|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ashcroft N.W., Mermin N.D. Ч Solid State Physics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
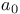 see "Bohr radius" see "Bohr radius"
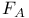 -center 626 -center 626
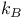 (Boltzmann's constant) 23 (Boltzmann's constant) 23
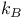 (Boltzmann's constant), accurate numerical value 757 (Boltzmann's constant), accurate numerical value 757
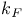 35 see 35 see
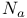 581 581
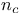 572 572
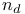 581 581
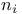 575 575
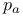 581 581
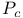 573 573
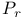 572 572
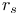 4 4
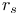 , numerical formula for 757 , numerical formula for 757
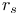 , table 5 , table 5
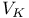 -center 625 -center 625
Abrupt junction 591
Acceptor impurities 577 see "p-n "Semiconductors"
Acoustic modes 435
Acoustic modes and polyatomic bases 442 see "Phonons"
Acoustic modes, vs. optical modes 437
Adiabatic approximation 425Ч426
Adiabatic approximation in metals 513
Adiabatic approximation, analytic justification of 529n
Adiabatic demagnetization 659Ч661 669
Alkali earths 298
Alkali halides 380Ч385
Alkali halides, band structure 382
Alkali halides, bulk moduli, table of 408
Alkali halides, charge distribution 381
Alkali halides, cohesive energy 402Ч407
Alkali halides, cohesive energy, table of 406
Alkali halides, color centers 622Ч626 640
Alkali halides, conductivity 621
Alkali halides, Debye temperatures, table of 459
Alkali halides, defects 620
Alkali halides, diamagnetic susceptibilities, table of 649
Alkali halides, dielectric constants, table of 553
Alkali halides, Grueneisen parameters, table of 494
Alkali halides, ionic radii 382Ч385
Alkali halides, lattice constants, table of 80 81
Alkali halides, nearest-neighbor distances, table of 408
Alkali halides, optical modes 547Ч552
Alkali halides, optical phonon frequencies, table of 553
Alkali halides, polarizabilities, table of 544
Alkali metals, 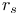 , table of 5 , table of 5
Alkali metals, atomic configurations 284
Alkali metals, band structure and Fermi surface 284Ч288
Alkali metals, bulk moduli, table of 39
Alkali metals, cohesion 410Ч412 413Ч414
Alkali metals, conduction electron densities, table of 5
Alkali metals, density and size of ion 413Ч414
Alkali metals, free electron parameters, table of 38
Alkali metals, Hall coefficients 15 288
Alkali metals, ionization potentials 391
Alkali metals, lattice constants, table of 70
Alkali metals, optical properties 18 293Ч296
Alkali metals, Pauli paramagnetism 664
Alkali metals, resistivities, table of 8
Alkali metals, specific heats, table of 48
Alkali metals, thermal conductivities, table of 21
Alkali metals, transparency in ultraviolet 18
Alloys 309Ч310
Alloys, dilute magnetic 685Ч687
Amorphous solids 62
Amorphous solids, anomalous thermal properties 504n
Amorphous solids, X-ray diffraction 96n
Anderson model 687
Angular momentum, notational convention 647n
Anharmonic terms 422 487Ч509
Anharmonic terms and crystal momentum conservation 498Ч499
Anharmonic terms and elastic constants 489
Anharmonic terms and Grueneisen parameter 508 509
Anharmonic terms and n-phonon processes 796
Anharmonic terms and one-phonon widths 476Ч478
Anharmonic terms and reststrahl resonance 552
Anharmonic terms and scattering of phonons 497Ч499
Anharmonic terms and second sound 506Ч508
Anharmonic terms and soft modes 556
Anharmonic terms and specific heat at high temperature 428Ч429 455
Anharmonic terms and thermal conductivity 495Ч505
Anharmonic terms and thermal expansion 490Ч492 495
Anharmonic terms and thermodynamic properties 490Ч492
Anharmonic terms and umklapp processes 501Ч505
Anharmonic terms, cubic terms and conservation laws 490 509
Anharmonic terms, cubic terms and conservation laws, instability of 489 508
Anharmonic terms, cubic terms and conservation laws, transitions resulting from 497Ч499
Anharmonic terms, quartic vs. cubic terms 489Ч490 498
Anion 380
Anisotropy energy 720Ч721
annealing 621
Annihilation operator (phonon) 781
Anomalous skin effect 277Ч278
Anti-Stokes component 481
Antibonding states 678n
Antiferromagnetism 672 694Ч696
Antiferromagnetism in Hubbard model 685
Antiferromagnetism of free electrons 684
Antiferromagnetism, energy of ground state 704 722
Antiferromagnetism, Heisenberg model 704
Antiferromagnetism, linear chain (Bethe solution) 704
Antiferromagnetism, mean field theory 718n 723Ч724
Antiferromagnetism, susceptibility 699 702 718n
Antiferromagnetism, table 697
Antimorph of color center 625
APW see "Augmented plane-wave method"
Atomic form factor 107Ч108
Atomic Hamiltonian 176 180n
Atomic levels broadened into bands 182Ч183
Atomic orbitals, linear combination of (LCAO) 179
Atomic wave functions and interatomic distance in sodium 177
Atomic wave functions of neon, compared with sodium 375
Augmented plane-wave method (APW) 200Ч202
