Àâòîðèçàöèÿ
Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì
Bogolubov N.N., Logunov A.A., Todorov I.T. — Introduction to Axiomatic Quantum Field Theory
Îáñóäèòå êíèãó íà íàó÷íîì ôîðóìå Íàøëè îïå÷àòêó?
Íàçâàíèå: Introduction to Axiomatic Quantum Field TheoryÀâòîðû: Bogolubov N.N., Logunov A.A., Todorov I.T.Àííîòàöèÿ: At the end of 1960 we made plans to write a monograph about the general principles of quantum field theory and their experimental implications. We intended primarily to give an account of the progress of the theory of dispersion relations since the appearance of the book of Bogolubov, Medvedev and Polivanov ([BMP]. As an introduction we wanted to include a review of the various approaches to axiomatic field theory. This introduction had to cover not only the formulation of Bogolubov, Medvedev and Polivanov, based on the apparatus of functional derivatives of the 5-matrix and the condition of microcausality, but also the field formulation associated with the names of Wightman, Haag, Lehmann, Symanzik, Zimmermann, and others. In the course of the work the tasks (and with them the size) of the introduction grew larger and larger, until eventually it developed into this book.
ßçûê: Ðóáðèêà: Ìàòåìàòèêà /Ñòàòóñ ïðåäìåòíîãî óêàçàòåëÿ: Ãîòîâ óêàçàòåëü ñ íîìåðàìè ñòðàíèö ed2k: ed2k stats Ãîä èçäàíèÿ: 1975Êîëè÷åñòâî ñòðàíèö: 707Äîáàâëåíà â êàòàëîã: 18.04.2010Îïåðàöèè: Ïîëîæèòü íà ïîëêó |
Ñêîïèðîâàòü ññûëêó äëÿ ôîðóìà | Ñêîïèðîâàòü ID
Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü
334—335 511 528 (see “Homogeneous distributions”) 620 625—626 137 478—481 533 156 568—569 91 95 426—427 598 (see “Quasilocal observables” “Algebra of (see “Algebra of (see “Functionals positive”) 22—25 27—28 32 48 69 105 27 48 55 69 85 105 16 30 38—40 (see “Domain common”) 287—296 310 256 455 04 468—469 582 612—620 625- 626 32 43—44 119—121 197—199 303 17—18 20—22 25 Abelian (commutative) group 209 Abelian algebra 223 597 607 Absolutely continuous function 37 Acharya, R. 575 632 633 Additive operator 139 239 Adjoint (Hermitian conjugate) 36—37 569 586 Adjoint (Hermitian conjugate) in algebra (see “Involution”) Adjoint (Hermitian conjugate) of field operator 253 260 262 529 531—532 538 Adjoint representation 224 Adler, S. L. 402 627 Admissible observable 115 116 Advanced distribution (see “Retarded and advanced distributions”) Advanced product 392—399 Affinors 174 Akhiezer, N. I. 37 39 105 627 Akilov, G. P. 15 19 20 21 24 35 37 47 105 630 Aks, S. 0 575 655 Algebra 95 256 584 Algebra of bounded operators 586 589 Algebra of fields 255—257 297—300 599-601 602 609 610 614 616 624 625 Algebra of open set 257—258 350 581 596—597 599-610 Algebra of quasilocal observables 596—599 Algebra of unbounded operators 624 Algebra, normed 301 584—585 Algebra, nuclear 287—289 301 Algebraic approach 4 525 573 577 581—611 624—625 Algebraic approach, field theory and 582 583 590 597 607—611 Algebraic approach, scattering theory in 610—611 Almost local field 351 357 364—366 374—378 384-390 Analytic completion 429 Analytic continuation 332 445—446 Analytic extension 509 Analytic vector 608 Analyticity causality and 432—433 476 Analyticity in manifold 493—495 Analyticity in several variables 467 Analyticity of Fourier transform of retarded function 91—98 267—268 432—434 473 476 Analyticity of Green functions 359—360 429—449 454460 473 476 Analyticity of Lie group coordinates 214—215 Analyticity of Wightman functions 267—268 473 476 487 504—510 Analyticity on open real set 605—606 Analyticity, Lorentz invariance and 434 473—497 574 Analyticity, primitive domain of 429 438—441 447—449 Angular momentum of two-particle state 200—204 (see also “Spin” “Poincare “Lie Angular momentum, 147 156 175 205 596 “Poincare “Lie Angular momentum, complex 227 (see also “Spin” “Poincare “Lie Angular momentum, orbital 189 516 “Poincare “Lie Anomalous commutation relations 