|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ashcroft N.W., Mermin N.D. Ч Solid State Physics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Exchange energy and cohesion in metals 411
exchange interaction 679
Exchange interaction, coupling constants 681
Exchange interaction, direct, indirect, itinerant, and super 681Ч682
Exchange term in Hartree Ч Fock equation 333
Exchange term in Hartree Ч Fock equation, approximated by one electron potential 337
Exchange term in Hartree Ч Fock equation, screening of 344 518
Exchange term in Hartree Ч Fock equation, screening of, and conduction electron magnetism 684
excitons 626Ч628
Excitons, Frenkel 626
Excitons, Mott Ч Wannier 628
Exclamation marks 61 185 219 224 291 305 403 631 808
Exclusion principle see "Pauli exclusion principle"
Extended zone scheme 159Ч160
Extremal orbits, and de Haas Ч van Alphen effect 268Ч269 273
Extremal orbits, and density of levels 273
Extremal orbits, and Gantmakher effect 280
Extremal orbits, and magnetoacoustic effect 277
Extremal orbits, in cyclotron resonance 279
Extrinsic semiconductors 564 see
Extrinsic semiconductors, carrier densities 575Ч577
F-bands 308Ч309
F-center (Farbzentrum) 624
F-center (Farbzentrum), simple model 639Ч640
f-function 350
Face centered orthorhombic Bravais lattice 118
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice 68Ч49
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice and close-packed spheres 79
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice vs. hexagonal close- packed structure 78
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, conventional cell 75
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, coordination number 71
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, elements with 70
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, first Brillouin zone 89
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, first Brillouin zone, nomenclature for symmetry points 183
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, free electron Fermi surface 165Ч166
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, free electron levels in 161
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, higher Brillouin zones 164
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, lattice sums of inverse powers 400
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, packing fraction 83
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, primitive reciprocal lattice vectors 88
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, primitive vectors 69
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, reciprocal of 88
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, relation to centered tetragonal 117
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, tight binding p-bands 189Ч190
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, tight bindings-bands 181Ч184
Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, Wigner Ч Seitz cell 74
FCC see "Face-centered cubic Bravais lattice"
Fermi (contact, hyperfine) interaction 665n
Fermi energy see also "Chemical potential"
Fermi energy of semiconductor 142n 573n
Fermi energy vs. chemical potential 43 46 573n
Fermi energy, Bloch electrons 142
Fermi energy, compared with Debye frequency 529
Fermi energy, free electron 36
Fermi energy, free electron, table 38
Fermi energy, negative values 357n
Fermi function 43 see
Fermi gas see "Free electron approximation"
Fermi level of semiconductor 573n see
Fermi liquid theory 345Ч351
Fermi liquid theory, electron electron scattering 346Ч348
Fermi liquid theory, f-function 350
Fermi liquid theory, quasiparticles 348Ч350
Fermi liquid theory, summary 351
Fermi momentum 36
Fermi sphere 36
Fermi sphere and alkali metals 285Ч288
Fermi sphere in bcc monovalent metal 285
Fermi sphere in fcc monovalent metal 289 310
Fermi sphere in fcc tetravalent metal 165
Fermi sphere in fcc trivalent metal 301 311
Fermi surface 141Ч143
Fermi surface at Bragg planes 162
Fermi surface of alkali metals 286
Fermi surface of aluminum 301
Fermi surface of beryllium 300
Fermi surface of lead 303Ч304
Fermi surface of noble metals 290Ч292
Fermi surface, extended zone scheme 159Ч160
Fermi surface, extremal, cross sectional areas 268
Fermi surface, free electron see "Fermi sphere"
Fermi surface, importance of 264
Fermi surface, measurement of 264Ч281
Fermi surface, nearly free electron construction 162Ч166 169 172Ч173
Fermi surface, reduced zone scheme 142
Fermi surface, repeated zone scheme 142
Fermi temperature 38Ч39
Fermi temperature, table 38
Fermi velocity 36
Fermi velocity, table of free electron values 38
Fermi wave vector 36
Fermi wave vector and free electron density 36
Fermi wave vector, in terms, of 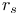 36 36
Fermi wave vector, relation to Debye wave vector 458n
Fermi wave vector, table 38
Fermi Ч Dirac distribution 30Ч31 40Ч42
Fermi Ч Dirac distribution in thermionic emission 363