Augmented plane-wave method (APW), compared with Green's function (KKR) method 205
Avogadro's number (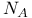 ) 4 49 ) 4 49
Band gap 142
Band gap at Bragg planes 161Ч162 172
Band gap in insulators 562
Band gap in one dimension 148
Band gap in semiconductors 562
Band gap in semiconductors, measurement of 566 568
Band gap in semiconductors, table of 566
Band gap in semiconductors, temperature dependence of 566Ч567
Band index 134n 140
Band index for nearly free electrons 153
Band overlap 146 223
Band repulsion 155
Band structure 141 see "Density "Fermi
Band structure and distinction between insulators and metals 223
Band structure and ferromagnetism 684n
Band structure in one dimension 146Ч149
Band structure of alkali halides 382
Band structure of selected metals 284Ч311
Band structure of selected semiconductors 568Ч570
Band structure, methods for calculating 192Ч211 see "Tight-binding
Band structure, methods for calculating, augmented plane wave (APW) method 200Ч202
Band structure, methods for calculating, cellular method 195Ч200
Band structure, methods for calculating, Green's function (KKR) method 202Ч206
Band structure, methods for calculating, orthogonalized plane-wave (OPW) method 206Ч208
Band structure, methods for calculating, pseudopotential method 208Ч210
Band width in one dimension 148Ч149
Band width in tight-binding method 182Ч183
Band width, d compared with s 307
Band width, free electron, in Hartree Ч Fock approximation 335
Bands, "bending" of 594
Bands, filled 221Ч224 250
Bands, partially filled 223
Bands, vs. atomic levels 182Ч183
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory 739Ч747 see "Superconductivity"
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory and Cooper pairs 740Ч743
| Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory and Meissner effect 746Ч747
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory and persistent currents 750Ч751
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory, critical field 745
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory, critical temperature 744
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory, effective interaction 743
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory, energy gap 744
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory, excited states 742Ч543
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory, ground state 741
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory, specific heat (electronic) at low temperature 746
Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer theory, specific heat discontinuity 745
Bare ions 513
Base-centered orthorhombic Bravais lattice 117
Basis 75
BCC see "Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice"
BCs see "Bardeen Cooper Schrieffer
Biased junction 598
Binding energy see "Cohesive energy"
Birefringence 776
Blackbody radiation 466Ч467
Bloch 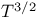 law 708 law 708
Bloch 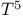 law 526 law 526
Bloch electrons see also "Band gap" "Band "Density "Effective "Fermi "Nearly "Semiclassical "Tight-binding
Bloch electrons at surfaces 367Ч369 369Ч371
Bloch electrons in one dimension 146Ч149 159Ч161
Bloch electrons in static electric, field 224
Bloch electrons, density of levels 143Ч145
Bloch electrons, dynamics of 214Ч241
Bloch electrons, effective mass (dynamic) 227Ч229
Bloch electrons, effective mass theorem 765Ч766
Bloch electrons, holes 225Ч229
Bloch electrons, no collisions with static lattice 215 418
Bloch electrons, orbits in a magnetic field 229Ч233
Bloch electrons, orbits in a magnetic field, period 232Ч233
Bloch electrons, orbits in a magnetic field, quantization 271Ч272
Bloch electrons, s- and p-like 159
Bloch electrons, velocity 141 765
Bloch electrons, vs. free electrons 214
Bloch electrons, wave vector 136 139
Bloch wail 719Ч721
Bloch's theorem 133
Bloch's theorem and surface levels 367Ч369
Bloch's theorem, first proof 134
Bloch's theorem, second proof 137
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice 67Ч68
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice as simple cubic with structure factor 105
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, conventional cell 75
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, coordination number 71
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, elements with 70
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, first Brillouin zone 89
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, higher Brillouin zones 164
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, lattice sums of inverse powers 400
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, packing fraction 83
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, primitive vectors 68
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, reciprocal of 88
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, relation to centered tetragonal Bravais lattice 117
Body-centered cubic Bravais lattice, Wigner Ч Seitz cell 74
Body-centered orthorhombic Bravais lattice 118
Bohm Ч Staver relation 514
Bohr magneton 646
Bohr magneton, effective number 656Ч658
Bohr radius (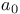 ) 4 ) 4
Bohr radius (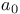 ) of impurity level in semiconductor 579 ) of impurity level in semiconductor 579
