Àâòîðèçàöèÿ
Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì
Bogolubov N.N., Logunov A.A., Todorov I.T. — Introduction to Axiomatic Quantum Field Theory
Îáñóäèòå êíèãó íà íàó÷íîì ôîðóìå Íàøëè îïå÷àòêó?
Íàçâàíèå: Introduction to Axiomatic Quantum Field TheoryÀâòîðû: Bogolubov N.N., Logunov A.A., Todorov I.T.Àííîòàöèÿ: At the end of 1960 we made plans to write a monograph about the general principles of quantum field theory and their experimental implications. We intended primarily to give an account of the progress of the theory of dispersion relations since the appearance of the book of Bogolubov, Medvedev and Polivanov ([BMP]. As an introduction we wanted to include a review of the various approaches to axiomatic field theory. This introduction had to cover not only the formulation of Bogolubov, Medvedev and Polivanov, based on the apparatus of functional derivatives of the 5-matrix and the condition of microcausality, but also the field formulation associated with the names of Wightman, Haag, Lehmann, Symanzik, Zimmermann, and others. In the course of the work the tasks (and with them the size) of the introduction grew larger and larger, until eventually it developed into this book.
ßçûê: Ðóáðèêà: Ìàòåìàòèêà /Ñòàòóñ ïðåäìåòíîãî óêàçàòåëÿ: Ãîòîâ óêàçàòåëü ñ íîìåðàìè ñòðàíèö ed2k: ed2k stats Ãîä èçäàíèÿ: 1975Êîëè÷åñòâî ñòðàíèö: 707Äîáàâëåíà â êàòàëîã: 18.04.2010Îïåðàöèè: Ïîëîæèòü íà ïîëêó |
Ñêîïèðîâàòü ññûëêó äëÿ ôîðóìà | Ñêîïèðîâàòü ID
Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü
Current(s), V — A (weak) 500—501 Current(s), VEV of 441—442 Cutoff 468—469 613—623 625 Cyclic group (Zw) 211 Cyclic representation 581 586 588—589 Cyclic vector 605—607 (see also “Cyclicity” “Cyclic Cyclicity, of vacuum (completeness condition) 245 253—259 283 297 323—324 350 514 599 Dashen, R. F. 402 627 Davies, E. B. 624 640 Decomposability (see “Functional indecomposable” “Representation decomposable”) Decomposition of unity (see “Partition of unity”) Degrees of freedom, finitely many (see “Quantum mechanics”) Delbourgo, R. 242 672 Dell’Antonio, G. — F. 353 545 546 576 604 624 640 Delta function 45—48 56—57 63—66 70 83—85 100-102 Delta function 59 63—64 83 435 466 Density matrix 593 Derivation, in algebra 431 Derivative (see “Distributions differentiation”) Diamond, Diamond property 597 603—604 616 Differential equations of fields (see “Wave equation” “Dirac “Klein Differential equations, Fourier-transform solution 72 75—82 Dimension, relative 590 Dirac equation 181 183—192 207—208 241 313—314 321 Dirac equation, invariant solutions and Green functions 335 Dirac equation, orthogonality and completeness relations for solutions 185—186 208 314 Dirac equation, spinor solutions 185—186 207—208 321 “Particles spinor” “Gamma Dirac matrices (see “Gamma matrices”) Dirac spinor (see “Spinors four-component”) Dirac, P. A. M. 578 640 Direct product 242 348—349 Direct sum 35 126 Direct-integral decomposition 143 152 162—163 203—205 Discrete transformations (discrete symmetries) 163—167 176—180 183 191—192 241 319—327 405 498—499 562 Discrete transformations (discrete symmetries), gauge transformations and 352 Discrete transformations (discrete symmetries), phases 163—167 176—180 325-327 352 499 502—503 “Time “Space-time “Charge “TCP “CP Dispersion relations 3 4 399 465—466 Distributions (see also “Generalized functions “Tempered Distributions of finite order 26 63 425 Distributions, addition and scalar mutltiplication 51—53 Distributions, as classes of sequences 50—54 106 Distributions, as functionals 45—50 105 Distributions, causal 100—104 106 Distributions, change of variables 54—55 Distributions, concentrated at origin 63 83—84 Distributions, convolution (see “Convolution”) Distributions, differentiation 54—59 76 103—104 Distributions, division 