474—475 Anticommutation relations canonical 566 572 577 Anticommutation relations of 171 Anticommutation relations of field with creation-annihilation operators 403 410 Anticommutation relations of nonlocal scalar field 511—512 Anticommutation relations, discrete transformations and 322 Antiparticles 205—208 322 515 517 Antisymmetric unit tensor 133—134 146—147 Antiunitary operator 110 139 140 164—165 167 241 298 322 515 Antoine, J. — P. 240 633 Araki, H. 281 351 466 523 545 573 575 576 604 610 624 625 633 634 Arbuzov, B. A. 499 634 Artin, A. 241 627 Associative algebra 584 Asymptotic completeness 358 378—380 Asymptotic completeness, 406 523 Asymptotic conditions 3 357—358 362—363 365—367 381—384 389-390 465 Asymptotic fields 358 359 366—368 381—382 422 430—432 465 549 Asymptotic fields, relative weak locality and 5 20 Asymptotic fields, TCP transformation of 514—515 Asymptotic states 358 365—368 385—386 402—407 515-517 Asymptotically abelian algebra 625 Automorphism(s) 136 139—140 210 596 Automorphism(s), inner, outer 136 Automorphism(s), space-time, in 616—618 625 Axial vector 146 154 344 500—501 Axiomatic approach 1—5 362—363 460 612 “BMP “LSZ “Algebraic Axioms, enumerated 117—118 142 151 152 248—252 256 379 B* -algebra 585 (see also “C*-algebra”) Banach algebra (Banach ring) 584—585 Banach space 15 Bardakci, K. 466 575 634 Bargmann — Hall — Wightman theorem 473—477 481—486 513 518 533 548 574 Bargmann, V. 574 Bargmann’s proof, of Wigner’s theorem 234—239 242 Bargmann’s theorem 141—142 Barton, G. 464 627 Baryon number 122 153 206 352 379 406 600 Baryons 151 406 “Proton”). Baumann, K. 351 465 635 669 Belinfante, F. J. 241 635 Bender, C. M. 469 635 Berezansky, Yu. M. 105 608 625 627 635 Berezin, F. A. 577 627 635 Bessel functions 70 81 335 370 Bialynicki — Birula, I. 540 636 Bibliographical conventions 6 632—633 Bicompactness 213 Bilenky, S. M. 575 636 Bilinear form (see “Functional bilinear” “Scalar Bilinear invariant forms of Dirac equation 178 322—323 499—501 Bilinear invariant forms of Majorana representations 567—568 Bispinor (see “Spinor four-component”) Bjorken, J. D. 2 8 460 468 627 Blokhintsev, D. I. 351 508 636 BMP approach 3 400—422 430—432 450—453 465—468 525 Bochner — Schwartz theorem 269 271 Bochner, S. 495 627 Bogolubov transformation (see “Canonical transformation”) Bogolubov, N. N. xvii xviii 3 8 72 102 106 146 171 186 241 242 322 333 336 352 399 401 405 409 414 422 429 445 455 465 466 467 468 556 561 574 577 625 628 636 637 Bohm, A. 240 637 Bohr, N. 350 637 Bollini, C. 468 638 Boost (see “Lorentz transformation pure”) Borchers classes 474 517—525 575 583 604 609 Borchers classes and 519—520 (see also “Irreducibility of Borchers — Zimmermann criterion 603 607—608 Borchers, H. J. 257 259 292 297 300 350 351 352 517 575 606 607 625 638 Born term 463 Bose operator 274 Bosons, Bose — Einstein statistics 194 252 402—403 526 564 572 Bound states 465 Boundedness of linear functional 18—19 Boundedness of operator 34—35 116 Boyce, J. F. 242 672 Bremermann, H. J. 467 638 Brenig, W. 363 464 639 Broken symmetry 475 562—563 577 Bros, J. 106 415 467 574 639 Bruhat, F. 252 639 Burgoyne, N. 576 639 C*-algebra 4 581—611 614 616 624—625 C-convex envelope 508 Cannon, J. T. 617 625 639 Canonical basis, in 340—343 564 570 Canonical commutation relations for infinite-component field 566 (see also “Anticommutation relations” “Commutator”) Canonical commutation relations for position and momentum 118 195 “Commutator”) Canonical commutation relations for scalar field 305 311 465 557—561 “Commutator”) Canonical commutation relations in 617 (see also “Anticommutation relations” “Commutator”) Canonical commutation relations in discrete basis 558—560 (see also “Anticommutation relations” “Commutator”) Canonical commutation relations inequivalent representations 548 556—561 577 “Commutator”) Canonical commutation relations of creation-annihilation