|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ashcroft N.W., Mermin N.D. Ч Solid State Physics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Bulk modulus of alkali halides 407Ч408
Bulk modulus of alkali halides, table 408
Bulk modulus of noble gas solids 401Ч402
Bulk modulus of noble gas solids, table 401
Bulk modulus of selected metals 39
Burgers vector 634Ч635
c-axis, hexagonal systems 77
c-axis, tetragonal systems 115
c/a ratio in hexagonal reciprocal lattice 88Ч89
c/a ratio, hexagonal close-packed elements, table for 77
c/a ratio, ideal value 78
calories/mole to eV/molecule conversion 396n
Carrier densities in semiconductors 572Ч577 581Ч584 586Ч587
Carrier densities in semiconductors, extrinsic 575Ч577
Carrier densities in semiconductors, in equilibrium p-n junction, graph 597
Carrier densities in semiconductors, in nonequilibrium p-n junction, graph 597
Carrier densities in semiconductors, intrinsic 575
Carrier densities in semiconductors, minority 595n 598 606n
Carrier densities in semiconductors, minority, position dependence 609
Carrier densities in semiconductors, thermal generation 603
Carrier types 218Ч219
Cart, before horse 92
Casimir limit 504
Cation 380
cell see "Conventional unit cell" "Primitive
Cellular method 195Ч200
Cellular method, difficulties with 199
Cellular wave function vs. atomic 197Ч198
Centered monoclinic Bravais lattice 118
Centered tetragonal Bravais lattice 115
Centered tetragonal Bravais lattice, relation to face centered and body-centered cubic 117
Cesium chloride structure 80
Cesium chloride structure in alkali halides 380
Cesium chloride structure, compounds with, table of 81
Chambers path integral 247n
Charge density in alkali halides 381
Charge density in alkali halides, near surface of crystal 358
chemical potential 41
Chemical potential of electron gas at zero temperature 43
Chemical potential of intrinsic semiconductor 575Ч576
Chemical potential vs. Fermi energy 43Ч46 142n 573n
Chemical potential, electrochemical potential 257n 593Ч594
Chemical potential, local 245
Chemical potential, local, in AC electric field 260
Chemical potential, quasichemical potential 613
Chemical potential, temperature dependence in metals 46Ч47
Chemical potential, thermodynamic treatment of 759
Chemical shift 665n
Classical limit 50Ч51
Clausius Ч Mossotti relation 542
Clausius Ч Mossotti relation, spelling 542n
Close packing of spheres 77Ч79
Close packing of spheres and face-centered cubic structure 79
Close packing of spheres and hexagonal close-packed structure 78
Close packing of spheres and other structures 79
Close packing of spheres, packing fraction 82Ч83
Coercive force 721 722
Coherence length in superconductors 738n
Coherence length in superconductors and size of Cooper pair 742
Cohesion in covalent crystals 409Ч410
Cohesion in free electron metals 410Ч412 413
Cohesion in noble gas solids 398Ч402
Cohesive energy 396Ч414
Cohesive energy of ionic crystals 402Ч407
Cohesive energy of ionic crystals, table 406
Cohesive energy of noble gas solids 401
Cohesive energy of noble gas solids, table 401
Collision term 320
Collision time see "Relaxation time"
Collisions see also "Relaxation time" "Relaxation-time "Scattering"
Collisions and thermal equilibrium 6 245
Collisions between phonons 499 see "Second
Collisions in Drude model 6
Collisions with magnetic impurities 687Ч689
Collisions with nonmagnetic impurities (elastic) 320Ч322
Collisions, effect on nonequilibrium distribution function 317Ч319
Collisions, electron-phonon 523Ч528
Collisions, of Bloch electrons 215
Collisions, probability of 316Ч317
Collisions, sources of 216 315Ч316
Color centers 622Ч626
Color centers, 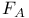 -center 626 -center 626
Color centers, 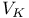 -center 625 -center 625
Color centers, F-center 624
Color centers, H-center 625
Color centers, M-center 624
Color centers, R-center 624
Color centers, width of optical absorption line 625
Compensated materials 236
Compensated materials, Hall coefficient 237 240
Compensated materials, magnetoresistance 236 240
Compressibility, isothermal vs. adiabatic 492 see
Compton scattering 480
Conduction band in metals 223
Conduction band in semiconductors 562
Conduction electrons 3 see "Electron "Free "Independent
Conductivity tensor 240
Conductivity tensor in cubic systems 250
Conductivity tensor in hexagonal systems 259
Conductivity, AC electrical, and interband transitions 253n
Conductivity, AC electrical, and reflectivity 778
Conductivity, AC electrical, at finite wavelengths 260Ч261
Conductivity, AC electrical, in Diode model 16 59
Conductivity, AC electrical, in semiclassical model 252Ч253
Conductivity, AC electrical, nonlocal 17
Conductivity, AC electrical, quantum mechanical 252
Conductivity, AC electrical, vs. dielectric constant 776Ч778
Conductivity, DC electrical and energy gap of intrinsic semiconductors 568
Conductivity, DC electrical and Fermi surface area 259Ч260