61—66 72 76—77 106 Distributions, functions as 46—47 Distributions, homogeneous (see “Homogeneous distributions”) Distributions, local properties 48—49 422—428 466 Distributions, Lorentz-invariant 12 82—89 103—104 106 269—271 473-497 Distributions, multiplication by functions 59—60 Distributions, multiplication by other distributions 59—61 90—91 99—104 106 383 415 453—460 Distributions, nonnegative, see Measure operator-valued 245—249 Distributions, on mass shell 420—421 Distributions, physics, role in 45—46 Distributions, renormalization and 453—460 468 Distributions, retarded (see “Retarded and advanced distributions”) Distributions, terminological convention 48 Distributive laws 584 Dixmier, J. 584 587 588 605 624 Domain of analyticity (see “Analyticity primitive Domain of holomorphy 5 09 Domain of unbounded operator 34—35 38 615 Domain, common, of fields 2 248 294—295 310 Doplicher, S. 598 599 600 625 640 641 Dotted indices (see “Spinors indices”) Double-valued representations (see also “Spin-and-statistics theorem” “Spinors” “Poincare “Representations ray”) Drell, S. D. 2 8 460 468 627 Dual matrix 168—169 Dual space (see “Conjugate space”) Duality 604 Duffin — Kemmer algebra 542—544 576 Duffin, R. J. 576 641 Dunford, N. 20 105 598 628 Dyson product (see “Time-ordered product”) Dyson, F. J. 332 353 467 468 575 641 Ecker, G. 150 641 Edwards, C. M. 624 641 Efimov, G. V. 466 641 332 352 641 Ehrenpreis, L. 106 642 Eisenhart, L. P. 242 628 Electrodynamics (electromagnetic interaction) (see “Quantum electrodynamics”) Electron 206 316 Elliptic equations 469 Energy 122 184 Energy, positivity (see “Spectral condition”) Energy, sign of 148—150 Envelope of holomorphy 509—5 10 Epstein, H. 106 415 446 467 522 573 574 575 610 625 639 642 Equal-time commutation relations (see “Canonical commutation relations”) Equivalence relation (equivalence classes) 125 294—295 519 Equivalence, of representations 216 558—561 581 Error, in measurements 594 599 Essential self-adjointness (see “Linear operator essentially Estimates, in constructive theory 615 616 619 Euclidean group (Euclidean motions, 211 549—551 Euclidean group (Euclidean motions, in dimension 2 156 162 217—218 Even distributions 84—88 Even invariant function (see Even-odd rule 537 Ex (asymptotic notation) 366 expectation value 109 113—114 116 138 591 593 Extension, of operator 35 38 External field 242 352 Extremal functional (see “Functional indecomposable” “States extremal Extreme points 282 E_{3} (see “Euclidean group”) f group 210 211 Fabri, E. 562 577 642 Factor group 211 Factor space 295 588—589 Factor, in algebra 581 589—590 604 Factor, in algebra, 607 624 Fainberg, V. Ya 281 428 466 468 642 652 Faithful representation 587 594—595 597 Fast decrease, sequences of (see “\mathcal{S}”) Federbush, P. G. 576 642 Feinberg, G. 150 352 642 Feldman, G. 464 577 642 643 679 Fell, J. M. G. 595 643 Fermi operator 274 Fermions, Fermi — Dirac statistics 252 281 318 402—403 526 571—573 610 Fermions, Fermi — Dirac statistics, gauge transformation and 405—406 (see also “Particles spinor” “Spinor Feynman diagrams 103 274 454—455 459—460 466 Field equation (see “Wave equation” “Klein “Dirac Field operators (fields) 245—249 Field operators (fields), algebra of (see “Algebra of Field operators (fields), defined at fixed time 258 364—365 548—561 603 616-617 Field operators (fields), defined at point 245 282—286 35 Field operators (fields), homogeneous distribution formalism 343—345 Field operators (fields), index convention 253—254 262 Field operators (fields), products, polynomials 253—256 260 296 Field operators (fields), self-adjointness 252 607—609 616—617 625 “Heisenberg Fierz, M. 241 576 643 Filippov, A. T. 499 634 Fock basis 119 Fock space, Fock representation 118—121 162—163 193—208 