operators 304—305 (see also “Anticommutation relations” “Commutator”) Canonical commutation relations, singular 561 (see also “Anticommutation relations” “Commutator”) Canonical commutation relations, strange representations 475 560—561 “Commutator”) Canonical commutation relations, Weyl form 559 569 “Commutator”) Canonical coordinates 220 227—232 Canonical formalism (see “Lagrangian formalism” “Hamiltonian” “Canonical Canonical transformation, linear 559—560 Cantor, G. 50 294 Cartan, E. 225 Cartan, E. J. 241 628 Cartesian product 30 Casimir operators 225 (see also “Poincare' group invariants” “Lorentz “Casimir Cauchy inequality 588 Cauchy principal value 5 Cauchy sequence (see “Fundamental sequence”) Causal distribution (“Distributions causal” “Green causal”) Causal envelope 597 603—604 Causal Green function (see “Green functions causal”) Causal shadow 597 Causality 2 247 414 465 Causality in algebraic approach 597 Causality, analyticity and 432—433 476 Causality, primitive 258—259 597 “Microcausality”) Cayley parametrization 479—480 Center of algebra 589 Center-of-mass frame (see “Lorentz transformation into Characteristic subgroup 210 Charge conjugation 131 179—180 183 192 206 320—323 325—326 352 529 568 Charge conjugation in homogeneous distribution formalism 344—345 Charge conjugation, space reflection and 325—326 Charge renormalization 613 Charge, electric 122 153 206—207 250 311—318 596 599 600 Charged field (see “Complex field”) Chen, T. W. 460 468 639 Chernikov, N. A. 576 639 Chou Kuang — Chao 242 327 640 664 Circumflex, denoting omission 408 Classical theory, algebra of 597 Clifford algebras 241 499 “Anticommutation Closed graph theorem 35 Closed operator 35 Closed subspace 216—217 Closure, of operator 37 Cluster decomposition property 151 272—282 293 351 531 576 Coherent subspace (Superselection sector) 123—127 139 142 250—251 312 602 605 607 609 Coherent subspace (Superselection sector), discrete transformations and 326—327 (see also “Superselection rule”) Commutant 299—300 589 601—605 Commutation relations (see “Commutator” “Anticommutation “Canonical “Anomalous “Spin-and-statistics Commutator in group 221 Commutator in Lie algebra 221—222 Commutator in parafield theory 540—546 Commutator Kaellen — Lehmann representation 330—331 Commutator of current with field 417—418 Commutator of field with creation-annihilation operators 403 Commutator of free scalar field [D(x)] 302—303 328 333—335 382 418 554—556 Commutator of functional differentiations 409 Commutator of generalized free field 328—331 Commutator of Heisenberg and asymptotic fields 465 Commutator of S-operator with creation-annihilation operators 409—412 Commutator of vector field 561 (see also “Canonical commutation relations” “Anticommutation Compact energy, vector of 605—606 617 Compact group 143 213 219 225—226 600 Compact support, functions of (see “\mathcal{D}”) Compactness 213 Compactness, Haag — Swieca 573 Compactness, relative 24 Compactness, weak 618 Compatible norms 21—22 Compatible topologies 27 Complement, of invariant subspace 217 Complete set, of operators 152—153 451—452 Complete space 15 Completeness, of field theory (see “Cyclicity”) Completion, in norm 25 33 Complex (charged) field 250 283—284 311—314 610 Complex conjugation, antiunitary operators and 164 Composite models 379 Cone 74 151 440 488 494 Cone of positive functionals 592 594 Cone, double 606 Conjugate space 19—21 26—29 105 598 Conjugate, of spinor (Dirac conjugate) 178 183 186 Conjugation (see “Involution”) Connectedness 213 Connectedness, simply 135 213 Constructive field theory (see “Models”) Continuity 212 Continuity of functional 18—19 25 Continuity of operator in nuclear space 119—120 Continuity of representation 216—219 Continuity, absolute 37 Continuity, weak, of field 249 Continuity, weak, of representation 216 Continuous group (see “Topological group”) Continuous