Conductivity, DC electrical and holes 251
Conductivity, DC electrical and impurities in semiconductors 564Ч565
Conductivity, DC electrical and lattice vibrations 418 523Ч528
Conductivity, DC electrical in perfect crystals 216
Conductivity, DC electrical in semiclassical model 251
Conductivity, DC electrical in uniform magnetic field 259 261Ч262
Conductivity, DC electrical of disordered alloys 310
Conductivity, DC electrical of ionic crystals 621Ч622
Conductivity, DC electrical of semiconductors 563
Conductivity, DC electrical, anisotropy 59 250
Conductivity, DC electrical, Bloch 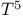 law 526 law 526
Conductivity, DC electrical, conversion of units 9
Conductivity, DC electrical, Drude formula for 7
Conductivity, DC electrical, perfect, distinguished from superconductivity 731 738
Conductivity, DC electrical, resistance minimum 687Ч689
Conductivity, DC electrical, temperature dependence 59 418 526 563
Conductivity, thermal, of insulators 495Ч505
Conductivity, thermal, of insulators, and lattice vibrations 419
Conductivity, thermal, of insulators, and umklapp processes 503
Conductivity, thermal, of insulators, Casimir limit 504
Conductivity, thermal, of insulators, high temperature 501
Conductivity, thermal, of insulators, infinite in harmonic approximation 497
Conductivity, thermal, of insulators, infinite without umklapp processes 503
Conductivity, thermal, of insulators, low temperature 501Ч505
Conductivity, thermal, of insulators, vs. metals 20 497n
Conductivity, thermal, of metals 20Ч24 see
Conductivity, thermal, of metals, Drude formula for 22
Conductivity, thermal, of metals, in semiclassical model 253Ч256
Conductivity, thermal, of metals, in Sommerfeld model 52
Conductivity, thermal, of metals, in superconductors 730Ч731
Conductivity, thermal, of metals, table 21
Conductivity, thermal, of metals, vs. insulators 20 497n
Conservation laws and relaxation-time approximation 327
Contact (Fermi, hyperfine) interaction 665n
Contact potentials 360 369 see
Contact potentials, Kelvin's method for measuring 361Ч362
Continuity, literary 626n
Conventional unit cell 73
Conventional unit cell for face-centered and body-centered cubic Bravais lattices 75
Cooper pairs 740Ч743
Cooper pairs vs. bosons 741
| Cooper pairs, crude calculation 755
Cooper pairs, size of 741n 742
Coordination number 71
Core electrons 3 374
Core electrons, wave function 194
Core electrons, wave function, compared with valence 195
Core-core repulsion 379 397
Core-core repulsion and phonons in metals 529
Core-core repulsion and polarizability of ionic crystals 545
Core-core repulsion in ionic crystals 405
Core-core repulsion in Lennard-Jones potential 398
Core-core repulsion, Born Ч Mayer potential 407
Correlation energy 336 see
correlation length 714
Correspondence principle 271
Coulomb potential see also "Long range interactions" "Screening"
Coulomb potential, and cohesive energy of ionic crystals 403Ч407
Coulomb potential, and constraint in defect concentrations 619
Coulomb potential, and ionic plasma 513
Coulomb potential, and lattice sums 403Ч405
Coulomb potential, and optical modes in ionic crystals 547
Coulomb potential, and surface effects 354
Coulomb potential, Fourier transform of 334 351Ч352
Coulomb potential, Madelung constants 405
Coulomb potential, screened 342
Coulomb potential, the "glue" of solids 378
covalent bond 379 389 552
Covalent bond, bond polarizability 552
Covalent bond, in metals 391
Covalent crystals 376 387Ч389
Covalent crystals, compared with ionic 388
Covalent crystals, dielectric constant 553
Covalent crystals, electronic charge distribution 377
Covalent crystals, polarizability of 552Ч553
Covalent crystals, semiconducting 564Ч566
Covalent radii 387n
Creation operator (phonon) 781
Critical current 730
Critical current in cylindrical wire 755
Critical current, Silsbee effect 730
Critical field (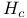 ) 728Ч729 732Ч734 see "Superconductivity" ) 728Ч729 732Ч734 see "Superconductivity"
Critical field (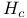 ), in type I superconductors 732 ), in type I superconductors 732
Critical field (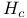 ), in type II superconductors 732Ч734 ), in type II superconductors 732Ч734
Critical field (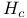 ), lower ( ), lower (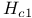 ) 732Ч734 ) 732Ч734
Critical field (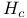 ), relation to latent heat 754 ), relation to latent heat 754
Critical field (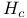 ), relation to specific heat discontinuity 754 ), relation to specific heat discontinuity 754
Critical field (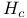 ), upper ( ), upper (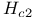 ) 732Ч734 ) 732Ч734
Critical point 699n 712Ч714 see
Critical point, exponents 699Ч701
Critical point, exponents, mean field theory 723
Critical point, exponents, two-dimensional Ising model 713
