|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ashcroft N.W., Mermin N.D. Ч Solid State Physics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
De Haas Ч Van Alphen effect 264Ч275
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect and density of levels 272Ч274
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect and electron spin 274Ч275
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect and field uniformity 281
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect and scattering 274
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect in alkali metals 285Ч287
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect in noble metals 289Ч291
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect in transition metals 307
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect, measurement of 265Ч266
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect, minimum specimen size 271n
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect, quantization of orbit area 271Ч272
de Haas Ч van Alphen effect, thermal broadening 774
Debye 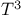 law 457 see law 457 see
Debye frequency ( ) 458 ) 458
Debye frequency ( ), compared with Fermi energy 529 ), compared with Fermi energy 529
Debye model of phonon spectrum 457Ч461 465Ч466 see
Debye model of phonon spectrum, density of levels 465Ч466
Debye model of phonon spectrum, Grueneisen parameter 493
Debye model of phonon spectrum, specific heat interpolation formula 459Ч461
Debye model of phonon spectrum, specific heat interpolation formula, graph 460
Debye model of phonon spectrum, specific heat interpolation formula, table 461
Debye model of phonon spectrum, vs. Einstein model 462Ч463
Debye temperature ( ) dependence on temperature 459Ч460 ) dependence on temperature 459Ч460
Debye temperature ( ) of alkali halides 459 ) of alkali halides 459
Debye temperature ( ) of selected elements 461 ) of selected elements 461
Debye unit 559
Debye wave vector (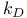 ) 458 ) 458
Debye wave vector (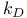 ), relation to Fermi wave vector 458n ), relation to Fermi wave vector 458n
Debye Ч Hueckel theory 342n
Debye Ч Hueckel theory of depiction layer 611
Debye Ч Scherrer method 102Ч104
Debye Ч Scherrer method, Ewald construction for 104
Debye Ч Waller factor 486 793
Defects in crystals 616Ч641 see "Dislocations"
Defects in crystals and charge neutrality 619
Defects in crystals and color centers 622Ч626
Defects in crystals and conductivity of ionic crystals 621Ч622
Defects in crystals and magnetization process 722
Defects in crystals as source of scattering 216 315
Defects in crystals, annealing 621
Defects in crystals, dislocations 628Ч638
Defects in crystals, Frenkel type 620
Defects in crystals, grain boundaries 638
Defects in crystals, magnetic impurities 687Ч689
Defects in crystals, mixed Frenkel and Schottky type 639
Defects in crystals, point, line, and surface 616
Defects in crystals, Schottky type 616
Defects in crystals, stacking faults 637
Defects in crystals, surface defects 637Ч638
Defects in crystals, thermodynamics of line and surface defects 620Ч621
Defects in crystals, thermodynamics of point defects (Frenkel, Schottky, or mixed) 616Ч620 638
Deformation twin 637
Degenerate semiconductors 573 see
Delta, Kronecker 87
Demagnetization factor 722
Density of levels (election) and electron spin 143n
Density of levels (election) and specific heat 47
Density of levels (election) in rare earth metals 308Ч309
Density of levels (election) in semiconductors 574 586
Density of levels (election) in semiconductors, graph for impure case 579
Density of levels (election) in semiconductors, graph for pure case 576
Density of levels (election) in transition metals 307
Density of levels (election) in two band nearly free electron model 170
Density of levels (election) in two dimensions 53
Density of levels (election), and Pauli paramagnetism 661Ч662 663n
Density of levels (election), Bloch electrons 143Ч145 149
Density of levels (election), free electron 44Ч45
Density of levels (election), phonon correction to 520
Density of levels (election), singularities in strong magnetic field 272Ч274
Density of levels (election), van hove singularities 145 150
Density of levels (k-space) 35 136
Density of levels (phonon) 464Ч466
Density of levels (phonon) in Debye model 465
Density of levels (phonon) in Einstein model 466
Density of normal modes see "Density of levels (phonon)"
Density of states see "Density of levels"
Depletion layer (space charge region) 591 see
Depolarization factor 540n
Detailed balancing 322
Diamagnetism see also "de Haas Ч van Alphen effect" "Susceptibility"
Diamagnetism, atomic (Larmor) 648Ч652
Diamagnetism, atomic (Larmor), compared with conduction electron magnetism in metals 668
Diamagnetism, atomic (Larmor), compared with Curie law paramagnetism 668
Diamagnetism, atomic (Larmor), in doped semiconductors 666
Diamagnetism, atomic (Larmor), in ionic crystals 649
Diamagnetism, atomic (Larmor), in noble gas solids 649