Bohr radius (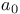 ), accurate numerical value 757 ), accurate numerical value 757
Bohr Ч van Leeuwen theorem 269 646
Boltzmann distribution see "Maxwell Ч Boltzmann distribution"
Boltzmann equation 319Ч328 see
Boltzmann equation and conservation laws 327
Boltzmann equation, derivation of relaxation-time approximation for isotropic elastic impurity scattering 324Ч326
Boltzmann equation, solution to in relaxation-time approximation 320
Boltzmann equation, variational principle 327Ч328
Boltzmann's constant (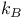 ) 23 ) 23
Boltzmann's constant (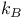 ), accurate numerical value 757 ), accurate numerical value 757
Bond polarizability 552
Bonding 378Ч379 389
Bonding states 678n
Born Ч Mayer potential 407
Born Ч Oppenheimer method see "Adiabatic approximation"
Born Ч von Karman boundary condition see "Boundary conditions"
Bose gas, ideal 454
Bose Ч Einstein condensation 37n
Bose Ч Einstein distribution 454n
Bound charge vs. free charge 534n 777
boundary conditions 32
Boundary conditions at surfaces 368
Boundary conditions for free electron gas 32
Boundary conditions, Born Ч von Karman (periodic) for Bloch electrons 135
Boundary conditions, Born Ч von Karman (periodic) for free electrons 33
Boundary conditions, Born Ч von Karman (periodic) for linear chain 431
Boundary conditions, Born Ч von Karman (periodic) for spin waves 705n
Boundary conditions, Born Ч von Karman (periodic) for tight-binding method 178n
Bragg condition 97
Bragg formulation of X-ray diffraction 96Ч97
Bragg formulation of X-ray diffraction, equivalence to formulation of von Laue 99Ч100
Bragg peaks 96
Bragg peaks and Debye Ч Waller factor 795
Bragg peaks and magnetic reflections 696Ч697
Bragg peaks as zero-phonon scattering 473
Bragg planes 99
Bragg planes and nearly free electrons 156Ч159
Bragg reflection 100
Bragg reflection, order of 97
Bravais lattice 64Ч75 see "Reciprocal
Bravais lattice and finite crystals 66
Bravais lattice of average positions in dynamic system 422
Bravais lattice, definitions of 64Ч65 70n
Bravais lattice, inversion symmetry of 128
Bravais lattice, nontranslational symmetries of 112Ч129
Bravais lattice, number of 120
Bravais lattice, origin of name 115
Bravais lattice, symmetry group of 112 114 116
Bravais lattice, symmetry operations 113 120Ч123
Bravais lattice, symmetry operations, allowed rotation angles 121 129
Bravais lattice, types enumerated 115Ч119
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, base-centered orthorhombic 117
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, body-centered cubic 67Ч68
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, body-centered orthorhombic 118
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, centered monoclinic 118
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, centered tetragonal 115
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, face-centered cubic 68Ч69
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, face-centered orthorhombic 118
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, rhombohedral (trigonal) 119
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, simple cubic 65
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, simple hexagonal 77 119
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, simple monoclinic 118
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, simple orthorhombic 117
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, simple tetragonal 115
Bravais lattice, types enumerated, triclinic 118
Bravais lattice, use of term 70
Breakdown and Wannier functions 188
Breakdown in inhomogeneous semiconductors 592
Breakdown, conditions for absence in semiclassical model 219Ч220 773Ч775
Breakdown, electric 220
Breakthrough, magnetic 220
Breakthrough, magnetic, and spin-orbit coupling 220
Breakthrough, magnetic, and Wannier functions 188
Breakthrough, magnetic, conditions for absence in semiclassical model 219Ч220 773Ч775
Breakthrough, magnetic, in hexagonal divalent metals 299
Brillouin function 655
Brillouin scattering 419 481Ч486
Brillouin scattering, classical picture of 482Ч486
Brillouin scattering, Stokes and anti-Stokes components 481
Brillouin zone, first 89
Brillouin zone, first, and reduced zone scheme 142Ч143
Brillouin zone, first, for face-centered and body-centered cubic lattices 89
Brillouin zones, higher 162Ч166 171Ч173
Brillouin zones, higher, as primitive cells 163
Brillouin zones, higher, for face-centered and body-centered cubic lattices 164
Brillouin zones, higher, for square lattice 163 171
bulk modulus 39
Bulk modulus free electron 39Ч40
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



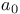
 -center
-center 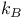 (Boltzmann's constant)
(Boltzmann's constant) 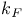
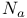
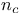
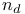
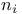
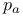
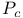
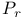
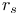
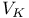 -center
-center 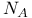 )
) 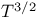 law
law  law
law