Àâòîðèçàöèÿ
Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì
Bogolubov N.N., Logunov A.A., Todorov I.T. — Introduction to Axiomatic Quantum Field Theory
Îáñóäèòå êíèãó íà íàó÷íîì ôîðóìå Íàøëè îïå÷àòêó?
Íàçâàíèå: Introduction to Axiomatic Quantum Field TheoryÀâòîðû: Bogolubov N.N., Logunov A.A., Todorov I.T.Àííîòàöèÿ: At the end of 1960 we made plans to write a monograph about the general principles of quantum field theory and their experimental implications. We intended primarily to give an account of the progress of the theory of dispersion relations since the appearance of the book of Bogolubov, Medvedev and Polivanov ([BMP]. As an introduction we wanted to include a review of the various approaches to axiomatic field theory. This introduction had to cover not only the formulation of Bogolubov, Medvedev and Polivanov, based on the apparatus of functional derivatives of the 5-matrix and the condition of microcausality, but also the field formulation associated with the names of Wightman, Haag, Lehmann, Symanzik, Zimmermann, and others. In the course of the work the tasks (and with them the size) of the introduction grew larger and larger, until eventually it developed into this book.
ßçûê: Ðóáðèêà: Ìàòåìàòèêà /Ñòàòóñ ïðåäìåòíîãî óêàçàòåëÿ: Ãîòîâ óêàçàòåëü ñ íîìåðàìè ñòðàíèö ed2k: ed2k stats Ãîä èçäàíèÿ: 1975Êîëè÷åñòâî ñòðàíèö: 707Äîáàâëåíà â êàòàëîã: 18.04.2010Îïåðàöèè: Ïîëîæèòü íà ïîëêó |
Ñêîïèðîâàòü ññûëêó äëÿ ôîðóìà | Ñêîïèðîâàòü ID
Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü
Parke, W. C. 242 665 Parseval equation 69 Parthasarathy, K. R. 241 665 Partial derivative (see “Distributions differentiation”) Particles 149—150 152 156 259 272 362 380 395—396 398 402 526 539 Particles, asymptotically free 368 405 526 Particles, quantum numbers of 441 Particles, scalar 193—205 306—308 312 465 Particles, scattering processes 436—437 495—497 Particles, spinor 175 205—208 315—318 Particles, symmetry groups and 242 Particles, TCP operator and 322 Particles, unstable (resonances) 406 441 517 Partition (decomposition) of unity 49—50 279 388 Pauli matrices 132 134 Pauli realization, of 181—183 Pauli — Villars 103 Pauli — Villars in perturbation theory 360—361 460—463 468 Pauli — Villars regularization 103 Pauli, W. 172 241 575 576 665 666 Pauli’s lemma 172—174 241 Perfect (Montel) space 24 28 29 32 Perturbation theory 2 103—104 274 360—361 382 383 413 415 421 423 450—463 467—469 556 561 612 619—621 Perturbation theory, convergence of 468—469 (see also “Feynman diagram” “Lagrangian Petermann, A. 465 673 Petiau, G. 576 666 Petit, J. L. 241 649 Petrina, D. Ya 508 575 625 637 666 Phase-space volume 100 04 Photon 150 Physical equivalence 581 594—595 599 Physical quantities (see “Observables”) Physical representation 614 618—619 Picasso, L. E. 562 577 642 Pictures, in quantum theory 137—138 (see also “Interaction representation”) Pietsch, A. 32 105 631 Pion ( 128 151 406 441 453—455 465 496 Piron, C. 113 653 Plane waves 114 Pohlmeyer, K. 575 577 638 666 Poincare group 109—111 131 “Relativistic Poincare group, complex 505 (see also “Lorentz group” “Relativistic Poincare group, components 131 (see also “Lorentz group” “Relativistic Poincare group, covering groups 110 135—136 140—142 “Relativistic Poincare group, extended 131 163—167 “Relativistic Poincare group, invariants (Casimir operators) 111 147—151 153 200 “Relativistic Poincare group, Lie algebra (generators, infinitesimal operators) 110—111 143—149 153 161 189 595-596 “Relativistic Poincare group, orthochronous spinor 183 (see also “Lorentz group” “Relativistic Poincare group, representation of, in field theory 109—111 140—142 151—152 200—205 249—250 289 295—296 299—300 595-596 “Relativistic Poincare group, representations 110—111 142—167 187—192 200—205 240—242 262 “Relativistic Poincare group, restricted 110 131 137 140—142 144 162 “Relativistic Polar decomposition 135 158—159 161 Polivanov, M. K. xvii 3 399 401 422 429 445 460 465 467 468 628 667 662 666 Polynomial growth, functions of 47 5 3—54 Polynomial invariants (see “Casimir operators”) Polynomials in field (see “Field operators products” “Wick Polynomials, homogeneous 339—342 Ponomarev, V. A. 339 644 Pontryagin, L. S. 135 213 214 220 232 242 631 Position operator 194—195 309 351 Positive-frequency solutions, convention 334 336 368—369 381 Poulsen, E. T. 121 240 657 Powers, R. T. 469 577 624 625 653 666 Primitive causality 258—259 597 Primitive domain, of analyticity 429 438—441 447—449 Primitivity 597 Principal value 57—58 probability 36 113—115 117—118 138 140 362 407 592—593 624 Product of distributions (see “Distributions multiplication Product of fields (see “Field operators products” “Wightman Projection operator 42 113—114 116 123—124 126 138—139 590 602 Projection operator as observable 113 123 126 Projection operator, orthogonal 113 Projection operator, regularized 460—463 Propagator 459—460 575 causal”) Proper subgroup 210 Proton 316 454 468 496 497 Prugovecki, E. 352 666 Pseudo-orthogonal group 568 Pseudo-orthogonality 477 Pseudoscalars currents and particles 344 441 442 454 Pseudoscalars currents and particles, formed from 4— Pseudoscalars currents and particles, vectors 490—492 Pseudotensors 344 PT symmetry 573 Pugh, R. E. 460 466 468 666 667 Pure operation 592 Pure state 591 Quadratic estimates 615 616 Quantum electrodynamics 109 112 150 352 382 413 496 562 Quantum field (see “Field operators” “Axioms Scalar quantum mechanics 118—121 138 142 240 423 549 552 557—560 Quantum numbers 441 Quarks 576 Quartets (see “Steinmann identities”) Quasianalytic functions 427 Quasianalytic vector 608 Quasilocal observables 596—599 (see also “Local observables” “Algebra of Quasilocal operator 360 416—422 435 450—451 461—462 466 Quasilocal operator, inevitability of 421—422 Question, as observable 113 Quotient algebra 587—589 R-points 505 R-product 392—399 Radiation operators 3 4 399 412—416 423 430—432 Radiation operators, fourth-order 435 Range, of forces 281 385—386 Rashevsky, P. K. 174 241 352 631 667 Rays (unit rays) 112 113 117 127 138 142 234—239 593 Rays (unit rays) of unitary operators 140—141 (see also “States”) Reconstruction theorem 246 260—261 293—301 351-352 Reconstruction, from von Neumann algebras 609—610 Redmond, P. 465 667 Reducible representation 217 (see also “Representation decomposable Reduction formula 358—359 382—384 392—399 465 Reed, M. C. 577 584 624 667 Reeh, H. 258 292 350 351 605 667 Reflections (see “Discrete transformations”) Reflexivity 589 Regular parametrization, in 478—480 Regular states 115 194 Regularization analytic 468 Regularization analytic of distribution 102 103 Reiss, H. R. 469 667 Relative dimension 5 90 Relative locality, Relative weak locality 518—521 524 532 575 Relative parity 327 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance) 109—110 129 208 240 283 473—475 550 552 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance) in 617—618 619 625 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance) in algebraic approach 596 609 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance) in homogeneous distribution formalism 345—346 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance) of asymptotic fields and states 367 404—405 464 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance) of T-product 383 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance) of Wightman functional 291—292 295—296 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance) of Wightman functions 261—264 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance), axioms 142 249—250 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance), in S—matrix theory 2 404—405 417 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance), locality and 329 350—351 508 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance), of S—operator 380 405—406 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance), physical meaning 138 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance), regularization and 463 Relativistic invariance (Lorentz invariance, Poincare invariance), translation