242 303 560 612—615 618 Fock space, Fock representation for infinite-component field 569—570 572 Fock space, Fock representation for parafield 539—544 Fock, V. 193 242 643 Forces, range of 281 385—386 Four-momentum (see also “Poincare group” “Lie “Spectral Four-point functions 270—271 360 429 435—449 562 Four-vector, Hermitian matrix and 110 132—137 notation”) Fourier transforms 11 12 67—89 106 269 523 Fourier transforms of derivatives 72 Fourier transforms of free fields 304 313—314 Fourier transforms of generalized free field 332 Fourier transforms of Hermite function 121 Fourier transforms of Hermitian field 387 Fourier transforms of quasilocal distribution 435 Fourier transforms of retarded and advanced 4—point functions 438—441 Fourier transforms of retarded distributions 90—99 267—268 Fourier transforms of TVEV 274 Fourier transforms of Wightman functions 265—268 Fourier transforms, in 20 289 Fourier transforms, local properties and 424—428 Fourier transforms, sign convention 67—69 265—266 289 367 Frank, W. M. 469 643 Free fields, references 352 (see also “Scalar field free” “Spinor free” “Generalized Freshet space 22 Fried, H. M. 468 643 Friedrichs, K. O. 352 626 628 Frobenius, F. G. 209 Froissart, M. 576 643 Full reducibility (see “Representation decomposable”) Function analytic (see Analyticity) Function of operator (see “Linear operator function Function, test (see “\mathcal{S}”) Functional (variational) derivative 359—360 401 407—412 416 430—431 444 465 Functional analysis 1 11—44 Functional(s) analytic 466 Functional(s) analytic, bilinear (bilinear form) 29—30 36 616—617 Functional(s), Hermitian 290 598 Functional(s), indecomposable 282 292—294 297—301 588 591 593 Functional(s), linear 18—21 25—26 34 Functional(s), normalized 292 598 Functional(s), positive, in 20 Functional(s), positive, in algebra 290—291 587-589 591—594 Functional(s), S-operator as 403—404 409—414 430-432 Functional(s), space of 592 Functional(s), subordinate 301 Fundamental (Cauchy) sequence 15 22 50—54 294 Fundamental solution 304—305 (see also “Green functions”) Gachok, V. P. 577 608 625 644 Galilei group 142 Galindo, A. 539 576 644 Galois, E. 209 Gamma matrices ( 170—176 241 Gamma matrices ( 183 Gamma matrices ( 181 Gamma matrices ( 172—174 499—500 Gamma matrices ( 176 180—183 321—322 Gamma matrices ( 620—621 (see also “Bilinear invariant forms” “Spinors four-component” “Dirac Gauge, Gauge transformation 311 352 404—406 423 532 600—601 Gel’fand — Naimark classification 338—342 Gel’fand — Naimark — Segal (GNS) construction 581 587—589 594 598 618 Gel’fand, I. M. 22 24 25 27 29 31 32 42 48 49 63 70 73 105 106 240 242 252 269 338 339 340 342 344 347 353 466 567 577 628 629 644 645 General linear group 131 Generalized eigenvector (generalized state) 39—42 105 109 114—118 197 Generalized eigenvector (generalized state) of momentum 39—40 157 199 307—308 Generalized eigenvector (generalized state), normalization 117 (see also “Rigged Hilbert space”) Generalized free field 259 328—332 337 352—353 380 524 Generalized functions 48 57—58 422—428 466 Generator (see “Infinitesimal operator” “Lie George, C. 242 645 Giambiagi, J. J. 468 638 Girding, L. 73 85 88 106 241 252 350 577 644 677 GL(2) 131 Glazer, V. 106 415 467 574 639 645 Glazman, I. M. 37 39 105 627 Glimm, J. 614 615 616 617 618 619 621 622 625 626 645 646 Global nature of locality 507—509 575 GNS (see “Gel’fand-Naimark-Segal construction”) Goldberger, M. L. 8 629 Golodets, V. Ya 577 646 Gonzales Dominguez, A. 468 638 Good, R. H. 174 241 547 Gourdin, M. 575 647 Govorkov, A. B. 546 576 647 Graev, M. I. 106 339 340 353 628 Graph, Graph limit 35 622 Grawert, G. 575 647 Green functions 384 392 398 423 468 562 Green functions and 436—437 Green functions for spinor field 335 455 Green functions