spin 150 Convergence 212 Convergence in 23 29 Convergence in 287—288 Convergence in 21 25 6 Convergence in C*-algebra 585—586 Convergence in conjugate of countably normed space 28—29 Convergence in countably normed space 22 Convergence in norm (uniform) 17 585—587 Convergence in normed space 15 17 Convergence in nuclear space 32 Convergence, strong 15 28 32 586 587 615 Convergence, weak 28 32 216 381 586 598 616 Convex set 282 Convolutes 73—74 375 Convolution 72—76 95 104 456—459 Convolution multiplication and 73 93 99—100 Coordinates, generalized 118 Coulomb law 281 Countably normed space (see “Vector space countably Coupling constant 450—451 455 469 614 Covariance in algebraic approach 596 609 Covariance of analytic functions 473—497 574 Covariance of fields 249—251 (see also “Relativistic invariance” “SL(2) representations”) Covering group 135 Covering, by open sets 49 213 CP transformation, CP violation 498—499 501 “Parity”) Creation and annihilation operators 118—121 304—308 312 315—318 320—321 336 404 577 613 Creation and annihilation operators for parafield 539—544 Creation and annihilation operators in x-space 309 619 Creation and annihilation operators, asymptotic 389—390 403 Creation and annihilation operators, commutation relations with fields and S-operator 403 409—410 Creation and annihilation operators, majorana representations and 568—570 578 Creation and annihilation operators, normal commutation relations, derived 528 Creation and annihilation operators, notation 389 Current(s) 401—402 413—419 421 441—445 577 Current(s) as derivative of S-operator 3 359 401 413 415 430—432 Current(s) in Borchers class of field 521—522 Current(s) in Yang — Feldman equations 358 382 415 417 Current(s), algebras of 402 Current(s), electric 322—323 382 413 Current(s), Kaellen — Lehmann representation 432 Current(s), reconstruction theorem for 466 Current(s), satisfy axioms 432 514 Current(s), TCP transformation of 514
Ðåêëàìà
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



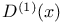 (even invariant function)
(even invariant function) 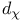
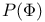 models
models 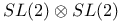
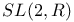
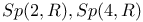
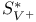
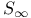
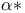 (dual of Hermitian elements of
(dual of Hermitian elements of  )
) 
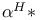
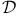
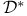 (spaces of distributions)
(spaces of distributions) 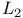 (space of square-integrable functions)
(space of square-integrable functions) 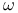
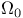 (space of finite test-function sequences)
(space of finite test-function sequences)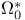
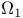 (nuclear space generated by fields)
(nuclear space generated by fields) 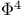 interaction, in Yukawa theory
interaction, in Yukawa theory 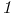 (space of sequences of fast decrease)
(space of sequences of fast decrease) 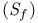
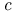 (spaces of differentiable functions)
(spaces of differentiable functions) 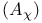
![$[\beta(H)]$](/math_tex/fdca4869168ddab119192d71fa21843582.gif)
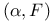
![$[\alpha(O), \mathcal{R}(O) ]$](/math_tex/5ff3a9cdcadaccf827a898c2e3121d7c82.gif)
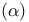
 -matrices
-matrices 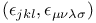
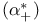
 and
and