invariance implies 300 Removable singularities 495 Renormalization 361 453—460 462—463 468 612 613 Renormalization of Hilbert space 614 618—619 Representation 215—233 Representation by argument transformations 145—146 Representation of algebra 586—589 594—595 614 618-619 Representation of simply connected group 135 Representation, adjoint 224 Representation, complex conjugate 262 Representation, decomposable 217—218 339 Representation, finite-dimensional 218—219 227 Representation, irreducible 143 216—219 588 Representation, Lie’s theorems for 232—233 Representation, of (see “Gamma matrices realizations”) Representation, ray (projective, “up to a factor”) 109—110 138—142 163-164 Representation, ray Real representation 501 528—529 Representation, unitary 215 216 218 219 226 “Star “Lorentz etc. representations”) Resolution of identity 43 Resonances 406 441 Rest frame (see “Lorentz transformation into Restriction 210 Retarded and advanced distributions 12 74—75 90—98 99 106 269—270 433 retarded “Smeared Riemann — Lebesgue lemma 523 Riesz’s theorems 19 20 24 36 88 255 Rigged Hilbert space 12 32—34 39—44 105 109 114—118 157 194—199 240 256 space Ring 115 585 Rivier, D. 465 673 Roberts, J. E. 599 600 640 Robinson, D. W. 332 352 353 625 641 656 667 668 Rohrlich, F. 2 460 468 629 639 668 Rollnik, H. 575 647 Rosen, L. 620 626 668 Rosenfeld, L. 350 637 Rotation group [SO(3)] 155—156 211 213 216 550 Rotation group [SO(3)], generators (see “Angular momentum”) Rotation group [SO(3)], representations 156 240 242 Rotation group [SO(3)], structure constants, metric 226 Rue lie, D. 257 275 276 281 350 351 363 378 464 467 510 585 625 631 634 651 668 S (spaces of test functions) 11 23—25 29—30 32 46—48 73 105 287-288 S (spaces of test functions), 121 S (spaces of test functions), Fourier transforms 48 67—68 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude) 2—3 358—359 362 382—383 392 395—399 401 418-419 465 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), Borchers classes and 474 520—525 575—576 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), Born term 463 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), covariant terms in 495—497 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), general properties 404—407 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), interpolating field for 513 517 524—525 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), local properties 411—414 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), nontrivial, in models 5 575—576 625- 626 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), one-particle singularities 399 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), polynomial boundedness 423 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), relation to 4—point functions 436—437 562 S-matrix (scattering matrix, scattering amplitude), TCP and 514—517 610 S-matrix approach (see “BMP approach”) S-operator (scattering operator) 3 359—361 380 401 403—417 422 430—432 442—443 450—453 461-462 S-operator (scattering operator) in Lagrangian formalism 413—414 451—453 S-operator (scattering operator) in terms of TCP operators 514—515 Salam, A. 242 468 575 655 668 669 672 Samoilenko, Yu. S. 271 669 Scalar field 250 263—264 269—271 275—276 283—284 287 294 363—368 381—384 402—404 465 552-556 612-620 Scalar field, algebra of 602—610 624 Scalar field, Borchers class 521—525 575 609 Scalar field, formed from derivatives 523 Scalar field, free 72 302—313 328 333—335 422 522—524 552—557 575 602-604 608 612—613 624 Scalar field, Lagrangian 557 Scalar field, retarded Green function 443—444 Scalar field, TVEVs 273—274 (see also “Particles scalar”) Scalar produce(s) 15—16 19—20 38 138 139 Scalar produce(s) for spinor functions 188—190 Scalar produce(s) in 2-particle space 203—204 Scalar produce(s) in factor space 589 Scalar produce(s) in Fock space 194 208 331 Scalar produce(s) in n complex vectors 490—495 Scalar produce(s) in nuclear space 33 Scalar produce(s) in pseudo — Euclidean space 7 65 67 129—130 Scalar produce(s) in