Critical point, mean field theory 715Ч718 723
Critical point, scaling equation of state 713Ч714
Critical point, scaling form of correlation function 714n
Critical temperature, ferroelectric 556Ч557 see
Critical temperature, ferroelectric, table 557
Critical temperature, magnetic 694 699 see "Ferrimagnetism" "Ferromagnetism" "Magnetic
Critical temperature, magnetic, antiferromagnets, table for 697
Critical temperature, magnetic, ferrimagnets, table for 698
Critical temperature, magnetic, ferromagnetic and strength of dipolar interaction 674n
Critical temperature, magnetic, ferromagnets, table for 697
Critical temperature, magnetic, mean field vs. exact 717
Critical temperature, superconducting 728 see
Critical temperature, superconducting in magnetic field 728 732
Critical temperature, superconducting, BCS prediction 744
Critical temperature, superconducting, table 729
Crossed fields, electron motion in 233Ч239
Crystal field splitting 657Ч658
Crystal momentum see also "Umklapp processes"
Crystal momentum and interband transitions 294
Crystal momentum and optical properties of semiconductors 567
Crystal momentum and umklapp processes 502
Crystal momentum and vector potentials 771
Crystal momentum of electrons 139
Crystal momentum vs. momentum 139 219 472 784Ч785
Crystal momentum, classical view of conservation 482Ч486
Crystal momentum, conservation of, in electron-phonon scattering 524 788
Crystal momentum, conservation of, in neutron scattering 471Ч473 788Ч789
Crystal momentum, conservation of, in phonon-phonon scattering 499 787
Crystal momentum, general theory of 784 789
Crystal momentum, operator 787
Crystal structure 75
Crystal structure, cesium chloride structure 80Ч81
Crystal structure, cesium chloride structure, table 81
Crystal structure, determination by neutron scattering 473
Crystal structure, determination by X-ray scattering 96Ч110
Crystal structure, diamond structure 76
Crystal structure, diamond structure, table 76
Crystal structure, hexagonal close-packed structure 76Ч79
Crystal structure, hexagonal close-packed structure, table 77
Crystal structure, perovskite structure 557
Crystal structure, sodium chloride structure 80
Crystal structure, sodium chloride structure, table 80
Crystal structure, white tin structure 127
Crystal structure, wurzite structure 387n
Crystal structure, zincblende structure 76 81
Crystal structure, zincblende structure, table 81
Crystal systems 114Ч120
Crystal systems as Bravais lattice point groups 114 116Ч120
Crystal systems, cubic 115
Crystal systems, hexagonal 119
Crystal systems, hierarchy of 120
Crystal systems, monoclinic 118
Crystal systems, number of 119Ч120
Crystal systems, orthorhombic 117
Crystal systems, tetragonal 115
Crystal systems, triclinic 118
Crystal systems, trigonal 119
Crystallinity, criterion for 64
Crystallographic point groups 114 119Ч125 see
Crystallographic point groups, cubic 121
Crystallographic point groups, international nomenclature 121Ч124
Crystallographic point groups, noncubic 122
Crystallographic point groups, number of 119Ч120
Crystallographic point groups, operations 120Ч123
Crystallographic point groups, relation to crystal systems 119Ч120
Crystallographic point groups, Schoenflies nomenclature 121Ч123
Crystals, growth of 636Ч637
Crystals, strength of 630 635Ч636
Cubic Bravais lattices see "Body-centered cubic" "Face "Simple
Cubic crystal system 115 see "Face-centered "Simple
Cubic crystal system, point group, nomenclature 124Ч125
Cubic crystal system, point group, table 121
Cubic crystal system, relation to trigonal system 119
Curie temperature see "Critical temperature ferroelectric" "Critical magnetic"
Curie Ч Weiss law 712n 718
Curie's law 655Ч656 see
Curie's law and effective Bohr magneton number 656Ч657
Curie's law and effective Bohr magneton number, rare earth ions, table of 657
Curie's law and effective Bohr magneton number, transition metal ions, table of 658
Curie's law from high temperature expansion 669 711
Curie's law, corrections to 709Ч712
Curie's law, free ions vs. solids 656Ч559
Current density, electrical 7
Current density, thermal 254
Cyclotron frequency 14
Cyclotron frequency in semiconductors 571
Cyclotron frequency, numerical formulas for 15 758
Cyclotron mass 233 239 see
Cyclotron mass in metals 278
Cyclotron mass in semiconductors 571
Cyclotron resonance in metals 278Ч279
Cyclotron resonance in semiconductors 278n 570Ч571
d-bands 181
d-bands in noble metals 288Ч289
d-bands in transition metals 306Ч307
de Boer parameter 412Ч413
de Boer parameter, table 412
de Broglie wavelength 34
de Broglie wavelength, numerical relation to energy of electrons 365
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



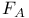 -center
-center 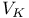 -center
-center 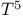 law
law 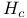 )
) 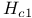 )
) 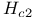 )
)