Fermi Ч Dirac distribution in velocity space 30 50
Fermi Ч Dirac distribution, classical limit 54
Fermi Ч Dirac distribution, compared with Maxwell Ч Boltzmann distribution 30Ч31
Fermi Ч Dirac distribution, derived 40Ч42
Fermi Ч Dirac distribution, graph 31
Ferrimagnetism 595Ч696 see
Ferrimagnetism, critical (Curie) temperature 699
Ferrimagnetism, critical (Curie) temperature, table 698
Ferrimagnetism, distinguished from ferromagnetism 695Ч696 712n
Ferrimagnetism, mean field theory 723Ч724
Ferrimagnetism, susceptibility 712n
Ferrimagnetism, table 698
Ferroelectricity 556Ч557
Ferroelectricity, table 557
ferromagnetism 672 694Ч696 see "Magnetic
Ferromagnetism and dipolar interactions 674 718Ч722
Ferromagnetism in band theories 684n
Ferromagnetism in free electron gas 682 684
Ferromagnetism, anisotropy energy 721
Ferromagnetism, coercive force 721Ч722
Ferromagnetism, conventions on use of term 672n 695
Ferromagnetism, critical exponents 699
Ferromagnetism, critical temperature 672n 699
Ferromagnetism, critical temperature, table 697
Ferromagnetism, distinguished from ferrimagnetism 695Ч696 712n
Ferromagnetism, domains 718Ч722
Ferromagnetism, easy and hard axes 721
Ferromagnetism, Heisenberg model 701Ч709
Ferromagnetism, hysterisis 722
Ferromagnetism, low temperature spontaneous magnetization 707Ч709
Ferromagnetism, magnetization process 721Ч722
Ferromagnetism, mean field theory 715Ч718
Ferromagnetism, spin waves 704Ч709
Ferromagnetism, susceptibility 699 711Ч712 718
Ferromagnetism, table 697
Fick's law 602
Field ion microscope 366Ч367
Field theoretic methods 332 349 727
First Biillouin zone see "Biillouin zone"
Floquet's theorem 133n
Fluctuating dipole (van der Waals) force 389Ч390
Fluctuating dipole (van der Waals) force and Lennard-Jones potential 398
Fluctuating dipole (van der Waals) force in ionic crystals 402
Fluctuating dipole (van der Waals) force, origin of 392Ч393
Flux quantization 734n 749
Fluxoid 749
Force constants 426
Form factor atomic 107Ч108
Fourier transform, inversion formulas 762Ч764
Fourier transform, notational convention 339n
Fourier transform, of Coulomb interaction 334 351Ч352
Fourier transform, of screened Coulomb infraction 342 351Ч352
Fourier's law 20
| Frankenheim, M.L., and enumeration of Bravais lattices 115 119
Free charge bound charge 534n 777
Free electron approximation 4 60Ч61
Free electron approximation and alkali metals 285Ч288
Free electron approximation and cohesion in metals 410Ч412 413
Free electron approximation and interactions among electrons 330Ч352
Free electron approximation and screening 337Ч344
Free electron approximation in two dimensions 53
Free electron approximation vs. independent electron approximation 4 60Ч61
Free electron approximation, basic formulas (noninteracting) summarized 757Ч758
Free electron approximation, bulk modulus 39Ч40
Free electron approximation, chemical potential 47
Free electron approximation, correlation energy 336
Free electron approximation, density of conduction electrons 4 59
Free electron approximation, density of conduction electrons in terms of 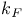 36 36
Free electron approximation, density of conduction electrons, table 5
Free electron approximation, diamagnetism 664Ч665
Free electron approximation, dielectric constant 17 338Ч344
Free electron approximation, Drude model 2Ч27
Free electron approximation, energy density, ground state, interacting 336
Free electron approximation, energy density, ground state, noninteracting 38
Free electron approximation, energy density, ground state, thermal 47
Free electron approximation, equation of state 39 54
Free electron approximation, exchange energy 336
Free electron approximation, failure of 58Ч60
Free electron approximation, Fermi liquid theory 345Ч351
Free electron approximation, ground state properties 32Ч40
Free electron approximation, Hartree Ч Fock approximation 334Ч337
Free electron approximation, high density limit 336
Free electron approximation, level quantization in magnetic field 270Ч271 281
Free electron approximation, levels in fee lattice 161
Free electron approximation, paramagnetism 661Ч664
Free electron approximation, paramagnetism, nondegenerate case 669
Free electron approximation, Sommerfeld model 30Ч55
Free electron approximation, specific heat 47Ч49
Free electron approximation, specific heat, table 48
Free electron approximation, spin density wave 684
Free electron approximation, thermal properties 40Ч49
Free electron approximation, Wigner crystal 684
Free energy, Gibbs 754
Free energy, Helmholtz 40 490
Free energy, magnetic 645
Frenkel defect 620 see
Frenkel exciton 626
Friedel oscillations 343
g-factor, electron 274 646
g-factor, Lande 654Ч797
Galvanomagnetic effects see "Hall effect" "Magnetoresistance"
Gantmakher effects 280Ч281
Gap see "Band gap" "Energy
Gapless superconductivity 727n