reconstruction theorem 295 Scalar produce(s) in rigged Hilbert space 115—116 Scalar produce(s), analytic function of 474 489—497 Scalar produce(s), distributions in 47—48 115—116 Scalar produce(s), in 2 565 Scattering generalized states and 114 Scattering theory 8 362 388 398 399 400—402 525 610—611 625 626 “LSZ “BMP “S—matrix”) Schlieder, S. 258 292 350 351 605 667 Schmidt, W. 351 669 Schroedinger picture 137—138 Schroer, B. 258 259 350 351 352 428 466 523 575 609 624 634 638 650 657 669 Schur, I. 209 Schur’s lemma 218—219 242 Schwartz, J. T. 20 105 598 628 Schwartz, L. 31 46 48 74 105 106 631 669 Schweber, S. S. 2 8 170 171 241 335 352 422 460 631 Schwinger, J. 575 669 Second quantization 197—198 (see also “Fock space” “Scalar free” “Spinor free”) Segal, I. E. 615 624 625 626 669 670 Seiler, R. 476 574 663 Self-adjoint element, of algebra 587—588 590 591 598 Self-adjoint operator (see “Linear operator self-adjoint”) Self-adjoint representation 219 Self-dual representation 344—345 Self-energy 103 360 453—463 468 620 Seminorm 15 Semisimple algebra 223—225 Semisimple group 210 211 223—225 Separability 17 32 Separating vector 605—607 Separation axiom 212 Sesquilinearity 16 Several complex variables, functions of 467 Shapiro, Z. Ya 240 242 340 342 344 347 353 567 628 Shilov, G. E. 22 24 25 27 29 48 49 63 70 73 105 106 241 338 353 466 629 644 Shirkov, D. V. xviii 2 3 8 72 102 146 171 186 322 333 336 352 401 409 414 422 455 465 466 467 468 556 561 577 628 636 637 Shirokov, M. I. 205 242 575 640 670 Shirokov, Yu. M. 204 241 670—671 Sign function 79 Sikorski, R. 106 630 Simon, B. 31 106 469 671 Simple algebra 223 Simple group 210 211 224 Simply connected set 135 Single-particle states 193—196 200 205—208 311—312 362 368 379 407 442—443 610 Single-particle states, projection onto 363—364 Single-valuedness, of Wightman functions 264—265 SL(2) (special linear group, unimodular group) 110 131—137 158—159 240 241 SL(2) (special linear group, unimodular group), representations 144—145 168—176 188 247—251 337—349 353 482-483 528—529 564—570 578 Slash notation (p) 170—171 5- Smeared products of fields 392—399 Smirnov, V. I. 226 481 491—492 631 Smith, L. 624 634 Smith, M. — S. B. 624 634 SO(2, 1) 156 162 SO(3, 2) 568—569 5 Sobolev, S. L. 105 671 Space reflection 130 136 146 154 164 169—170 176—179 191 319-327 475 496—497 562—563 Space reflection in homogeneous distribution formalism 343—344 Space reflection of V — A current 500 Space reflection, charge conjugation and 325—326 Space-time inversion 474 478 497 532— 533 Spacelike hull 606 Spacelike separation, notation 414 597 Special linear group (see “SL(2)”) Spectral condition(s) 111 151—152 164 276 283 406 441—445 465 512 554—555 619 Spectral condition(s) for infinite-component field 566 Spectral condition(s) in algebraic approach 599 604—606 625 Spectral condition(s), advanced products and 399 Spectral condition(s), cluster decomposition property and 151 Spectral condition(s), generalized free field and 330 Spectral condition(s), ideal associated with 291—292 Spectral condition(s), strong (see “Mass gap”) Spectral condition(s), weak 151 265 Spectral projections (spectral decomposition, spectral function) 42—43 114 252 590 603 Spectral representation (see “Kaellen — Lehmann representation”) Spectral theorem 34—44 105 Spectrum, continuous 114 117 Spectrum, discrete 113—114 Spectrum, simple 152 Speer, E. R. 242 352 468 631 671 Spherical coordinates 80 Spherical functions, generalized 347—348
Ðåêëàìà
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



 -matrices
-matrices  -meson)
-meson) 
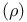


 -function
-function 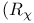

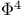 model
model 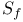 -and
-and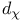 [representation of SL(2)]
[representation of SL(2)] ![$[\epsilon(x)]$](/math_tex/b5a960b0fcc8e8e06cb562d0a1f64bb182.gif)
![$[T_{\chi}(x_{1},...,x_{n}), etc.]$](/math_tex/c1556a0637b118ed81d69a8f4c858a8a82.gif)