789
Lattice vibrations, Debye model of spectrum 457Ч461 465Ч466
Lattice vibrations, density of normal modes 464Ч466
Lattice vibrations, determination of spectrum by light scattering 481Ч486
Lattice vibrations, determination of spectrum by neutron scattering 470Ч480 793Ч794
Lattice vibrations, determination of spectrum by X-ray scattering 794Ч795
Lattice vibrations, dynamical matrix 439
Lattice vibrations, Einstein model of spectrum 462Ч463 466
Lattice vibrations, harmonic approximation 422Ч425
Lattice vibrations, in ionic crystals 534 547Ч549
Lattice vibrations, interaction of radiation with 470Ч486
Lattice vibrations, ionic displacements and momenta and normal mode raising and lowering operators 781Ч783
Lattice vibrations, Kohn anomalies 515
Lattice vibrations, optical branch 435 437 442
Lattice vibrations, polarization 440Ч442 449 781 783
Lattice vibrations, quantum theory of 452Ч453 780Ч783
Lattice vibrations, summary of major physical consequences 417Ч420
Lattice vibrations, thermal energy density 454
Lattice vibrations, van Hove singularities 465Ч468
Lattice vibrations, volume dependence of frequencies 490Ч492
Lattice vibrations, wave packets of 496
Lattice with a basis 75
Lattice with a basis, reciprocal lattice for 86n
Lattice, Bravais see "Bravais lattice"
Lattice, direct 86
Lattice, reciprocal see "Reciprocal lattice"
Laue condition 99
Laue formulation of X-ray diffraction 97Ч99
Laue formulation of X-ray diffraction and reciprocal lattice 97Ч99
Laue formulation of X-ray diffraction, equivalence to formulation of Bragg 99Ч100
Laue method 101Ч102
Laue method, Ewald construction for 102
Law of mass action 574
LCAO (linear combination of atomic orbitals) see "Tight-binding method"
LEED see "Low energy electron diffraction"
Lennard-Jones 6-12 potential 398
Lennard-Jones 6-12 potential, graph 399
Lennard-Jones 6-12 potential, parameters for noble gases 398
Level vs. state 32n
Light, scattering of see "Brillouin scattering" "Raman
Lindhard dielectric constant 343Ч344 352 see "Screening"
Lindhard dielectric constant, compared with Thomas Fermi 340Ч343
Line defects 616 see "Dislocations"
Linear chain 431Ч433
Linear chain and Grueneisen parameter 508
Linear chain with basis 433Ч437
Linear chain with mth nearest-neighbor interactions 448
Linear chain, diatomic 448
Liouville's theorem 222 771
Liouville's theorem and derivation of Boltzmann equation 319n
Liquid 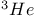 and triplet pairing 741 and triplet pairing 741
Liquids, theory of, vs. theory of solids 62
LO (longitudinal optical) phonons see "Optical modes"
Local field theory 539Ч542
Locality assumption 16Ч17 277 776
Localized moments 685Ч689
Localized moments and resistance minimum 687Ч689
Localized moments, criterion for 686
London equation 737Ч739
London equation and Ginzburg Ч Landau equation 748Ч749
London equation, applied to slab 754
London penetration depth 739
Long range interactions see also "Coulomb potential"
Long range interactions, and lattice sums 403Ч405
Long range interactions, and lattice vibrations 433n 440n 448
Long range interactions, and lattice vibrations, in ionic crystals 547Ч548
Long range interactions, and lattice vibrations, in metals 513
Long range interactions, and work function 354
Longitudinal see "Polarization"
Lorentz force 12
Lorentz relation 541
Lorentz theory of metals 63 585n
Lorentz Ч Lorenz relation 542n
Lorenz number 20 see
Lorenz number, table 21
Lorenz number, theoretical value 52
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 )
)