Gas, classical, compared with electrons in nondegenerate semiconductors 585
Gas, classical, compared with phonon gas 500n 503n 506Ч507
Gas, classical, sound propagation in 506Ч507
Gas, electron see "Free electron approximation"
Generation current 598
Generation current, formula for 605 611 see
Generation of carriers 603 see
Geometrical structure factor see "Structure factor"
Gibbs free energy (superconductor) 754
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 747Ч749
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory and flux quantization 749
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory and London equation 748Ч749
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory and vortices 748n
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory, current 748
Glasses, specific heats and thermal conductivity 504n
Glide plane 114n 126
Graded junction 591
Grain boundary 638
Graphite structure 304
Green's function (field theoretic) techniques 332
Green's function (field theoretic) techniques and Fermi liquid theory 349
Green's function (field theoretic) techniques and phonons in metals 518n
Green's function (field theoretic) techniques and screened exchange 344n
Green's function (field theoretic) techniques and superconductivity 727
Green's function method (KKR) 202Ч206
Green's function method (KKR), compared with augmented plane-wave (APW) method 205
Green's theorem (for periodic functions) 772
Ground state energy of free electron gas 336
Group see "Point group" "Space
Growth of crystals 636Ч637
Grueneisen law see "Bloch 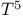 law" law"
Grueneisen parameter 492Ч494 508Ч509 see
Grueneisen parameter in Debye model 493
Grueneisen parameter, alkali halides, table for 494
H-center 625
Hall angle 14
Hall angle in materials with open orbits 238
Hall coefficient 13
Hall coefficient in two band model 240
Hall coefficient, Drude form for 14
Hall coefficient, high field, from semiclassical model 235
Hall coefficient, quantum oscillations in high field 265
Hall coefficient, sign of 13Ч14
Hall coefficient, table 15
Hall effect 11Ч13
Hall effect and density of carriers 14 235Ч236
Hall effect and sign of carriers 13Ч14 235Ч236
Hall effect in aluminum 15 300Ч302
Hall effect in compensated materials 240
Hall effect in Drude model 11Ч15
Hall effect in semiconductors 563
Hall effect in two band model 240
Hall effect, high field, from semiclassical model 234Ч236
Hall effect, problems with free electron theory of 58
Hall field 12
Hall voltage 12
Harmonic approximation 424Ч425 488 see "Lattice "Phonons"
Harmonic approximation and infinite thermal conductivity 497
Harmonic approximation and theory of specific heats 452Ч468
Harmonic approximation and volume dependence of normal mode frequencies 491Ч492
Harmonic approximation, applied to lattice vibrations 422Ч450
Harmonic approximation, distinguished from small oscillations assumption 488
Harmonic approximation, dynamical structure factor in 792Ч794
Harmonic approximation, energy levels of N-ion crystal 452
Harmonic approximation, failure of 488Ч489
Harmonic approximation, form for pair potentials 424
Harmonic approximation, form in general 425
Harmonic approximation, quantum theory of 780Ч783
Harmonic oscillator (quantum) 780
Hartree equations 331 see
Hartree equations from variational principle 332 351
Hartree Ч Fock equations 344Ч519
Hartree Ч Fock equations and effective mass 337 352
Hartree Ч Fock equations and free electron "band width," 335
Hartree Ч Fock equations and free electron ferromagnetism 682Ч684
Hartree Ч Fock equations and Landau f-function 350
Hartree Ч Fock equations and Pauli susceptibility of free electrons 669Ч670
Hartree Ч Fock equations and specific heat 337
Hartree Ч Fock equations and spin density waves 684
Hartree Ч Fock equations for free electrons 334Ч337
Hartree Ч Fock equations, approximation by one electron potential 337
Hartree Ч Fock equations, one electron levels 334Ч335
hcp see "Hexagonal close-packed structure"
heat capacity see "Specific heat"
Heisenberg model 679Ч681 see "Spin
Heisenberg model, anisotropic 723
Heisenberg model, antiferromagnetic ground state 704 722
Heisenberg model, antiferromagnetic spin waves 708
Heisenberg model, ferromagnetic ground state 701Ч703
Heisenberg model, ferromagnetic spin waves 704Ч709
Heisenberg model, Hamiltonian 681
Heisenberg model, high temperature susceptibility 709Ч712
Heisenberg model, lack of ordering in isotropic one and two dimensional 708
Heitler Ч London approximation 678Ч679 689
Heitler Ч London approximation in Hubbard model of hydrogen molecule 689Ч691
Heitler Ч London approximation, formula for exchange splitting in hydrogen molecule 679
Heitler Ч London approximation, limitations of 678
Helicons 26Ч27
Helium, solid, and harmonic approximation 425
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



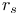
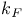
 law"
law"