Diamagnetism, Landau 664Ч665
Diamagnetism, perfect (Meissner effect) 727 731 739
Diamond structure 76
Diamond structure and inversions 128
Diamond structure, bond angle 82
Diamond structure, elements, table of 76
Diamond structure, packing fraction 83
Diamond structure, structure factor 106
dielectric constant see also "Polarizability"
Dielectric constant and conductivity 776Ч778
Dielectric constant and index of refraction 534
Dielectric constant and optical modes 548
Dielectric constant and reflectivity 778
Dielectric constant in ionic crystals 548Ч550
Dielectric constant of a metal 17 515Ч518
Dielectric constant of covalent crystals 553
Dielectric constant of electron gas 338Ч344
Dielectric constant of electron gas, Drude 17
Dielectric constant of electron gas, Lindhard 343Ч344 352
Dielectric constant of electron gas, Thomas Ч Fermi 341Ч342
Dielectric constant of ferroelectrics 556
Dielectric constant of semiconductors 578Ч579
Dielectric constant, "high frequency" 546n
Dielectric constant, alkali halides, table for 553
Dielectric constant, Clausius Ч Mossotti relation 542
Dielectric constant, Lyddane Ч Sachs Ч Teller relation 548Ч549
Dielectric constant, quantum mechanical form 779
Diffraction see "Electron diffraction" "Neutron "X-ray
Diffusion constant 602
Diffusion current 601
Diffusion lengths 604Ч605
Diffusion region (p-n junction) 606Ч610
Dipolar interaction see "Magnetic dipolar interaction"
Dipole moment (electric) see "Ferroelectricity" "Polarizability" "Pyroelectricity"
Dipole moment (magnetic) see "Magnetic moment"
Direct exchange 681Ч682
Direct lattice 86
Direct optical transition 567
Direct term in Hartree Ч Fock equation 333
Directions, conventions for specifying 92Ч93
Dislocations 616 628Ч638 see
Dislocations and grain boundaries 638
Dislocations and growth of crystals 636Ч637
Dislocations and slip 632Ч633
Dislocations and stacking faults 637
Dislocations and strength of crystals 635Ч636
Dislocations and twinning 637
Dislocations and work hardening 636
Dislocations, Burgers vector 634Ч635
Dislocations, densities of 632
Dislocations, edge 632
Dislocations, elastic energy 640
Dislocations, general dislocation 633Ч635
Dislocations, observation of 637
Dislocations, screw 632
Disordered alloys 309Ч310 584n
Dispersion curve 432 see "Phonons"
Dispersion curve for linear chain with basis 434Ч435
Dispersion curve for monatomic linear chain with mth nearest neighbor interactions 448
Dispersion curve for monatomic linear chain with nearest-neighbor interactions 432Ч433
Dispersion curve for three-dimensional lattice with basis 443
Dispersion curve for three-dimensional monatomic Bravais lattice 441
Dispersion relation (Kramers Ч Kronig) 778
Displacement (translation) of Bravais lattice 70
| Displacement electric 534Ч535 541
Distribution function see also "Boltzmann equation" "Fermi "Relaxation-time
Distribution function, Bose Ч Einstein 454
Distribution function, equilibrium electronic 40Ч43
Distribution function, Fermi Ч Dirac 30Ч31 40Ч42
Distribution function, Maxwell Ч Boltzmann 30Ч31
Distribution function, nonequilibrium, electronic 244
Distribution function, nonequilibrium, electronic, calculation of in relation-time approximation 246Ч250
Distribution function, nonequilibrium, electronic, linearization of 249
Distribution function, phonon 454
Distribution function, rate of change due to collisions 317Ч319
Distribution function, rate of change due to collisions, in relaxation-time approximation 318Ч319
Divalent metals 298Ч299
domains 718Ч722
Domains and anisotropy energy 720Ч721
Domains and dipolar energy 718Ч720
Domains, Bloch wall 719Ч720
Donor impurities 577 see "p-n "Semiconductors"
Doping of semiconductors 590Ч591
Doping of semiconductors, doping profile 591
Doppler shift of scattered waves 484
Double layer 358
Dressed ions 513
Dressed ions and dielectric constant of metals 515Ч518
Drift current 601
Drift term 320
Drift velocity in crossed fields 233
Drude model 2Ч27
Drude model, basic assumptions 4Ч6
Drude model, shortcomings arising from classical statistics 23 25 30 58
Dulong and Petit law 426Ч429 see
Dulong and Petit law and Rayleigh-Jeans catastrophe 466
Dulong and Petit law, failure of 429
Dulong and Petit law, quantum corrections at high temperature 455 467Ч468
Dynamical matrix 439
Dynamical matrix for face-centered cubic crystal 449
Dynamical matrix, symmetries of 438
Dynamical structure factor 792
Dynamical structure factor in harmonic approximation 792Ч794
Edge dislocation 632 see
Effective Bohr magneton number 656Ч658
Effective mass and DC conductivity 251
Effective mass in Hartree Ч Fock approximation 337 352
Effective mass of holes 227
Effective mass of semimetals 305n
Effective mass with screened exchange 344
Effective mass, cyclotron (metals) 233Ч239
Effective mass, cyclotron (metals), measurement of 278Ч279
Effective mass, cyclotron (semiconductors) 239 568
Effective mass, phonon contribution to 520 530
Effective mass, specific heat 239
Effective mass, specific heat, table 48
Effective mass, tensor 228Ч229 568n 766
Effective mass, theorem 765Ч766
Einstein model of phonon spectrum 462Ч463