in 392 400—401 464 Green functions in, reduction formula in 383—384 465 Green functions in, scattering theory results summarized 400—401 Green functions of Klein-Gordon equation 70—72 102—104 334—335 382 422 455 467 Green functions, analyticity 359—360 466—467 Green functions, causal 70—72 102—104 334—335 353 359—360 383 401—402 422 429 432—445 454—560 462-463 Green functions, four-point 360 429 435—449 466—467 562 Green functions, Kaelle'n-Lehmann representation (see “Kallen-Lehmann representation of Green functions, n-point 467 Green functions, retarded and advanced 334—335 382 401 430—434 437—441 443—445 446—449 464 466-467 Green functions, smeared 394 400—401 Green functions, time-ordered (see “Causal”) Green functions, unphysical singularities in 466 Green, H. S. 540 576 647 Greenberg, O. W. 328 332 352 353 526 539 544 545 546 575 576 577 Green’s ansatz 541—546 Grodsky, I. T. 349 648 Grossmann, A. 240 648 Grothendieck, A. 32 105 629 Group 209—219 242 “Poincare etc.”) Group extensions 352 Guenin, M. 584 607 624 625 648 Guersey, F. 242 649 Guillot, J. C. 241 649 Gupta — Bleuler formulation 109 112 Haag — Araki field 609—610 Haag — Kastler axioms 581 582 596—597 599 602 603 603 618 Haag — Ruelle theory 357—358 362—380 385 388 399 464 Haag, R. 3 4 127 258 259 350 351 Haag-Araki-Kastler approach (see “Algebraic approach”) Haag’s theorem 475 548—562 576—577 612-614 Hadrons 151 406 “Proton etc.”) Hagedorn, R. 240 650 Hahn — Banach theorem 21 Hall — Wightman theorem 151 434 474 489—497 Hall, D. 481 489 492 552 574 576 Hamermesh, M. 219 242 526 629 Hamiltonian, Hamiltonian formulation 8 475 548—549 556 561 576 597 612—616 620—622 626 Hankel function (see “Bessel functions”) Harish — Chandra 242 650 Hausdorff space 212 Heisenberg current (see “Current” “Heisenberg Heisenberg field 3—4 362 382 401 415 422 465 614—617 622—623 Heisenberg picture 3 137—138 Heisenberg, W. 2 362 401 465 650 Heisenberg’s nonlinear theory 112 Helicity 150 (see also “Spin” “Massless Henley, E. M., xviii 8 629 Hepp, K. 106 281 351 363 374 383 395 397 399 464 465 468 490 492 574 626 634 650 651 654 Hermite functions 24 120—121 558 Hermitian conjugate (see “Adjoint”) Hermitian element, of algebra (see “Self-adjoint element”) Hermitian field (see “Neutral field” “Majorana Hermitian operator (see “Linear operator symmetric Hilbert problem, fifth 214—215 Hilbert space 15—17 19 30 33—44 105 112—114 122—126 240 Hilbert space in algebraic approach 593—596 599—600 602-607 “States”) Hilgevoord, J. 465 629 Hoeegh — Krohn, R. 625 651 Hoermander, L. 106 652 Holomorphic function (see “Analyticity”) Holomorphy envelope, Holomorphy domain 509—510 Homogeneous distributions 338—349 502 564—565 Homomorphism 135 136 Homotopy 624 Hyperbolic rotation (see “Lorentz transformation pure”) Hyperboloid (see “Mass shell” “Measure on Hypermaximal symmetric operator 37 (see also “Linear operator self-adjoint”) Hyperons 406 Ideal 223 290—293 296 310 587 Ideal, right, left 290—291 588 In-states (see “Asymptotic states”)
Ðåêëàìà
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



![$[\delta(x)]$](/math_tex/cb244ed9c689c7a986f84a2bf58ffc7b82.gif)
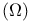
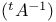
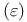
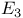 )
) 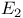 )
) 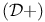
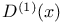 )
)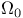
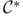
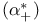
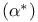
 -matrices)
-matrices)![$[S^{c}(x), ect.]$](/math_tex/e276d73d135167fb8528559af50a510b82.gif)
![$[D^{c}(x), D^{ret}(x), D^{adv}(x)]$](/math_tex/493e6391a086cd2dcfaab57b0d788bf982.gif)