Einstein model of phonon spectrum vs. Debye model 462Ч463
Einstein model of phonon spectrum, density of levels 466
Einstein model of phonon spectrum, formula for specific heat 463
Einstein model of phonon spectrum, formula for specific heat, graph 463
Einstein relation 602
Einstein relation, derived from kinetic theory 612
Einstein relation, in nondegenerate case 612
Einstein temperature (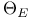 ) 463 ) 463
Elastic scattering and Wiedemann Ч Franz law 322Ч323
Elasticity, theory of 443Ч447 see
Elasticity, theory of, elastic constants 444Ч447
Elasticity, theory of, elastic constants, and anharmonic terms 489
Elasticity, theory of, elastic constants, compliance constant 446
Elasticity, theory of, elastic constants, number of independent, for seven crystal systems 445
Elasticity, theory of, elastic constants, stiffness constant (modulus) 446
Elasticity, theory of, elastic constants, tabulated for cubic crystals 447
Elasticity, theory of, related to theory of lattice vibrations 443Ч447
Electric displacement 534Ч535 541
Electric field, local 539Ч542
Electrochemical potential 257n
Electrochemical potential in semiconductors 593Ч594
Electron affinity 380n
Electron charge, sign convention 3n
Electron density 4
Electron density and classification of solids 374Ч379
Electron density in covalent crystals 377
Electron density in ionic crystals 381
Electron density, table (conduction) for selected metals 5
Electron diffraction 364Ч366
Electron g-factor 646
Electron gas 2Ч6 316n see
Electron spin see "Spin"
Electron volt (eV) 37n
Electron volt (eV), accurate conversion factors 757
Electron volt (eV), eV/molecule to calories/mole conversion 396n
Electron, free see "Free electron approximation"
Electron, independent see "Independent electron approximation"
Electron, nearly free see "Nearly free electron approximation"
Electron, tight-binding see "Tight-binding approximation"
Electron-electron interaction 330Ч352 see "Hartree "Independent "Screening"
Electron-electron interaction and exclusion principle 346Ч348
Electron-electron interaction and Fermi liquid theory 345Ч351
Electron-electron interaction and ground state energy of free electron gas 336
Electron-electron interaction and Hubbard model 685
Electron-electron interaction and magnetic structure 672Ч691
Electron-electron interaction and Pauli paramagnetism 669Ч670
Electron-electron interaction and periodic potential 132 192 330Ч331
Electron-electron interaction and superconductivity 739Ч740
Electron-electron interaction and tight-binding method 186
Electron-electron interaction in Drude model 4Ч5
Electron-electron interaction scattering 5 316 346Ч348
Electron-electron interaction via phonons 518Ч519
Electron-electron interaction, Hartree approximation 743
Electron-electron interaction, Hartree Ч Fock approximation 334Ч337
Electron-electron interaction, lifetime 347Ч348
Electron-ion interaction (static), and negative Fermi energies 357n see
Electron-ion interaction (static), in Drude model 4
Electron-neutron interaction (magnetic) 470
Electron-phonon interaction 519Ч528
Electron-phonon interaction and electron effective mass 520
Electron-phonon interaction and magnetic susceptibility 663n
Electron-phonon interaction and one electron energy 519Ч521
Electron-phonon interaction and resistivity 523Ч528
Electron-phonon interaction and superconductivity 739Ч740
Electron-phonon interaction, coupling constant 523
Electrostatic approximation 547n 548n 551n
Electrostatic field of array of dipoles 558
Electrostatic field of array of uniformly polarized sphere 557
Energy band 141 see "Band "Band "Density
Energy gap (normal materials) see "Band gap"
Energy gap (superconducting materials) 727
Energy gap (superconducting materials) and acoustic attenuation 736
Energy gap (superconducting materials) and electromagnet.c energy absorption 735
Energy gap (superconducting materials) and magnetic impurities 727n
Energy gap (superconducting materials) and tunneling 735
Energy gap (superconducting materials), BCS, relation to 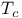 744 744
Energy gap (superconducting materials), measured values 745
Energy, binding see "Cohesive energy"
Entropy current of 253
Entropy current of, generation of 253n
Entropy current of, lack of ill persistent currents 730
Entropy current of, of free electron gas 54
Entropy current of, of ice 392
Entropy current of, of spin system 659Ч661
Equation of state of insulators 490Ч494
Equation of state of insulators and volume dependence of normal mode frequencies 490Ч492
Equipartition of energy 9
Estheticism 403n
Ettingshausen effect 258n
Ewald construction 101
Ewald construction for Laue method 102
Ewald construction for powder method 103
Ewald construction for rotating crystal method 102
Ewald sphere 101
Exchange energy 334Ч337
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



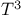 law
law  )
)  ) dependence on temperature
) dependence on temperature 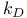 )
) 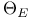 )
)